Large Language Models (LLMs) may lack enterprise-specific or real-time data. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology enhances the accuracy and relevance of model responses by providing LLMs with contextual access to private knowledge bases. You can use LangStudio to develop and deploy a RAG application for specialized domains such as finance and healthcare.
Background information
In modern information retrieval, RAG models combine the advantages of information retrieval and generative artificial intelligence to deliver more accurate and relevant answers in specific scenarios. For example, in specialized fields such as finance and healthcare, users often require precise and relevant information to support decision-making. Traditional generative models excel in natural language understanding and generation but may lack accuracy in specialized knowledge. RAG models improve the accuracy and contextual relevance of answers by integrating retrieval and generation technologies. Platform for AI (PAI) provides a RAG solution tailored for finance and healthcare scenarios.
Prerequisites
LangStudio supports Faiss or Milvus as the vector database. If you want to use Milvus, you must first create a Milvus database.
NoteFaiss is typically used for staging environments and does not require you to create a database. In a production environment, use Milvus because it can process larger data volumes.
The corpus for the RAG knowledge base has been uploaded to OSS. The following sample corpora are provided for finance and healthcare scenarios:
Financial news: This dataset is in PDF format and primarily consists of news reports from public news websites.
Disease introductions: This dataset is in CSV format and primarily consists of disease introductions from Wikipedia.
1. (Optional) Deploy an LLM and an embedding model
The RAG application flow requires LLM and embedding model services. You can quickly deploy the required model services using Model Gallery. If you already have a compliant model service that supports the OpenAI API, you can skip this step and use your existing service.
Go to QuickStart > Model Gallery and deploy the models for the following two scenarios. For more information about deployment, see Model deployment and training.
Select an LLM that uses instruction tuning. Base models cannot correctly follow user instructions to answer questions.
Set Scenario to AIGC > large-language-model and deploy the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B model as an example.

Set Scenario to NLP > embedding and deploy the bge-m3 embedding model as an example.

2. Create a connection
The LLM and embedding model service connections in this topic are based on the model services (EAS services) deployed in QuickStart > Model Gallery. For more information about other connection types, see Connection configuration.
2.1 Create an LLM service connection
Go to LangStudio, select a workspace, and then on the Model Service tab of the Service Connection Configuration page, click New Connection to create a general-purpose LLM model service connection.
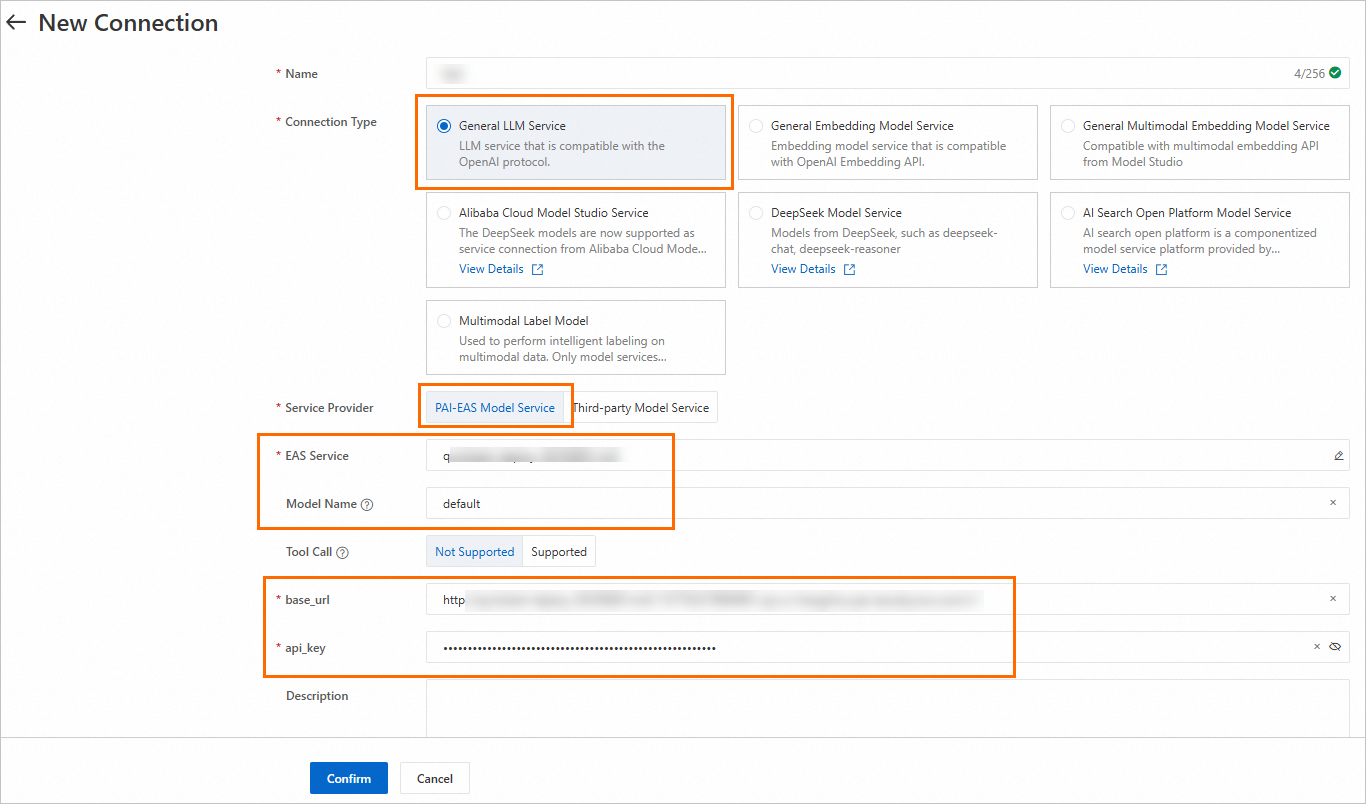
Key parameters:
Parameter | Description |
Model Name | When you deploy a model from Model Gallery, you can find the method to obtain the model name on the model's product page. To go to the product page, click the model card on the Model Gallery page. For more information, see Create a model service connection. |
Service Provider |
|
2.2 Create an embedding model service connection
Similar to creating an LLM service connection in Step 2.1, you can create a general-purpose embedding model service connection.
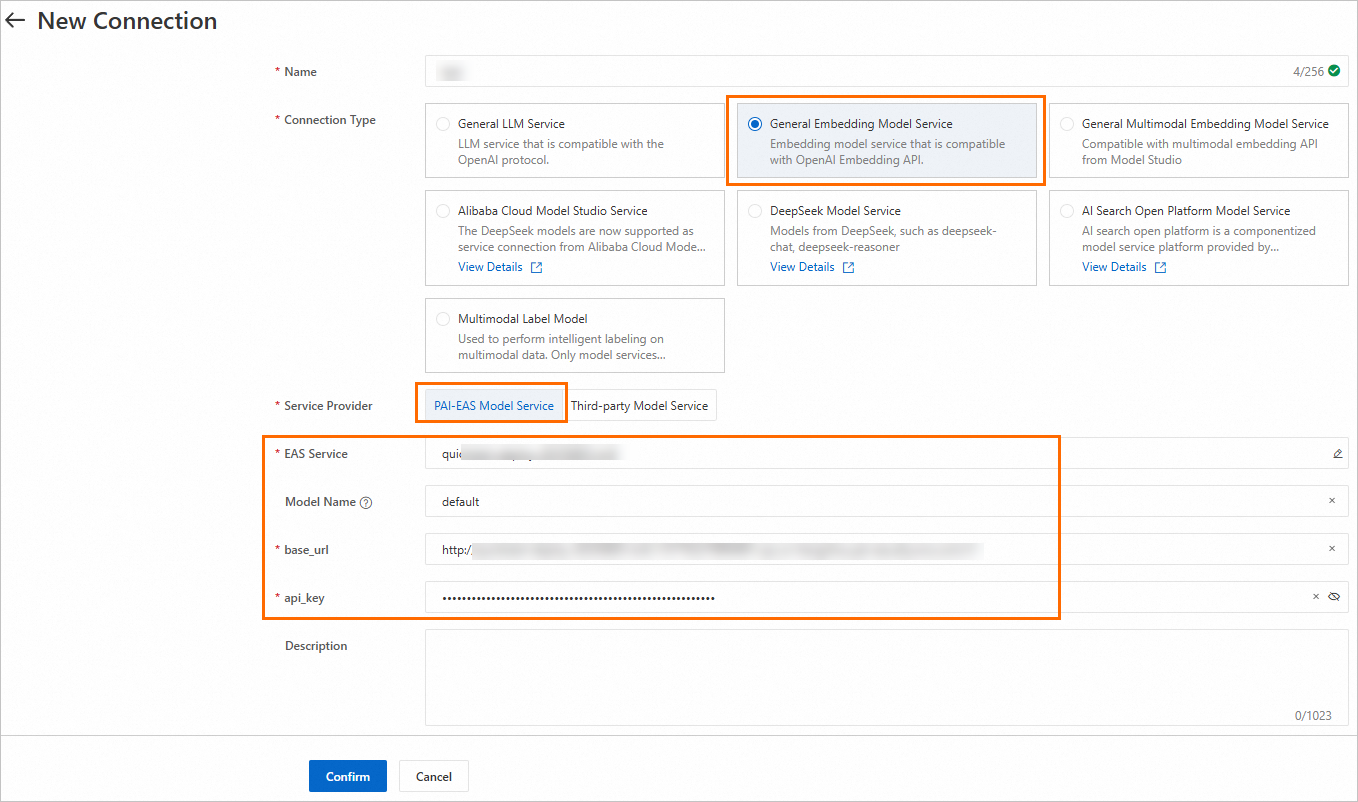
2.3 Create a vector database connection
On the Database tab of the Service Connection Configuration page, click New Connection to create a Milvus database connection.

Key parameters:
Parameter | Description |
uri | The endpoint of the Milvus instance. The format is |
token | The username and password to log on to the Milvus instance. The format is |
database | The database name. The following example uses the default database |
3. Create a knowledge base index
You can create a knowledge base index to parse, chunk, and vectorize the corpus. The results are then stored in the vector database to build the knowledge base. The following table describes the key parameters. For more information about other configurations, see Knowledge base management.
Parameter | Description |
Basic Configurations | |
Data Source OSS Path | The OSS path of the RAG knowledge base corpus from the Prerequisites section. |
Output OSS Path | The path to store the intermediate results and index information generated from document parsing. Important When you use FAISS as the vector database, the application flow saves the generated manifest to OSS. If you use the default PAI role (the instance RAM role set when you start the runtime for application flow development), the application flow can access the default storage bucket of your workspace by default. Therefore, set this parameter to any directory in the OSS bucket where the workspace default storage path is located. If you use a custom role, you must grant the custom role the access permissions to OSS. We recommend that you grant the AliyunOSSFullAccess permission. For more information, see Manage the permissions of a RAM role. |
Embedding Model and Database | |
Embedding Type | Select General Embedding Model. |
Embedding Connection | Select the embedding model service connection that you created in Step 2.2. |
Vector Database Type | Select Vector Database Milvus. |
Vector Database Connection | Select the Milvus database connection that you created in Step 2.3. |
Table Name | The collection of the Milvus database that you created in the Prerequisites section. |
VPC Configuration | |
VPC Configuration | Make sure that the configured VPC is the same as the VPC of the Milvus instance, or that the selected VPC is connected to the VPC where the Milvus instance is located. |
4. Create and run a RAG application flow
Go to LangStudio, select a workspace, and then on the Application Flow tab, click New Application Flow to create a RAG application flow.

Start the runtime: In the upper-right corner, click Create Runtime and configure the parameters. Note: You must start the runtime before you can parse Python nodes or view more tools.

Key parameters:
VPC Configuration: Select the VPC that you used when you created the Milvus instance in the Prerequisites section, or ensure that the selected VPC is connected to the VPC where the Milvus instance is located.
Develop the application flow.

Keep the default settings for the other configurations in the application flow or configure them as needed. The key node configurations are as follows:
Knowledge Base Retrieval: Retrieves text relevant to the user's question from the knowledge base.
Knowledge Base Index Name: Select the knowledge base index that you created in Step 3. Create a knowledge base index.
Top K: The number of top-K matching data entries to return.
LLM Node: Uses the retrieved documents as context and sends them with the user's question to the LLM to generate a response.
Model Settings: Select the connection that you created in Step 2.1 Create an LLM service connection.
Chat History: Specifies whether to enable chat history and use historical conversation information as an input variable.
For more information about each node component, see Descriptions of pre-built components.
Debug/Run: In the upper-right corner, click Run to execute the application flow. For information about common issues that may occur when you run the application flow, see the FAQ.

View link: Below the generated answer, click View Link to view the trace details or topology.

5. Deploy the application flow
On the application flow development page, click Deploy in the upper-right corner to deploy the application flow as an EAS service. Keep the default settings for the other deployment parameters or configure them as needed. The key parameter configurations are as follows:
Resource Deployment > Number of Instances: Configure the number of service instances. This deployment is for testing only, so set the number of instances to 1. In a production environment, configure multiple service instances to reduce the risk of a single point of failure.
VPC > VPC: Select the VPC where the Milvus instance is located, or ensure that the selected VPC is connected to the VPC where the Milvus instance is located.
For more information about deployment, see Deploy an application flow.
6. Call the service
After the deployment is successful, you are redirected to the PAI-EAS page. On the Online Debugging tab, you can configure and send a request. The key in the request body must be the same as the "Chat Input" field in the "Start" node of the application flow. The following example uses the default field question.

For more information about other ways to call the service, such as using an API, see Call a service.