LangStudio provides a "RAG and web search chatbot" application flow template that integrates real-time web search with RAG capabilities. This enables models to generate more accurate answers by combining real-time information with domain-specific knowledge bases. The template is suitable for high-accuracy scenarios such as finance and healthcare, and supports flexible extension and customization.
Background information
The "RAG and web search chatbot" application flow combines two information sources:
Web search: Retrieves real-time data from the internet to keep information current
RAG capabilities: Retrieves relevant content from domain-specific knowledge bases for accuracy
This dual-source approach is particularly effective for finance, healthcare, and other fields requiring highly accurate information. Developers can customize the template to meet specific business requirements.
Prerequisites
You have registered an account at the SerpApi website and obtained an API key (the free tier provides 100 searches per month).
You have selected a vector database type:
Faiss: Suitable for test environments, no additional setup required
Milvus: Suitable for production environments, supports larger data volumes. You must create a Milvus instance before use
You have uploaded the RAG knowledge base corpus to OSS.
1. (Optional) Deploy models
The application flow requires LLM and embedding model services. If you already have OpenAI API-compatible model services, skip this step.
Go to QuickStart > Model Gallery and deploy models for the following scenarios:
Use instruction fine-tuned models only. Base models cannot correctly follow instructions to answer questions.
Select large-language-model for Scenarios. In this example, DeepSeek-R1 is used. For more information, see One-click deployment of DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1 models.

Select embedding for Scenarios. In this example, bge-m3 embedding model is used.

2. Create connections
2.1 Create an LLM service connection
Go to LangStudio and select a workspace.
On the Connection > Model Service tab, click New Connection.
Create a General LLM Model Service connection.
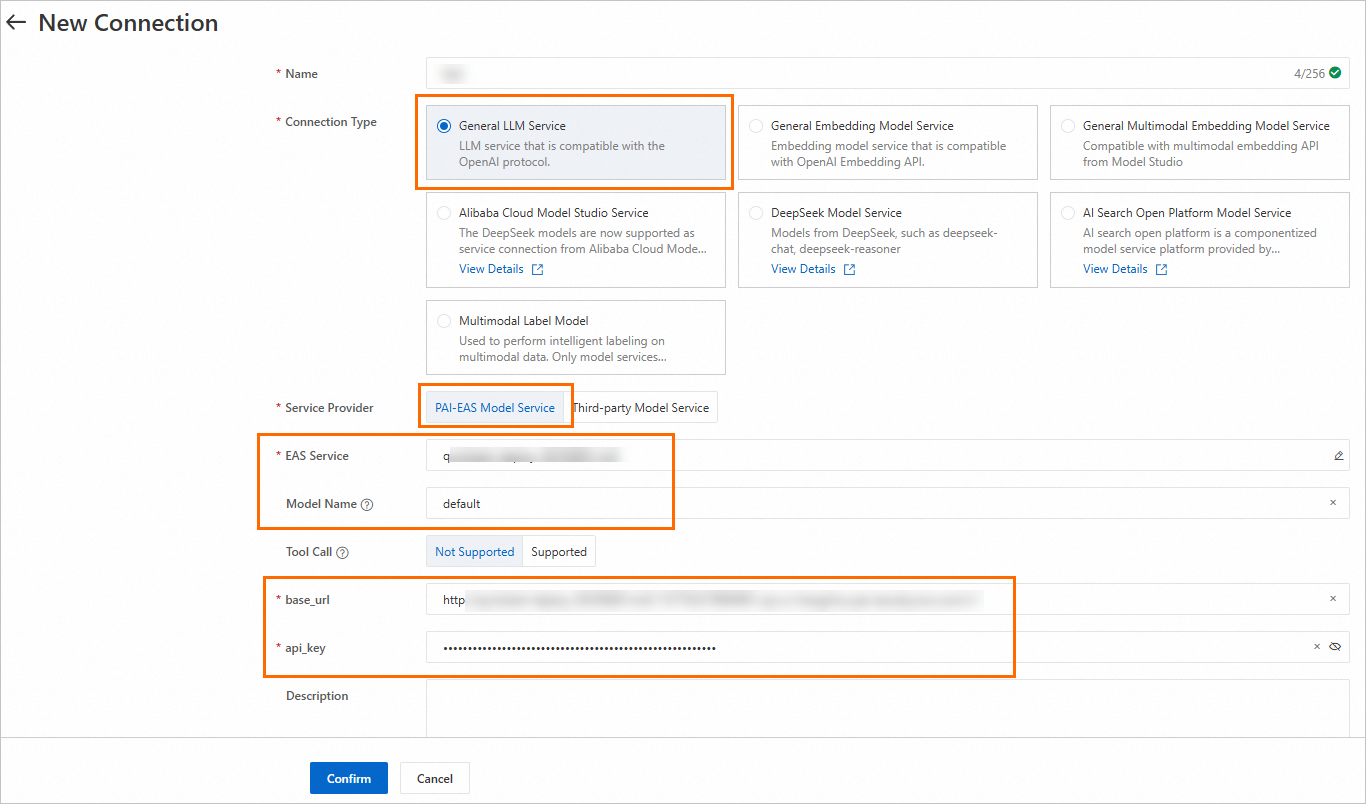
Key parameters:
Parameter | Description |
Service Provider |
|
Model Name | View the model details page in Model Gallery for instructions. For more information, see Create connections - Model service. |
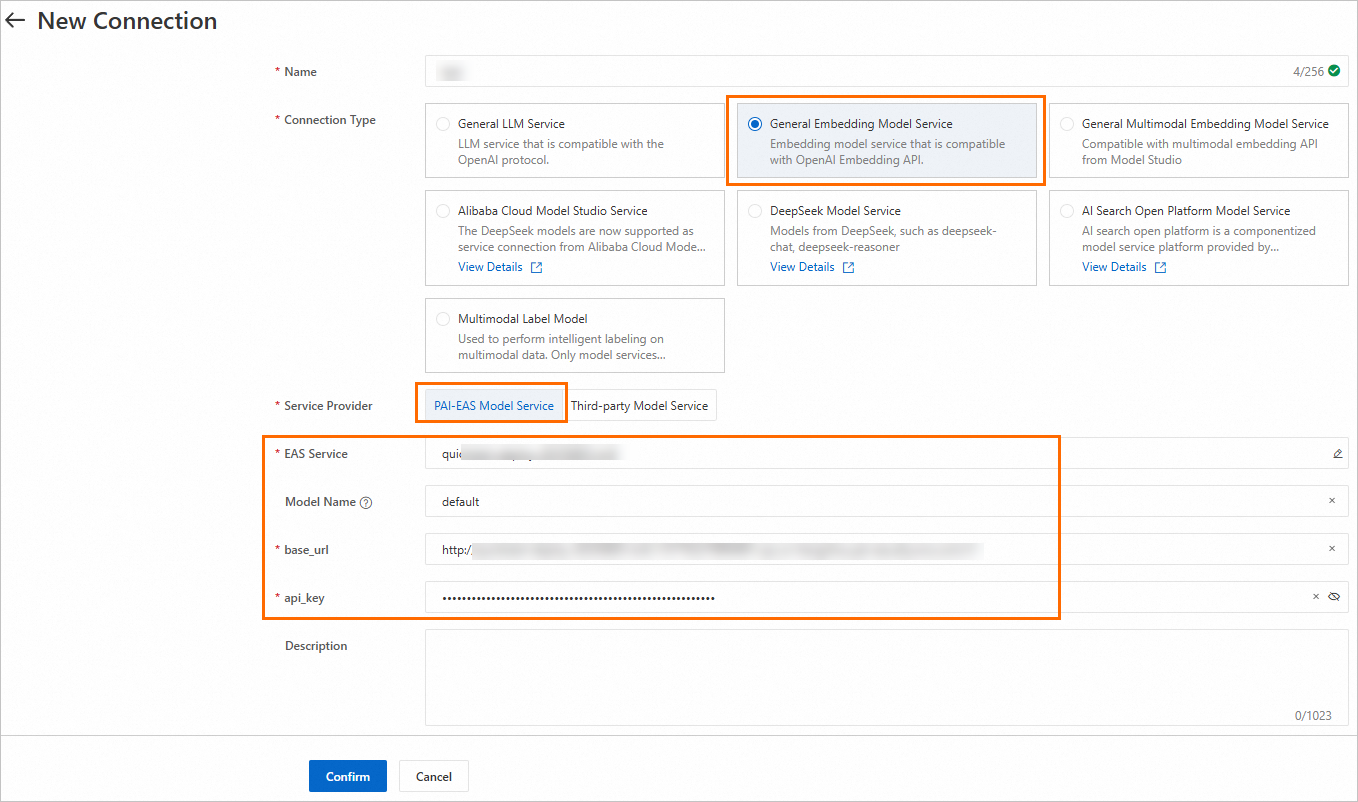
2.2 Create an embedding model service connection
Follow the same steps as 2.1 and select General Embedding Model Service type.
2.3 Create a SerpApi connection
On the Connection > Custom Connection tab, click New Connection.
Configure the api_key obtained in Prerequisites.

3. Create a knowledge base index
Create a knowledge base index to parse, chunk, and vectorize the corpus into a vector database. Key parameters are described below. For other configuration details, see Manage knowledge base indexes.
Parameter | Description |
Basic Configurations | |
Data Source OSS Path | The OSS path of the RAG knowledge base corpus uploaded in Prerequisites. |
Output OSS Path | The path for storing intermediate results and index files. Important When using FAISS, we recommend configuring this to a directory in the OSS bucket of the current workspace default storage path. Custom roles require AliyunOSSFullAccess permission. For more information, see Cloud resource access authorization. |
Embedding Model and Databases | |
Embedding Type | Select General Embedding Model. |
Embedding Connection | Select the connection created in Step 2.2. |
Vector Database Type | Select FAISS (used in this example). |
4. Create and run the application flow
On the LangStudio Application Flow tab, click Create Application Flow. Select the Chatbot with RAG and Web Search template.
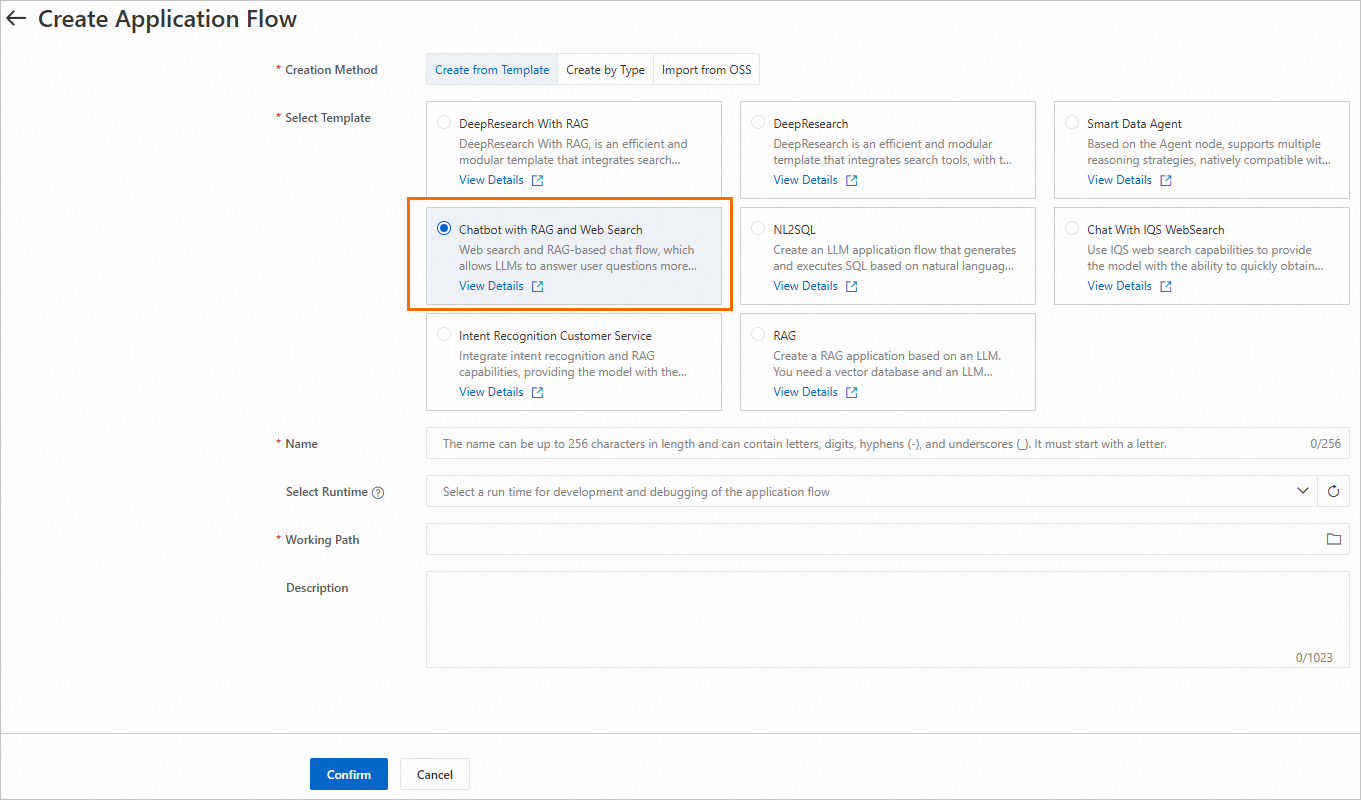
Click Select Runtime in the upper-right corner and select an existing runtime. If no runtime is available, click Create Runtime on the Runtime tab.

Note: The runtime must be started before you can parse Python nodes or view additional tools.
VPC configuration: When using Milvus, configure the same VPC as the Milvus instance, or ensure the VPCs are interconnected. When using FAISS, no VPC configuration is required.
Configure key nodes:

Knowledge Retrieval:
Index Name: Select the index created in Step 3
Top K: Number of matching results to return
Serp Search:
SerpApi Connection: Select the connection created in Step 2.3
Engine: Supports Bing, Google, Baidu, Yahoo, etc. For details, see the SerpApi website
LLM:
Model Configuration: Select the connection created in Step 2.1
Chat History: Whether to use chat history as input
For more information about each node, see Develop application flows - Node components.
Click Run in the upper-right corner to execute the application flow. For common issues, see LangStudio FAQ.

Click View Logs below the generated answer to view trace details or topology.

5. Deploy the application flow
On the application flow development page, click Deploy in the upper-right corner to deploy the application flow as an EAS service. Key parameters:
Resource Information > Instances: For testing, set to 1. For production, configure multiple instances to avoid single points of failure.
VPC: SerpApi requires internet access. Configure a VPC with internet access capability. For more information, see Service internet access. When using Milvus, ensure VPC connectivity with the Milvus instance.
For more deployment details, see Deploy and call application flows.
6. Call the service
After deployment, test the service on the Online Debugging tab of the EAS service details page.
The Key in the request body must match the "Chat Input" field in the application flow's Start Node. The default field is question.

For more calling methods (such as API calls), see Deploy application flows - Call the service.