DataWorks allows you to grant different permissions on workspace-level services in a workspace to workspace members by assigning the members different roles. The roles that can be assigned to members include built-in workspace-level roles and custom workspace-level roles. The built-in workspace-level roles are granted fixed permissions on specific workspace-level services. The custom workspace-level roles can be used to control the read and write permissions of members on workspace-level services. This topic describes the workspace-level roles that can be used to manage permissions on workspace-level services and the basic operations that can be performed to manage permissions of workspace members on workspace-level services.
Background information
DataWorks does not limit the number of members in a workspace. When you add RAM users to a workspace as members, you can configure permission settings for the RAM users to grant permissions on different workspace-level services to the RAM users. This way, after the RAM users are added to the workspace as members, the members can participate in data development in DataWorks.
No. | Description | References |
1 | A DataWorks workspace is a basic unit in which different roles can be used for collaborative data development. All data development operations are performed in a specific workspace. If you want to allow a RAM user to collaboratively perform data development operations, you must add the RAM user to a workspace as a member and assign roles to the member based on your business requirements. You can assign the built-in workspace-level roles provided by DataWorks to the member. For example, if you assign the Development role to the member, the member can perform data development operations in a workspace but cannot perform the deploy operation. | |
2 | If the built-in workspace-level roles cannot meet your business requirements, you can create a custom workspace-level role and assign the role to a RAM user. This way, you can control the permissions of the RAM user on a specific workspace-level service. For example, you can create a custom workspace-level role and assign the role to a RAM user to deny the access permissions on DataService Studio for the RAM user. | |
3 | Permission management on workspace-level services in DataWorks is performed based on the role-based access control (RBAC) model. After you add a RAM user to a workspace as a member and assign a workspace-level role to the member, the member is granted the permissions of the role on the related workspace-level service. |
Limits
Only workspaces of DataWorks Enterprise Edition support custom roles. For information about DataWorks editions, see Differences among DataWorks editions. If your workspace is not of DataWorks Enterprise Edition, you can upgrade the DataWorks service that you use to this edition. For information about the billing of DataWorks advanced editions, see Billing of DataWorks editions.
NoteIf you want to adjust the subscription duration when you upgrade the edition of your DataWorks service, we recommend that you unsubscribe from the current edition and then purchase the edition that you want to use. If you directly upgrade the edition of your DataWorks service, you must make up the price difference for the remaining period in the current billing cycle. For information about how to unsubscribe from a DataWorks edition, see the Unsubscribe from DataWorks subscription features or resources section in the "General reference: Stop using DataWorks features or resources" topic.
You can use only the Workspace Administrator and Workspace Owner roles to add members, change the roles that are assigned to members, remove members, and delete custom roles.
You can use only a RAM user that is assigned the Admin or Super_Administrator role of a MaxCompute project or an Alibaba Cloud account to configure the mapping between a DataWorks custom workspace-level role and a role of a MaxCompute project.
You cannot change the permissions of the built-in roles.
Workspace-level roles
DataWorks provides different identities, such as members and roles, at the workspace level. You can assign different roles to users based on the requirements of users for the workspace. DataWorks provides built-in workspace-level roles that are granted fixed permissions on specific workspace-level services. If the built-in workspace-level roles cannot meet your business requirements, you can create a custom workspace-level role on the Workspace Roles tab of the Workspace page in the DataWorks console.
Built-in workspace-level roles
By default, the built-in workspace-level roles provided by DataWorks have read permissions on all workspace-level services. The management and operation permissions of different built-in workspace-level roles on workspace-level services vary. The following table describes the built-in workspace-level roles and the permissions of each built-in workspace-level role on workspace-level services.
The owner of a workspace is the Alibaba Cloud account that is used to create the workspace. If a workspace is created by a RAM user, the owner of the workspace is the Alibaba Cloud account to which the RAM user belongs. The Workspace Owner role cannot be assigned to RAM users. For more information about the permissions of built-in workspace-level roles on workspace-level services, see Permissions of built-in workspace-level roles.
Role | Description |
Workspace Owner | This role has all permissions on a workspace. The owner of a workspace is an Alibaba Cloud account. For example, the Workspace Owner role can be used to assign a role to a RAM user and remove a member that is not the owner of a workspace from the workspace. |
Workspace Administrator | This role has permissions that are second only to the permissions of the Workspace Administrator role. The Workspace Administrator role can also be used to perform operations such as adding a user to a workspace as a member, removing a member from a workspace, or assigning a role to a member. |
Data Analyst | This role has permissions only on DataAnalysis. |
Develop | This role has permissions to perform data development and maintenance operations on the DataStudio page of a workspace. Note
|
O&M | This role has permissions to deploy tasks to the production environment on the Create Deploy Task page and perform O&M operations on all tasks in a workspace in Operation Center. |
Deploy | This role has permissions to review the code of a task and determine whether to commit the task to Operation Center in a workspace in standard mode. |
Visitor | This role has read-only permissions on workflows and code on the DataStudio page of a workspace. |
Security Administrator | This role has permissions only on Data Security Guard. |
Model Designer | This role has permissions to view models in Data Modeling and modify parameter configurations in Data Warehouse Planning, Data Standard, Dimensional Modeling, and Data Metric. This role does not have permissions to publish models. |
Data Governance Administrator | This role has permissions to view and manage data governance content of the workspace to which this role belongs in Data Governance Center. Note
|
Custom workspace-level roles
When you create a custom workspace-level role in the DataWorks console, you can control the permissions of the role on a workspace-level service. The following figure shows the permission settings that are supported by DataWorks for workspace-level services. If you want to use a MaxCompute compute engine in the workspace, you can configure the mapping between the custom role and a role of the MaxCompute compute engine. This way, the custom role is granted permissions on the resources in the MaxCompute compute engine. For information about how to create a custom workspace-level role, see the operations shown in the figure in this section.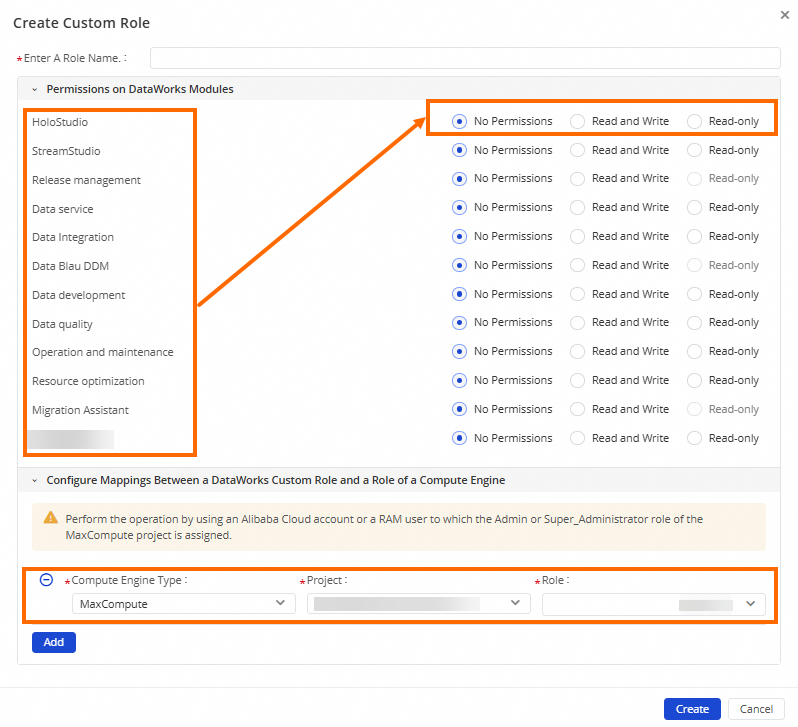
No Permissions: The role does not have permissions on the related service.
Read-only: The role can only view data information in the related service.
Read and Write: The role can modify data in the related service.
Add a RAM user to a workspace as a member and assign roles to the member
After you add a RAM user to a workspace as a member, you can assign a built-in workspace-level role to the member based on your business requirements. By default, after a RAM user is added to a workspace as a member, the member can access all workspace-level services. If you want to prohibit the member from accessing a specific workspace-level service, you can create a custom workspace-level role for which access permissions on the service are denied and assign the role to the member. This way, the member cannot access the workspace-level service.
Step 1: Go to the Workspace Members tab
In the left-side navigation pane, click Workspace Members and Roles. On the Workspace page, click the Workspace Members tab.
Step 2: Add a RAM user to a workspace as a member and manage members in the workspace
In the upper-right corner of the Workspace Members tab, click Add Members.
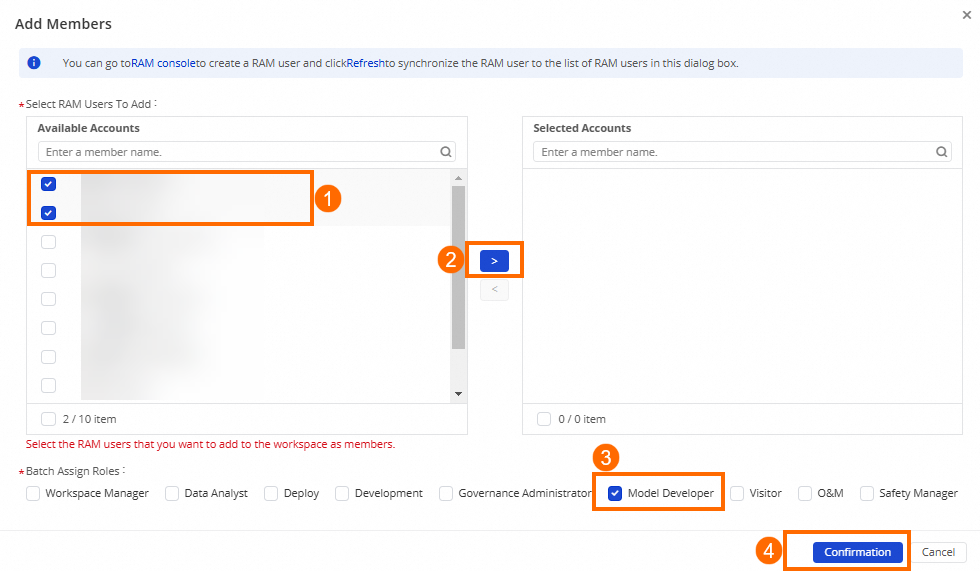
In the Add Members dialog box, select one or more RAM users from the Available Accounts list.
Operation
Description
Select the RAM users that you want to add to the workspace as members
The Available Accounts list displays all RAM users that belong to the current Alibaba Cloud account. You can select one or more RAM users that you want to add to the workspace as members from the list and click the > icon to move the selected RAM users to the Selected Accounts list. This way, the RAM users become the members in the workspace and can participate in data development.
NoteIf the RAM user that you want to add to the workspace is not displayed in the Available Accounts list, you can click Refresh in the prompt message that is displayed in the upper part of the dialog box to refresh the Available Accounts list.
Assign multiple roles to a RAM user at a time
You can select the roles that you want to assign to the selected RAM user and click Confirmation. This way, the selected roles are assigned to the RAM user at the same time, and the RAM user is granted the permissions of the roles. You can assign built-in workspace-level roles or custom workspace-level roles to the RAM user. Before you assign a custom workspace-level role to the RAM user, you must refer to the operations described in the following subsection to create a custom workspace-level role.
NoteMaxCompute provides built-in roles for a MaxCompute compute engine. Mappings exist between the built-in workspace-level roles of DataWorks and the built-in roles of a MaxCompute compute engine instance in the development environment. This way, after a RAM user is assigned a built-in workspace-level role of DataWorks, the RAM user is automatically granted the permissions of the mapped built-in role of the MaxCompute compute engine instance in the development environment. However, the RAM user does not have the permissions of the mapped built-in role of the MaxCompute compute engine instance in the production environment by default.
For information about how to grant permissions on a MaxCompute compute engine instance to a member in a workspace, see Manage permissions on data in a MaxCompute compute engine.
For information about mappings between the built-in workspace-level roles of DataWorks and the built-in roles of a MaxCompute compute engine, see Appendix: Mappings between the built-in workspace-level roles of DataWorks and the roles of MaxCompute.
If you want to use another type of compute engine in a workspace as a workspace member, you cannot grant permissions on the compute engine to the member by assigning a workspace-level role to the member.
Click Confirmation.
Then, you can view information such as all members in the workspace and the account and roles of each member on the Workspace Members tab. You can also specify the filter conditions to search for the desired member and change the workspace-level roles that are assigned to the member in the Role column. In addition, you can click Remove in the Actions column of a member to remove the member from the workspace.
(Optional) Create a custom workspace-level role
You cannot change the permissions of built-in workspace-level roles. If the built-in workspace-level roles cannot meet your business requirements for permission management, you can create a custom workspace-level role on the Workspace Roles tab.
On the Workspace page, click the Workspace Roles tab. On the Workspace Roles tab, click Create Custom Role.
In the Create Custom Role dialog box, specify a name for the role and configure permission settings on each workspace-level service for the role.
No Permissions: The role does not have permissions on the related service.
Read-only: The role can only view data information in the related service.
Read and Write: The role can modify data in the related service.
In the Configure Mappings Between a DataWorks Custom Role and a Role of a Compute Engine section, click Add to configure the mapping between the custom workspace-level role and a role of a compute engine.
If you want to use a MaxCompute compute engine in the workspace, you can specify a built-in role of the MaxCompute compute engine and configure a mapping between the custom workspace-level role and the role of the MaxCompute compute engine when you create the custom workspace-level role. This way, after the custom workspace-level role is assigned to a member in the workspace, the member is automatically granted the permissions of the built-in role of the MaxCompute compute engine. For information about the mappings between the roles of different types of compute engines and the roles of DataWorks, see Appendix: Mappings between the built-in workspace-level roles of DataWorks and the roles of MaxCompute.
Click Create.
When the Created message appears, the custom workspace-level role is created. When you add a user to the workspace as a member, you can assign this role to the member. In addition, you can modify or delete the custom workspace-level role on the Workspace Roles tab.