DataWorks provides code templates that you can use to quickly mark and manage nodes. You can enable the scheduling feature to configure properties and rerun rules for auto triggered tasks. DataWorks also uses isolation, code comparison, and mandatory smoke testing to ensure task correctness and security. This topic describes how to configure these features.
Limitations
Only Workspace Administrators can configure system settings. To allow a user to perform these operations, you can grant them the workspace administrator role. For more information, see Add a workspace member and manage member roles and permissions.
The configured templates take effect only on new auto triggered tasks.
The default scheduling properties take effect only on new auto triggered tasks.
Security settings and other configurations take effect only in the current workspace.
Feature access
Go to the Workspaces page in the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select a desired region. Find the desired workspace and choose in the Actions column.
At the bottom of the navigation pane on the left, click to go to the Settings page.
Configure code templates
A code template is the default content that is displayed after you create a node. It includes information such as the node type, the user who created the node, and the creation time. This helps you quickly mark the node. Code templates are typically used for managing nodes at the business layer.
Set a code template
On the Scheduling Settings tab, find the target Code Type and click the Edit button for that code type. Then, modify the Code Template for that node type as needed.
For a list of node types for which you can modify the template in DataWorks, see Node types that support template configuration.
After you finish editing, click Save and confirm the changes.
You can create a new node of the corresponding type to view the changes.
Available template variables
When you define a code template, you can use variables to record information when a new task of that type is created. The following variables are supported in templates:
${author}: Records the user who created the node.When a node is created, this variable is automatically populated with the current logon account.
${createTime}: Records the time when the node was created.When a node is created, this variable is automatically populated with the current system time.
Node types that support template configuration
DataWorks supports custom code templates for the following node types:
Engine type | Node type |
MaxCompute | |
Hologres | |
EMR | |
CDH | |
ClickHouse | |
General | |
Set default scheduling configurations for auto triggered tasks
To run a new auto triggered task periodically, you must first enable the scheduling feature. This allows the task's scheduling configurations to take effect. You can also set the default resource group, rerun properties, number of reruns, and time interval.
These settings take effect only on new auto triggered tasks.
On the Scheduling Settings tab, click Modify to set the default configurations for scheduling features.
Feature
Description
Enable Scheduling
After you enable this feature, auto triggered tasks in the current workspace are automatically scheduled and run.
NoteIf you disable scheduling, the tasks that are already generated on the current day still run as normal. However, recurring instances for the next day will not be generated that night.
Scheduling Time Zone
The scheduling time zone is the time zone that corresponds to the region where the DataWorks workspace is located. This is the time zone used for timed scheduling of tasks. DataWorks lets you modify the scheduling time zone in some regions. For more information, see Regions that support scheduling time zone modification and How to switch time zones.
Timed Scheduling Time
By default, the timed scheduling time is randomly generated between
00:00 and 00:30. You can customize it as needed.Scheduling Resource Group
The default resource group used when a scheduled task runs.
Data Integration Resource Group
The default integration resource group used when a data integration task runs.
Rerun Property
The default rerun policy for an auto triggered task.
NoteWhen the Rerun Property is set to allow reruns, ensure the idempotence of the task to avoid Data Quality issues caused by multiple reruns.
Number Of Automatic Reruns
The default number of times an auto triggered task is automatically rerun if it fails to be scheduled and run.
The minimum number of reruns is 1, which means the task is automatically rerun once after an error occurs. The maximum number of reruns is 10. You can change this value as needed.
Rerun Interval
The default time interval between reruns for an auto triggered task.
The minimum interval is 1 minute, and the maximum interval is 30 minutes.
Click Save Configuration to save the default scheduling configurations.
After you configure the Scheduling Settings, new auto triggered tasks will use these default configurations.
Security settings and others
DataWorks provides an isolation feature that supports code and log isolation, code comparison, and mandatory smoke testing to ensure the correctness of tasks and the reliability of code. You can configure these features on the Security and Other Settings tab as needed.
Enable code and log isolation
After code and log isolation is enabled, users who are not members of this workspace cannot view its task code or run logs. To view the code and logs, contact an administrator to be added as a workspace member. For more information, see Add a workspace member and manage member roles and permissions.
Enable baseline display upon task submission
After you enable this feature, the baseline for a job is displayed when you publish a job. This helps you determine whether changes to the job affect the normal execution of the baseline job.
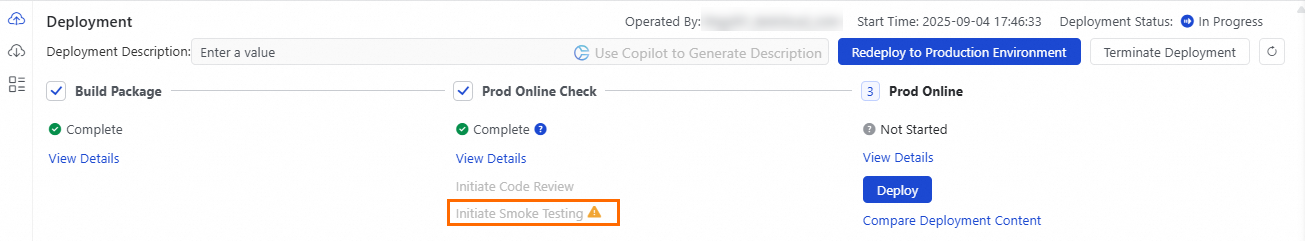
Enable mandatory smoke testing
After you enable this feature, when you publish a job, a smoke test must be passed before the job can be published. For more information, see Smoke Testing.
Enable the code comparison feature
After you enable this feature, you must complete the Compare Content review before you can publish a task.

Enable the dependency check feature
After this feature is enabled, when you publish a task, the system automatically checks whether the upstream dependencies configured for the current node match the results of the code kinship analysis. The task can be published only if the dependencies and results match. For more information, see Scheduling Dependencies.