The DataWorks Shell node allows data engineers to run standard Shell scripts. It is ideal for tasks such as file operations and interacting with Object Storage Service (OSS) or Network Attached Storage (NAS). You can configure scheduling parameters, reference resources, use the pre-installed ossutil tool to securely access OSS, and run the node with an associated RAM role.
Permissions
The RAM account used for node development must be added to the workspace and assigned the Developer or Workspace Administrator role. For more information, see Add members to a workspace.
Usage notes
Syntax limitations
Standard Shell syntax is supported. Interactive syntax is not supported.
Execution environment and network access
When you run a Shell node on a Serverless resource group, if the target service has an IP address allowlist, you must add the IP addresses of the Serverless resource group to the allowlist.
When using a Serverless resource group, a single task supports a maximum of
64CU. We recommend not exceeding16CU to prevent resource shortages that could affect task startup.
Custom development environment
If a task requires a specific development environment, you can use the custom image feature in DataWorks to build a tailored image for task execution. For more information, see Custom images.
Resources and multiple script calls
Avoid launching a large number of child processes within a Shell node. Shell nodes have no resource limits, so an excessive number of child processes can affect other tasks on the same resource group.
If a Shell node calls another script, such as a Python script, the Shell node waits for the called script to complete before finishing.
Quick start
This section walks you through the entire process of creating, debugging, configuring, and deploying a Shell node using a simple "Hello DataWorks!" example.
Develop the node
Log on to the DataWorks console. After switching to the target region, click the icon, select the target workspace from the drop-down list, and then click Go to DataStudio.
On the Data Studio page, create a Shell node.
In the script editor, enter the standard Shell code. Interactive syntax is not supported.
echo "Hello DataWorks!"After writing the code, click Run a task in the right panel. Select the resource group for debugging and specify any other necessary execution parameters. Then, click the
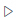 Run button to start a debugging run.
Run button to start a debugging run.After the script passes debugging, click Properties in the right panel. Configure the scheduling settings for production, such as the scheduling cycle, dependencies, and parameters, to enable the node to run automatically on a schedule.
After configuring the scheduling settings, you must save the node before proceeding.
Deploy and manage the node
After configuring the scheduling settings, you can submit and deploy the Shell node to the production environment. For more information about the deployment process, see Node and workflow deployment.
After deployment, the task runs periodically as scheduled. To view the deployed task, click the
 icon in the upper-left corner. In the navigation pane that appears, go to to open Operation Center. Then, in the left-side navigation pane, choose . For more information about the features, see Getting started with Operation Center.
icon in the upper-left corner. In the navigation pane that appears, go to to open Operation Center. Then, in the left-side navigation pane, choose . For more information about the features, see Getting started with Operation Center.
Advanced usage
Referencing resources
DataWorks allows you to upload resources for your Shell nodes using the Resource Management feature. For more information, see Resource management.
NoteA resource must be published before a node can reference it. If a production task uses a resource, you must also deploy that resource to the production environment.
Open an existing Shell node to open the script editor.
In the left-side navigation pane, click the
 icon to open the Resource menu. Find the resource you want to reference, right-click it, and select Reference Resource. This adds a reference to the resource in your Shell script.
icon to open the Resource menu. Find the resource you want to reference, right-click it, and select Reference Resource. This adds a reference to the resource in your Shell script.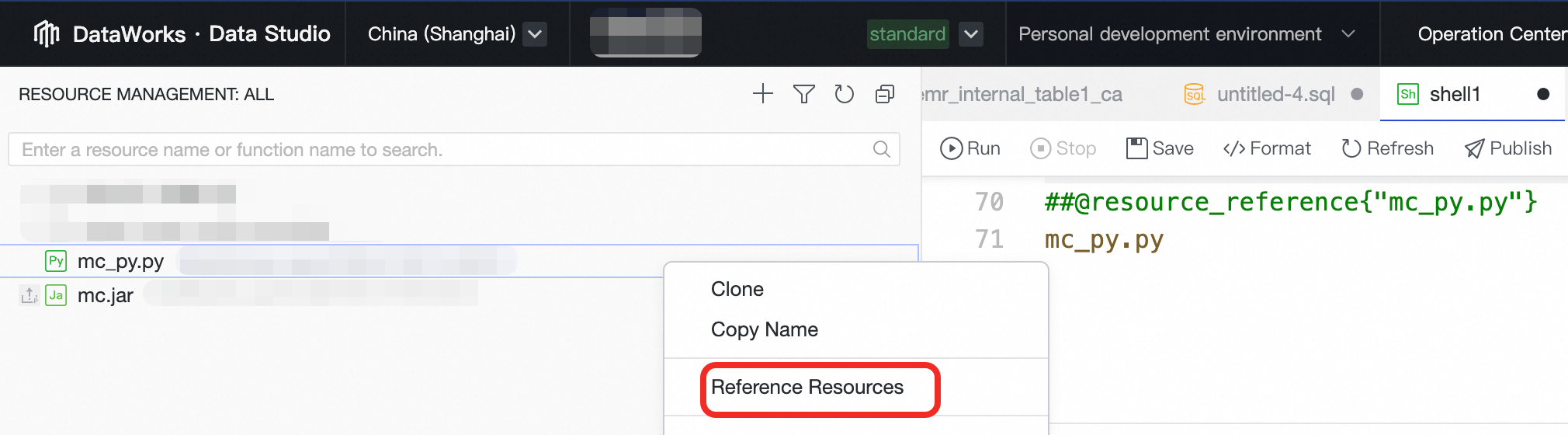 Note
NoteWhen you reference a resource, the system automatically inserts a declaration comment like
##@resource_reference{resource_name}at the top of the script.This required identifier lets DataWorks recognize resource dependencies and automatically mount the corresponding resource to the execution environment at runtime. Do not modify or delete this comment.
Using scheduling parameters
Scheduling parameters are injected into Shell nodes as positional parameters; custom variable names are not supported. DataWorks passes the parameter values you set in the tab to the Shell script sequentially as positional parameters, such as $1, $2, and $3. If there are more than nine parameters, you must use braces, for example, ${10} and ${11}, to ensure they are parsed correctly. Parameter values must be separated by spaces, and their order must exactly match the positions referenced in the script.
For example:
Parameter $1 is assigned the current date: $[yyyymmdd].
Parameter $2 is assigned the fixed string
Hello DataWorks.
If a parameter value contains spaces, enclose it in quotation marks. The entire content within the quotation marks is treated as a single parameter.
To retrieve the output parameters from an upstream node, you must add a parameter in the tab. Set the parameter value to the output parameter of the upstream node.
Using ossutil to access OSS
The DataWorks Shell node natively supports ossutil, the command-line tool for Alibaba Cloud OSS, allowing you to perform tasks such as bucket management, file uploads and downloads, and batch operations. You can configure access credentials for ossutil using either a configuration file or command-line parameters to access OSS.
To access OSS with ossutil using command-line parameters, see Access OSS using command-line parameters.
To access OSS with ossutil using a configuration file, see Access OSS using a configuration file.
In the new version of Data Studio, Shell nodes also support associating a RAM role. This allows a node to use Alibaba Cloud Security Token Service (STS) to dynamically obtain temporary security credentials for the role. These credentials can then be used with ossutil. This method provides secure access to target cloud resources and eliminates the need to hardcode a long-term AccessKey in your script. For more information, see Configure node-associated roles.
The ossutil tool is pre-installed in the DataWorks environment and does not require manual installation. The default path is /home/admin/usertools/tools/ossutil64.
Using datasets to access OSS or NAS
DataWorks allows you to create a dataset for OSS or NAS. You can then use this dataset in a Shell node to read from and write to OSS or NAS storage during task execution.
Running a node with an associated role
You can associate a specific RAM role to run a node task. This enables fine-grained permission control and enhanced security.
Appendix: Exit codes
A script's exit code indicates whether it ran successfully.
Exit code 0: Indicates success.
Exit code -1: Indicates that the process was terminated.
Exit code 2: The platform automatically reruns the task once.
Other exit codes: Indicate failure.
The following image shows an example of a standard run log for a Shell node that executed successfully (exit code 0).

Due to the underlying Shell mechanism, the script's exit code is determined by the last command executed.
 icon in the upper-left corner. In the navigation pane that appears, go to
icon in the upper-left corner. In the navigation pane that appears, go to