You can configure fields, create folders, filter data, and perform other operations on the dataset editing page to further improve data processing in the dataset.
Configure a field
After the model is built, Quick BI automatically previews the data and parses it to obtain dimension and measure fields for subsequent data analysis.
You can edit the name or type of a field and the default display format of a numeric field or a date field.
Access methods
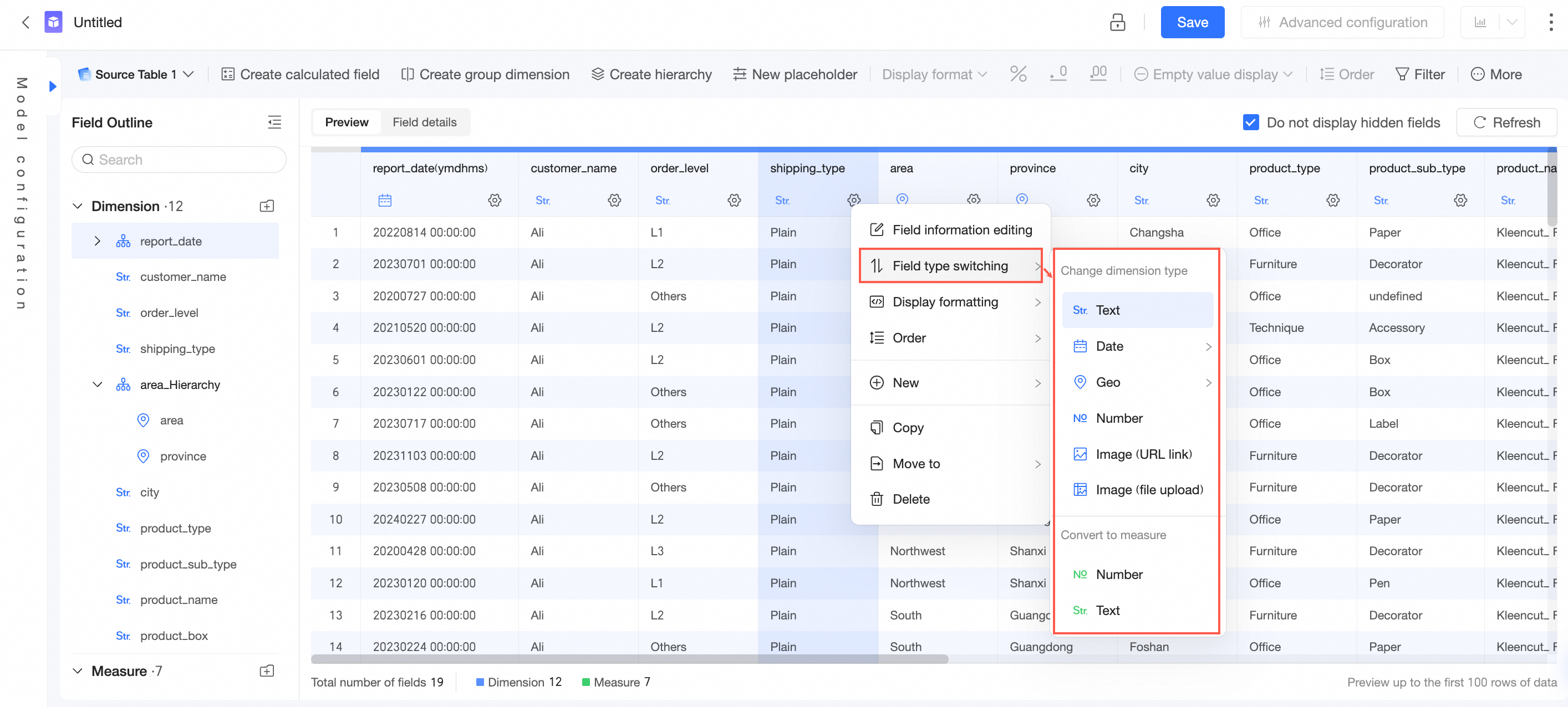
In the Field Outline section, hover over the desired field, click ① and configure the field.
In the Data Preview section, click ② and configure the field.
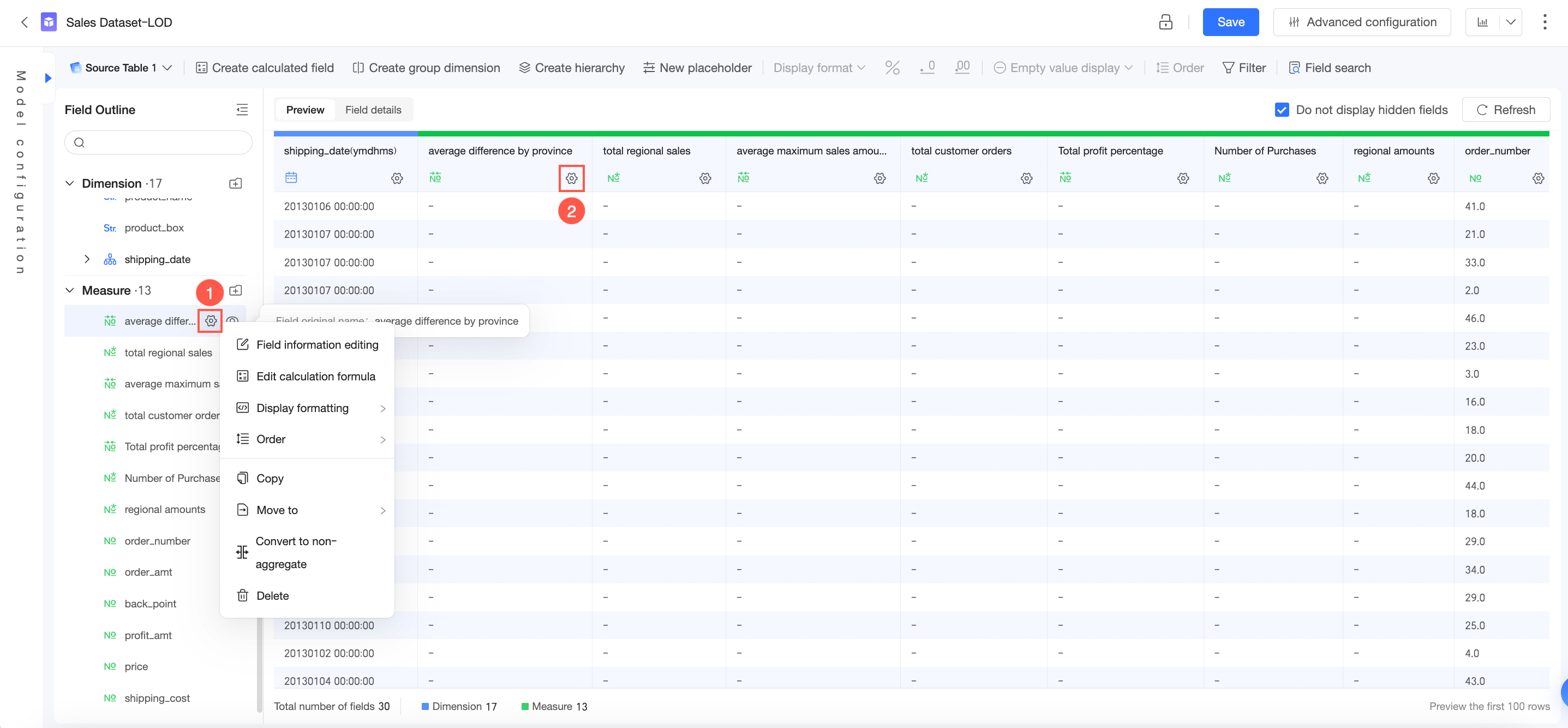
In the Field Details section, the basic information of the field is displayed. You can create a dataset on this interface.
Feature description
Operation | Description |
Edit Field Information | Edit the display name and description for a dimension or measure field. |
Edit calculation formula | Edit the calculation formula for a new calculated field. Note You can edit the calculation formula only for a new calculated field. |
Switch Field Type | You can set the field type to text, date, geographic, numeric, or image. You can also convert a dimension field to a measure field or convert a measure field to a dimension field. Note If a calculated field contains LOD functions:
|
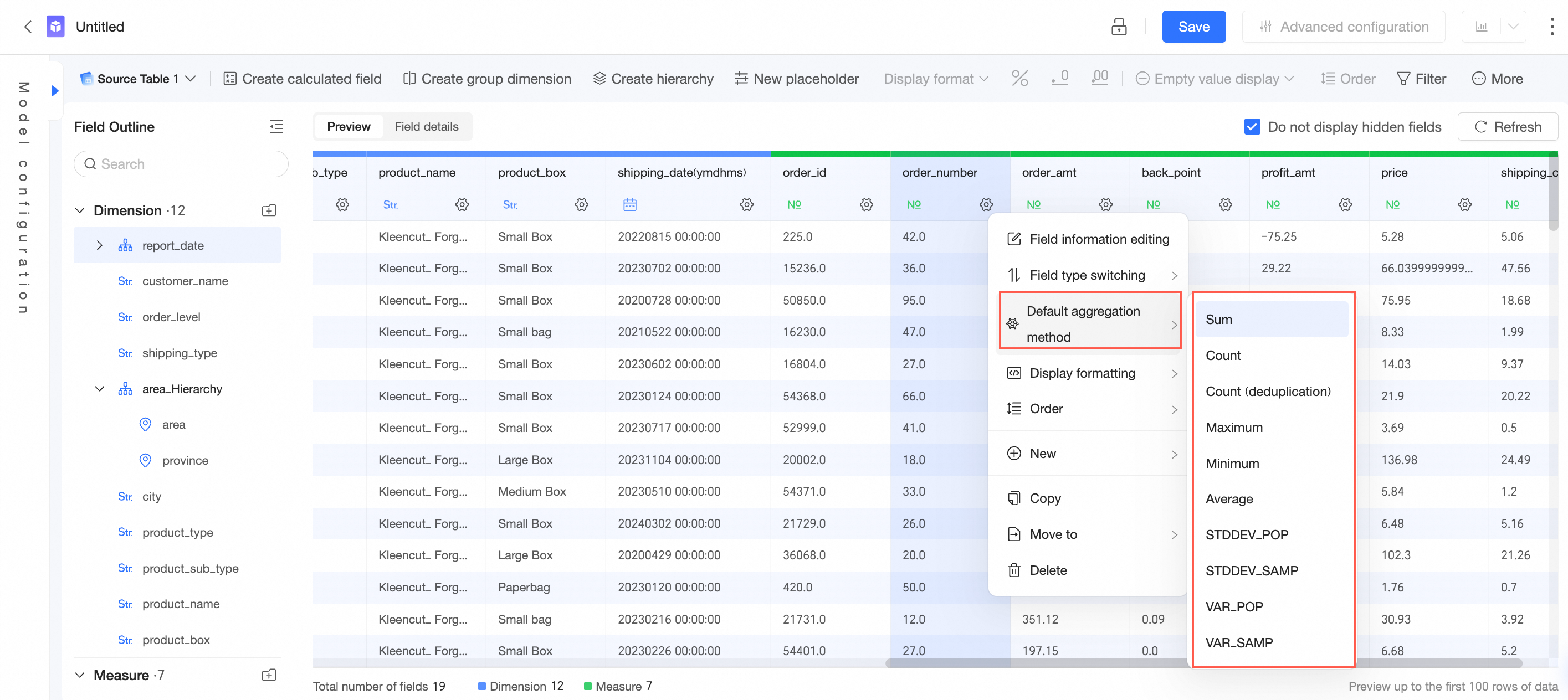
Default Aggregation Method | Specify the default aggregation method. You can specify the default aggregation method only for a measure field. During dashboard analysis, the aggregation method that you specified in the dataset is used by default.
|
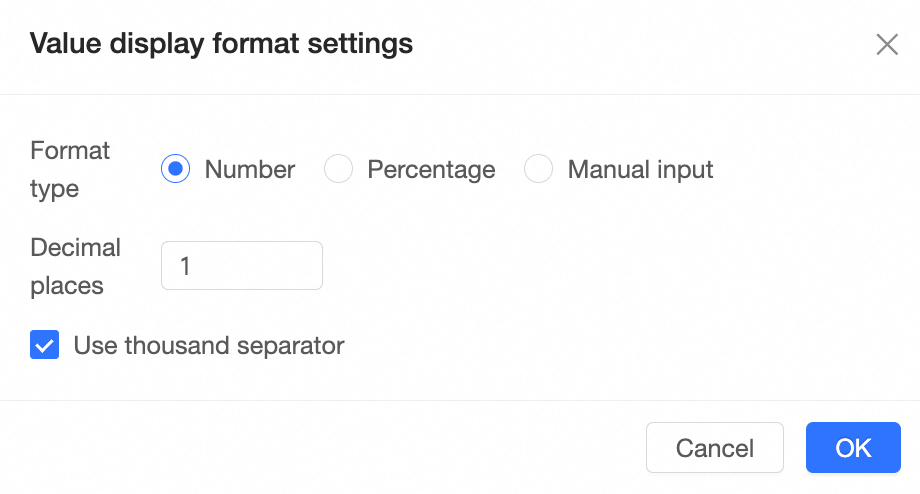
Display format settings |
Note Custom null value displays can only contain letters, numbers, underscores, slashes, backslashes, vertical lines, parentheses, and brackets, and cannot exceed 150 characters.
|
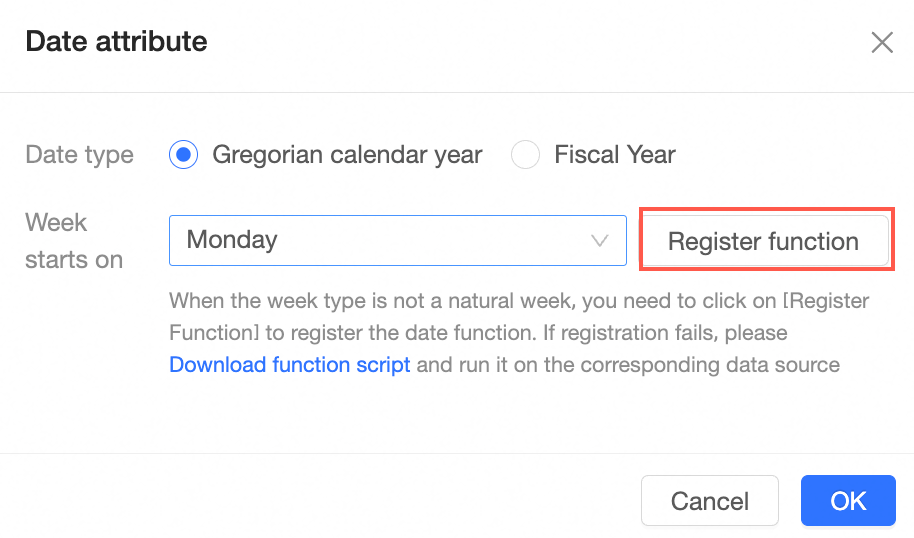
Date properties | Date fields support the Gregorian calendar year and fiscal years. When you select Fiscal Year, you can select which month the fiscal year starts in.
|
Synchronize Date Granularity | Synchronize only date fields. If you accidentally delete some date granularity fields, you can click Synchronize Date Granularity. The system automatically synchronizes all date granularity fields from the source data to the dataset. |
Sort | Set the default sorting method to no sorting, ascending, descending, or custom. During dashboard analysis, the sorting method that is configured in the dataset is used by default. |
Create |
|
Copy | Copy a field. The name of the duplicate dimension ends with _Duplicate. |
Move To | Quickly move a dimension to an existing hierarchy or a folder. |
Convert to aggregated/non-aggregated | New calculated fields of the measure type can be converted to be aggregated or non-aggregated.
Note You can convert a field to be aggregated or non-aggregated only if it is a new calculated field of the measure type. |
Delete | Delete a field. If you want to retrieve a field that you deleted, you can click the table on the canvas and select the field in the right-side panel to add the field. |
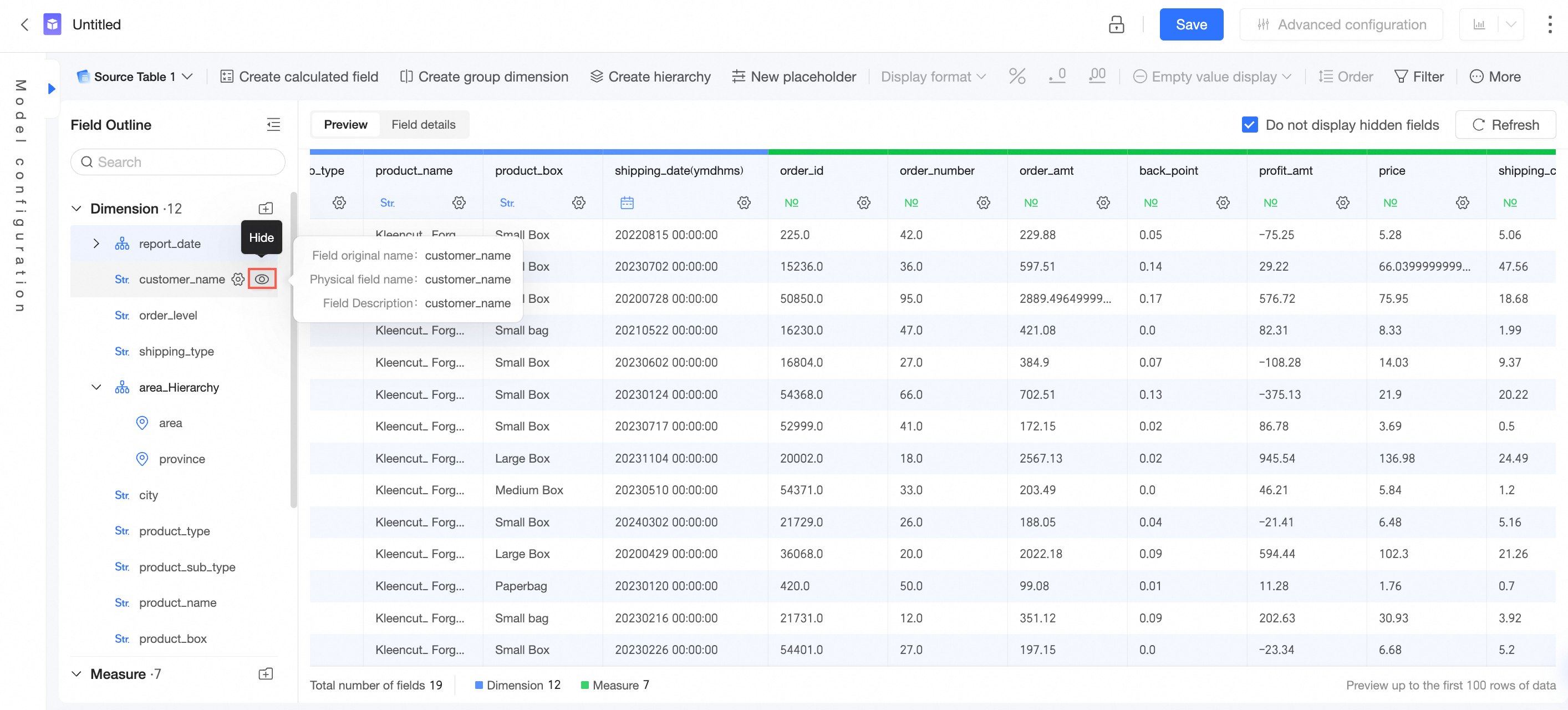
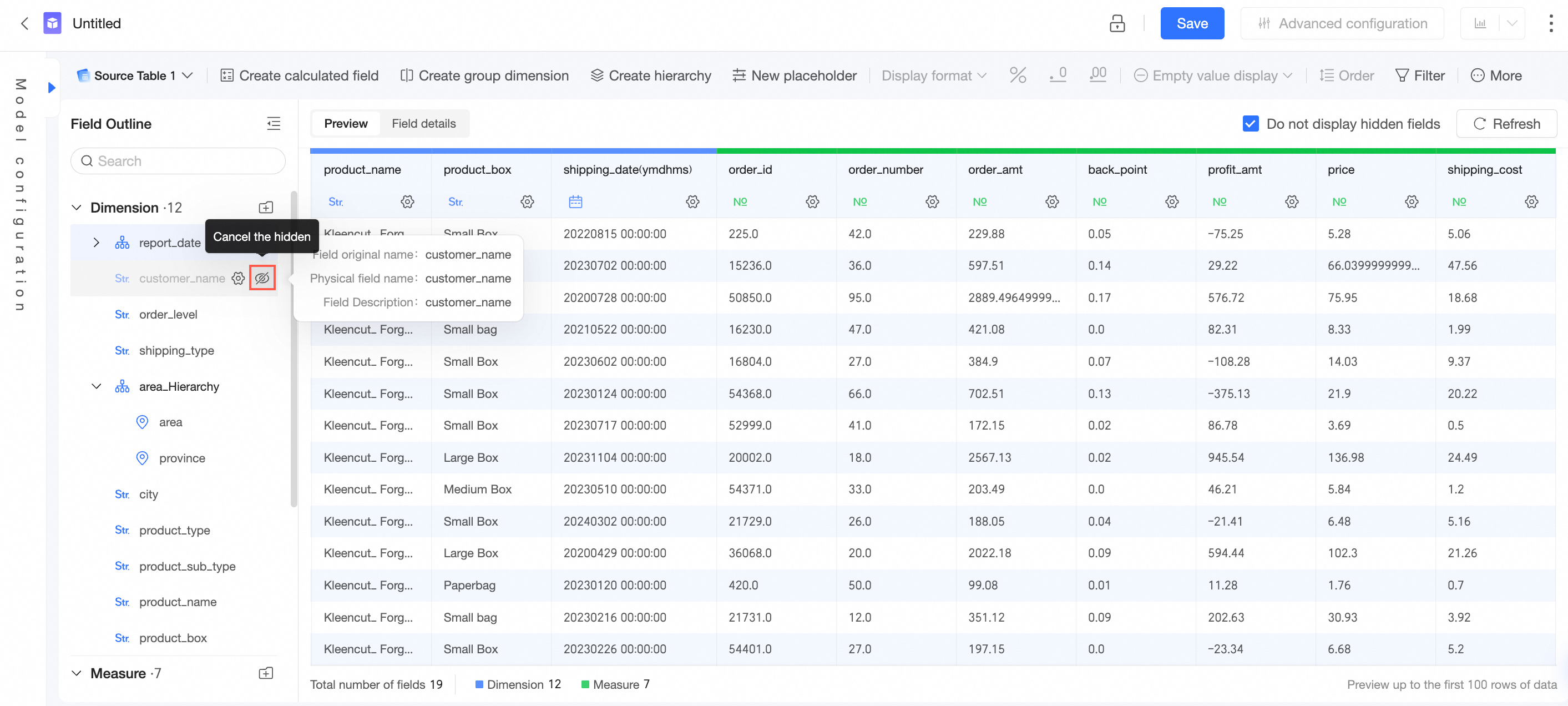
Hide | In the field list area or data preview area, hover over the target field and click the
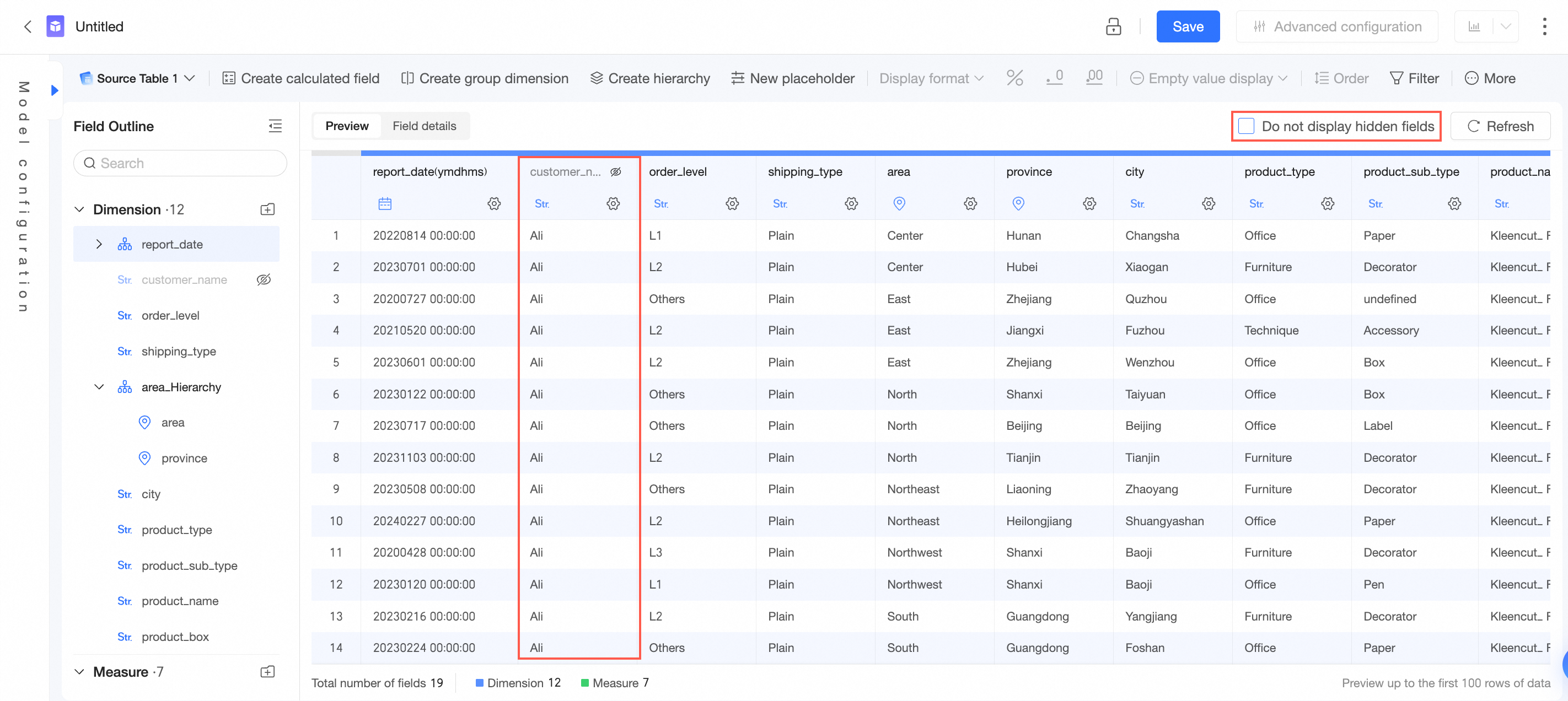
Hide a field. After a field in a dataset is hidden, the field does not appear when you select the dataset for analysis on a dashboard or in a workbook. If you want to display the target field, you can click the
You can choose whether to display hidden fields on the dataset editing page as needed:
|
Select Fields And Drag To Adjust Order | You can drag one or more fields to adjust their order or move them to other folders.
Note
|
Notes
If a field is used as a calculated field, group dimension, or filter condition, you cannot change the type of the field, switch the field between dimension and measure, or delete the field.
Configure multiple fields at a time
If you want to edit many fields, you can configure them all at once.
On the dataset editing page, click Field Details.
You can select multiple fields simultaneously and modify field configurations at the bottom of the page.
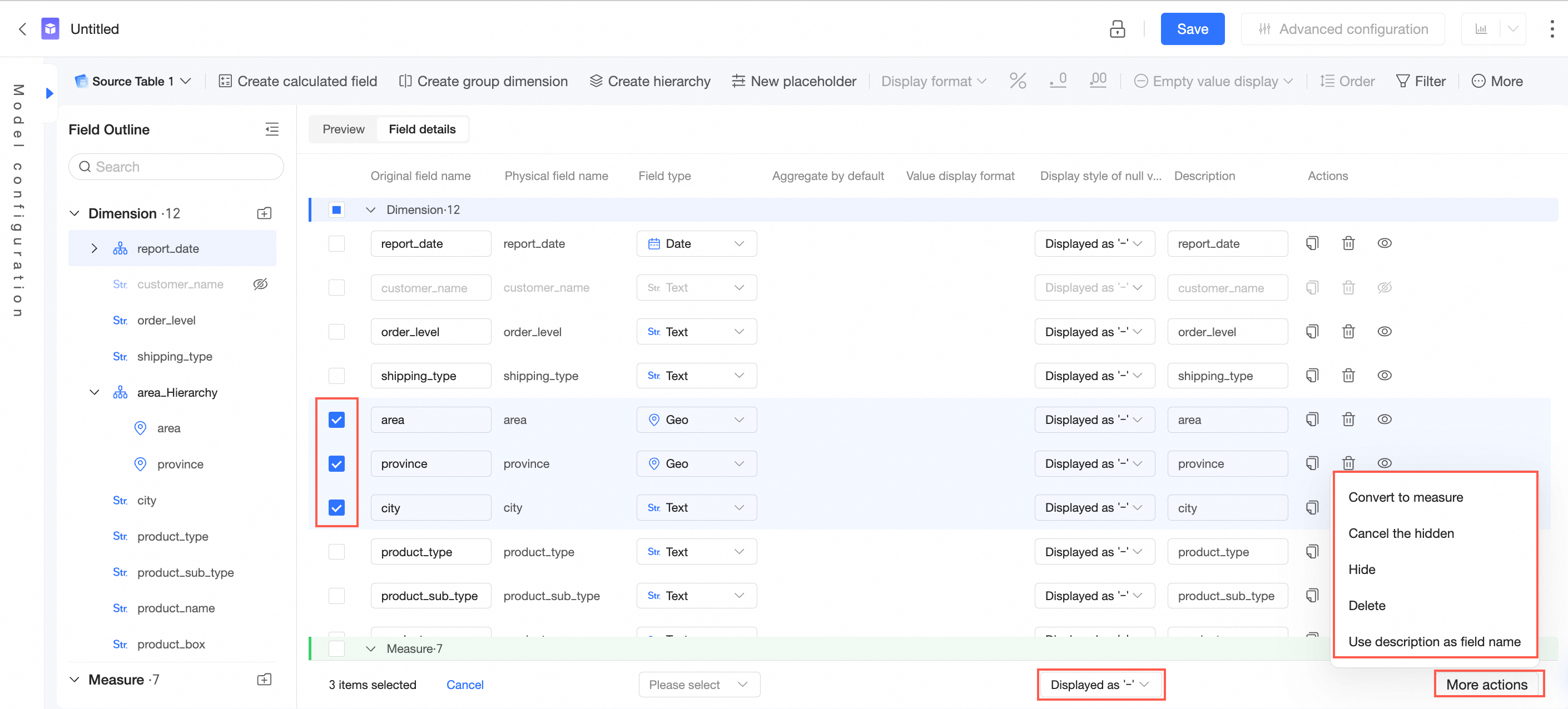
Configuration item
Description
Null value display style
You can set matching null value display styles.
Convert to measure/Convert to dimension
When all selected fields are dimension fields, you can convert them to measure fields in batches.
When all selected fields are measure fields, you can convert them to dimension fields in batches.
Hide and unhide
You can hide or unhide fields in batches.
Delete
You can delete fields in batches.
Use description as field name
You can use descriptions as field names in batches.
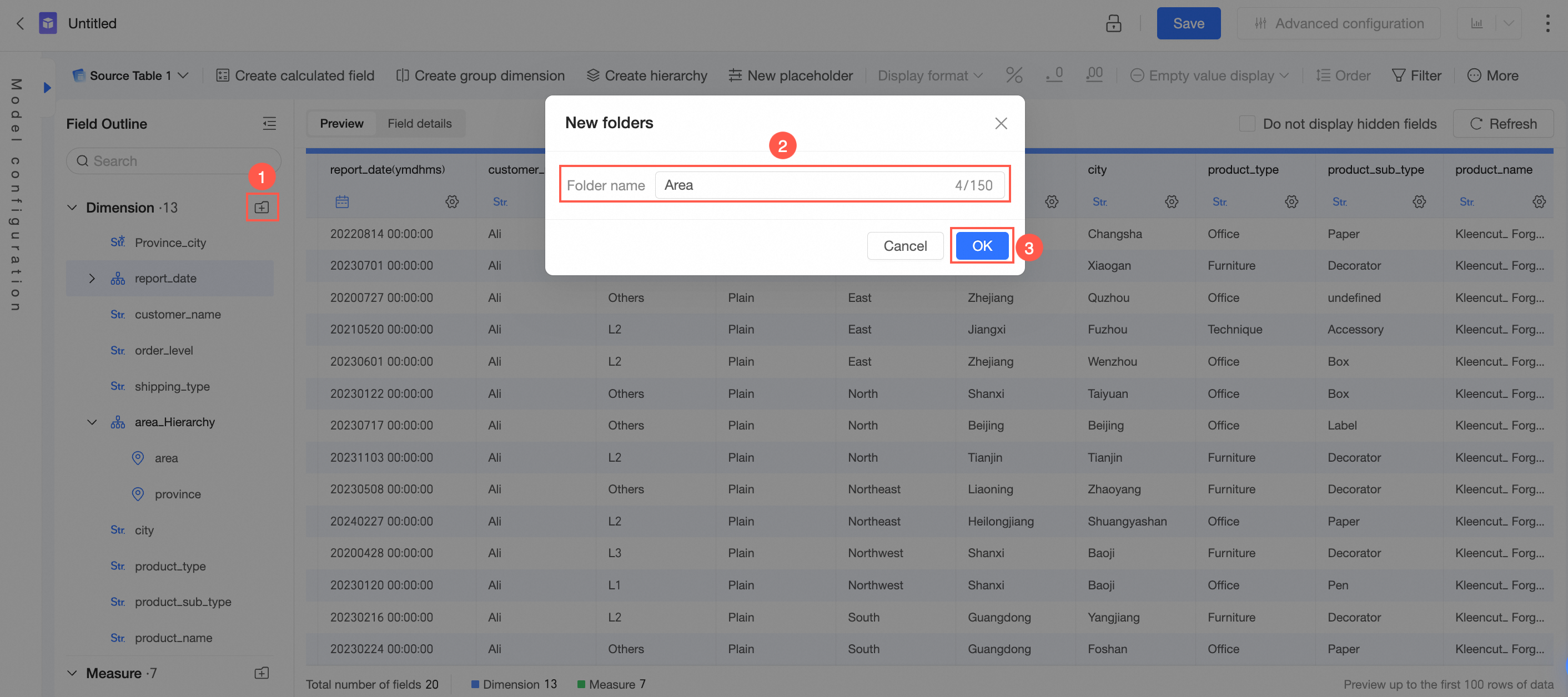
Create a folder
You can create folders for dimensions and measures by following the steps shown in the figure.
Filter data
If you need specific data during data analysis, you can add a filter to obtain the required data.
When you configure filters for multiple fields, data that meets all conditions is filtered and retained for subsequent analysis.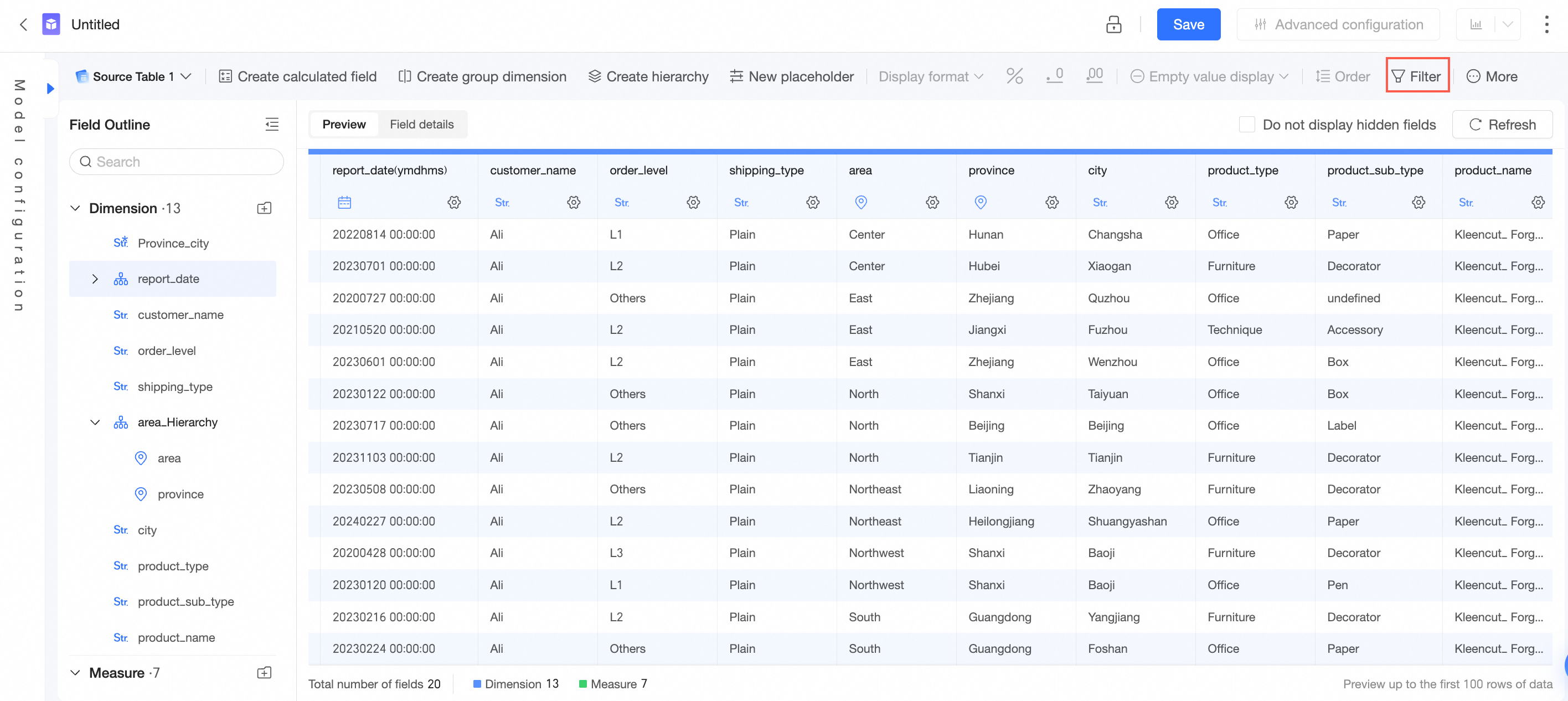
Set filter conditions in the dataset.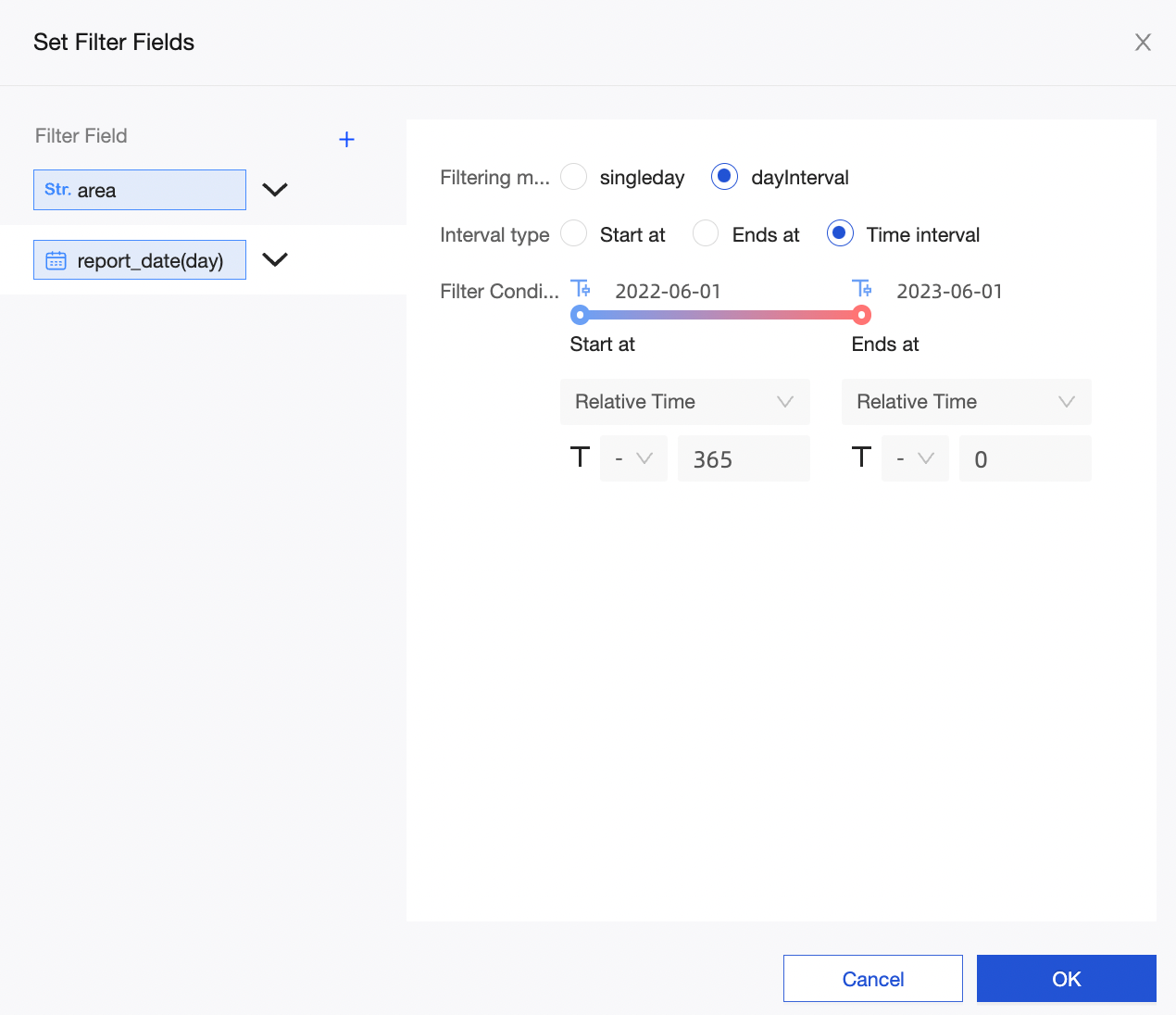
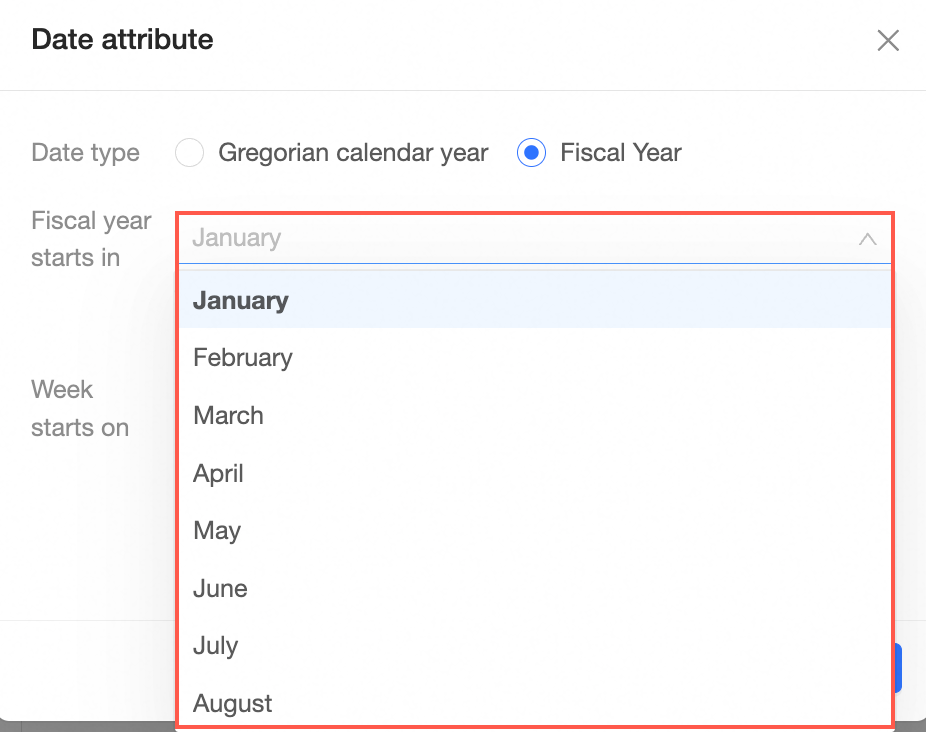
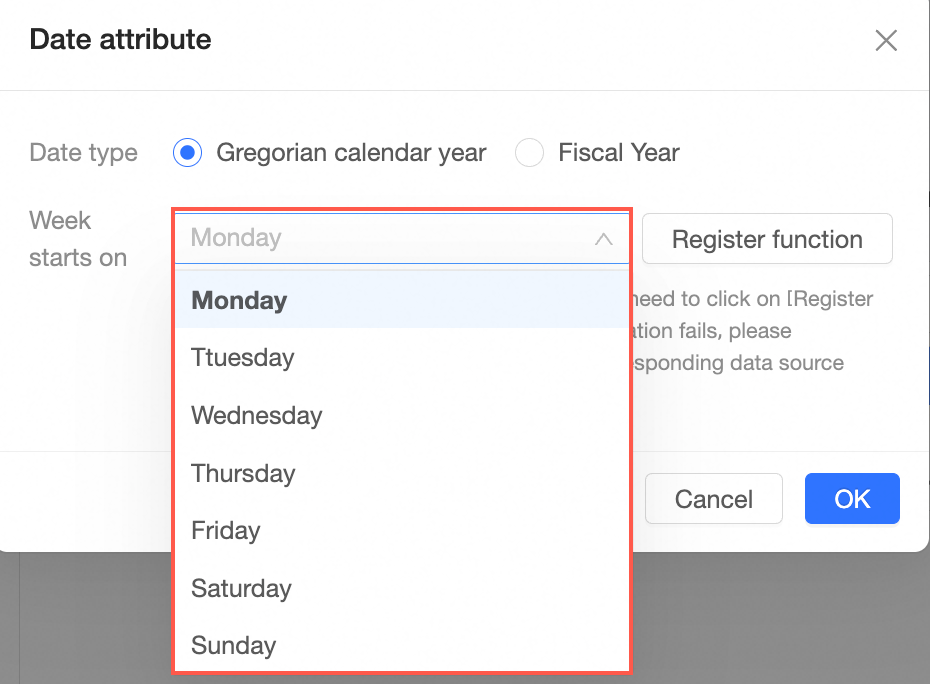 Click Register Function to automatically register date functions.
Click Register Function to automatically register date functions.