On the issue list page, you can view exceptions generated by data quality rule validations and problems reported for assets or tags. You can also perform governance operations on these issues, such as initiating remediation, ignoring exceptions, and adding issues to a whitelist. This topic describes how to add and manage issue lists.
Usage notes
The Data Quality module must be activated.
Permission description
Super administrators and quality administrators can view and manage all issue details. They can perform operations such as initiating remediation, adding issues to a whitelist, ignoring exceptions, and returning issues for reprocessing.
Other members can view the issues that they have reported. They can also perform operations on issues for which they are the owner. These operations include initiating remediation, adding issues to a whitelist, ignoring exceptions, and returning issues for reprocessing.
Any user with permission to view an object can add an issue.
The supported operation permissions vary by object type. For more information, see Issue list operation permissions.
View issue lists from different perspectives
Dataphin lets you view issue details from three perspectives: Global, Project, and Personal.
Global: Super administrators and quality administrators can view all issues from a global perspective.
Project: Super administrators and quality administrators can switch to any project and view the issues for asset objects in that project. Other members can select only the projects that they have joined and view the issues for those projects.
NoteGlobal tables, data sources, and tag object types are not displayed in the Project view.
Personal: Super administrators and quality administrators can switch to any member and view that member's issues. Other members can view only the issues that they have reported or are responsible for, and cannot switch to other members.
Add an issue
On the Dataphin home page, click Governance > Data Quality in the top menu bar.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Issue List. Click Add Issue to open the Report Quality Issue dialog box.
In the Report Quality Issue dialog box, configure the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Issue Object
Select the object for which you want to report an issue. Configure the corresponding parameters based on the object type. For data tables and real-time metatables, if you do not select a specific field, the issue is recorded at the table granularity. If you select a specific field, the issue is recorded at the specified field granularity.
Issue Type
Select the type of the issue. If a suitable issue type is not available, contact an administrator with the required permissions to create one. For more information, see Custom issue types.
Issue Description
Provide a brief description of the issue to help the issue owner understand the background information. The description cannot exceed 1,000 characters.
Attachment
Click the Upload button to select files from your local computer. You can upload a maximum of five files for a single issue.
Supported file formats include Doc (.doc, .docx, .dot, .dotx, .rtf, .html, .xml, and .txt), Excel (.xls, .xlsx, and .csv), PDF, and image (.jpg, .png, and .jpeg). The file size cannot exceed 10 MB.
Contact Information
Provide your contact information to help the issue owner contact you for more details. Supported contact methods are phone, email, and other.
Phone: You can enter numbers, hyphens (-), plus signs (+), half-width parentheses, and spaces. The value cannot exceed 20 characters in length.
Email: Enter an email address.
Other: The value cannot exceed 100 characters in length.
Click OK to add the issue.
View the issue list
The issue list page displays issues that are generated by data quality validation and issues that are reported for assets or tags. You can perform operations on these issues, such as initiating remediation, adding them to a whitelist, ignoring them, and sending notifications.
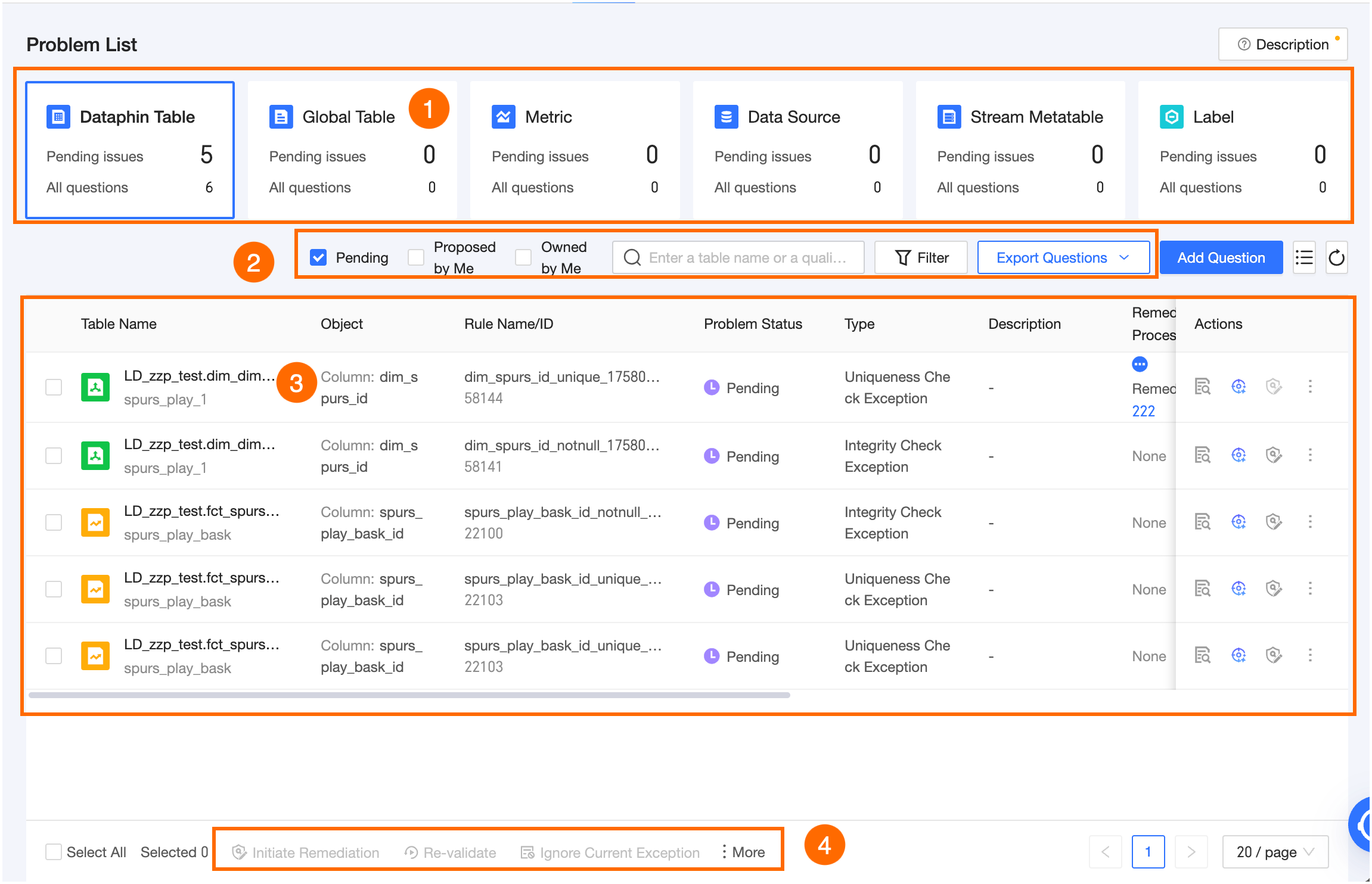
Parameter | Description |
①Legend card | Displays the number of pending issues and total number of issues for different types of objects, including Dataphin tables, global data tables, metrics, data sources, real-time metatables, and tags. You can switch to view the corresponding issue list. |
②Search and filter area | You can perform a fuzzy search based on the name of the monitored object or the name of the quality rule. For Dataphin tables, global data tables, metrics, data sources, and real-time metatables, you can filter by pending issues, issues that I reported, issues that I am responsible for, rule severity, issue status, issue type, submission method or submitter, and issue owner. For tags, you can filter by pending issues, issues that I reported, issues that I am responsible for, issue status, issue type, and issue owner. Custom Issue Types: Click Manage next to the issue type. In the Manage Issue Types dialog box, enter a name for the issue type. The name cannot exceed 20 characters in length. Click OK to create the issue type. You cannot edit or delete built-in issue types. You can edit or delete custom issue types. You can create a maximum of 50 issue types.
|
③Issue list | For system-identified issues that are generated by quality rule validations, the rule name, rule severity, check range, and check time are displayed. For manually submitted quality issues, the submitter information is displayed. Different governance operations are supported for different issue statuses. For more information, see Individual operations.
|
④Batch operation area | For system-identified issues, you can perform batch operations on issue objects, such as ignoring the current exception, canceling the ignore operation, adding to a whitelist, initiating remediation, modifying the issue type, and associating a knowledge base document. For manually submitted issues, you can perform batch operations on issue objects, such as ignoring the current exception, canceling the ignore operation, initiating remediation, marking as processed, returning for reprocessing, modifying the issue type, and changing the issue owner. The change owner operation is supported only for tag objects. You can perform different governance operations in batches based on different issue statuses. For more information, see Batch operations. |
Operation instructions
Issue status
Issue status | Operations |
Pending |
|
Validating | For system-identified issues, you can perform the following operations: View Details, Initiate Remediation, Notify Issue Owner, Add To Whitelist, Modify Issue Type, View Operation Record, and Associate Knowledge Base Document. |
Completed |
|
Ignored |
|
Single operations
Operation | Description |
View Details |
|
Intelligent Root Cause Analysis | This operation is available when the asset object is a Dataphin table (system-identified issue) and the issue status is Pending. Click the Intelligent Root Cause Analysis icon in the Actions column. The system uses a large model to analyze the quality issue and provide remediation suggestions. For more information, see View intelligent root cause analysis. |
Initiate Remediation | After you initiate remediation, you can track the entire remediation flow for the issue. For information about how to configure a remediation flow, see Initiate remediation. For information about how to manage remediation flows, see View and manage remediation flows. Note Only super administrators, quality administrators, issue owners, and custom global roles with permission to manage flows in the governance workbench can initiate flows. |
Ignore This Exception | After you set a pending issue to ignored, no further processing is required. We recommend that you ignore unimportant issues. Scenarios: A data source connection was interrupted but is now stable and does not need to be fixed. An exception occurred in a historical task, but the task is no longer used in the latest data processing. In these cases, you can choose to ignore the issue. |
Cancel Ignore |
|
Notify Issue Owner | You can notify the issue owner by Internal Message, Phone, Text Message, Email, or DingTalk. |
Change Issue Owner | You can change the owner of the current issue to another user. In the Change Issue Owner dialog box, select a recipient and click OK to immediately transfer ownership. We recommend that you sync with the recipient after the transfer. |
Mark As Processed | You can mark only manually submitted issues that are in the Pending state as processed. To initiate remediation, you can return the processing result. |
Return For Reprocessing | You can return only manually submitted issues that are in the Completed state for reprocessing. After an issue is returned, its status changes to Pending. You can notify the issue owner by internal message to ensure that the owner processes the issue promptly. Note Only super administrators, quality administrators, issue owners, and custom global roles with permission to manage flows in the governance workbench can return issues for reprocessing. |
Modify Issue Type | You can categorize issues by type to facilitate filtering and statistical analysis. System-identified issues are assigned a default system issue type based on the quality rule type. You cannot modify this type. You can add or delete manually configured issue types. If a suitable issue type is not available, you can create one. For more information, see Custom issue types. |
Delete Issue | After you delete an issue, it is also removed from the remediation flow. This operation cannot be undone. Evaluate the impacts before you proceed. |
Add To Whitelist | Scenario: The current table is in the testing phase, and the data is unstable. You can wait until the data stabilizes before you monitor it. For information about how to add an issue to a whitelist, see Add to a whitelist. For information about how to manage whitelists, see View and manage governance whitelists. Note
|
Recheck | You can recheck only system-identified issues that are in the Pending or Ignored state. If a data quality issue is resolved, you can re-execute the check rule for the current issue. The issue status is updated based on the check result. If the check is passed, the issue status changes to Completed. If the check fails, the issue status changes to Pending. |
View Operation Record | Displays the operation records for the current issue. The records include the issue object name, operation type, issue status, operation description, operator, and operation time. |
Associate Knowledge Base Document | You can associate knowledge only with system-identified issues. After a rule is associated with knowledge, you can view the associated knowledge in the quality rule and issue list. You can configure knowledge bases in batches for issue objects. To create a knowledge base, see Create a knowledge base. |
Batch operations
Operation | Description |
Ignore This Exception | You can set pending issues to ignored. After that, they do not require processing. We recommend that you ignore unimportant issues. Scenarios: A data source connection was interrupted but is now stable and does not need to be fixed. An exception occurred in a historical task, but the task is no longer used in the latest data processing. In these cases, you can choose to ignore the issue. |
Cancel Ignore | You can cancel the ignore operation only for issues that are in the Ignored state. After you cancel the ignore operation, the status of manually submitted issues changes to Pending. The status of system-identified issues is determined based on the result of the most recent rule check. If the check is passed, the issue status changes to Completed. If the check fails, the issue status changes to Pending. |
Add To Whitelist | Scenario: The current table is in the testing phase, and the data is unstable. You can wait until the data stabilizes before you monitor it. For information about how to add an issue to a whitelist, see Add to a whitelist. For information about how to manage whitelists, see View and manage governance whitelists.
|
Initiate Remediation | After you initiate remediation, you can track the entire remediation flow for the issue details. The procedure for initiating remediation flows in batches is the same as the procedure for a single operation. For more information, see Initiate remediation. For information about how to manage remediation flows, see View and manage remediation flows.
|
Recheck | You can recheck only system-identified issues that are in the Pending or Ignored state. If a data quality issue is resolved, you can re-execute the check rules for the selected issues on the current page. The issue status is updated based on the check result. If the check is passed, the issue status changes to Completed. If the check fails, the issue status changes to Pending. |
Mark As Processed | You can mark only manually submitted issues that are in the Pending state as processed. To initiate remediation, you can return the processing result. |
Return For Reprocessing | You can return only manually submitted issues that are in the Completed state for reprocessing. After an issue is returned, its status changes to Pending. Note Only super administrators, quality administrators, issue owners, and custom global roles with permission to manage flows in the governance workbench can return issues for reprocessing. |
Modify Issue Type | You can append or modify issue types. This operation applies only to custom issue types. It does not apply to system issue types that are automatically generated based on rule types.
|
Export Issues | Export the issues that you select on the current page. In the dialog box, select the content that you want to export and click OK. |
Change Issue Owner | You can change the owner of the current issue to another user. In the Change Issue Owner dialog box, select a recipient and click OK to immediately transfer ownership. We recommend that you sync with the recipient after the transfer. |
Associate Knowledge Base Document | You can associate knowledge only with system-identified issues. After a rule is associated with knowledge, you can view the associated knowledge in the quality rule and issue list. You can configure knowledge bases in batches for issue objects. To create a knowledge base, see Create a knowledge base. |
Add to a whitelist
You can add issues to a whitelist individually or in batches.
On the Issue List page, find the target issue, click the
 icon in the Actions column, and then select Add To Whitelist.
icon in the Actions column, and then select Add To Whitelist.In the Add To Whitelist dialog box, configure the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Whitelist Scope
You can add only system-identified issues that are not ignored to a whitelist.
If you select a single issue object, you can add the Current Rule or Current Monitored Object to the whitelist.
Current Rule: During the validity period, if new quality check failures occur for the current check record and all generated issues that are in the Pending or Validating state and belong to the same quality rule as the current issue, their status automatically changes to Ignored.
Current Monitored Object: During the validity period, if new quality check failures occur for all issues that are in the Pending or Validating state and belong to the same monitored object as the current issue, their status automatically changes to Ignored.
Validity Period
You can select 7 Days, 30 Days, 90 Days, 180 Days, Permanent, or Custom. The application day is not counted.
NoteAfter the whitelist expires, historical issues are not retroactively reported, but subsequent new issues are reported.
Operation Description
This parameter is required. Enter the reason for adding the issue to the whitelist. The reason cannot exceed 128 characters in length.
Click OK to add the issue to the whitelist.
Initiate remediation
You can initiate remediation for issues individually or in batches.
On the Issue List page, find the target issue and click the
 icon in the Actions column. The Initiate Remediation dialog box appears.
icon in the Actions column. The Initiate Remediation dialog box appears.In the Initiate Remediation dialog box, configure the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Remediation Scope
For system-identified issue objects, you can initiate remediation for the Current Issue, Current Rule, or Current Monitored Object. For manually submitted issue objects, you can initiate remediation only for the Current Issue.
Current Issue: Includes only the issue of the current check record. It does not include other pending issues that belong to the same rule as the current issue object.
Current Rule: Includes the issue of the current check record and all generated pending system-identified issues that belong to the same quality rule. It may include multiple check ranges.
Current Monitored Object: Includes the issue of the current check record and all pending system-identified issues that belong to the same monitored object as the current issue. It may include multiple issue objects and check ranges.
NoteIf the selected issue is already in a remediation flow, it remains in the original flow. Remediation is not initiated again.
Initiation Method
You can create a new flow or associate with an existing flow.
Create New Flow: Customize a name for the remediation flow. The name cannot exceed 128 characters in length.
Associate With Existing Flow: You can associate with a flow that is created for the current object type and is in the Remediating or Re-remediating state. Only super administrators, quality administrators, issue owners, and custom global roles with permission to manage flows in the governance workbench can select all flows.
Remediate By
The remediator is the person who is responsible for the remediation process. We recommend that you select the quality owner of the issue object. This allows the owner to edit system-identified issues or reinitiate checks in the remediation flow. Otherwise, the issue status may not be updated. If you set Initiation Method to Associate With Existing Flow, the remediator defaults to the remediator of the selected flow and cannot be modified.
Validated By
The validator is the person who is ultimately responsible for the remediation results. If you set Initiation Method to Associate With Existing Flow, the validator defaults to the validator of the selected flow and cannot be modified.
Priority
The priority levels are High, Medium, and Low. If you set Initiation Method to Associate with Existing Flow, the priority defaults to the priority of the selected flow and cannot be modified.
Operation Description
Enter the reason for initiating the remediation. The reason cannot exceed 128 characters in length.
Click OK to initiate the remediation.
Export an issue list
You can export only the issues that you have permission to view.
Each tenant supports a maximum of five concurrent export tasks.
If an issue list contains a large amount of data, the file generation may take some time. You can view historical export records in the batch export pane. For more information, see Issue export records.
On the Issue List page, click the Export Issues button in the upper-right corner and select either Export All Issues or Export By Search And Filter Criteria.
Export All Issues: Exports all issues of the specified object type in the current view.
Export By Search And Filter Criteria: Exports all issues in the current view that match the specified keyword search and filter criteria. For example, you can filter for and export all issues that are in the Pending status.

In the dialog box, select the content that you want to export.
Click OK to export the issues.
Issue export records
The pane displays your 50 most recent export operations.
You can download files that were successfully exported within the last 7 days.
On the Issue List page, click the Export Issues button in the upper-right corner, and select View Batch Export Records.
In the Batch Export Records pane, you can view the details of each export task, including the ordinal number, object type, submission time, and operation status. You can also click the
 icon in the Actions column to download the exported file to your local computer. This allows business personnel to perform statistical analysis and archiving.
icon in the Actions column to download the exported file to your local computer. This allows business personnel to perform statistical analysis and archiving.
