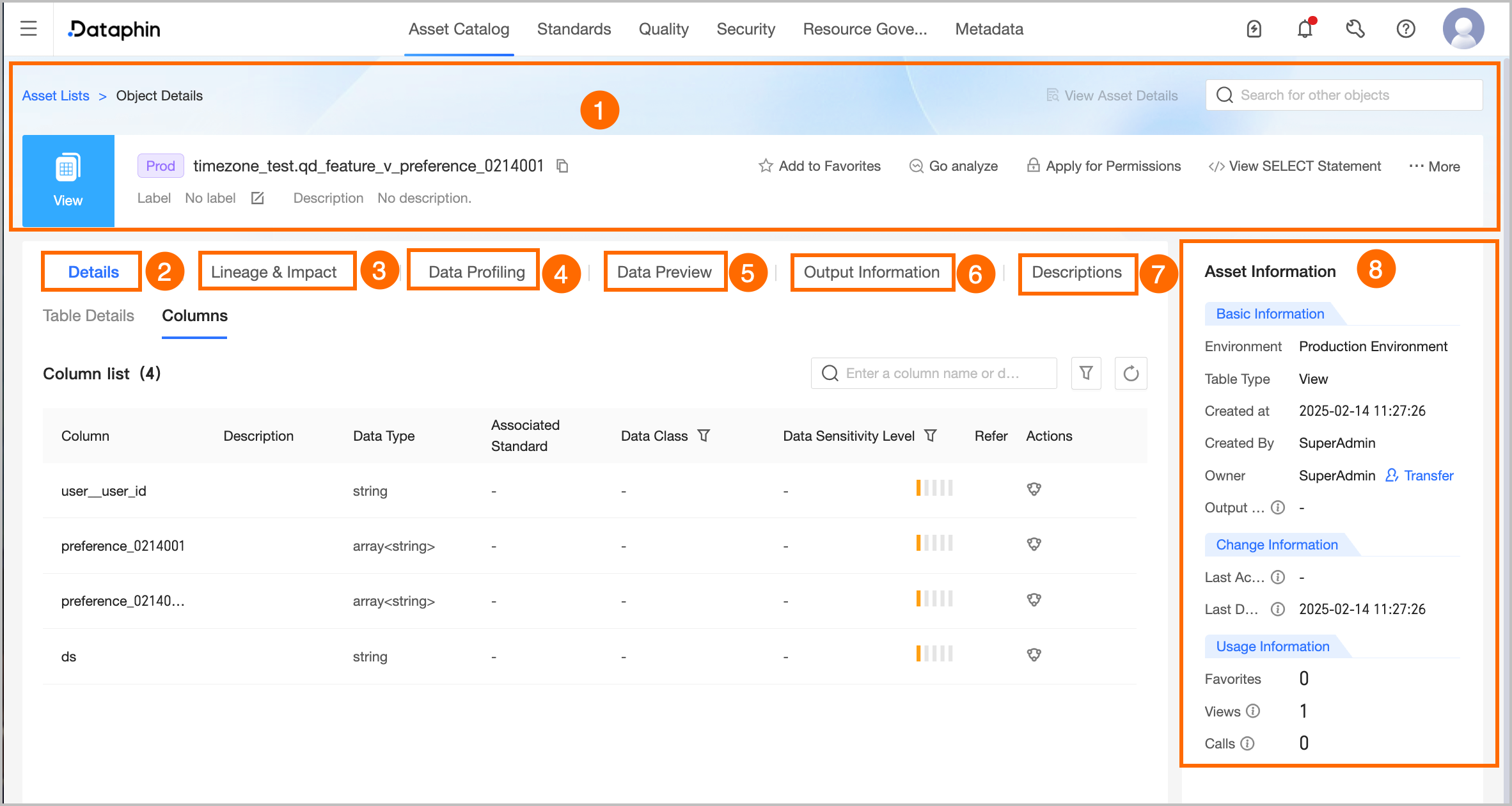
Area | Description |
①Summary Information | Displays the type, environment, name, tag, description, and other information of the table. You can also perform the following operations: Search Other Asset Objects: Quickly search and switch to view the details of other assets. View Asset Details: If the current object is listed in the Asset Directory, you can quickly jump to the directory details page to view the listed information. View Production/development Objects: Quickly switch the current object to the corresponding production/development environment object details. Tag: Displays the tag values configured for the current asset. To modify the tag, you can click Edit: The length of each tag value does not exceed 128 characters. Each asset object can be configured with up to 20 tag values. The super administrator can modify the asset tags of all table types. The current table owner can modify the asset tags of the tables they are responsible for. The project administrator can modify the asset tags of the physical views under their responsible project.
Favorite: Click to add to or remove from favorites. After adding to favorites, you can view the last 30 favorite assets in the Asset Checklist - My Footprints for easy subsequent queries. You can also view all favorite assets in the Personal Data Center. For more information, see the referenced document. Go Analysis: Click to jump to the Notebook page to automatically create the corresponding Notebook task. For more information, see the referenced document. Request Permission: Click to quickly jump to the permission request page of the current table. For more information, see the referenced document. Generate Select Statement: Click to generate the query statement for the current table. You can choose whether to add escape characters. You can copy the query statement to the ad hoc query or analysis page to query data. 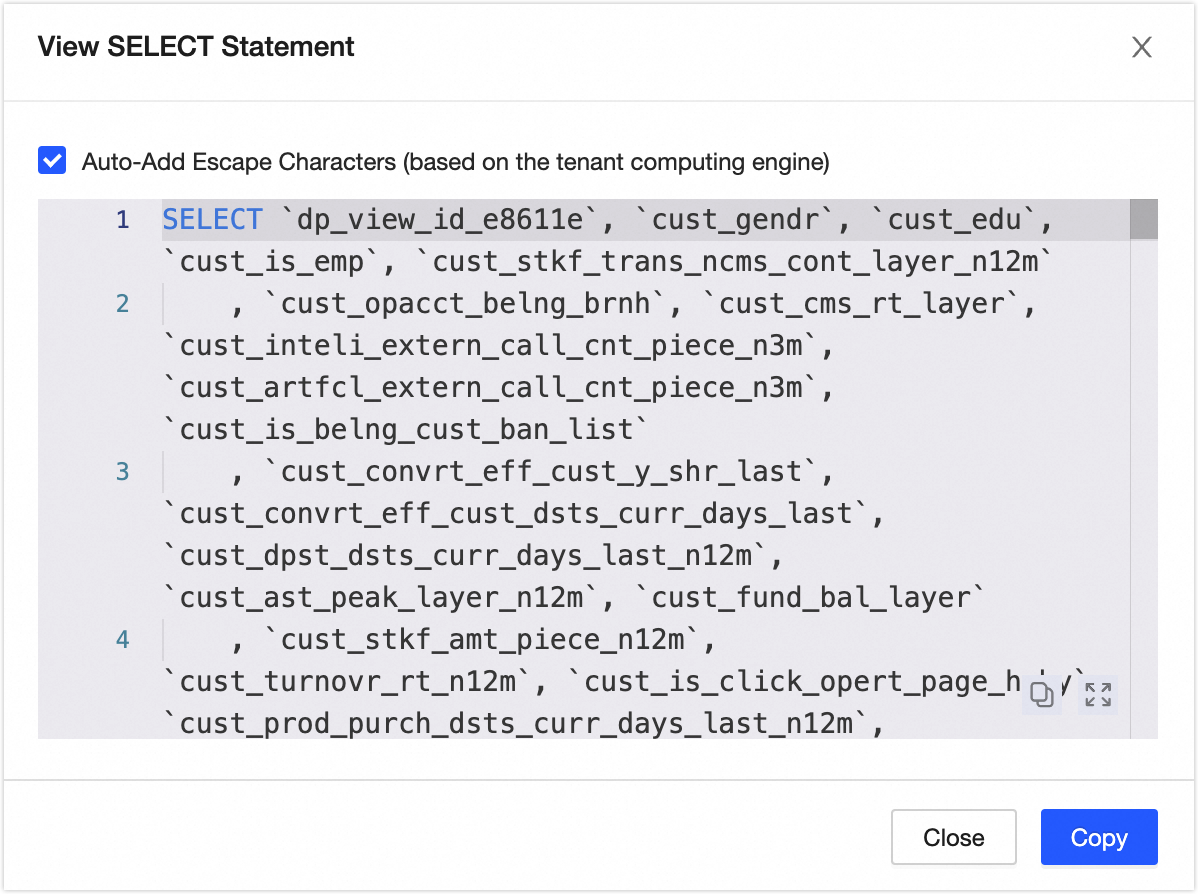
View DDL Statement: Click More in the upper right corner, select View DDL Statement, and click to view the DDL statement corresponding to the current data table in the tenant compute engine. In addition, you can select Data Source Type, click Generate DDL Statement, and the system will generate a DDL statement to create a table with the same structure as the current table in the specified type of data source system. If you select Automatically Add Escape Characters, the generated DDL statement will automatically add the corresponding escape characters according to the selected source type to reduce issues such as system keyword misinterpretation. 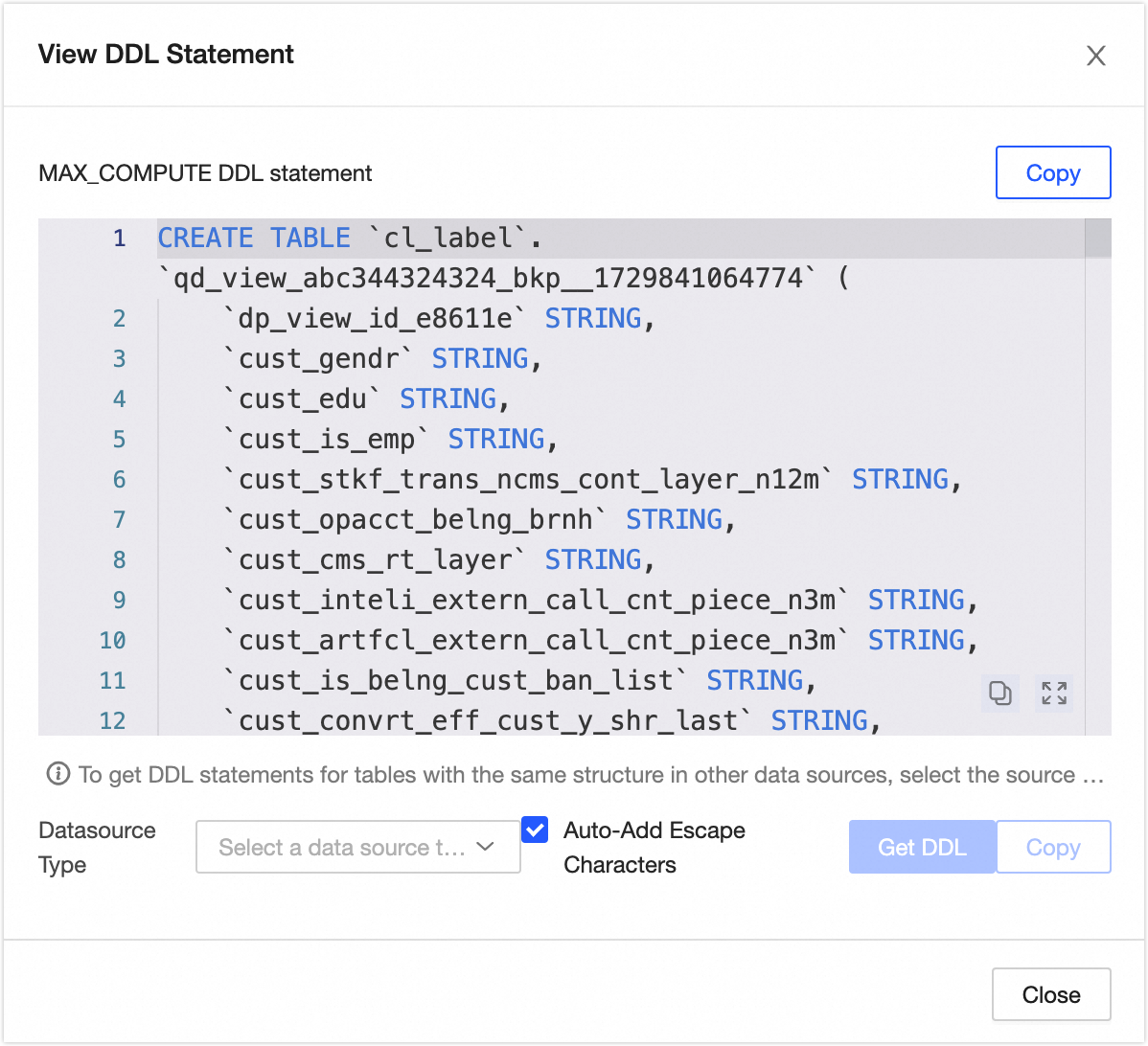
Export Fields: Click More in the upper right corner, select Export Fields, and export the field information in the table in CSV format for quick analysis and use by other developers or business personnel. View Transfer Records: Click More in the upper right corner, select View Transfer Records, and view the latest 100 transfer records of the current data table owner. View Permission List: Click More in the upper right corner, select View Permission List, and view the data table permission information. Refresh Metadata: Click More in the upper right corner, select Refresh Metadata. If the data table is not created through the Dataphin platform or the system metadata retrieval delay causes no results when querying the newly created table, you can click Refresh Metadata to obtain the latest metadata information and refresh the specified data table metadata into the Dataphin system.
Note The analysis platform table does not support operations such as Go Analysis, Request Permission, View Transfer Records, and View Permission List. |
②Detail Information | Displays the detailed information of the table, fields, and partitions. Detail: Displays the technical attribute information of the table, including data section, subject area, project, highest sensitivity level (requires purchasing the data security feature), whether it is a manually created table on the analysis platform, storage type, and Location. Project: The project information to which the current table belongs. Click the project name to jump to the asset details page of the project. Highest Sensitivity Level: The highest sensitivity level of the current table fields, which helps to quickly understand the data confidentiality of the current table. The Data Classification levels range from low to high as L1, L2, L3, L4 (public to top secret), and custom data classification. Storage Type: The storage type of the current table, including internal table and external table.
Note When the compute engine is GaussDB (DWS), the storage type is not displayed. Location: Only MaxCompute, Hive type compute source external tables support viewing the storage address of the current table, for example: hdfs://node01.exp5:8020/user/hive/warehouse.
Field Information: Includes field details, description, data type, associated standard (requires the Data Standard module), data classification (requires the data security module), sample data (displayed only if the data sampling feature is enabled), sensitivity level (requires the data security module), and popularity information. You can also search for fields, filter fields, and view field lineage. View Lineage Relationship: Click the lineage icon under the Actions  column to view the field lineage centered on the specified field. column to view the field lineage centered on the specified field. Search and Filter: You can search fields by name or description, and filter specific fields by data classification and data classification (requires enabling data security).
Note When the compute engine is Amazon EMR, primary key field information is displayed.
Partition Information: You can view the partition information of the data table. Multi-level partitions will be displayed as a combination of each level partition, with different partitions connected by /. For example: ds=20221001/pt1=a/pt2=b.
Note When the compute engine is Amazon EMR, partition information is displayed.
|
③Lineage & Impact | |
④Data Exploration | If you have enabled the data quality feature, you can configure data exploration tasks for the data table to quickly understand the data overview and assess the data availability and potential risks in advance. To enable automatic exploration, you can enable the corresponding configuration in Administration > Metadata Center > Exploration and Analysis. For more information, see the referenced document.
Note When the compute engine is Databricks or GaussDB (DWS), the data exploration feature is not supported. |
⑤Data Preview | If sample data is available for the data table, the sample data is displayed by priority. You can also manually trigger a query to retrieve the latest data. If no sample data exists, a data preview query is automatically triggered. Sample data: Sample data is displayed if the data sampling and data preview switches are both turned on. You can query sample data only for fields where you have column-level permissions and the data does not require masking. The system stores, sorts, and displays sample data for each field independently. However, the existence and correctness of row-level records are not guaranteed. Data preview: If you have the permissions to query the current table, you can use the data preview feature. You can preview the first 50 data entries for the fields for which you have permissions for SELECT statements, including field-level and row-level permissions. For more information about how to request permissions, see Request, renew, and return table permissions.
You can search or filter the filtered data based on fields, search, view single-row data details, perform automatic column width adjustment and row-column transformation operations. You can also click the sort icon after the field to perform No Sort, Ascending, Descending operations. Double-click the field value to copy the field value with one click. |
⑥Output Information | The output tasks include the data write tasks of the object, lineage automatic parsing or custom configuration tasks with the current table as the output table, and tasks with node output name = project name.table name. The output task list is updated in near real-time, and the output details are updated on a T+1 basis. 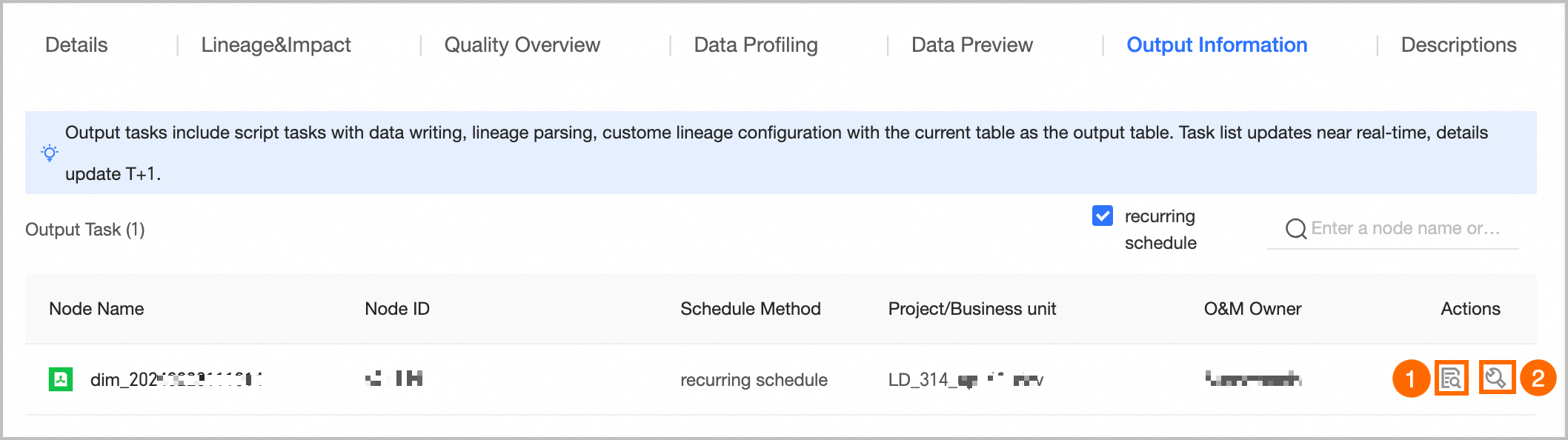
① View Output Details: Only supports viewing the output details of periodic tasks. For more information, see the referenced document. ② Go To Operation: Click the Go To Operation button to jump to the task list page of the Operation Center and filter out the current task for more information.
|
⑦Usage Instructions | You can add usage instructions for the data table to provide information references for data browsers and consumers. You can click Add Usage Instructions, fill in the usage instructions title and content to complete the addition. 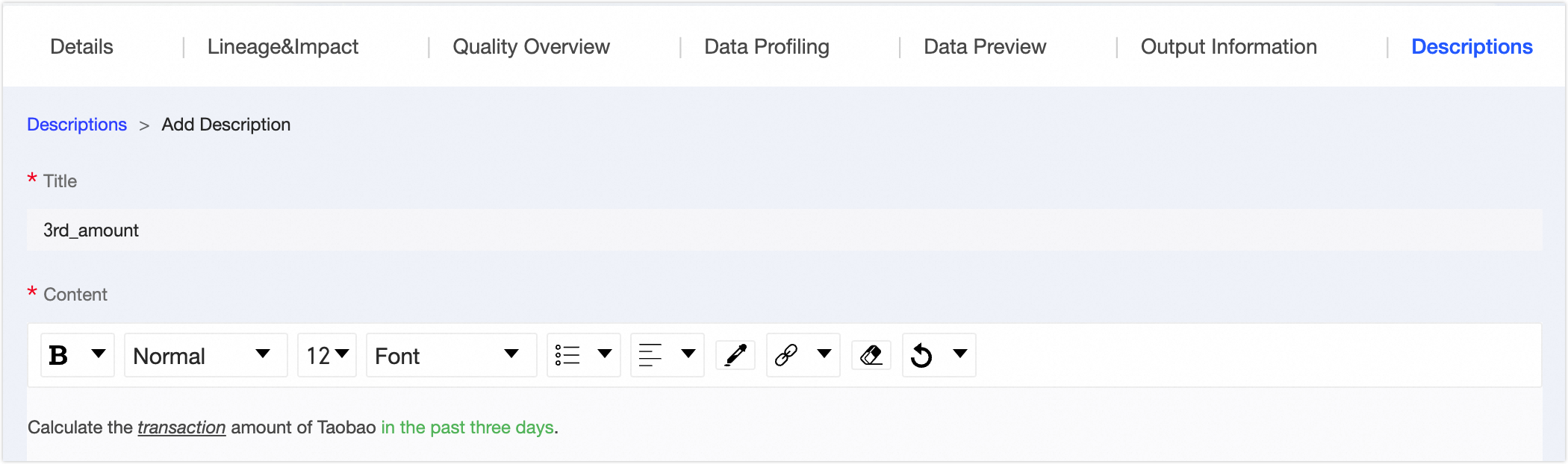 |
⑧Asset Information | Displays detailed information such as Basic Information, Change Information, and Usage Information of the physical view. Basic Information: Includes environment, table type, creation time, creator, owner, and output tasks. Owner: The owner of the current table. Supports transferring the owner of the current table to other users. In the Transfer Owner dialog box, you can choose whether to transfer the development/production environment table synchronously. After selecting the Recipient, click Confirm to transfer immediately. It is recommended to synchronize the recipient promptly after the transfer. You can view the transfer information on the transfer records page. For more information, see the referenced document.
Note The super administrator can transfer the owner of all table types. The current table owner can transfer the tables they are responsible for. The project administrator can transfer the owner of the physical tables under their responsible project.
Output Task: You can view the output tasks of the current table, including the data write tasks of the object, lineage parsing or configuration tasks with the current table as the output table, and tasks with node output name = project name.table name. Click the name of the output task to jump to the operation details page of the data table.
Note Only supports viewing the output details of periodic tasks.
Change Information: Includes last accessed, DDL changes. Last Accessed At: The last select time (corresponding to DQL operation) parsed by Dataphin based on SQL. Access triggered by external systems is not counted and is updated in real-time. Last Ddl Time: The last table structure change time (corresponding to DDL operation) parsed by Dataphin based on SQL. Changes triggered by external systems are not counted and are updated in real-time.
Usage Information: Includes number of favorites, page views, and visits. Number Of Favorites: Displays the number of users who have favorited the current table, updated in real-time. Page Views: Displays the number of page views (PV) of the current data table. Each refresh increases by one, updated in real-time. Visits: Based on SQL parsing, when the table is selected in the Dataphin task (corresponding to DQL operation), it is calculated as one visit, updated on a T+1 basis, and displays the total number of visits in the last 30 days.
Note When the compute engine is Databricks or Amazon EMR, the visit information is not displayed.
|
 icon to open the object details page.
icon to open the object details page.