When you use DataWorks to schedule a MaxCompute job at regular intervals, you can use general nodes in the DataWorks console, such as zero load nodes, branch nodes, merge nodes, and loop nodes, together with MaxCompute nodes to meet your complex business requirements. This topic describes the general nodes and their use scenarios.
Run a complex job that uses loop or traversal logic
DataWorks provides two types of loop nodes: for-each nodes and do-while nodes. If your job needs to use the loop logic, you can use for-each nodes and do-while nodes.
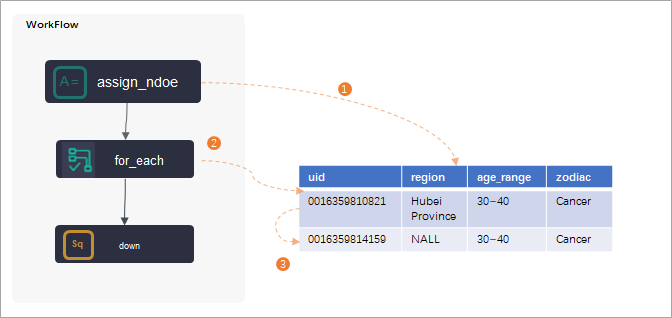
For-each node: A for-each node is used in loop traversal scenarios and must be used with an assignment node. An assignment node must be configured as the ancestor node of a for-each node. After the assignment node passes its output to the for-each node, the for-each node traverses the output in loops. For more information about assignment nodes, see Configure an assignment node.
 Note
NoteFor more information about how to use a for-each node, see Logic of for-each nodes.
Do-while node: You can rearrange the workflow inside a do-while node, write the logic to be executed in a loop into the node, and then configure an end node to determine whether to exit from looping. You can use a do-while node alone, or use a do-while node together with an assignment node to loop through the result set that is passed by the assignment node.
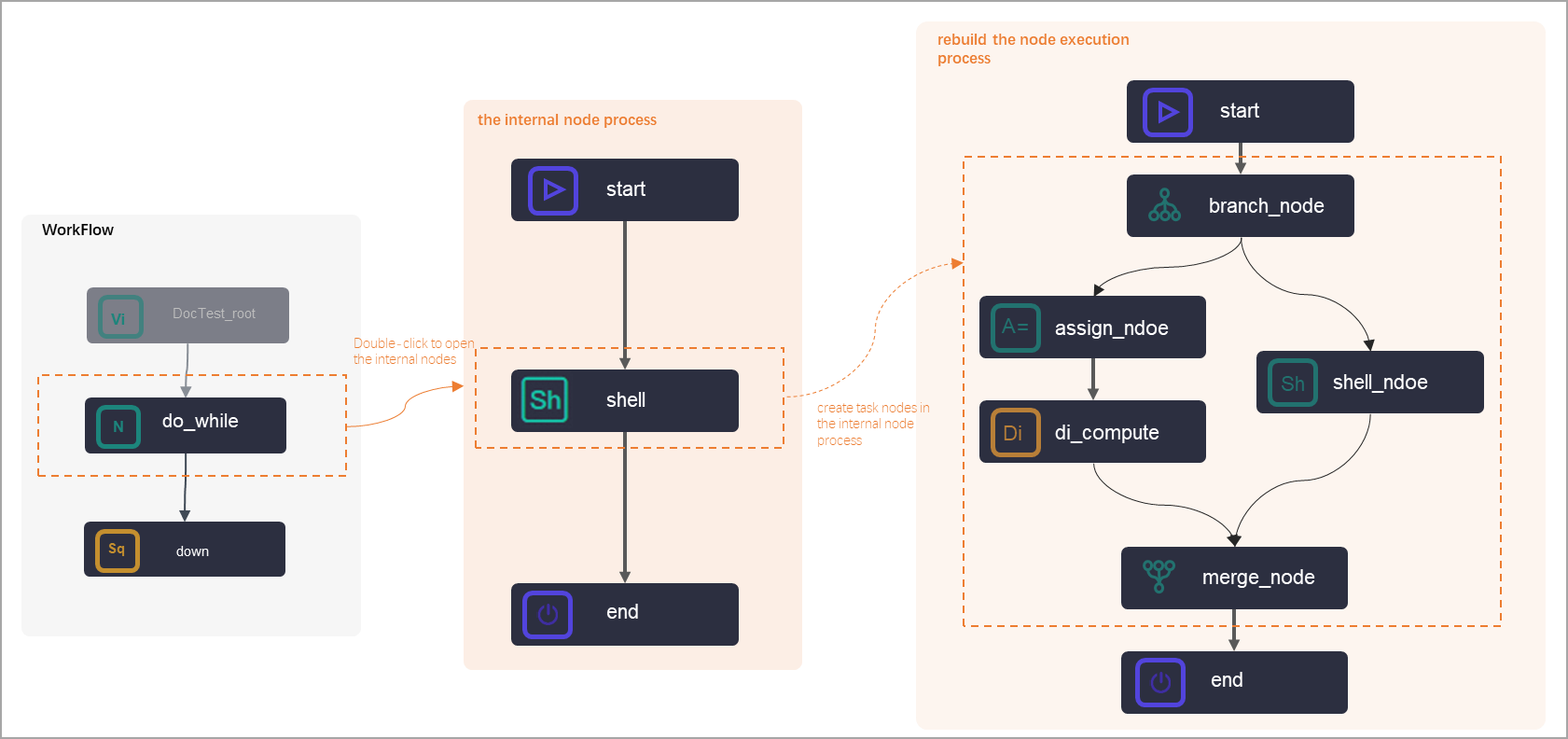 For more information about how to use a do-while node, see Logic of do-while nodes. Note
For more information about how to use a do-while node, see Logic of do-while nodes. NoteODPS SQL nodes for MaxCompute do not allow you to write the loop or traversal logic for a job. You can use the for-each nodes and do-while nodes to implement the job logic. You can also use PyODPS nodes to develop the loop or traversal logic code.
Run a job that implements parameter assignment between nodes
DataWorks allows you to transparently pass parameters between different nodes by using multiple methods. For example, you can use assignment nodes and parameter nodes to transparently pass parameters. If you want to assign a value to a variable for all nodes in a workflow, you can use workflow parameters.
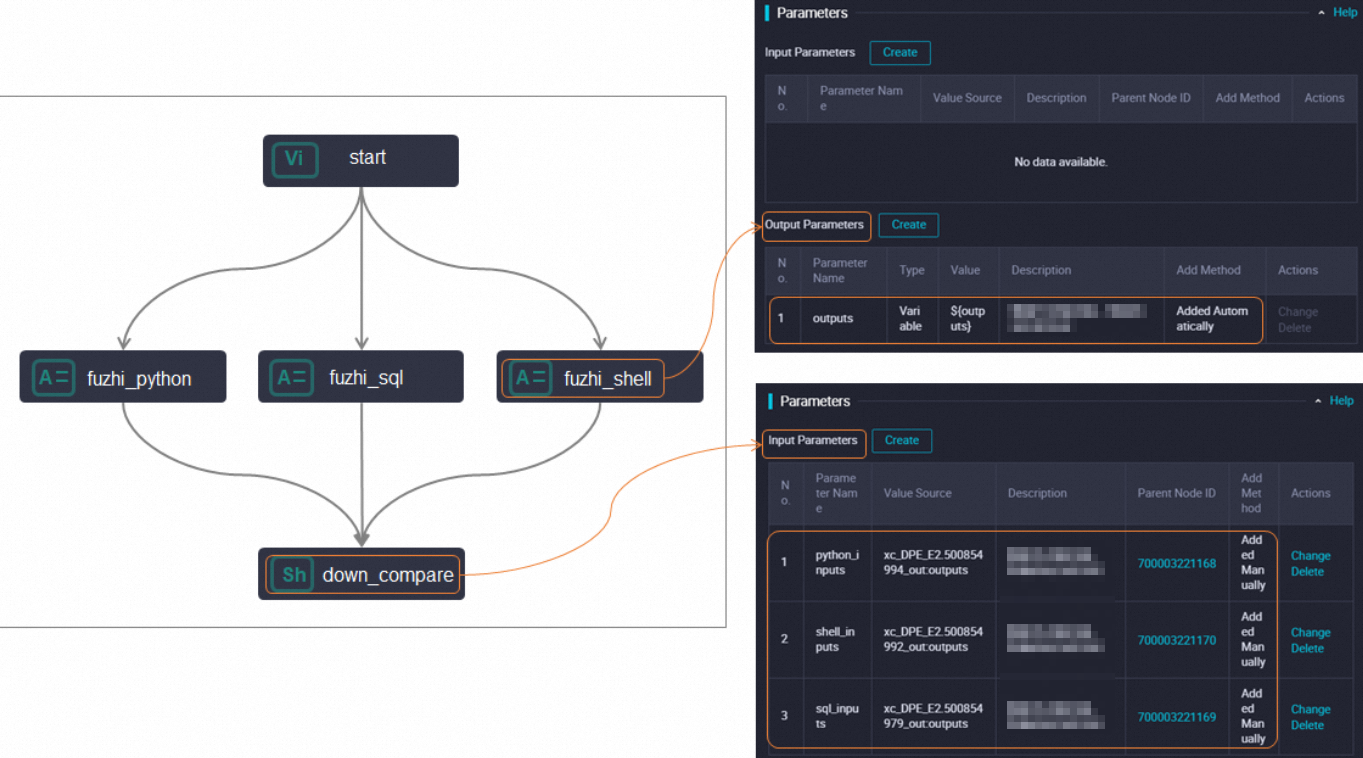
Assignment node: If you want a node to use the data of its ancestor node, you can use an assignment node to pass the data.
 Note
NoteFor more information about how to use an assignment node, see Configure an assignment node.
Parameter node: Parameter nodes are virtual nodes that do not run computing tasks. Parameter nodes are used to pass parameters between nodes and manage parameters in workflows.
Parameter passing between nodes
Parameter management
If Node A in a workflow needs to obtain the output parameters of its ancestor nodes, you can create a parameter node and use it as an ancestor node of Node A and a descendant node of the ancestor nodes of Node A. Then, add all the parameters required by Node A to the parameter node. This way, Node A can obtain all the required parameters from the parameter node.
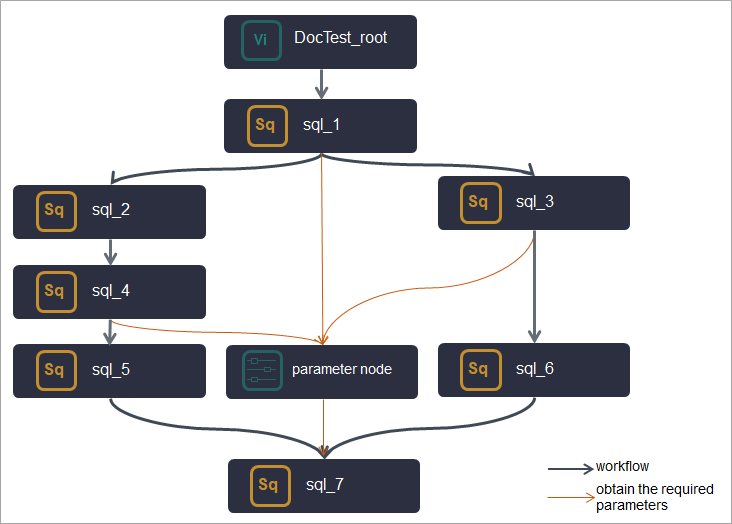
If nodes in a workflow need to use some constant and variable parameters, you can create a parameter node and use it as an ancestor node of the nodes. Then, add all the parameters required by the nodes to the parameter node. This way, the nodes can obtain all the required parameters from the parameter node. The parameter node allows you to manage all the parameters that are used in the workflow in a centralized manner.
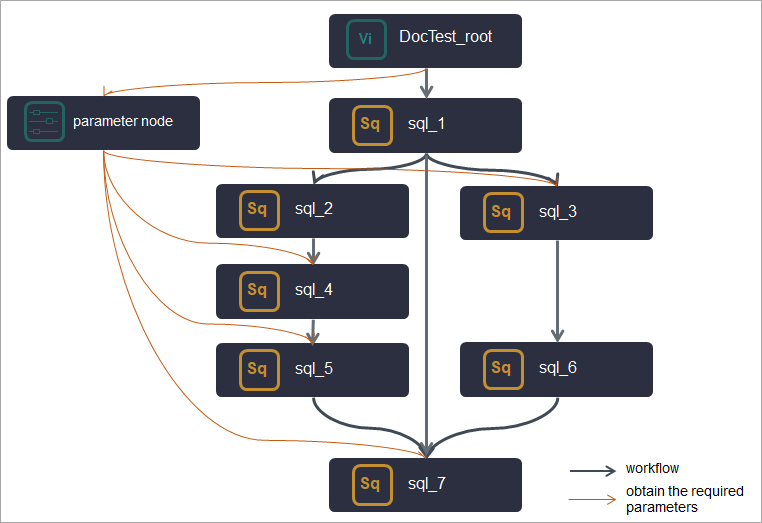 Note
NoteFor more information about how to use a parameter node, see Create a parameter node.
Workflow parameter: On the Workflow Parameters tab, you can assign a value to a variable or replace the value of a parameter for all nodes in the current workflow. For more information about how to use a workflow parameter, see Use workflow parameters.
Manage workflows
When you run a MaxCompute job in DataWorks, you can use zero load nodes of DataWorks to manage workflows. For example, you can use zero load nodes to manage workflows in scenarios in which dependencies between nodes are complex.
If you have multiple workflows, we recommend that you configure a zero load node as a start node for each workflow. This way, you can manage workflows with ease and clarify the data transmission process. 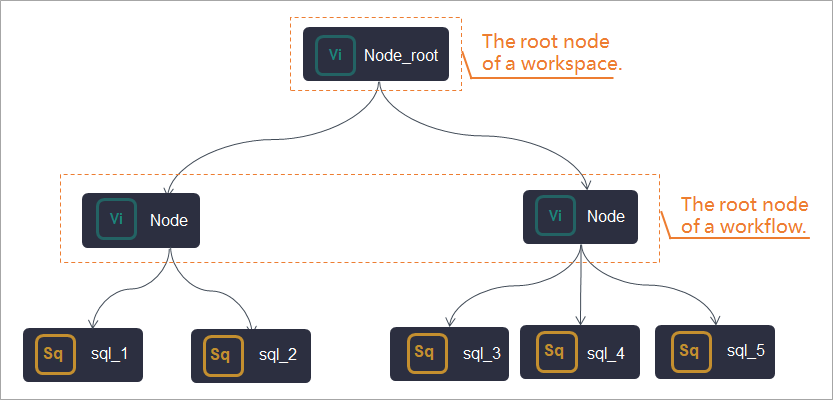
For more information about how to use a zero load node, see Create and use a zero load node.