This topic will walk you through the process for using the Application Monitoring sub-service of Application Real-Time Monitoring Service (ARMS) to monitor a Python application deployed in an Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster. You can analyze application performance and traces, and configure alerting for the application.
For information about how to monitor Python applications deployed in other environments, see Application monitoring.
Workflow
Install an ARMS agent for the application.
Install the ack-onepilot component (ack-onepilot): The ack-onepilot component is provided by ACK to connect Java, Go, or Python applications deployed in ACK clusters to ARMS.
Update the Dockerfile: Download the agent installer aliyun-bootstrap, install the agent, and start the Python application using the agent.
Update the YAML file: You can add
labelsto the YAML file of the application to enable monitoring through ARMS and configure the application name shown in ARMS.
View monitoring data.
Configure alerting.
Prerequisites
ACK:
An ACK dedicated cluster, an ACK managed cluster, or a registered cluster is created. For more information, see Create an ACK managed cluster.
A Python application is created.
For information about the supported components and frameworks, see Python libraries supported by Application Monitoring.
Start the Python application with the following command:
aliyun-instrument gunicorn -w 4 -k uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker -b 0.0.0.0:8000 app:appNoteThe
aliyun-instrumentcommand initializes the ARMS agent for Python and instruments data in a non-intrusive way.If Gevent is used, set the
GEVENT_ENABLEenvironment variable totrue.
If you do not have a Python application, you can use the following YAML template to create one. For more information, see Create a stateless application by using a Deployment.
NoteThe YAML template creates the following resources:
Namespace: arms-demo. All of the following resources are created in the arms-demo namespace.
Deployments: arms-python-client and arms-python-server.
Services: arms-python-client-svc and arms-python-server-svc.
The following lists the sample code for arms-python-server and arms-python-client.
ARMS:
Application Monitoring is activated, and the pay-by-observable-data billing mode is enabled.
Application Monitoring provides a free monthly quota of 50 GB. The quota of a month cannot be used after the end of the month. If the quota is used up, you are charged based on the excess observable data. For more information, see Billing.
Install an ARMS agent
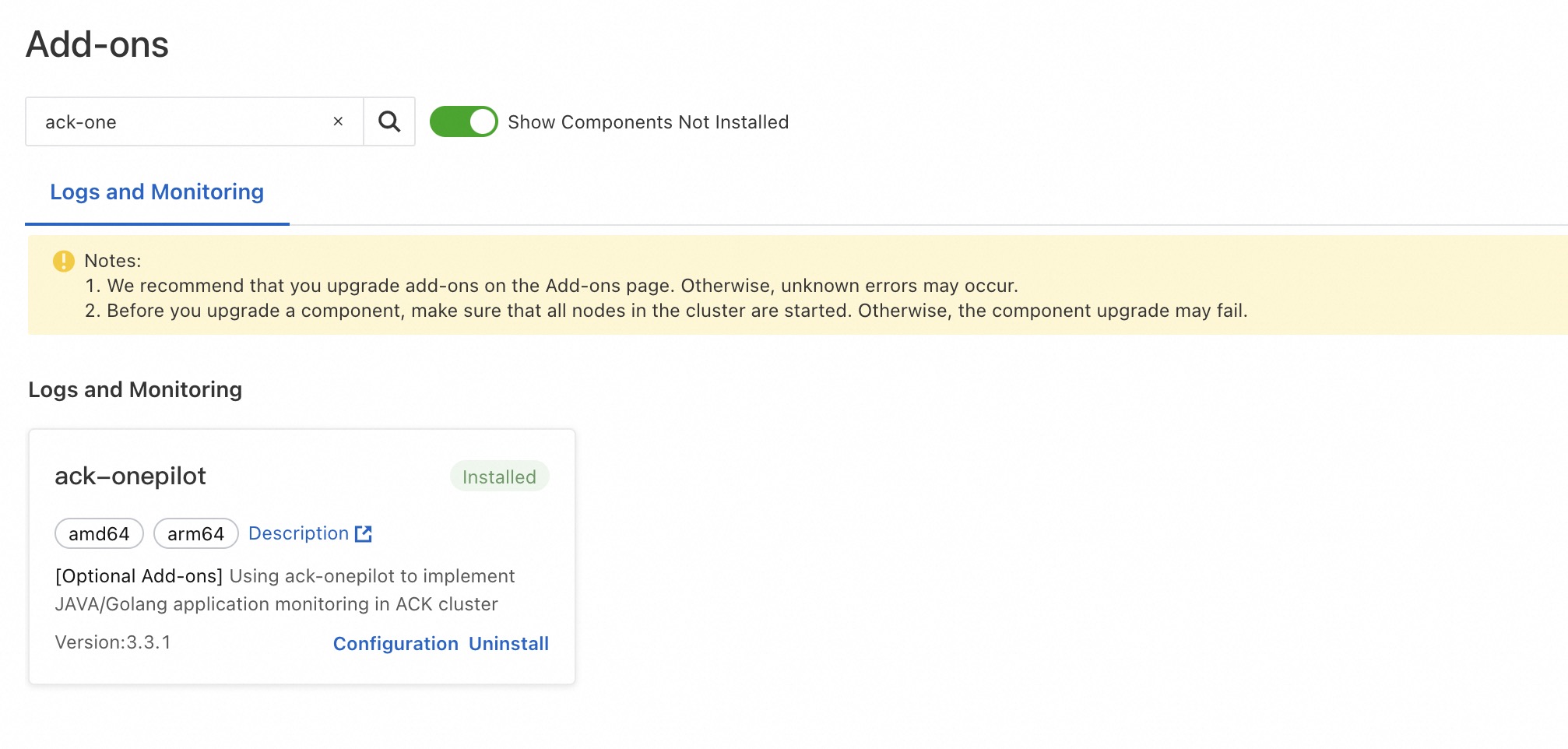
Step 1: Install the ack-onepilot component
Log on to the ACK console. On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster.
In the left-side navigation pane, click . On the Add-ons page, search for ack-onepilot.
In the ack-onepilot section, click Install. In the dialog box that appears, click OK.
NoteMake sure that the ack-onepilot version is 3.2.4 or later.
Step 2: Update the Dockerfile
Download the agent installer from the Python Package Index (PyPI) repository.
pip3 install aliyun-bootstrapInstall the ARMS agent for Python using aliyun-bootstrap.
aliyun-bootstrap -a installStart the application using the ARMS agent for Python.
aliyun-instrument python app.pyBuild an image.
Refer to the following sample Dockerfile to install an ARMS agent.
Step 3: Update the YAML file
In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the namespace where the Deployments reside. Find a Deployment and choose in the Actions column.
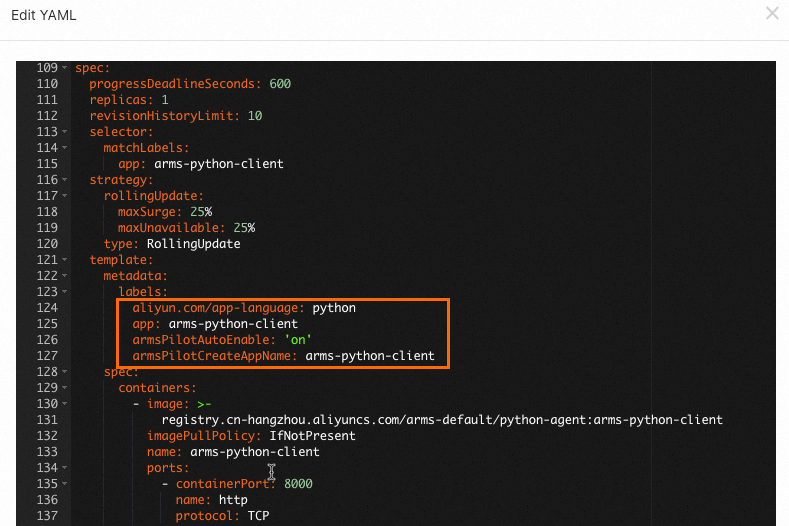
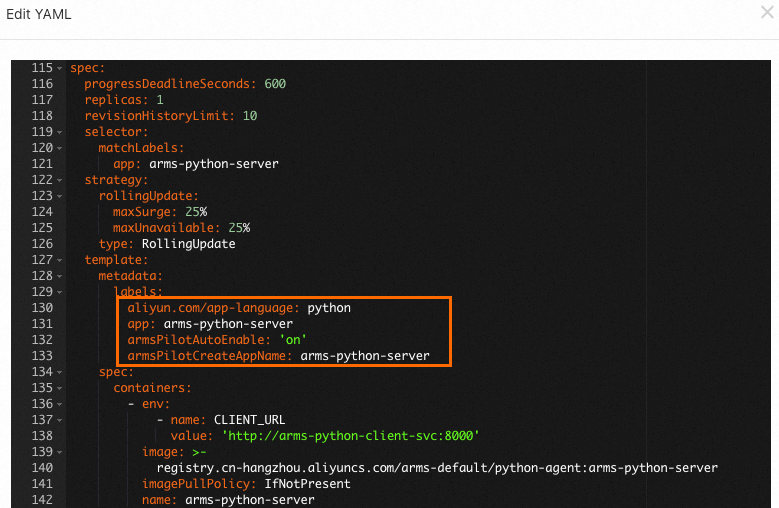
In the Edit YAML dialog box, add the following
labelsto the spec.template.metadata parameter and click Update.labels: aliyun.com/app-language: python # Specify a Python application. armsPilotAutoEnable: 'on' armsPilotCreateAppName: "<your-deployment-name>" # Specify the display name of the Deployment in ARMS.For example, you can modify the YAML files of the arms-python-client and arms-python-server Deployments, enable ARMS monitoring for the Deployments, and set arms-python-client and arms-python-server as their names shown in ARMS.
arms-python-client Deployment
arms-python-server Deployment
After the Deployments are automatically redeployed, wait for 1 to 2 minutes. In the left-side navigation pane of the ARMS console, choose . On the page that appears, click the name of each Deployment to view the metrics. For more information, see View monitoring details (new).
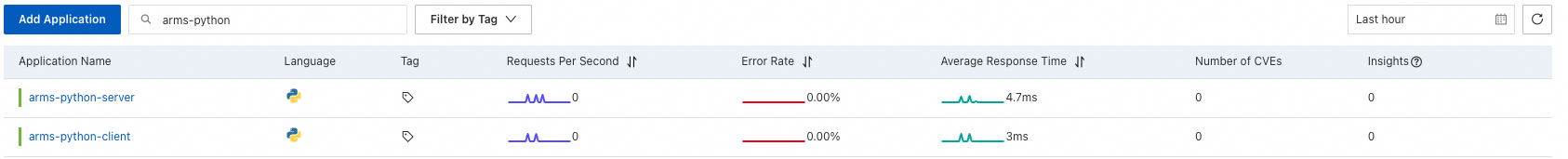
View the monitoring details
Trace Explorer
Microservice scenario:
Trace Explorer allows you to combine filter conditions and aggregation dimensions for real-time analysis. You can troubleshoot failed or slow calls of your application based on the failed or slow trace data.
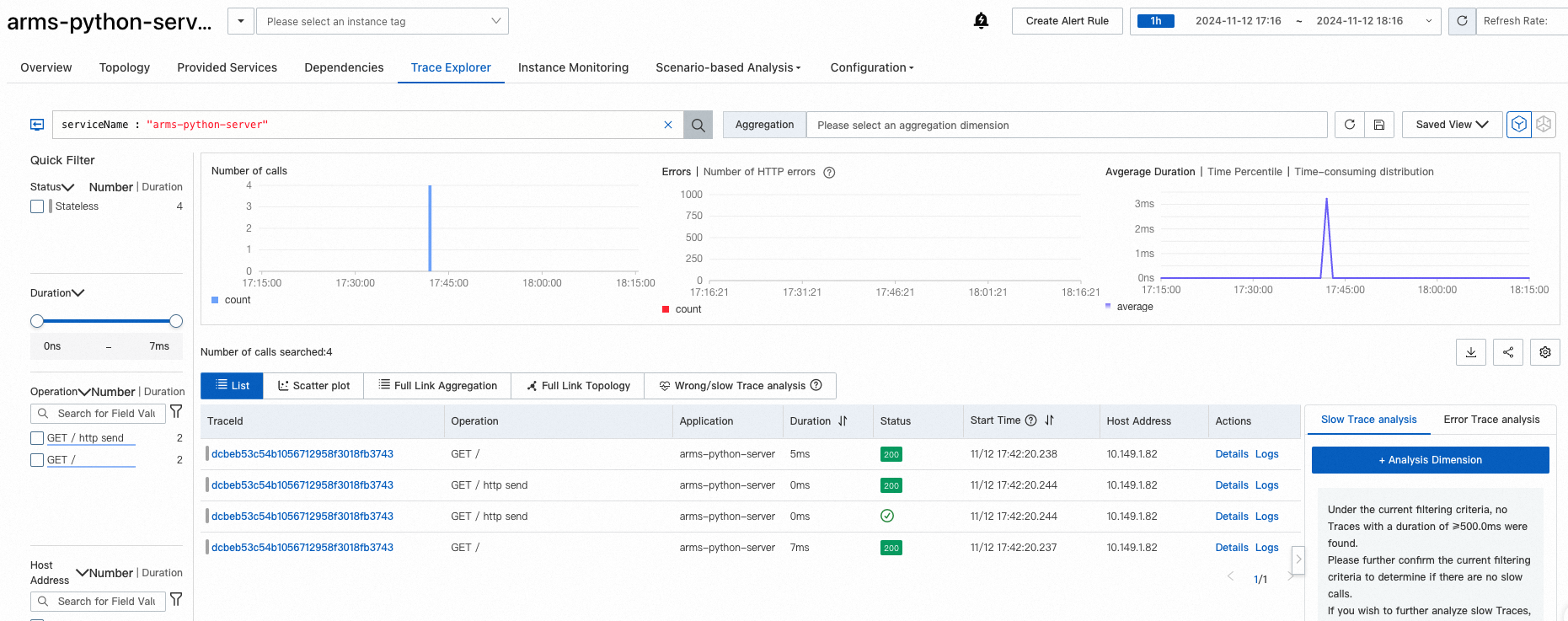
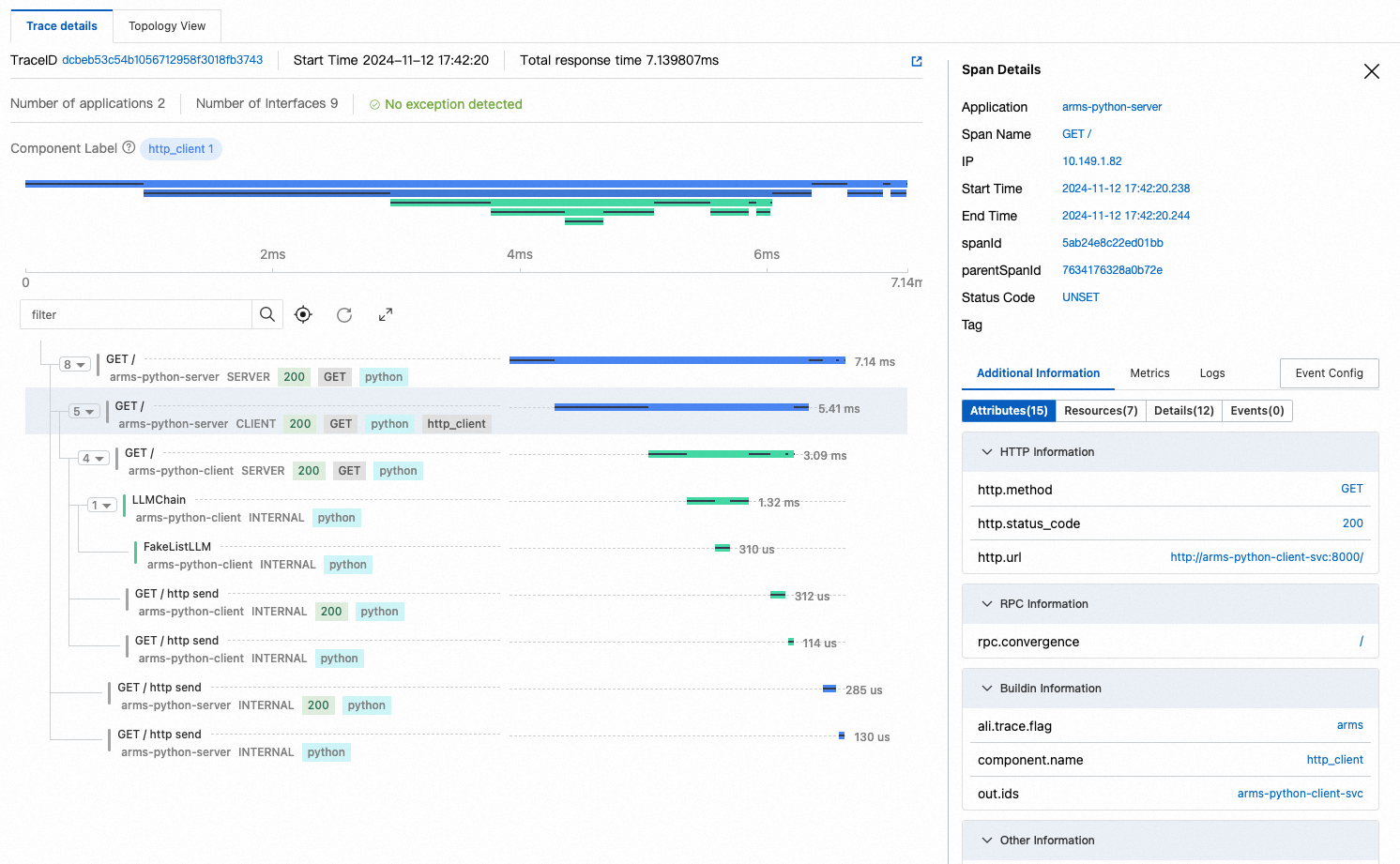
Trace details
In scenarios involving large language models (LLMs), the new LLM view offers an intuitive analysis of trace information, including the input and output of different operation types and token consumption.
Switch to the following LLM view:
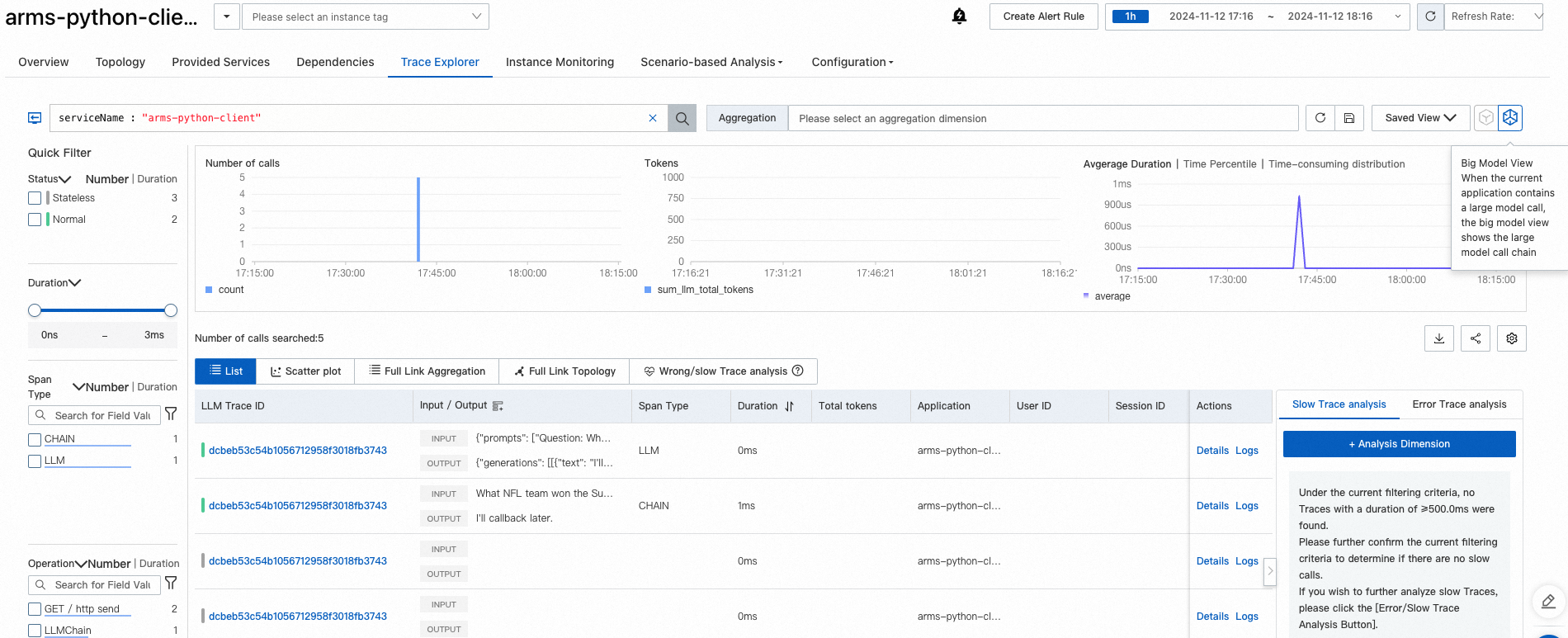
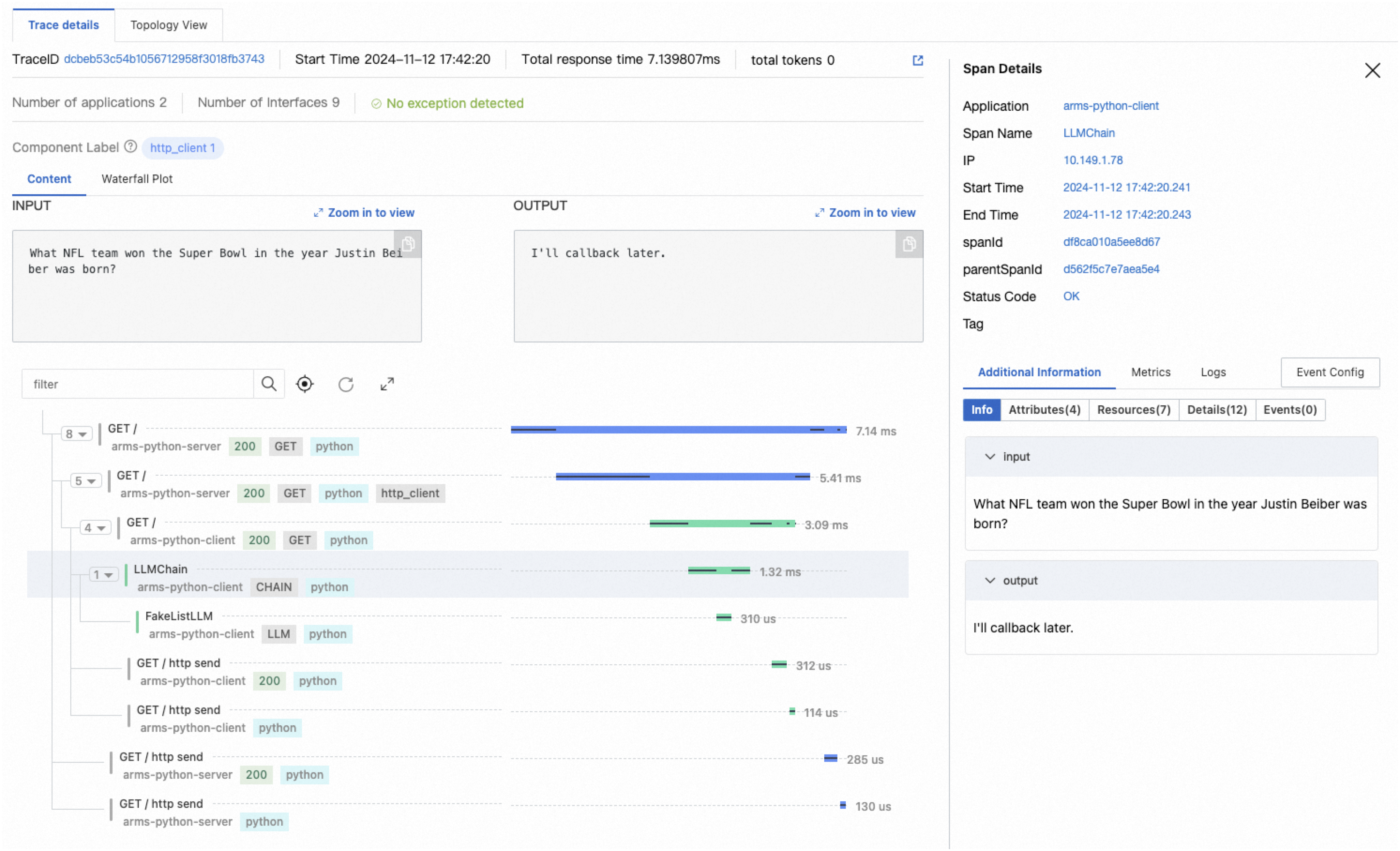
LLM calls:
Metrics
Application overview
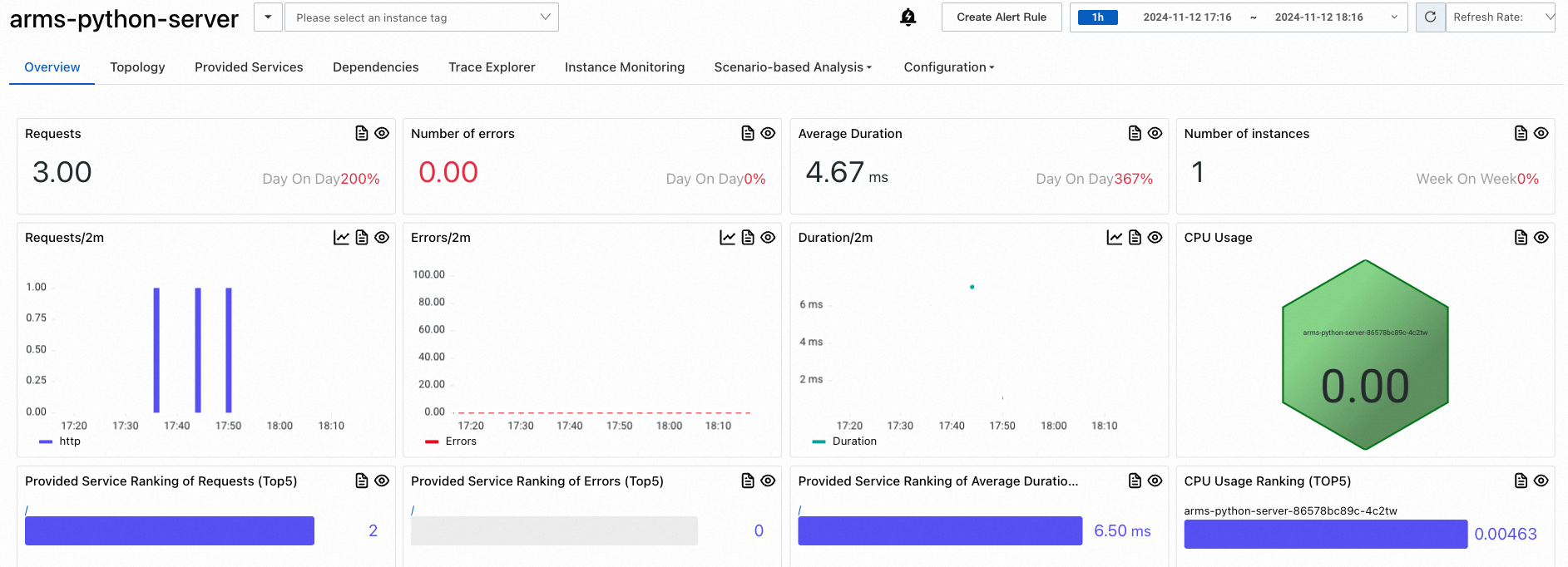
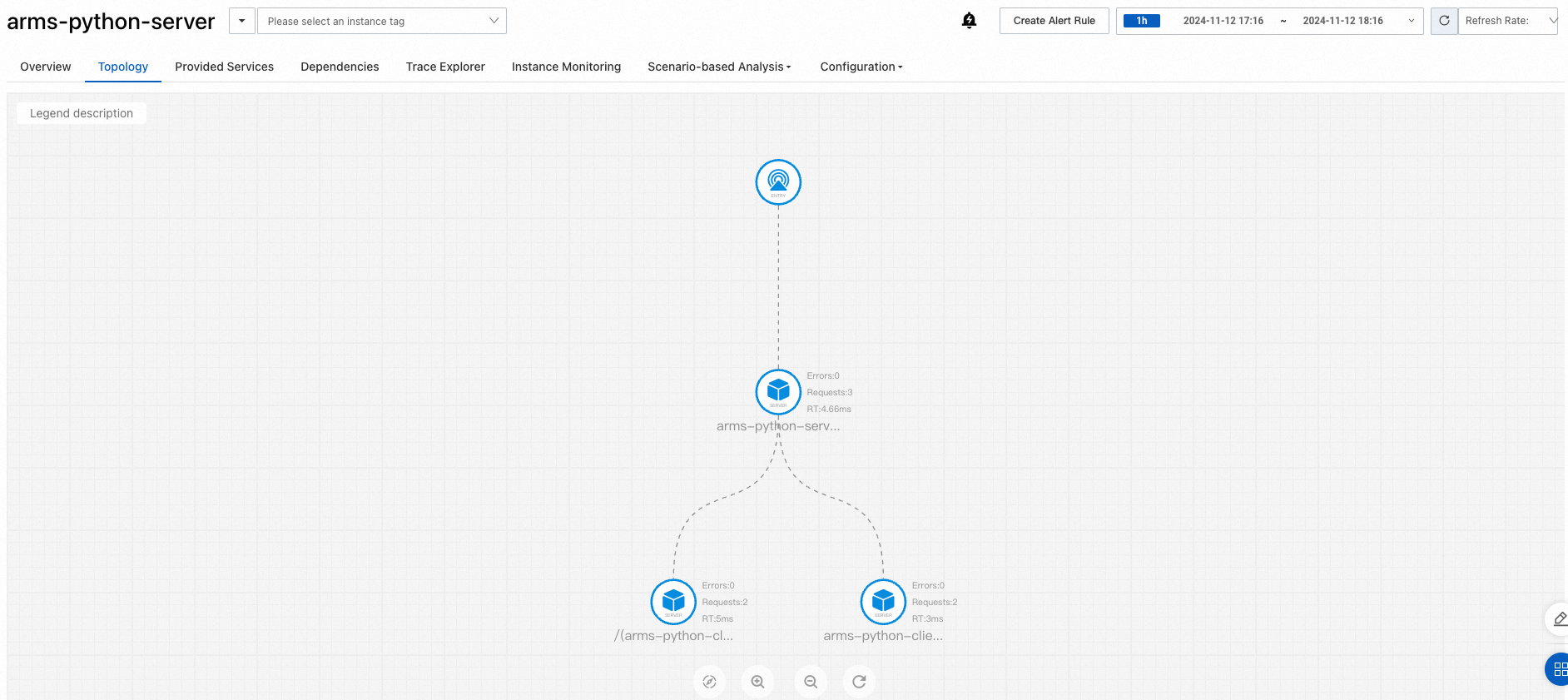
Topology
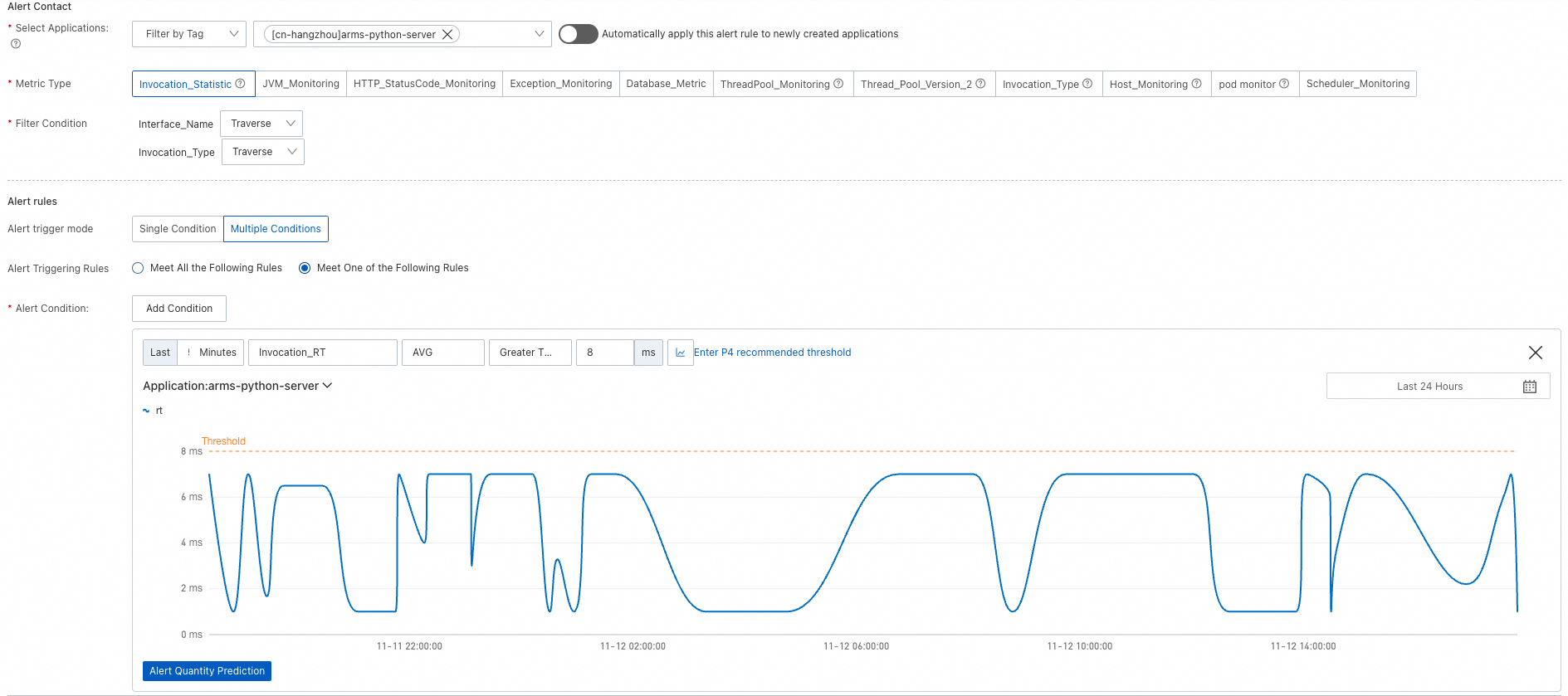
Configure alerting
You can configure alerting for the application. If an alert is triggered, alert notifications are sent to the contacts or DingTalk group chat based on the specified notification methods. For more information, see Alert rules.
Release resources
You can perform the following operations after you complete the whole process:
If you still want to monitor the application, make sure that your Alibaba Cloud account does not have overdue payments.
If you no longer want to monitor the application, uninstall the ARMS agent.
References
Application Monitoring allows you to associate trace IDs with the business logs of an application. This way, when an error occurs in your application, you can access the business logs associated with trace IDs to troubleshoot the error. For more information, see Associate trace IDs with logs for a Java application.
Alibaba Cloud Managed Service for Prometheus integrates with the Application Monitoring data source to visualize metrics. You can obtain application monitoring data, view preset dashboards, and perform secondary development based on your business requirements in Managed Service for Prometheus. For more information, see Use Managed Service for Prometheus to obtain application monitoring data.
 > Edit YAML
> Edit YAML