This topic describes permissions and provides solutions for common permission-related issues.
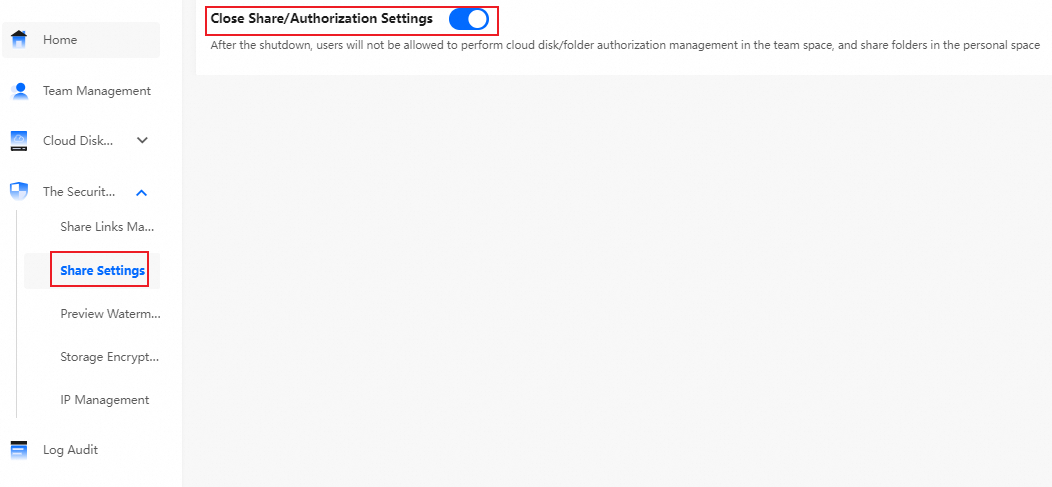
To manage authorization, ensure that you have enabled the sharing/authorization feature.
By default, super administrators and drive administrators have permission to manage all team drives in the enterprise.
Team administrators have permission to manage the disks of the teams they manage by default.
By default, regular users have only the Previewer permission for the disks of the teams to which they belong.
User role permissions
PDS supports four roles: three administrator roles and one regular user role. The administrator roles are super administrator, Drive administrator, and team administrator. This section describes the permissions of each role.
Super administrator
Super administrators have full permissions over all resources in the drive, such as enterprises, teams, users, spaces, and files. For example, they can create users, modify user roles, create teams, create spaces, grant permissions on team spaces, and upload and download files in team spaces.
Each drive can have only one super administrator. Configure the super administrator in the PDS console. The following figure shows an example:

For privacy reasons, super administrators cannot access files in users' personal spaces by default. If this access is required, contact us.
Drive administrator
Drive administrators have almost the same permissions as super administrators. However, they cannot perform certain important operations, such as promoting other users to the Drive administrator role or viewing files in users' personal spaces.
A super administrator can grant the Drive administrator role to a user. In the Management Console of the drive, go to the Team management page, select the target user, and click Change Role. The following figure shows an example:

Team administrator
Team administrators mainly manage team resources. For example, they can add users to or remove users from a team, set the space size for users, and view team audit logs. Team administrators also have full permissions for all files in the team space. These permissions include granting folder permissions, uploading, downloading, previewing, deleting, and editing files, and viewing the recycle bin. The management scope of a team administrator includes their own team and all its sub-teams. For example, if Department A has two sub-departments, B and C, the administrator of Department A can manage the users and team spaces of Department B and Department C.
A super administrator can grant the Team administrator role to a user. In the Management Console of the drive, go to the Team management page, select the target team, select the target user in the user list on the right, and click Change Role. The following figure shows an example:

Regular user
By default, regular users have operation permissions only for their personal spaces. These permissions include granting folder permissions, uploading, downloading, previewing, deleting, and editing files, and viewing the recycle bin. Regular users can perform operations in a team space only after they are granted the required permissions.
Permission details
Permission diagram
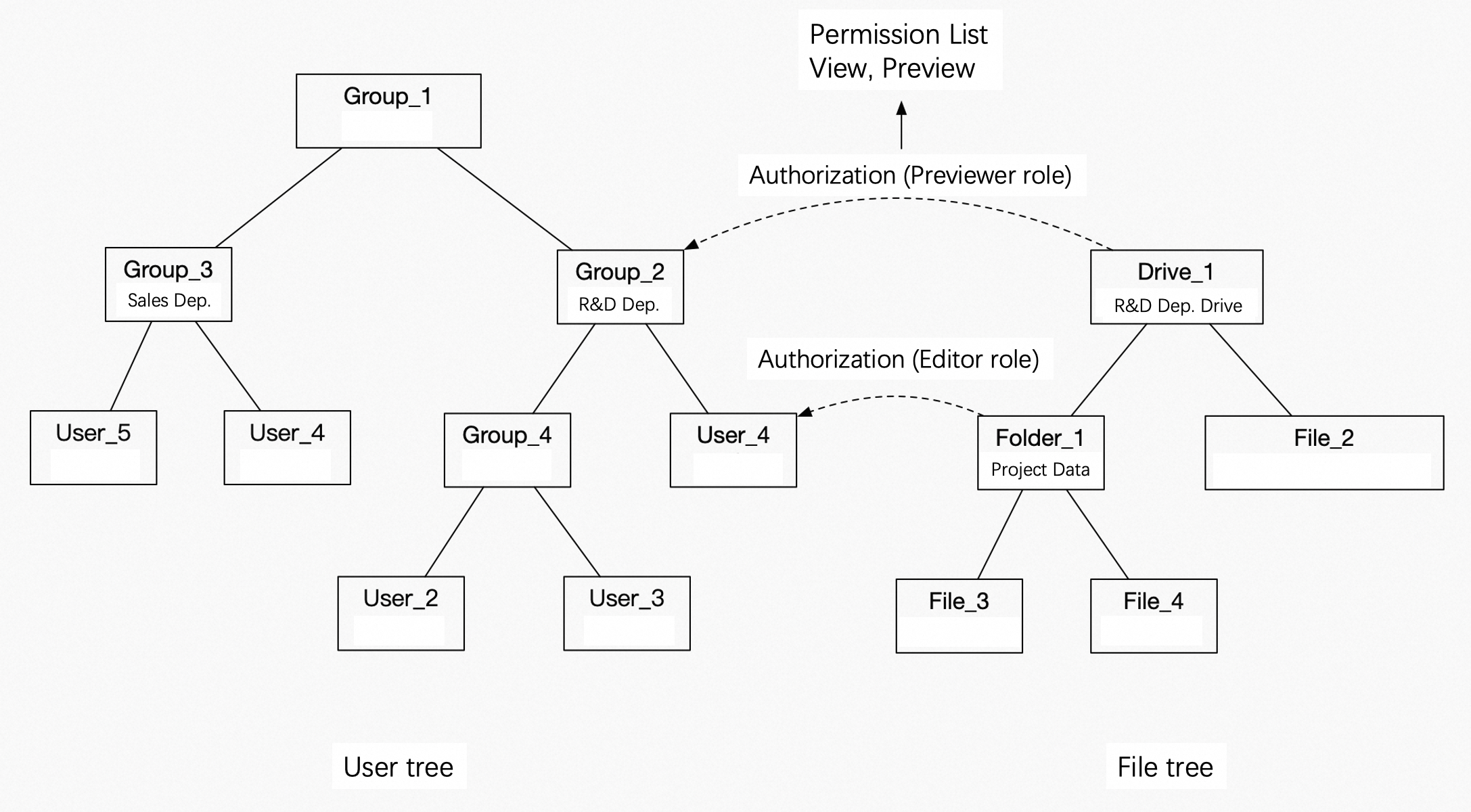
Concepts
A user tree is a tree structure that shows the parent-child relationships between users and teams. A user can be a member of multiple teams, but a team can belong to only one parent team.
A file tree is a tree structure that shows the parent-child relationships between files and folders, as shown in the preceding figure.
File authorization grants a user or team permissions for a folder. Permissions can be granted only on folders, not on individual files.
File authorization is granted through roles that define specific operation permissions. The system provides some common default roles, as shown in the following figure.
Team permission inheritance determines whether users in sub-teams can inherit the permissions granted to a parent team. For example, the "R&D Department Drive" is authorized to the "R&D Department" team. If inheritance is disabled, only "User_4", a direct member of the "R&D Department", can use this permission. "User_2" and "User_3" cannot.
File permission inheritance means that if a folder in a file tree is granted permissions, all its descendant files and folders inherit these permissions.
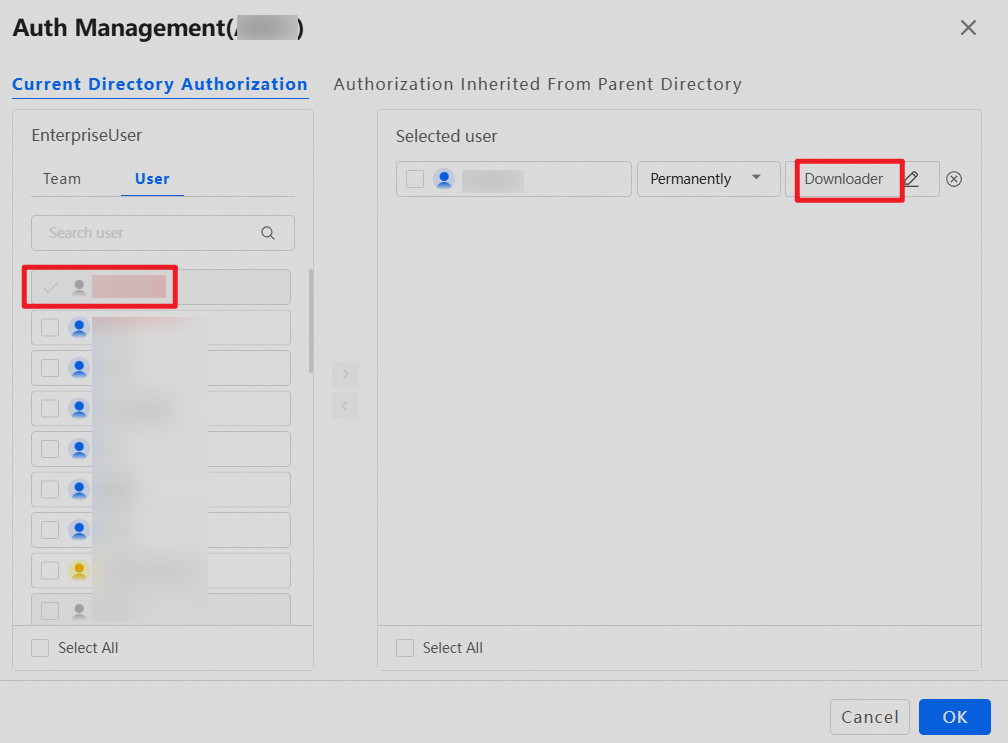
Permission overwriting occurs when a user has multiple active permissions for a resource. In this case, the permissions overwrite each other. For example, in the preceding figure, "User_4" has both "Previewer" and "Editor" permissions for the "Project Data" folder. The "Previewer" permission comes from the authorization to the parent team. The "Editor" permission comes from the authorization granted directly to the user. When multiple permissions apply to a user, the permission with the most specific scope takes precedence. Therefore, when "User_4" accesses the "Project Data" folder, the "Editor" permission is used. A special case exists. A user can be a member of multiple teams. If these teams are granted different permissions, the user's access permissions are the union of all granted permissions.
Permission names and roles
PDS provides the following 11 permissions and 15 default system roles. Default system roles are composed of different permissions. The 11 permissions are: visible List, Preview, Upload, Download, Share Link, Move, Copy, Rename, Delete, Update, and Create.

The permissions are described as follows:
Previewer: Can preview files such as images, documents, and videos online in the authorized space or folder. The list permission is a prerequisite.
Visible List: Can view which folders and files are in the authorized space or folder, but has no operation permissions.
Create: Can create files in the authorized space or folder. The list and upload permissions are prerequisites.
Upload: Can upload files to the authorized space or folder. The list and create permissions are prerequisites.
Download: Can download files from the authorized space or folder to a local device. The list and preview permissions are prerequisites.
Share Link: Can share folders and files in the authorized space or folder with other users or teams. The list and preview permissions are prerequisites.
Delete: Can delete folders and files in the authorized space or folder. The list permission is a prerequisite.
Move: Can shift folders and files in the authorized folder to another space or folder. The list and delete permissions are prerequisites.
Copy: Can copy folders and files in the authorized folder to another space or folder. The list permission is a prerequisite.
Rename: Can rename folders and files in the authorized space or folder. The list permission is a prerequisite.
Update: Can edit files and update or recover file versions in the authorized space or folder. The list and preview permissions are prerequisites.
Synchronizer: Can perform two-way synchronization or one-way upload for folders in a team space and in received shares.
Backer: Can perform one-way upload for folders in a team space and in received shares.
The download, share, and update permissions require the preview permission. This is to ensure that users can view the content of a file in the drive before operating on it.
Spaces
Enterprise space
After you purchase the Enterprise Edition, a root team with the same name as your enterprise is created by default. A space is also created for the root team to serve as the enterprise space. By default, all users in the enterprise have the preview permission for files in the enterprise space. Only super administrators and Drive administrators have permissions such as authorization, uploading, downloading, previewing, deleting, editing, and viewing the recycle bin.
The Developer Edition does not have a default enterprise space. You can create teams and spaces on your own.
By default, all users have the preview permission for files in the enterprise space. We recommend that you store only files that can be viewed by all users in the enterprise space, such as employee handbooks and public information. Store internal department files, such as project data, in team spaces. This facilitates fine-grained permission management.

Team space
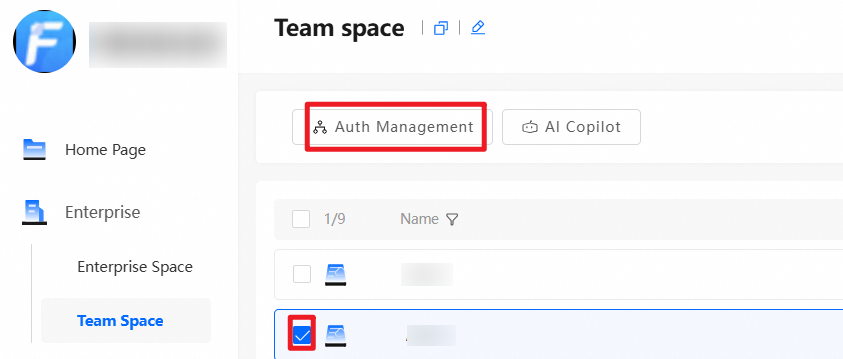
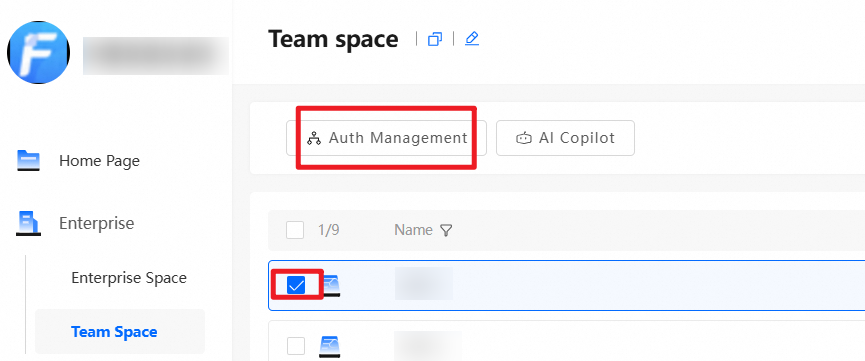
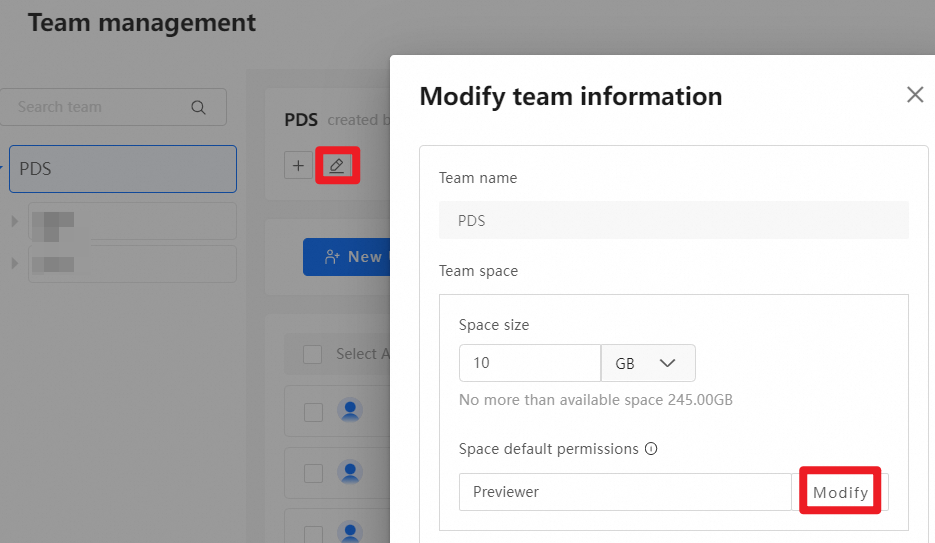
Teams are usually created based on the organizational structure of the enterprise. Team spaces are used to store files for different departments. Team administrators can grant permissions on folders in a team space to different teams or users based on business needs. Super administrators and Drive administrators can create team spaces. The following figure shows an example: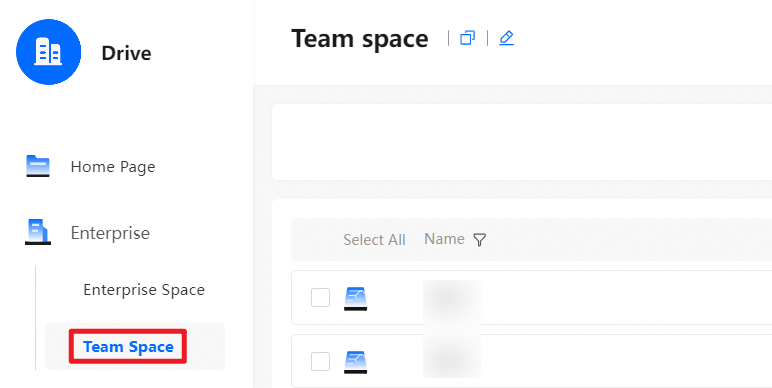
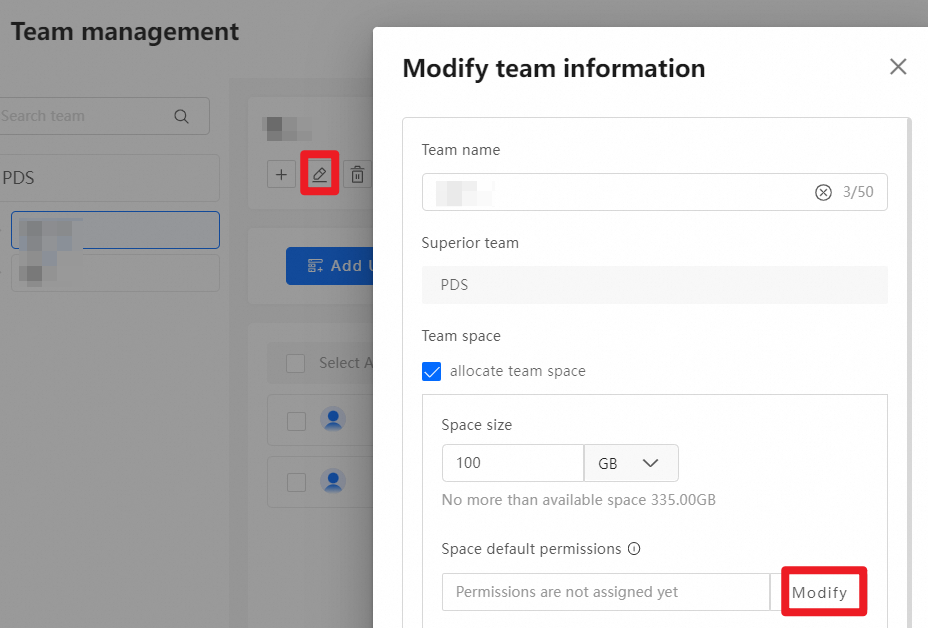
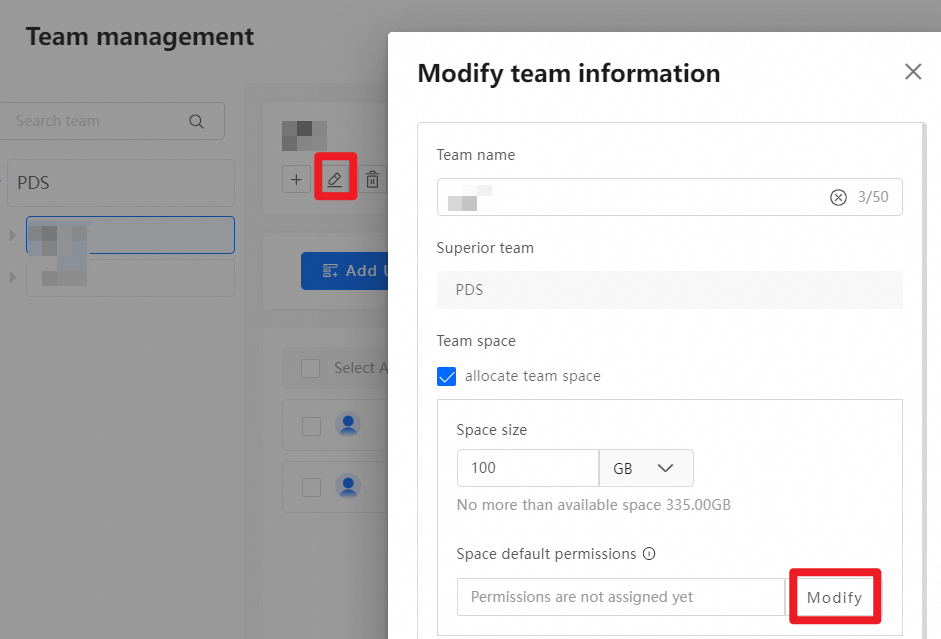
In the Management Console, click Team management. Select a team and click New sub team, as shown in the following figure:
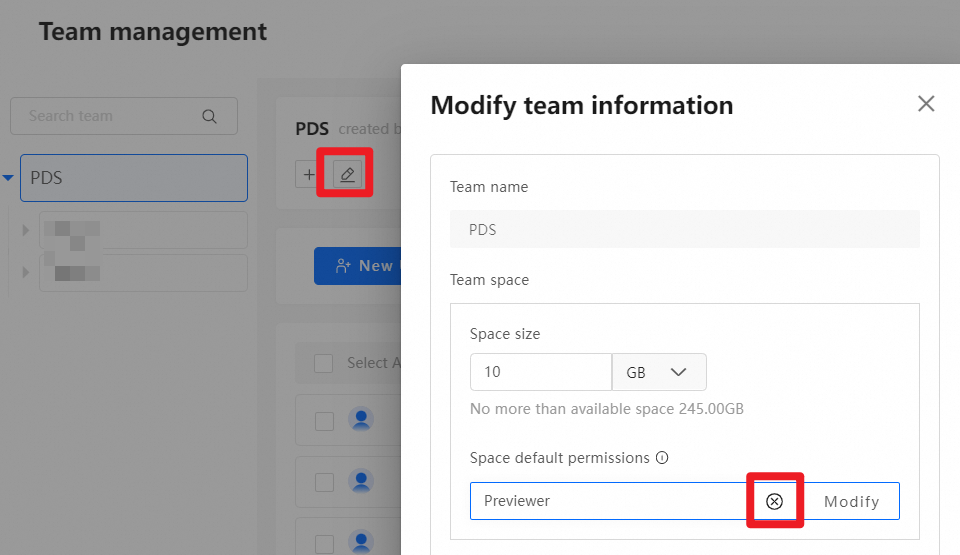
In the New sub team dialog box that appears, allocate a Space size to the team or set Space default permissions.
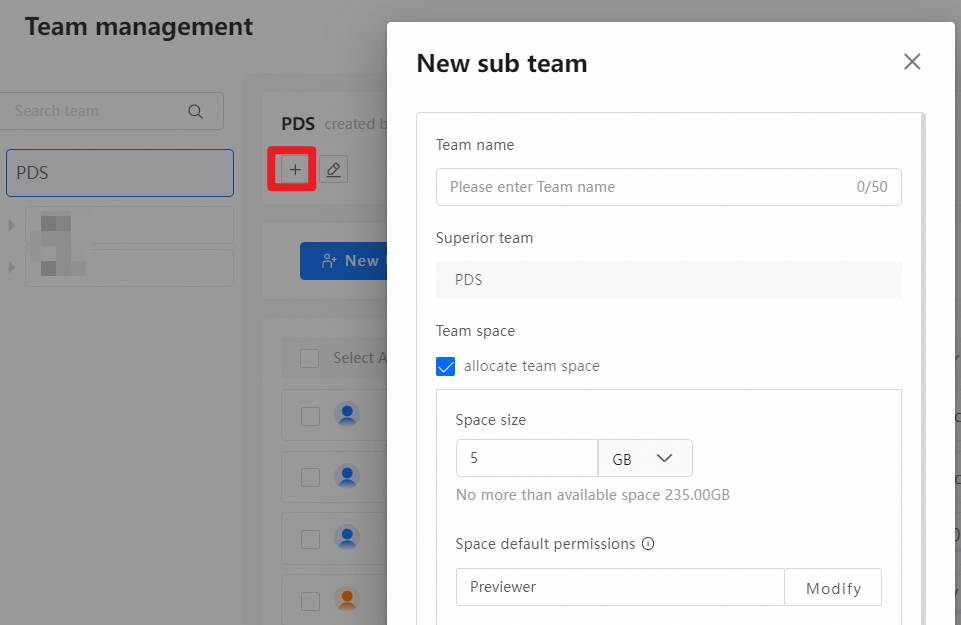
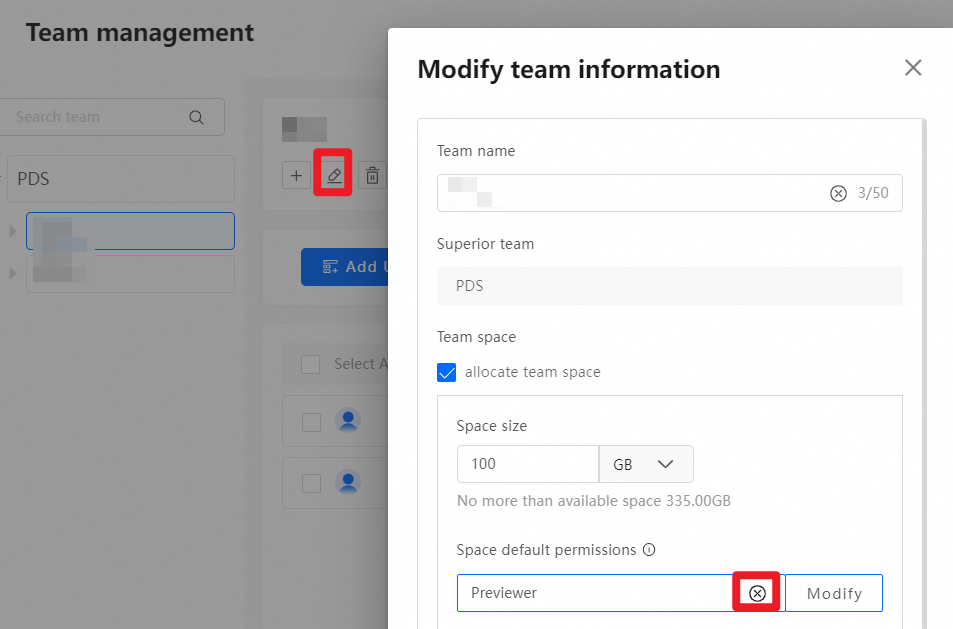
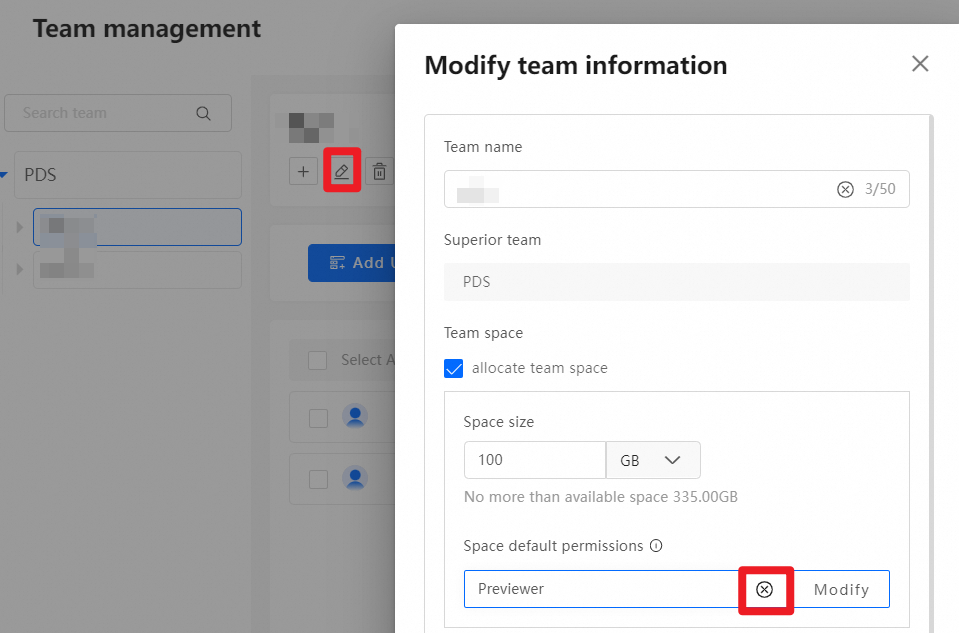
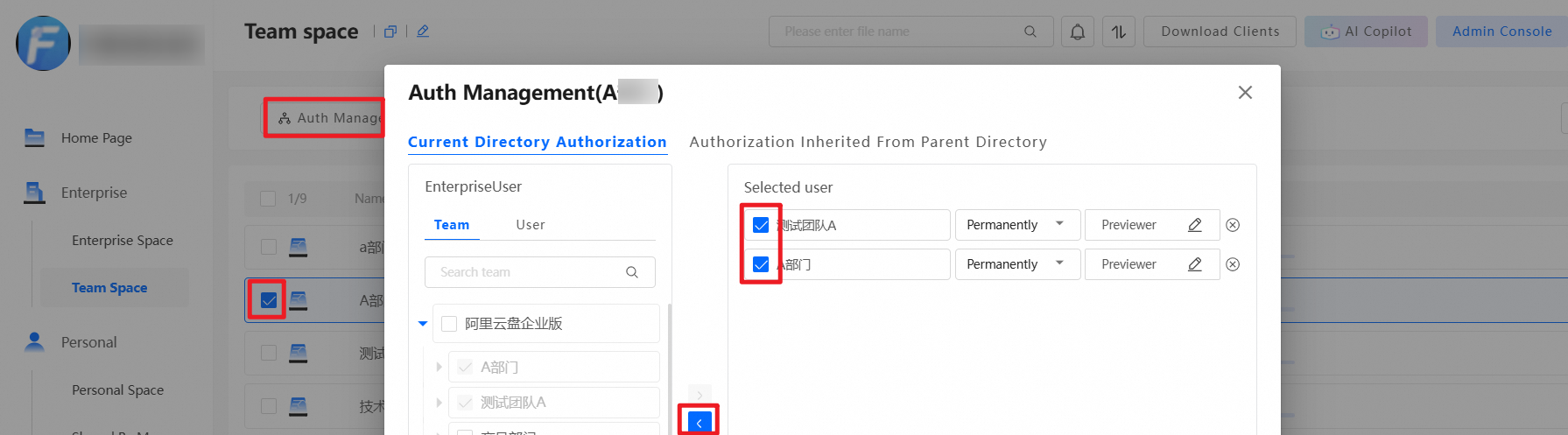
After a team space is created, the system assigns the Previewer role for the team space to the team by default. This means all members of the team can preview files in the team space by default. Administrators can modify or delete this default permission, or add other permissions. The following figure shows the default permission assigned by the system after a team space is created.
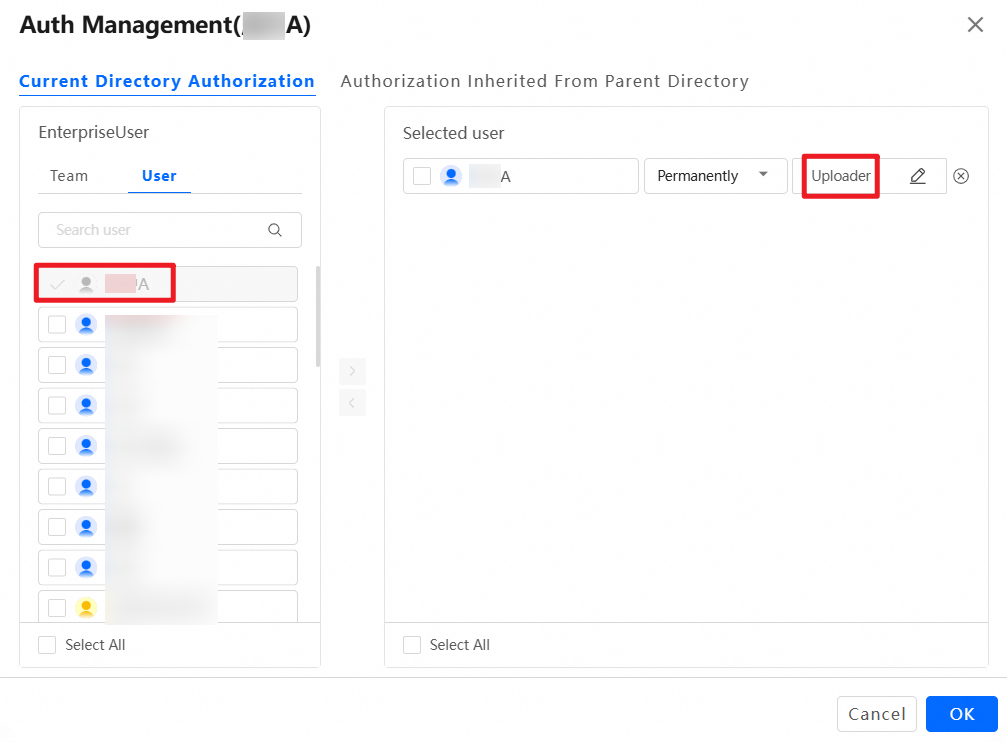
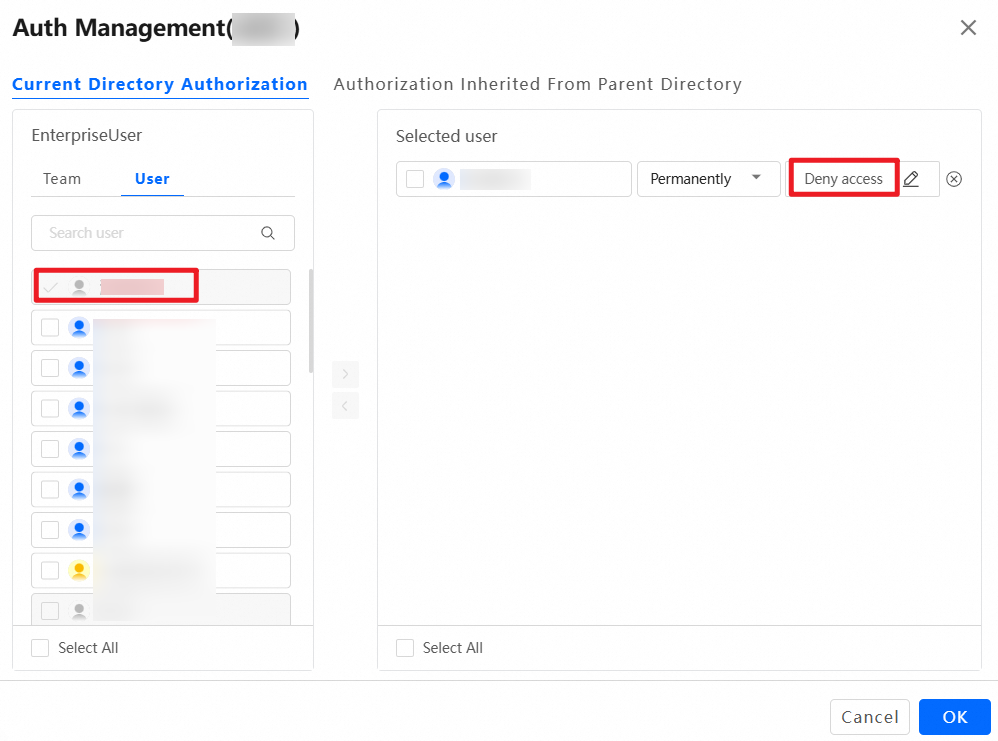
In addition to the default system permission, administrators can set other permissions for the team space as needed. For example, to allow User A from another team to preview files in this team space, drag User A from the left to the right and set the permission to Previewer. The operation is similar for granting permissions to other teams. Grant permissions on the entire team space or at the folder level. To grant folder-level permissions, log on as an administrator, go to the team space, select the folder for which you want to grant permissions, and perform the same operations.
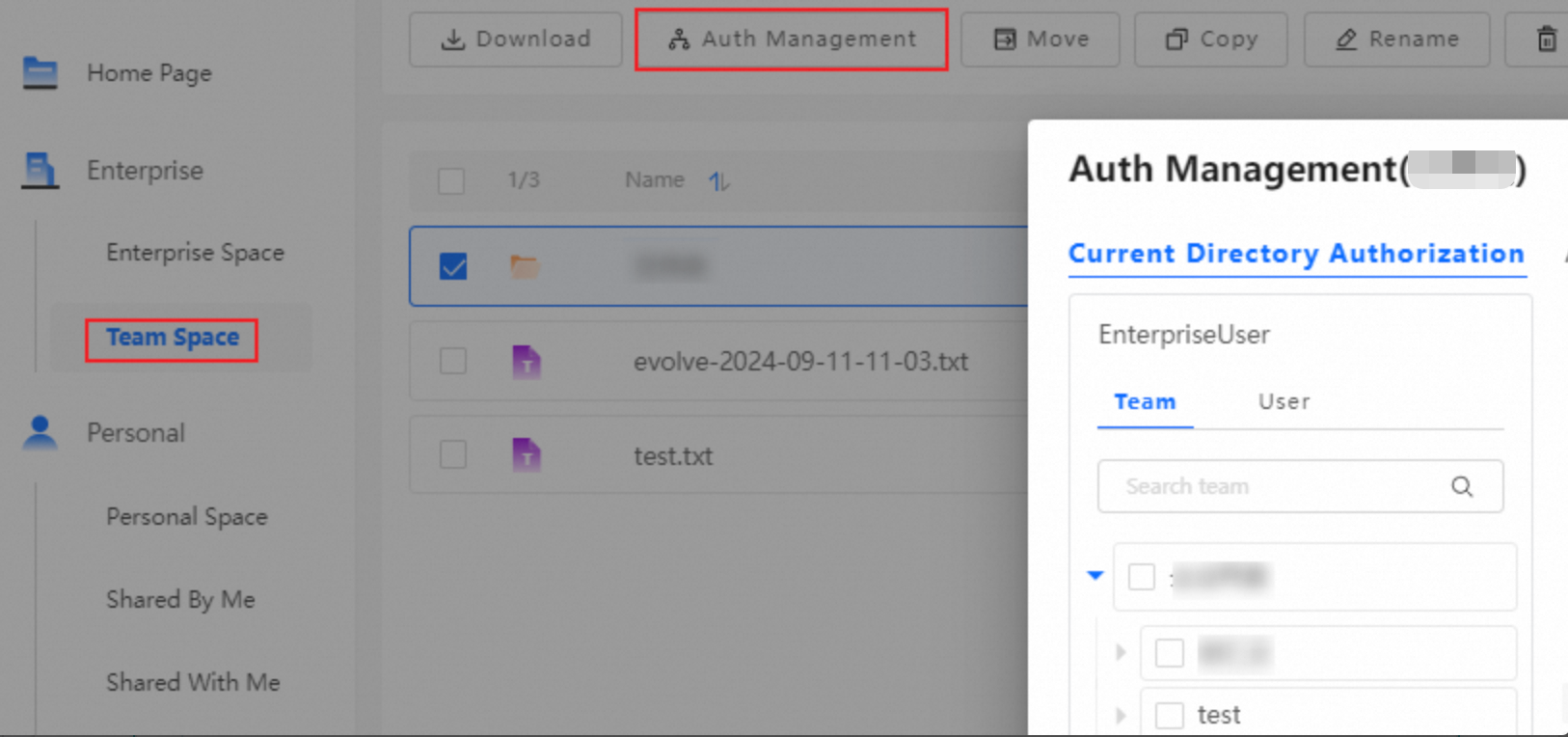
Authorization rules
When you grant permissions on a folder in a team space, the file path is retained. For example, a team space A contains the file "/B/C/D/1.jpg". You grant only the Previewer permission for folder D to User 1. In this case, User 1 can see team space A under "Team Space". After entering team space A, User 1 can see folder B. After entering folder B, User 1 can see folder C. After entering folder C, User 1 can see folder D. User 1 has only the Previewer permission for folder D. For folders B and C, User 1 has only the list permission. User 1 cannot see any folders in folder B other than folder C. User 1 cannot see any folders in folder C other than folder D. User 1 can preview all files and folders in folder D.
Inheritance rules
When you grant permissions to a team, choose whether its sub-teams inherit the permissions. If they do not inherit, only direct members of the team have the permissions.
Currently, you cannot block permissions inherited from a parent folder. You can only narrow the scope of permissions by granting new permissions to a subfolder.

Personal space
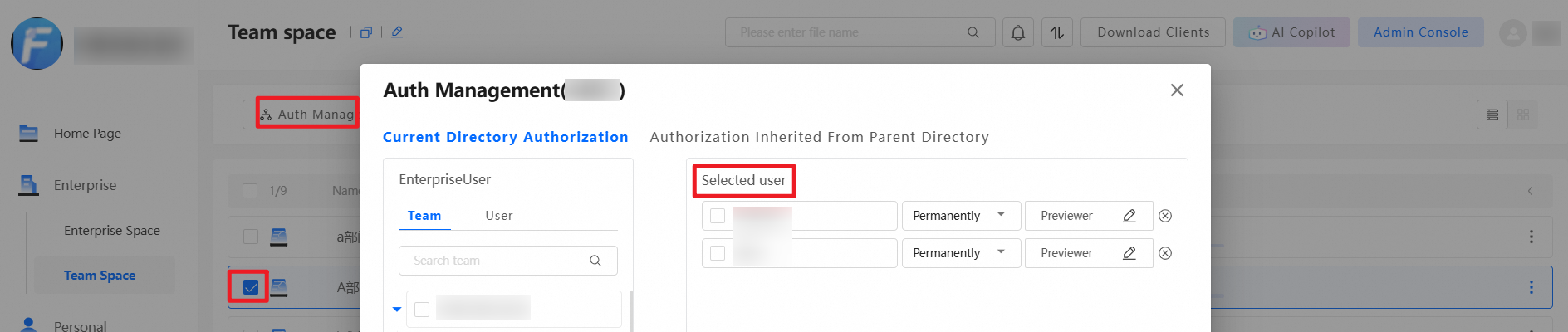
Personal spaces are mainly used to store users' personal files. By default, only the user can access their personal space. Even super administrators cannot view a user's personal space. The authorization operations for personal spaces are basically the same as for team spaces. An authorized user can view folders shared from another user's personal space in "Received Shares". The following figure shows an example:
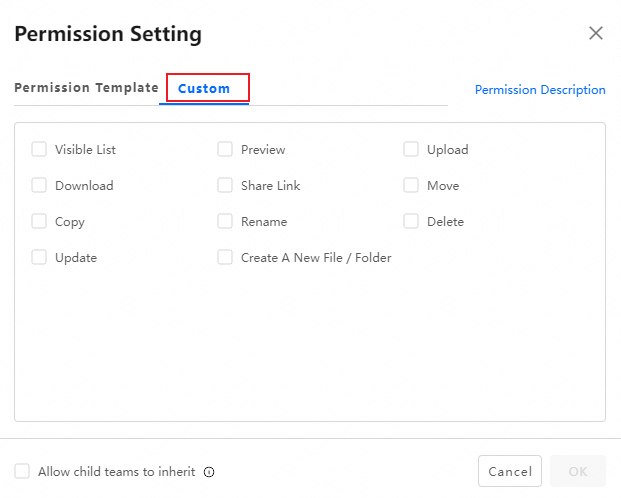
Custom permissions
Set custom permissions
In addition to using default permission roles, PDS lets you set custom permissions during authorization. Select the specific permissions you want to grant.
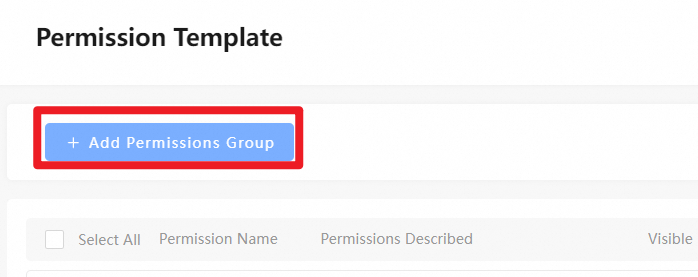
Add a permission template
If an administrator tries to delete a permission template that is in use, the deletion fails. A message appears indicating that the permission template is in use and cannot be deleted.
You can create a maximum of 50 preset permission templates.
In the Management Console, go to Enterprise Settings > Permission Template to add a custom permission template.
After a custom permission template is configured, use it on the authorization management page.

Delete files
Delete authorized files in a team space
Drive administrators, team administrators, or super administrators can directly delete files in a team space. The deleted files can be viewed in the recycle bin and can be recovered from it.
If a regular user is granted the delete permission, they can directly delete the corresponding files or folders. However, the deleted items do not appear in the regular user's recycle bin. Only a Drive administrator, team administrator, or super administrator can view these items in the recycle bin.
Delete shared files
If a user is granted full permissions, operations such as Co-administrator, Favorite, Delete, Move, and Rename are unavailable for the top-level folder. This means the top-level folder of a share cannot be deleted directly.
You can delete files or folders within a shared folder. The deleted items appear in the sharer's recycle bin and can be recovered. They do not appear in the recipient's recycle bin.