This topic describes how to view the details of a metadata asset.
Limits
You must enable the metadata acquisition and management feature to view metadata asset details.
You must configure the data source encoding to use the data preview feature for data source tables. For more information, see Data Source Management.
Support for operations, such as data preview and viewing DDL, varies by data source. For more information, see Supported operations for different types of collection sources.
Access the details page of a data source table
In the top navigation bar of the Dataphin homepage, choose Administration > Asset Checklist.
Select Other System Assets, and then click the name of the target metadata or the
 icon in the Actions column to open the object details page.
icon in the Actions column to open the object details page.
Data source table details
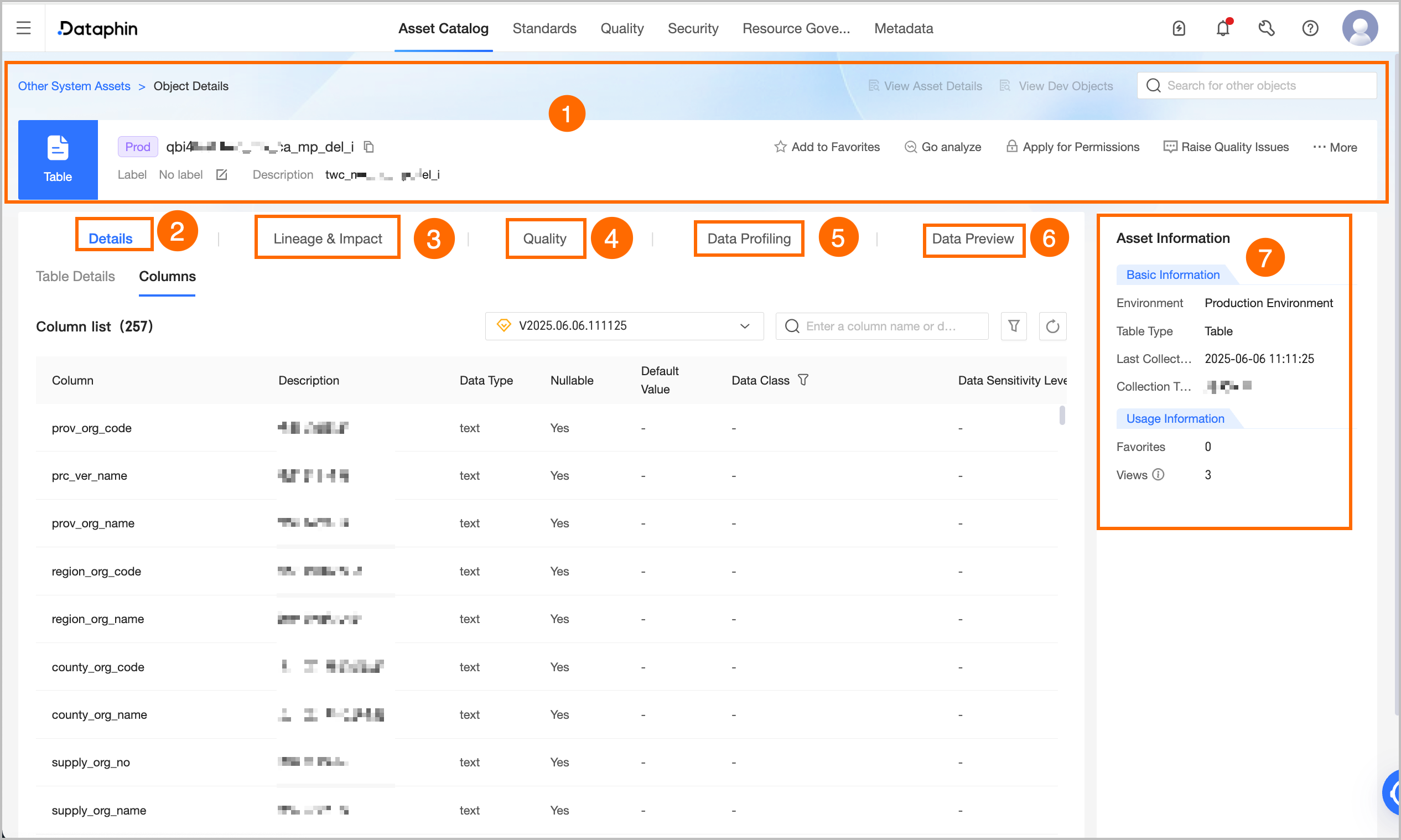
Area | Description |
① Basic information | Displays information about the metadata, such as its name, environment, tags, and description. You can also perform the following operations: For data source tables from an Elasticsearch data source, you can search for metadata, view asset details, view production or development objects, modify tags, add items to favorites, report quality issues, request data source permissions, and export fields. The export feature is supported only for table objects.
|
② Detail information | Displays the attribute and field information of tables and views.
|
③ Lineage & impact |
|
④ Quality overview | You need to enable the Data Quality feature to view the rule verification overview and quality monitoring rule list of the current data table. You can click the View Report Details button or the View Rule Details button to quickly jump to the corresponding page of the Data Quality module for more details. You can view the quality overview only for data tables that support data quality monitoring. For a list of supported data sources, see Data Sources Supported by Dataphin. You can create quality rules and view the quality overview only for data source tables in the production environment. |
⑤ Data exploration | If you have enabled the Data Quality feature, you can initiate and view data explorations for data source tables that support this feature to quickly understand the data overview and assess the data's availability and potential threats in advance. To enable automatic exploration, you can enable the corresponding configuration in Administration > Metadata Center > Exploration and Analysis. For details about how to configure exploration tasks, see Create a data exploration task. For data sources that support data exploration, see Exploration partitions and ranges supported by different data sources. |
⑥ Data preview | If you have permission to query data from the current table, you can use the data preview feature to query only the results corresponding to the fields for which you have SELECT permission. You can preview the first 50 data entries. For more information about how to request query permission, see Request, renew, and return table permission. After you filter the data, you can search or filter by field, view the details of a single row, automatically adjust column widths, and transpose rows and columns. You can also click the sort icon next to a field to sort the data. The options are No Sort, Ascending, and Descending. Double-click a field value to copy it. Note If the data source is Hive and the table is an internal table with the Iceberg (Hive version EMR 5.x 3.1.x) or Hudi (Hive version CDP 7.x 3.1.3) lakehouse format, you must enable the Spark configuration for the table's data source before you can query data. |
⑦ Asset information | Displays the basic and usage information of the data source table.
|
Table-level lineage
The table-level lineage page displays a lineage graph that is automatically parsed from sync tasks, custom lineage compute tasks, and SQL compute and logical table tasks.
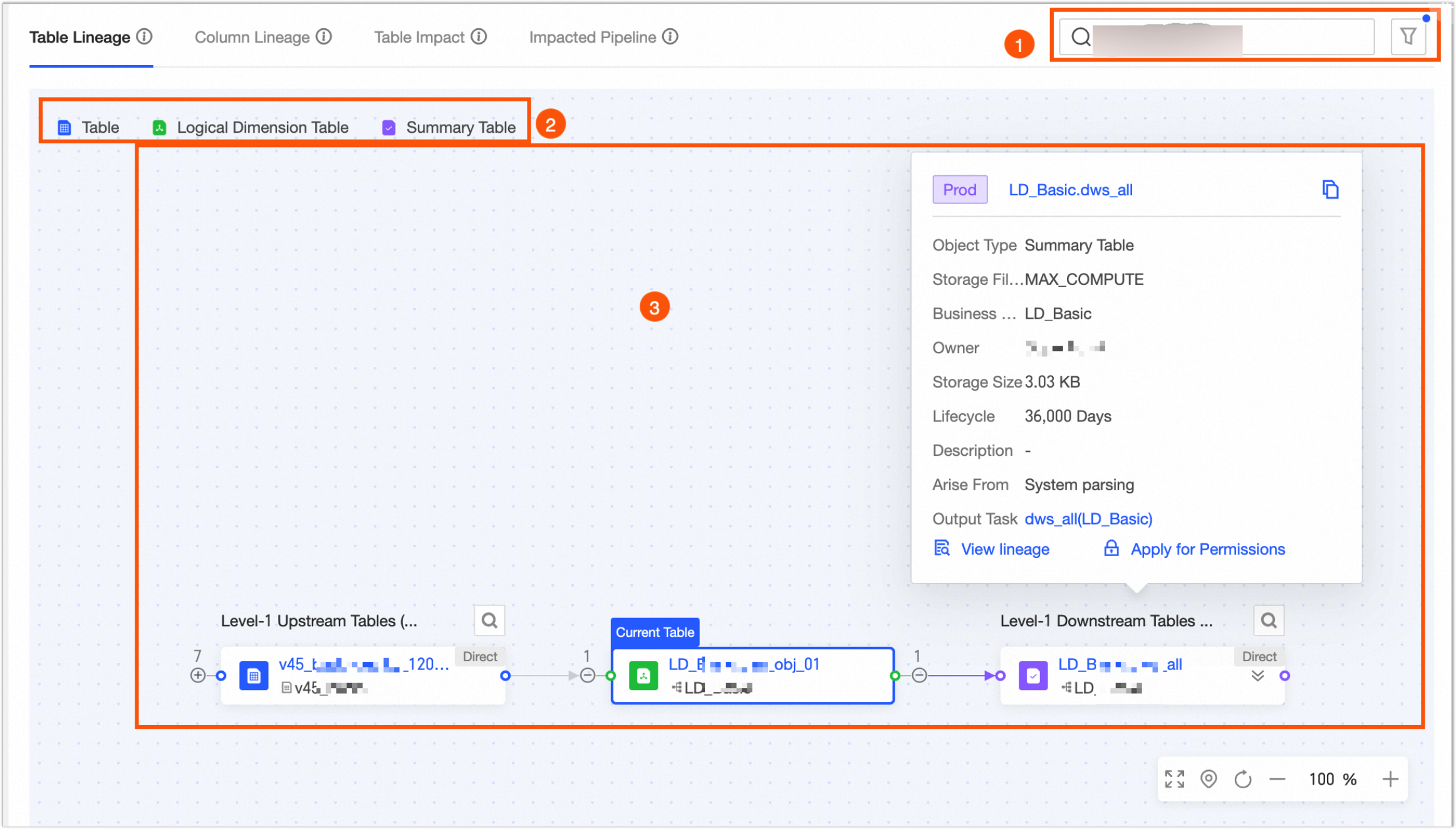
Ordinal number | Description |
① Quick actions |
|
② Legend | Table-level lineage supports the following data tables: Physical Table, Logical Dimension Table, Logical Fact Table, Logical Summary Table, Logical Tag Table, View, Materialized View, Logical View, Meta Table, Mirror Table, and Datasource Table. |
③ Lineage graph display | Displays the complete lineage graph. You can manually expand multiple levels of upstream or downstream nodes and perform a fuzzy search by table name. If a circular dependency exists, you cannot expand the lineage further. You must view the downstream lineage from the start node.
|
④ Object details | Hover over a table to view its details. For a data source table, the details include its Name, Object Type, Data Source Type, Data Source, and Lineage Source. You can also perform the following operations: View Lineage, View DDL, and Request Permission.
|
Field lineage
The field lineage page displays a lineage graph that is automatically parsed from custom lineage compute tasks, and SQL compute and logical table tasks.
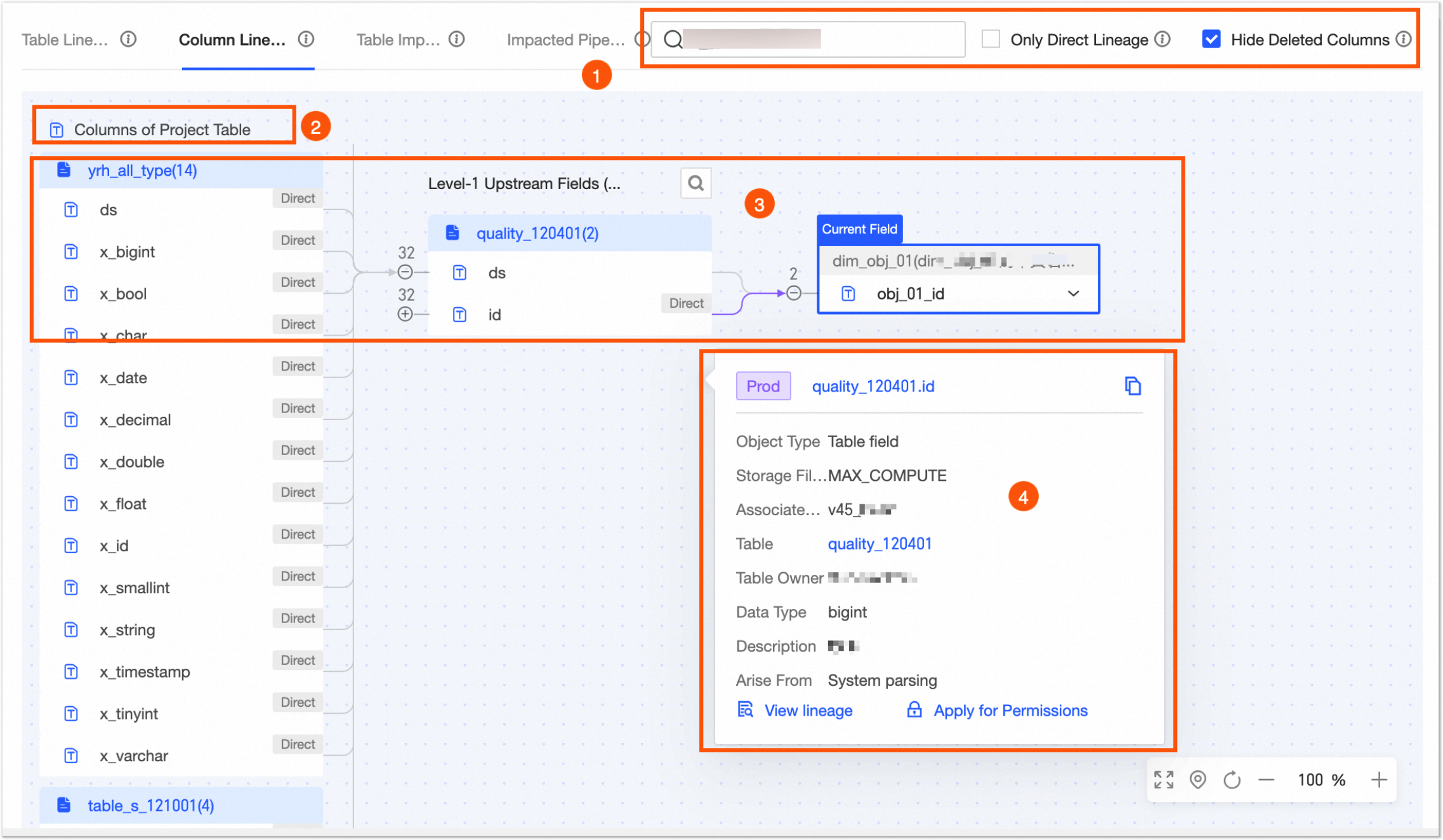
Ordinal number | Description |
① Quick actions |
|
② Legend | Field lineage supports the following fields: Compute Source Table Field and Data Source Table Field. |
③ Lineage graph display | Displays the complete lineage graph. You can manually expand multiple levels of upstream or downstream nodes and perform a fuzzy search by field name. If a circular dependency exists, you cannot expand the lineage further. You must view the downstream lineage from the start node. Central node: Displays the current field and its table name. The node is marked with Current Field in the upper-left corner. You can perform a fuzzy search by field keyword to switch the view to the lineage graph of a different field. |
④ Object details | Hover over a field to view its details. The details include the Name, Object Type, Data Source Type, Table, Owner, Data Type, Description, and Lineage Source. You can also perform the View Lineage operation.
Note If a metadata acquisition task is not configured for a data source table, you cannot click to view its asset details. You can only view basic information, such as the field's name, object type, table, data source type, and lineage source. |