This topic uses a public dataset to help you get started with PAI-Rec. You can follow the steps to configure key features, such as feature engineering, recall, and fine-grained ranking for custom recommendation algorithms. You can then generate the code and deploy it to the corresponding workflow in DataWorks.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, complete the following prerequisites:
Activate PAI. For more information, see Activate PAI and create a default workspace.
Create a virtual private cloud (VPC) and a vSwitch. For more information, see Create a VPC with an IPv4 CIDR block.
Activate PAI-FeatureStore. For more information, see the Prerequisites section of Create a data source. You do not need to activate Hologres. Instead, select FeatureDB as the data source. For more information, see Create an online store: FeatureDB.
Activate MaxCompute and create a MaxCompute project named project_mc. For more information, see Activate MaxCompute and Create a MaxCompute project.
Create an Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket. For more information, see Create a bucket.
Activate DataWorks and perform the following operations:
Create a DataWorks workspace. For more information, see Create a workspace.
Purchase a Serverless resource group for DataWorks. For more information, see Use a Serverless resource group. The resource group is used to synchronize data for PAI-FeatureStore and run eascmd commands to create and update PAI-EAS services.
Configure DataWorks data sources:
Create and attach an OSS data source. For more information, see Data Source Management.
Create and attach a MaxCompute data source. For more information, see Attach a MaxCompute computing resource.
Create a FeatureStore project and feature entities. Skip this step if you use a Serverless resource group. If you use a dedicated resource group for DataWorks, you must install the FeatureStore Python software development kit (SDK). For more information, see II. Create and register a FeatureStore and Install the FeatureStore Python SDK.
Activate Flink. For more information, see Activate Realtime Compute for Apache Flink. Note: Set Storage Type to OSS bucket, not Fully Managed Storage. Ensure that the OSS bucket for Flink is the same as the one configured for PAI-Rec. Flink is used to record real-time user behavioral data and calculate real-time user features.
If you choose EasyRec (TensorFlow), the model is trained on MaxCompute by default.
If you choose TorchEasyRec (PyTorch), the model is trained on PAI-DLC by default. To download MaxCompute data on PAI-DLC, you must activate Data Transmission Service. For more information, see Purchase and use a dedicated resource group for Data Transmission Service.
1. Create a PAI-Rec instance and initialize the service
Log on to the Personalized Recommendation Platform home page and click Buy Now.
On the PAI-Rec instance purchase page, configure the following key parameters and click Buy Now.
Parameter
Description
Region And Zone
The region where your cloud service is deployed.
Service Type
Select Premium Edition for this solution.
NoteCompared to the Standard Edition, the Premium Edition adds data diagnostics and custom recommendation solution features.
Log on to the PAI-Rec console. In the top menu bar, select a region.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Instance List. Click the instance name to go to the instance details page.
In the Operation Guide section, click Init. You are redirected to the System Configurations > End-to-End Service page. Click Edit, configure the resources as described in the following table, and then click Done.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose System Configurations > Permission Management. On the Access Service tab, check the authorization status of each cloud product to ensure that access is granted.
2. Clone the public dataset
1. Synchronize data tables
You can provide input data for this solution in two ways:
Clone data for a fixed time window from the pai_online_project project. This method does not support routine task scheduling.
Use a Python script to generate data. You can run a task in DataWorks to generate data for a specific period.
To schedule daily data generation and model training, use the second method. You must deploy the specified Python code to generate the required data. For more information, see the Generate data using code tab.
Synchronize data for a fixed time window
PAI-Rec provides three common tables for recommendation algorithms in the publicly accessible pai_online_project project:
User table: pai_online_project.rec_sln_demo_user_table
Item table: pai_online_project.rec_sln_demo_item_table
Behavior table: pai_online_project.rec_sln_demo_behavior_table
The subsequent operations in this solution are based on these three tables. The data is randomly generated and simulated and has no real business meaning. Therefore, metrics such as Area Under the Curve (AUC) obtained from training will be low. You must run SQL commands in DataWorks to synchronize the table data from the pai_online_project project to your DataWorks project, such as DataWorks_a. The procedure is as follows:
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top menu bar, select a region.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Data Development And O&M > Data Development.
Select the DataWorks workspace that you created and click Go To Data Development.
Hover over Create and choose Create Node > MaxCompute > ODPS SQL. Configure the parameters as described in the following table and click Confirm.
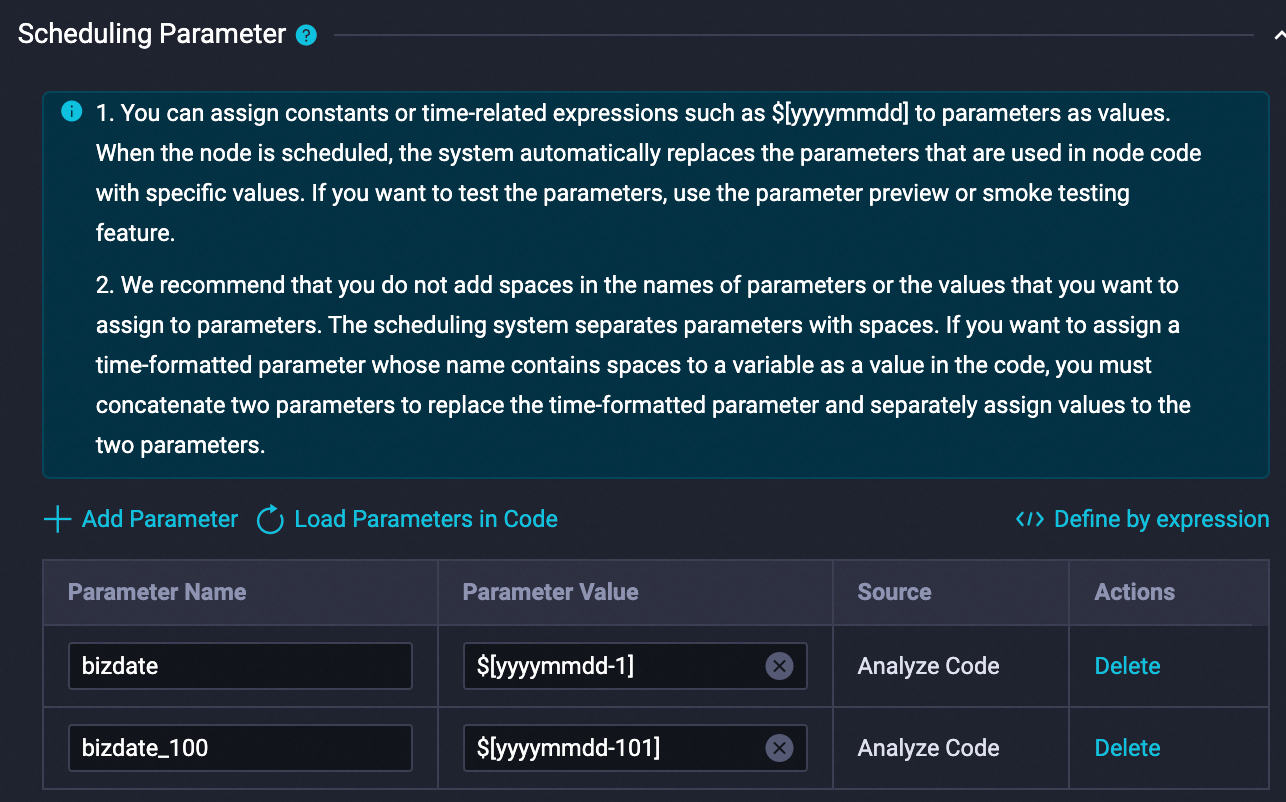
In the new node section, copy and run the following code to synchronize the user, item, and behavior tables from the pai_online_project project to your MaxCompute project, such as project_mc. To run the code, you must set variables to specify data from bizdate to 100 days before bizdate. Typically, you can set bizdate to the day before the current date. Configure the scheduling parameters as follows:
 Run the following code once to copy the data from the public pai_online_project project to your project:
Run the following code once to copy the data from the public pai_online_project project to your project:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS rec_sln_demo_user_table_v1(
user_id BIGINT COMMENT 'Unique user ID',
gender STRING COMMENT 'Gender',
age BIGINT COMMENT 'Age',
city STRING COMMENT 'City',
item_cnt BIGINT COMMENT 'Number of created items',
follow_cnt BIGINT COMMENT 'Number of follows',
follower_cnt BIGINT COMMENT 'Number of followers',
register_time BIGINT COMMENT 'Registration time',
tags STRING COMMENT 'User tags'
) PARTITIONED BY (ds STRING) STORED AS ALIORC;
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE rec_sln_demo_user_table_v1 PARTITION(ds)
SELECT *
FROM pai_online_project.rec_sln_demo_user_table
WHERE ds >= "${bizdate_100}" and ds <= "${bizdate}";
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS rec_sln_demo_item_table_v1(
item_id BIGINT COMMENT 'Item ID',
duration DOUBLE COMMENT 'Video duration',
title STRING COMMENT 'Title',
category STRING COMMENT 'Primary tag',
author BIGINT COMMENT 'Author',
click_count BIGINT COMMENT 'Total clicks',
praise_count BIGINT COMMENT 'Total likes',
pub_time BIGINT COMMENT 'Publication time'
) PARTITIONED BY (ds STRING) STORED AS ALIORC;
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE rec_sln_demo_item_table_v1 PARTITION(ds)
SELECT *
FROM pai_online_project.rec_sln_demo_item_table
WHERE ds >= "${bizdate_100}" and ds <= "${bizdate}";
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS rec_sln_demo_behavior_table_v1(
request_id STRING COMMENT 'Instrumentation ID/Request ID',
user_id STRING COMMENT 'Unique user ID',
exp_id STRING COMMENT 'Experiment ID',
page STRING COMMENT 'Page',
net_type STRING COMMENT 'Network type',
event_time BIGINT COMMENT 'Behavior time',
item_id STRING COMMENT 'Item ID',
event STRING COMMENT 'Behavior type',
playtime DOUBLE COMMENT 'Playback/Read duration'
) PARTITIONED BY (ds STRING) STORED AS ALIORC;
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE rec_sln_demo_behavior_table_v1 PARTITION(ds)
SELECT *
FROM pai_online_project.rec_sln_demo_behavior_table
WHERE ds >= "${bizdate_100}" and ds <= "${bizdate}";Generate data using code
Using data from a fixed time window does not support routine task scheduling. To schedule tasks, you must deploy specific Python code to generate the required data. The procedure is as follows:
In the DataWorks console, create a PyODPS 3 node. For more information, see Create and manage MaxCompute nodes.
Download create_data.py and paste the file content into the PyODPS 3 node.
In the right-side pane, click Scheduling Configurations, configure the parameters, and then click the Save
 and Submit
and Submit  icons in the upper-right corner.
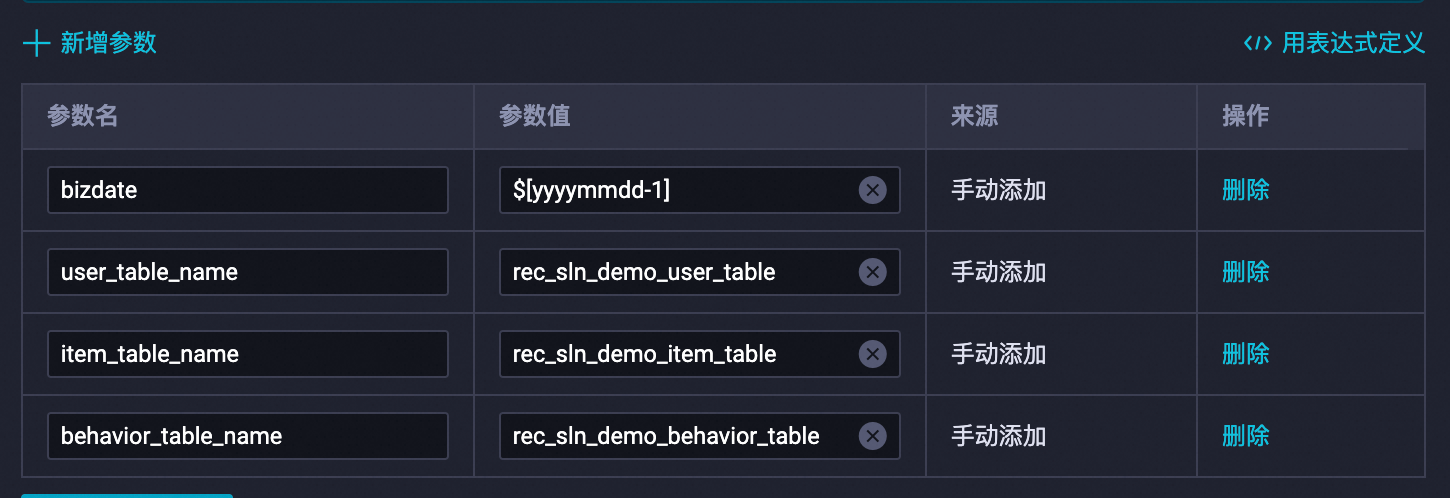
icons in the upper-right corner.Configure scheduling parameters:
Note the variable replacements:
Replace $user_table_name with rec_sln_demo_user_table.
Replace $item_table_name with rec_sln_demo_item_table.
Replace $behavior_table_name with rec_sln_demo_behavior_table.
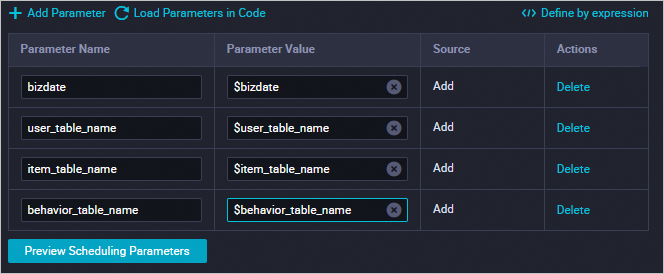
After replacement:
Configure scheduling dependencies.
Go to the Operation Center and choose .
In the Actions column of the target task, choose .
In the Backfill Data panel, set the data timestamp and click Submit And Go.
A good backfill time range is 60 days. We recommend that you set the data timestamp to
Scheduled Task Date - 60to ensure data integrity.
2. Configure dependency nodes
To ensure smooth code generation and deployment, add three SQL code nodes to your DataWorks project in advance. Configure the scheduling dependencies of these nodes to the root node of the workspace. After you complete all the settings, publish the nodes. The procedure is as follows:
Hover over Create and choose Create Node > General > Virtual Node. Create three virtual nodes as described in the following table and click Confirm.
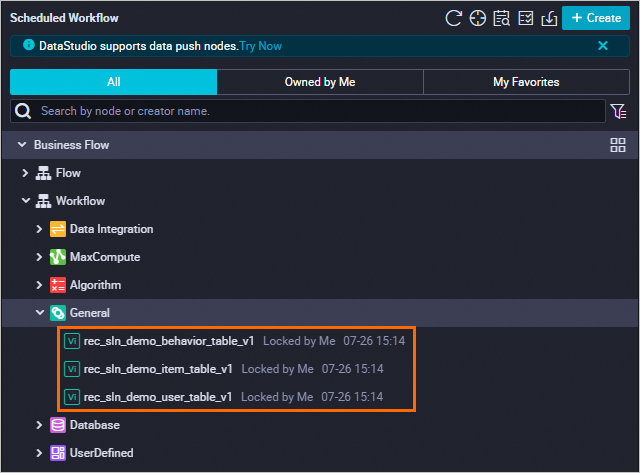
Select a node, set the node content to
select 1;for each node, and then click Scheduling Configurations in the right-side pane to complete the configurations:In the Time Property section, set Rerun Property to Rerun When Succeeded Or Failed.
In the Scheduling Dependencies > Upstream Dependencies section, enter the DataWorks workspace name, select the node with the _root suffix, and click Add.
Configure all three virtual nodes.
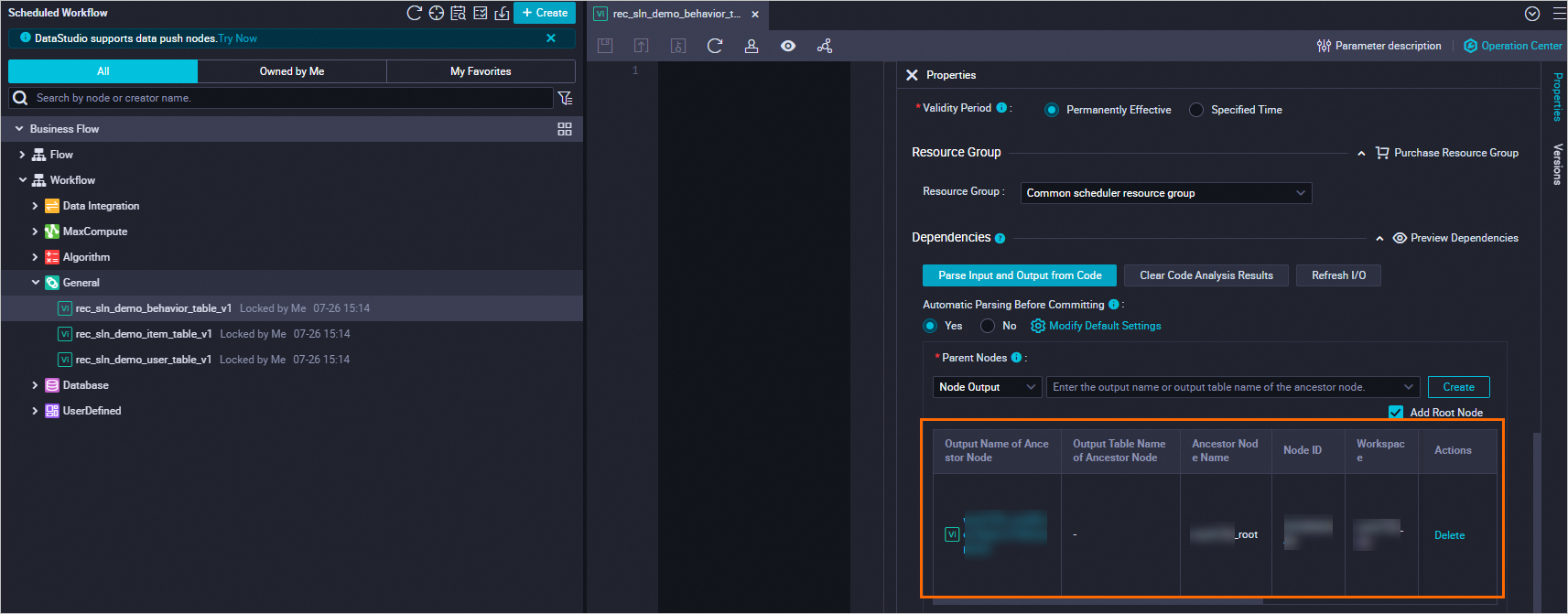
Click the
 icon in front of the virtual node to submit it.
icon in front of the virtual node to submit it.
3. Register data
To configure feature engineering, recall, and sorting algorithms in the custom recommendation solution, you must first register the three tables that you synchronized to your DataWorks project. The procedure is as follows:
Log on to the PAI-Rec console. In the top menu bar, select a region.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Instance List. Click the instance name to go to the instance details page.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Custom Recommendation Solution > Data Registration. On the MaxCompute Table tab, click Add Data Table. Add one user table, one item table, and one behavior table as described in the following table, and then click Start Import.
Parameter
Description
Example default solution
MaxCompute project
Select the MaxCompute project that you created.
project_mc
MaxCompute table
Select the data tables that you synchronized to the DataWorks workspace.
User table: rec_sln_demo_user_table_v1
Item table: rec_sln_demo_item_table_v1
Behavior table: rec_sln_demo_behavior_table_v1
Data table name
Enter a custom name.
User Table
Item Table
Behavior Table
4. Create a recommendation scenario
Before you configure a recommendation task, you must create a recommendation scenario. For information about the basic concepts of recommendation scenarios and the meaning of traffic IDs, see Terms.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Recommendation Scenarios. Click Create Scenario, create a recommendation scenario as described in the following table, and then click OK.
5. Create and configure an algorithm solution
To configure a complete real-world scenario, we recommend the following recall and fine-grained ranking configurations.
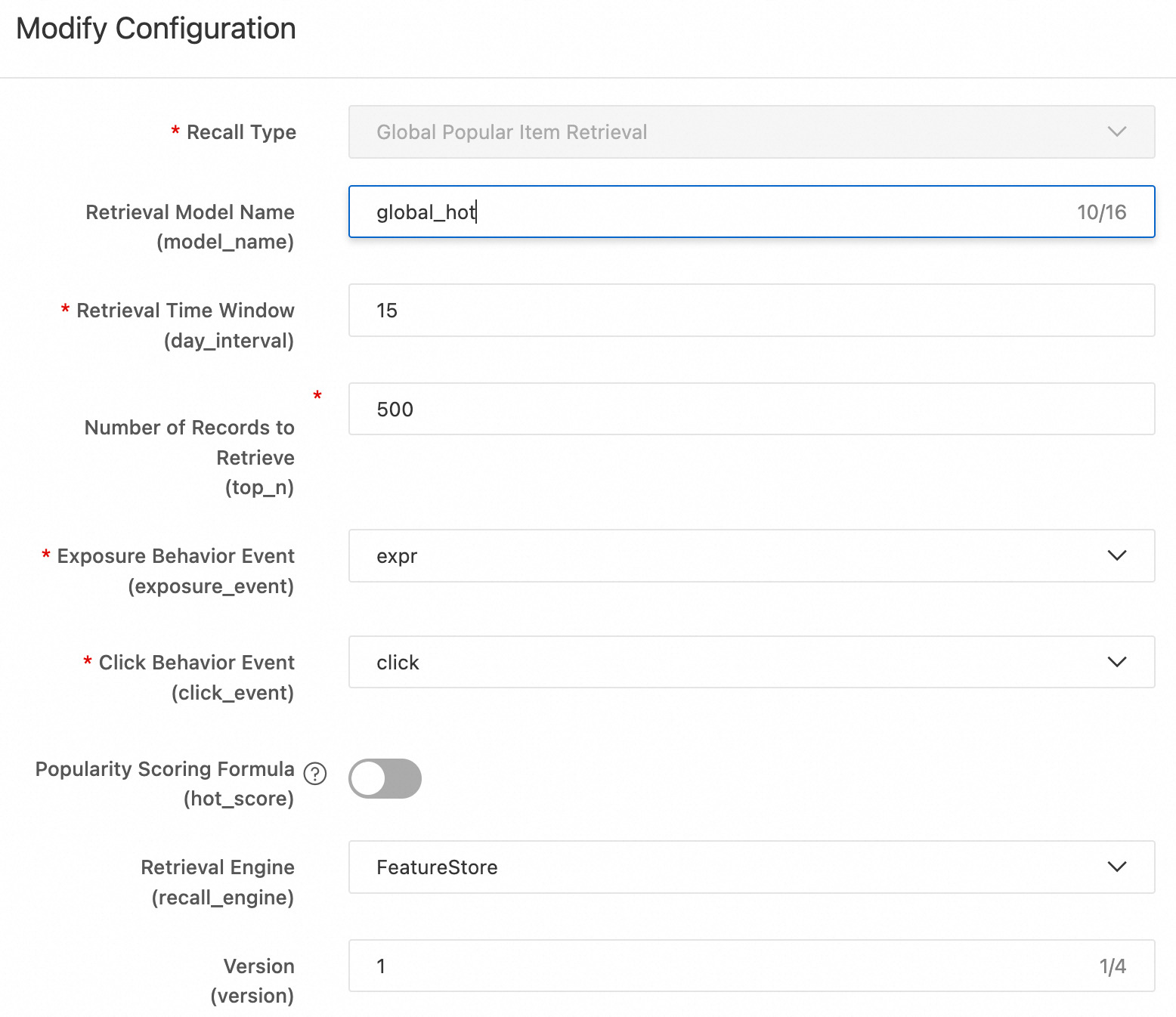
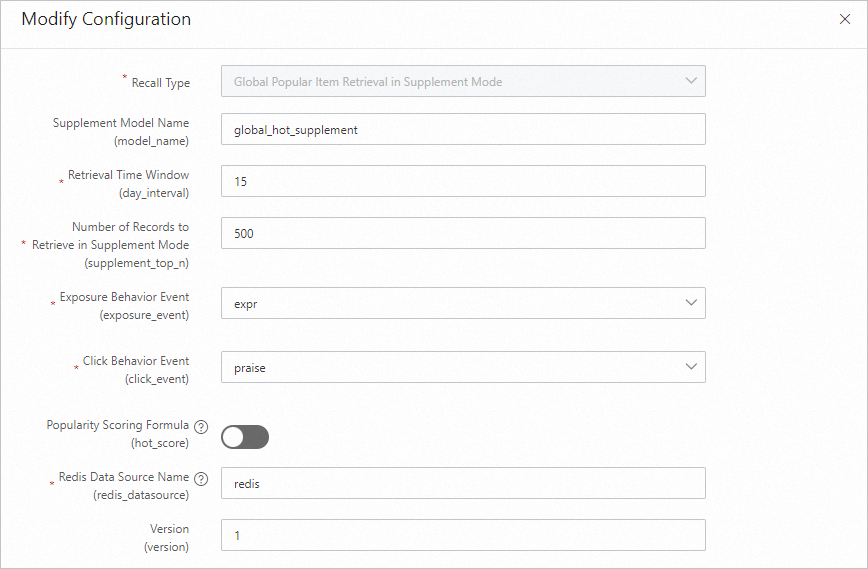
Global hot recall: Ranks the top k items based on statistics from log data.
Global hot fallback recall: Uses Redis as a fallback to prevent the recommendation API from returning empty data.
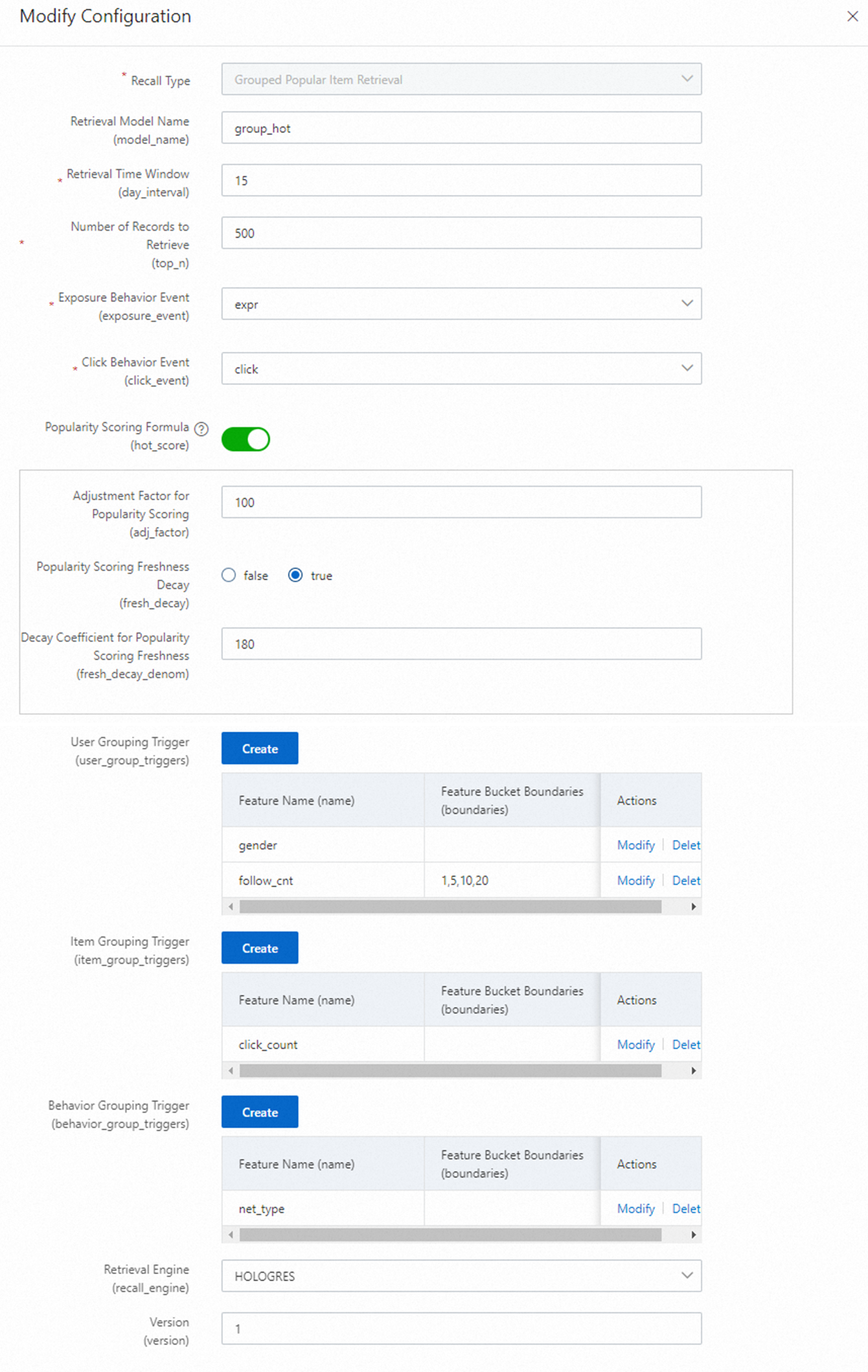
Grouped hot recall: Recalls items by categories, such as city and gender, to help improve the accuracy of popular item recommendations.
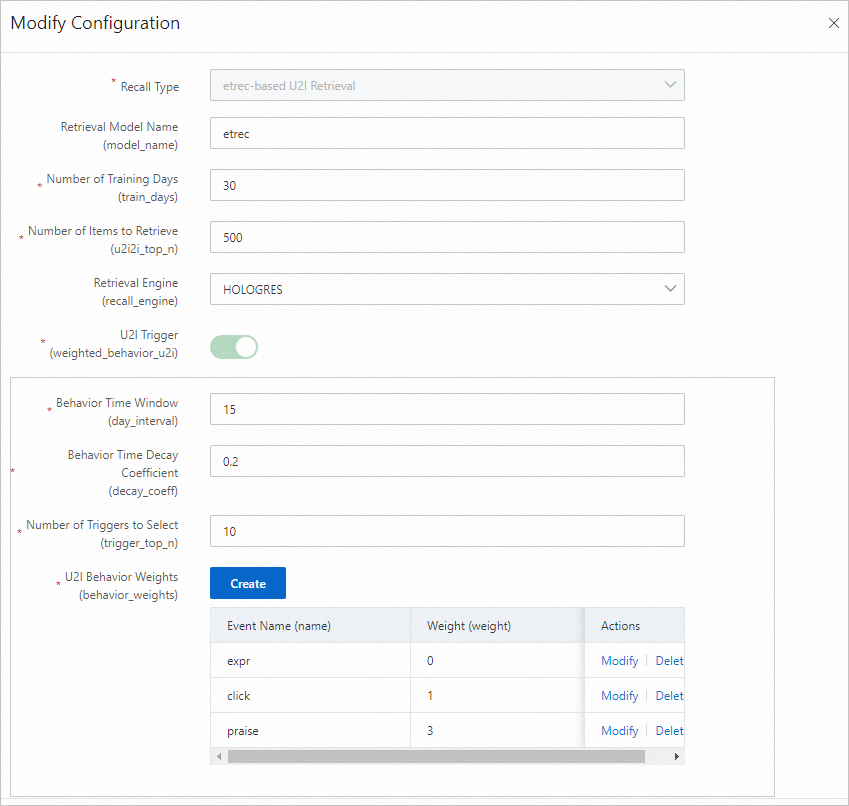
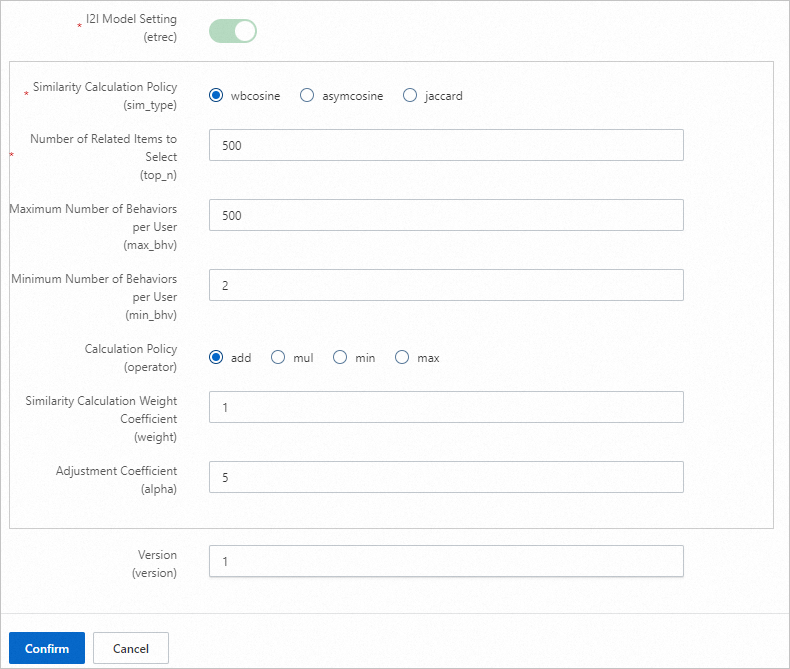
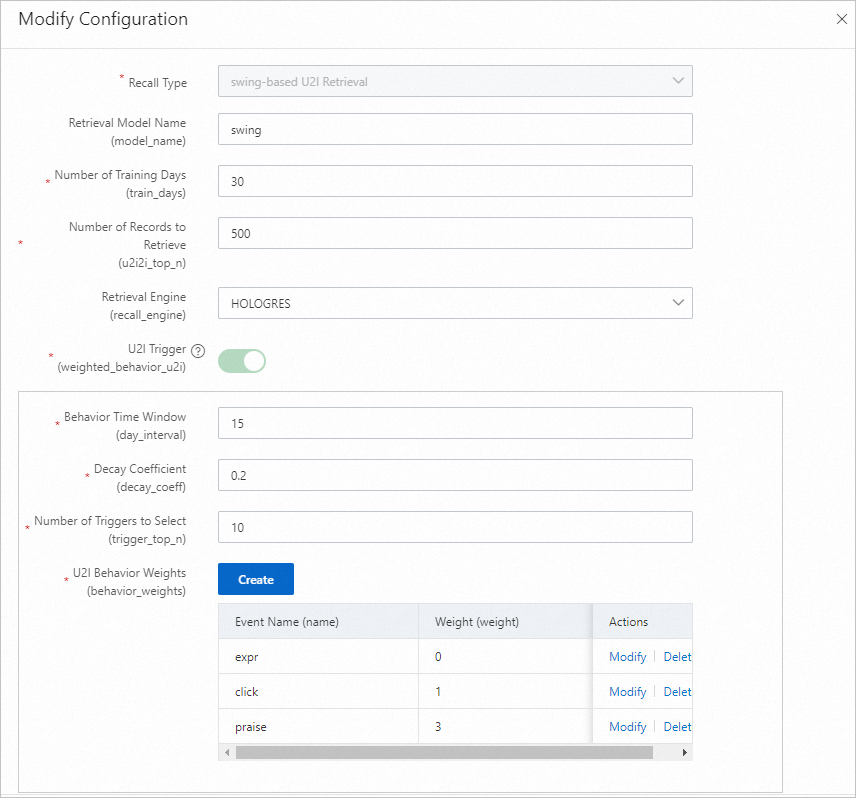
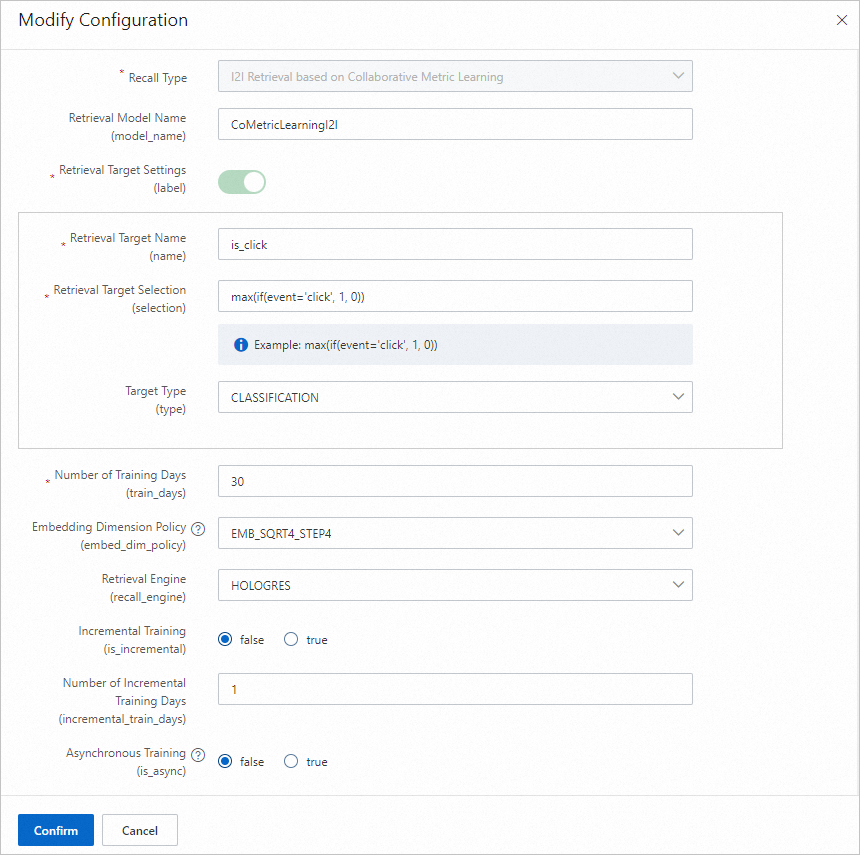
etrec u2i recall: Based on the etrec collaborative filtering algorithm.
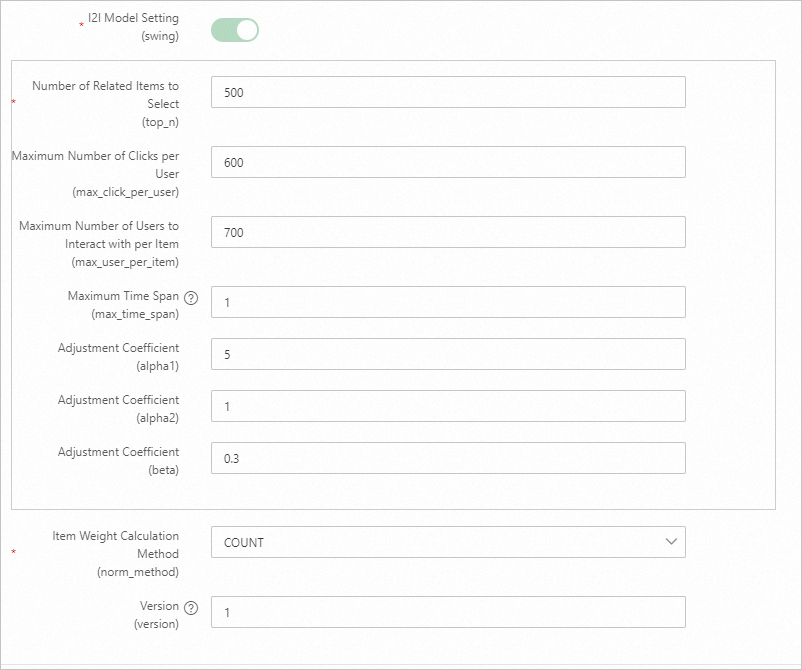
swing u2i recall (optional): Based on the Swing algorithm.
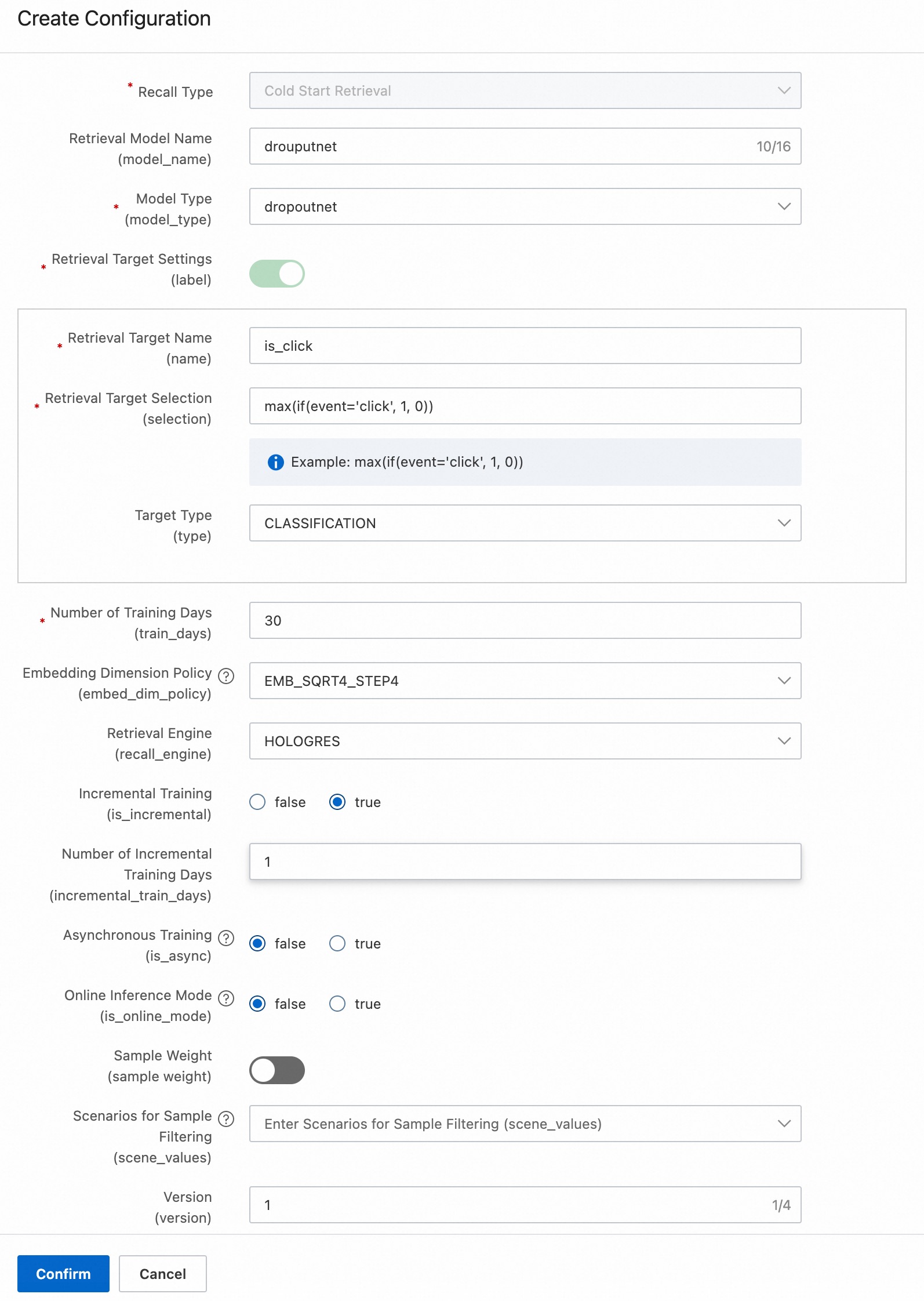
Cold-start recall (optional): Uses the DropoutNet algorithm for cold-start recall.
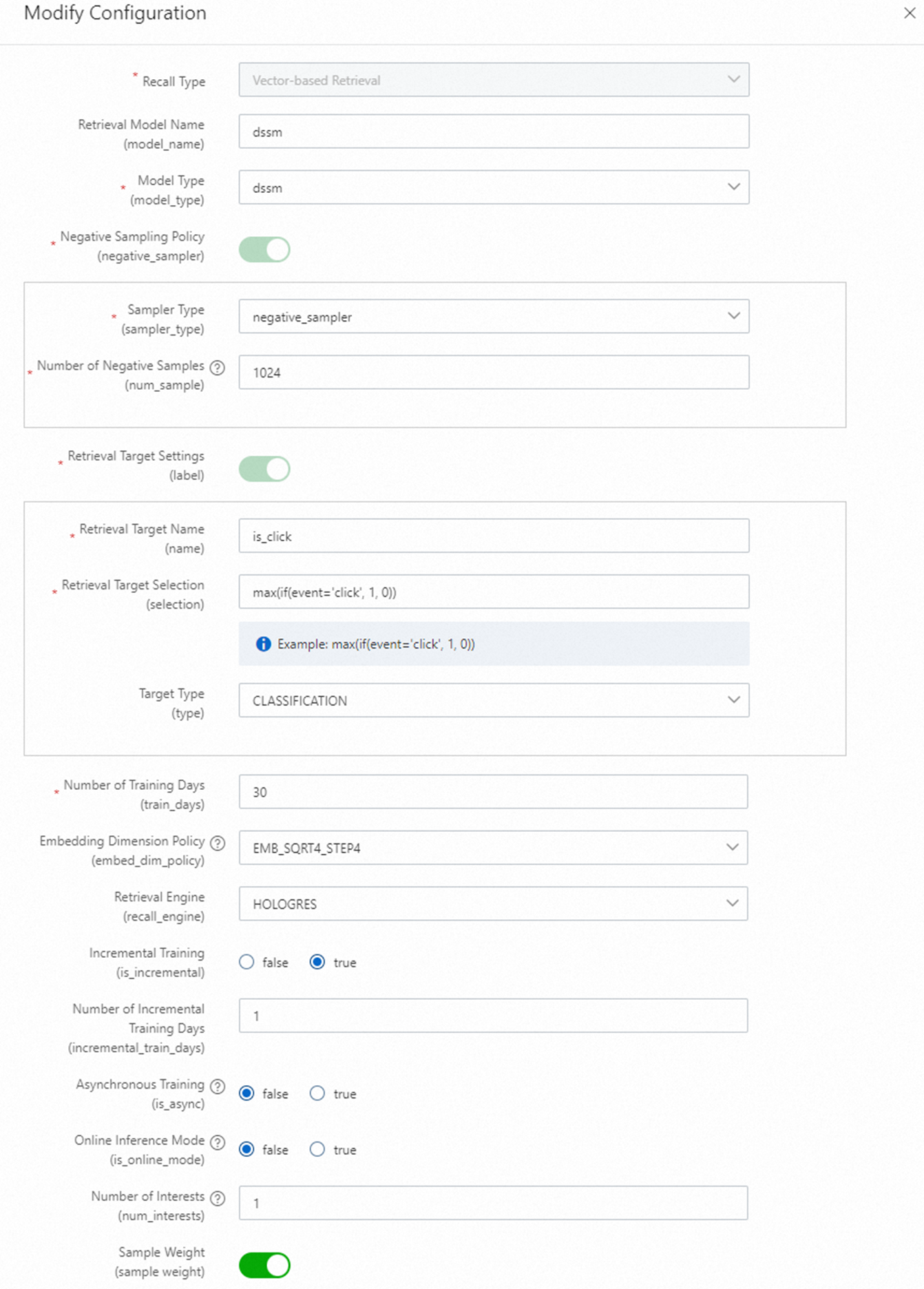
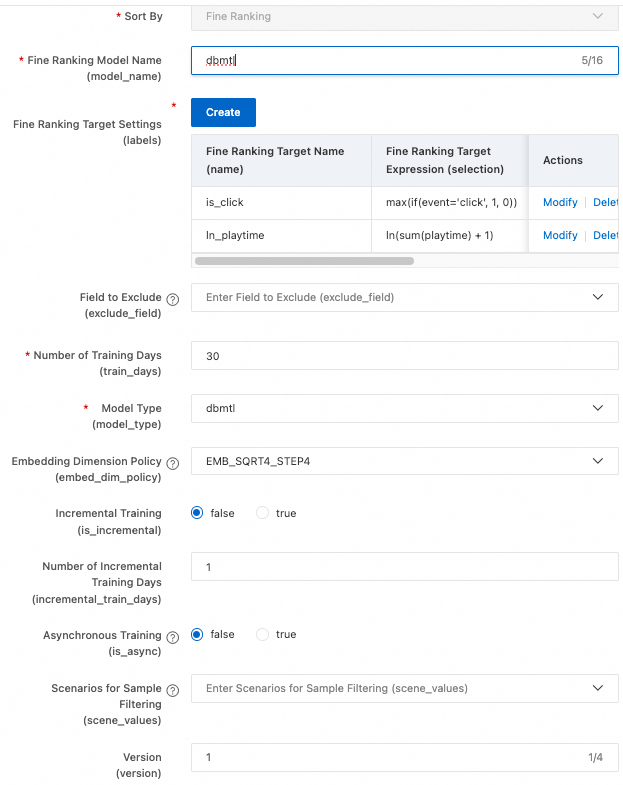
Fine-grained ranking: You can choose MultiTower for single-objective ranking or DBMTL for multi-objective ranking.
Vector recall or PDN recall algorithms are typically enabled after the recall stage is comprehensive. Vector recall requires a vector recall engine. We do not configure vector recall in this example because FeatureDB does not support it.
This topic is designed to guide you through the configuration and deployment process. Therefore, in the recall configuration stage, we configure only global hot recall and the u2i recall strategy of RECommender (eTREC, a collaborative filtering implementation). For the ranking configuration, we select fine-grained ranking to optimize the experience. The procedure is as follows:
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Custom Recommendation Solution > Solution Configuration. Select the scenario that you created, click Create Recommendation Solution, create a solution as described in the following table, and then click Save And Configure Algorithm Solution.
Keep the default values for parameters that are not described. For more information, see Data Table Configuration.
At the Data Table Configuration node, click Add to the right of the target data table. Configure the Behavior Log Table, User Table, and Item Table as described in the following tables. Set the partition, event, feature, and timestamp fields, and then click Next.
Keep the default values for parameters that are not described. For more information, see Data Table Configuration.
At the Feature Configuration node, configure the parameters as described in the following table, click Generate Features, set the feature version, and then click Next.
After you click Generate Features, various statistical features are derived for users and items. In this solution, we do not edit the derived features and keep the default settings. You can edit the derived features as needed. For more information, see Feature Configuration.
At the Recall Configuration node, click Add to the right of the target category, configure the parameters, click Confirm, and then click Next.
The following sections describe multiple recall configuration methods. To quickly guide you through the deployment process, you can configure only Global hot recall and etrec u2i recall. Other methods, such as vector recall and collaborative metric recall, are for reference only.
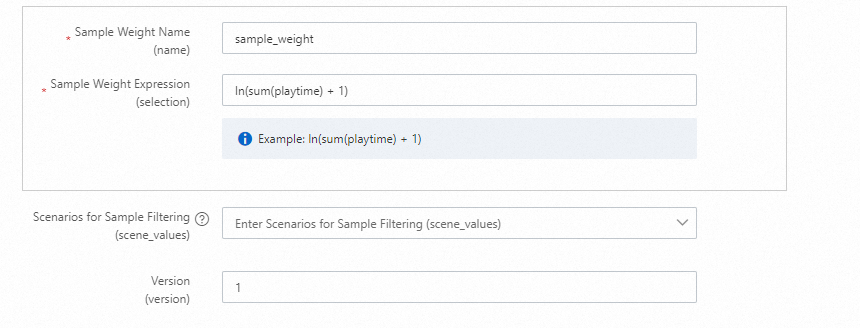
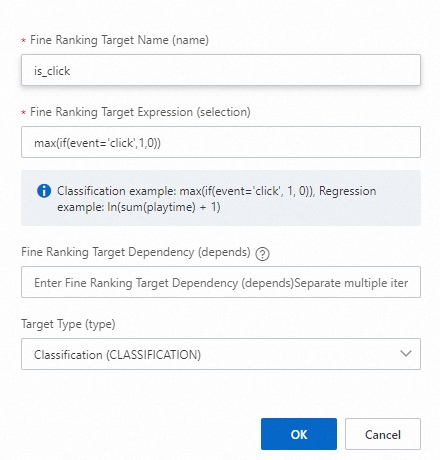
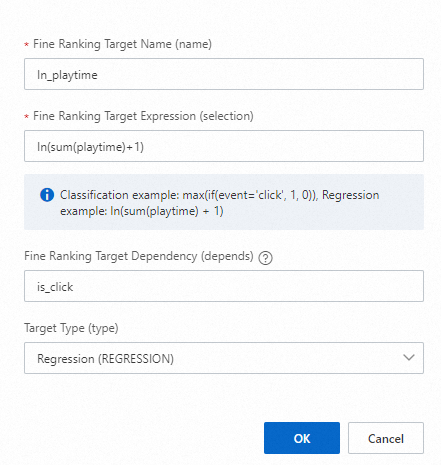
At the Ranking Configuration node, click Add to the right of Fine-grained Ranking, configure the parameters as described in the following table, click Confirm, and then click Next.
At the Generate Script node, click Generate Deployment Script.
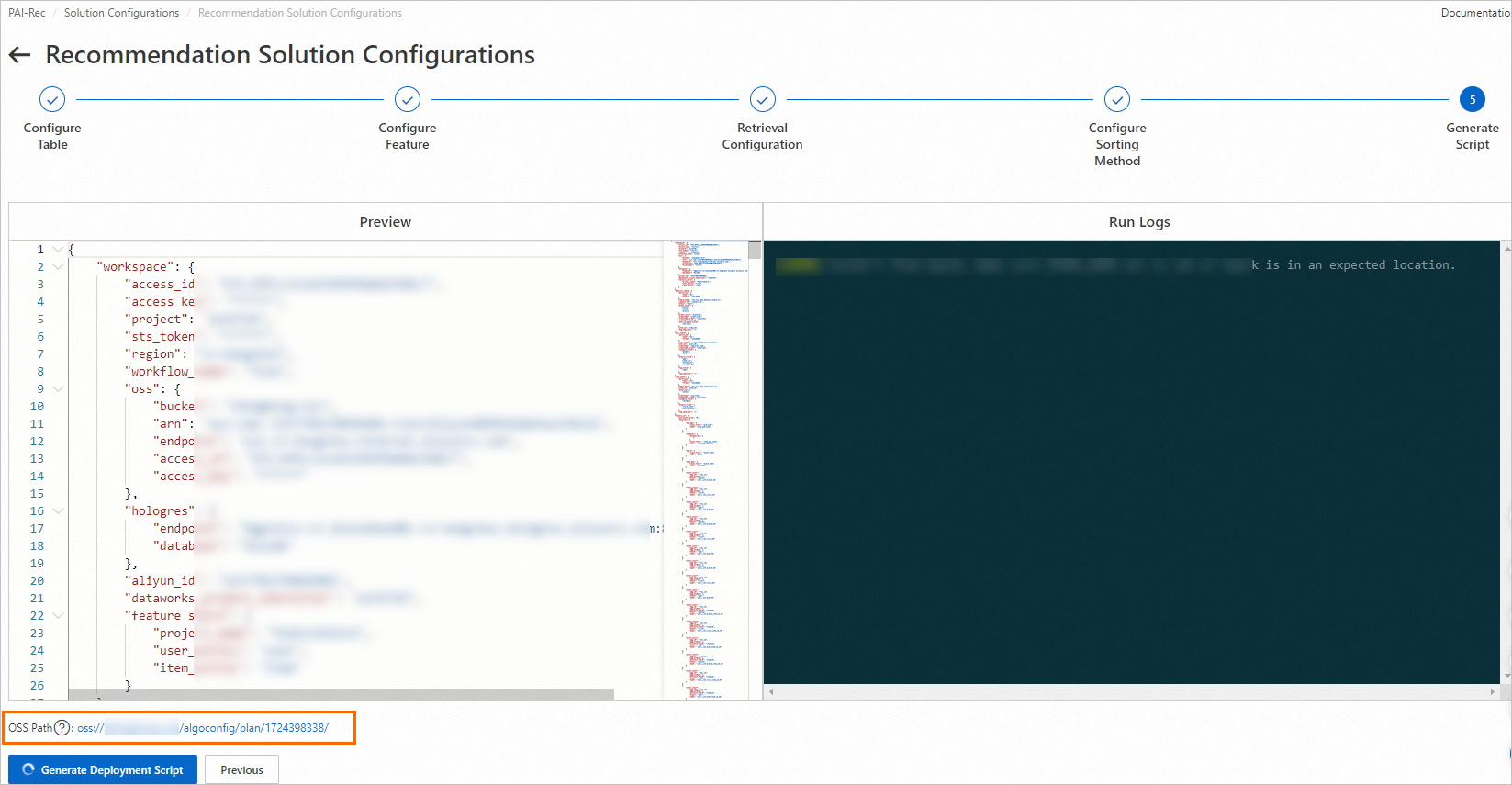 Important
ImportantAfter the script is successfully generated, the system generates an OSS address as shown in the preceding figure. This OSS path stores all the files to be deployed. You can save this address locally to manually deploy the script later.
After the script is generated, click OK in the dialog box. You are redirected to the Custom Recommendation Solution > Deployment Records page.
If the generation fails, view the run logs, analyze and resolve the specific error, and then generate the script again.
6. Deploy the recommendation solution
After the script is generated, you can deploy it to DataWorks in one of two ways.
Method 1: Deploy through the Personalized Recommendation Platform
Click Go To Deploy to the right of the target solution.
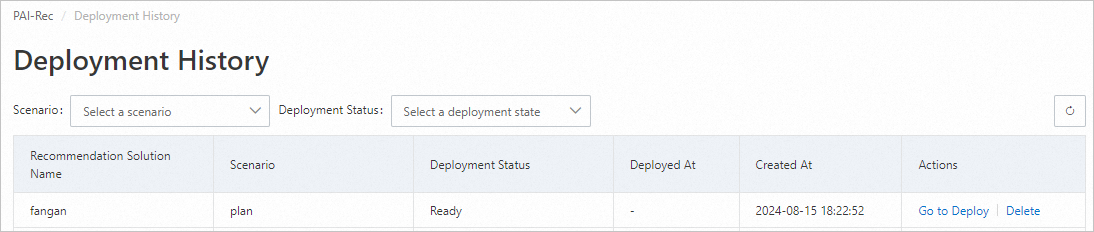
On the Deployment Preview page, in the File Diff section, select the files to deploy. Because this is the first deployment, click Select All and then click Deploy To DataWorks.
The page automatically returns to the Deployment Records page, which shows that the script deployment is in progress.
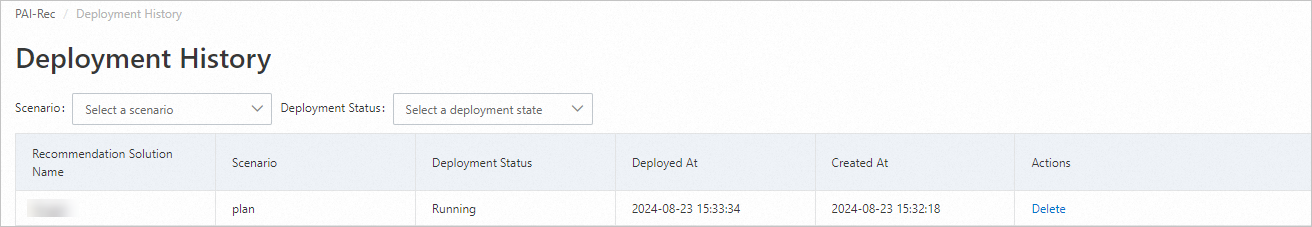
Wait for a moment, then click
 to refresh the list and check the deployment status.
to refresh the list and check the deployment status.If the deployment fails, click View Log in the Actions column, analyze and resolve the specific error, and then regenerate and deploy the script.
When the Deployment Status changes to Success, the script is successfully deployed. You can go to the Data Development page of the DataWorks workspace configured for this solution to view the deployed code. For more information, see Data development process guide.
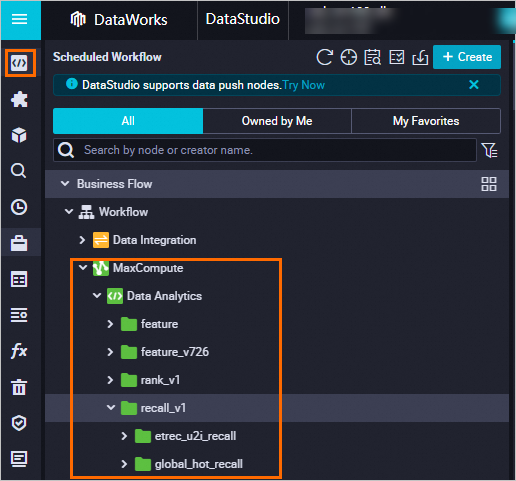
View the task data backfill process.
On the page, click Details in the Actions column of the successfully deployed recommendation solution.
On the Deployment Preview page, click View Task Data Backfill Process to understand the backfill process and related instructions to ensure data integrity.
Ensure that the user table, item table, and user behavior table partitions contain data for the last n days, where n is the sum of the training time window and the maximum feature time window. If you use the demo data from this topic, synchronize the latest data partitions. If you generate data using a Python script, backfill the data in the DataWorks Operation Center to produce the latest data partitions.
Click Create Deployment Task. Under the Backfill Task List, click Start Tasks Sequentially. Ensure that all tasks run successfully. If a task fails, click Details to view the log information, analyze and resolve the error, and then rerun the task. After a successful rerun, click Continue in the upper-left corner of the page until all tasks are successful.
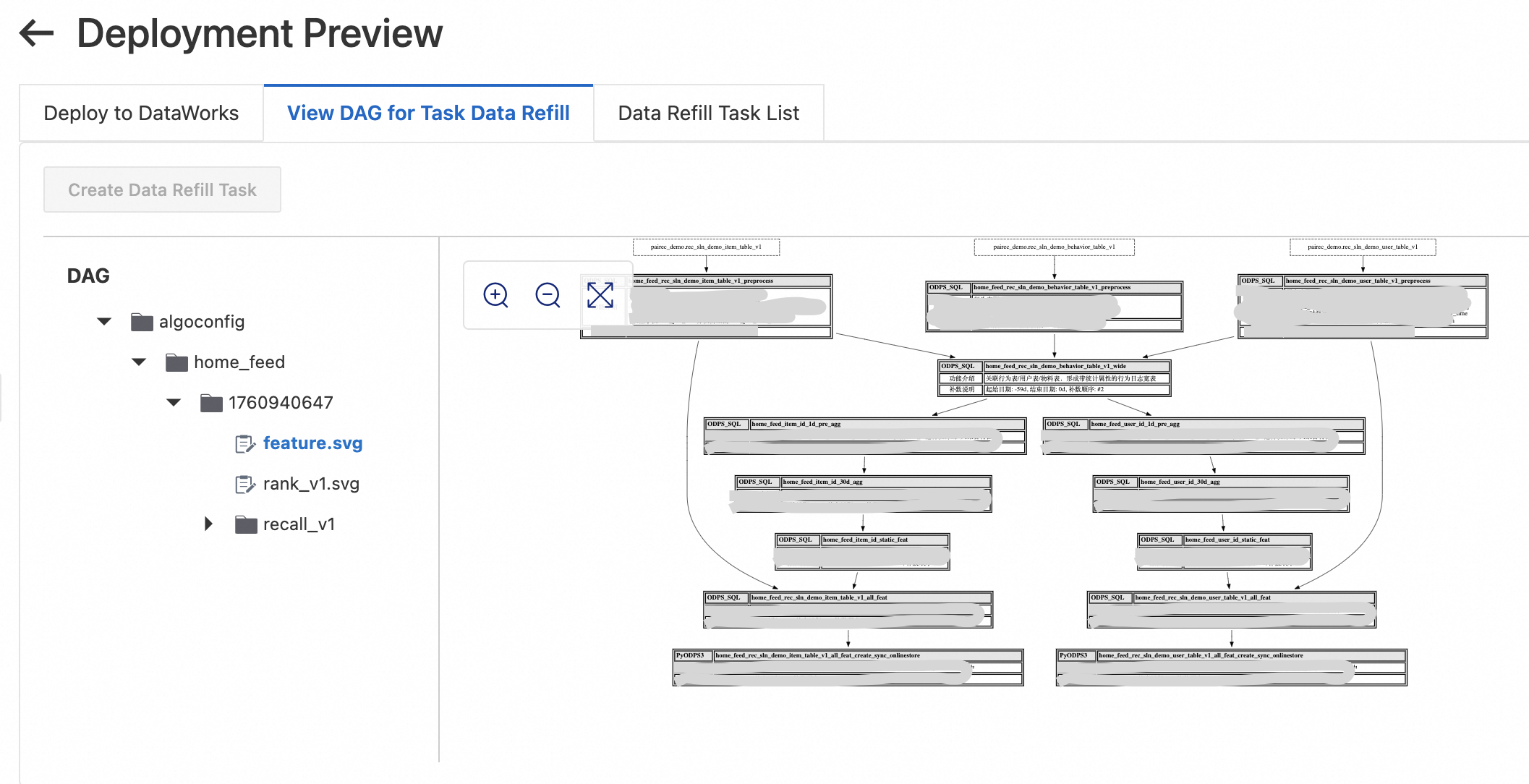
Method 2: Deploy using Migration Assistant
After the script is successfully generated, you can also go to the DataWorks console and manually deploy the script using the Migration Assistant feature. The key parameters are described below. For other operations, see Create and view a DataWorks import task.
Import Name: Set this as prompted in the console.
Upload Method: Select OSS File, enter the OSS Link, and click Verify.
The deployment file is stored at the OSS address generated in Step 5, such as
oss://examplebucket/algoconfig/plan/1723717372/package.zip. You can log on to the OSS console and follow the steps below to obtain the URL of the corresponding file.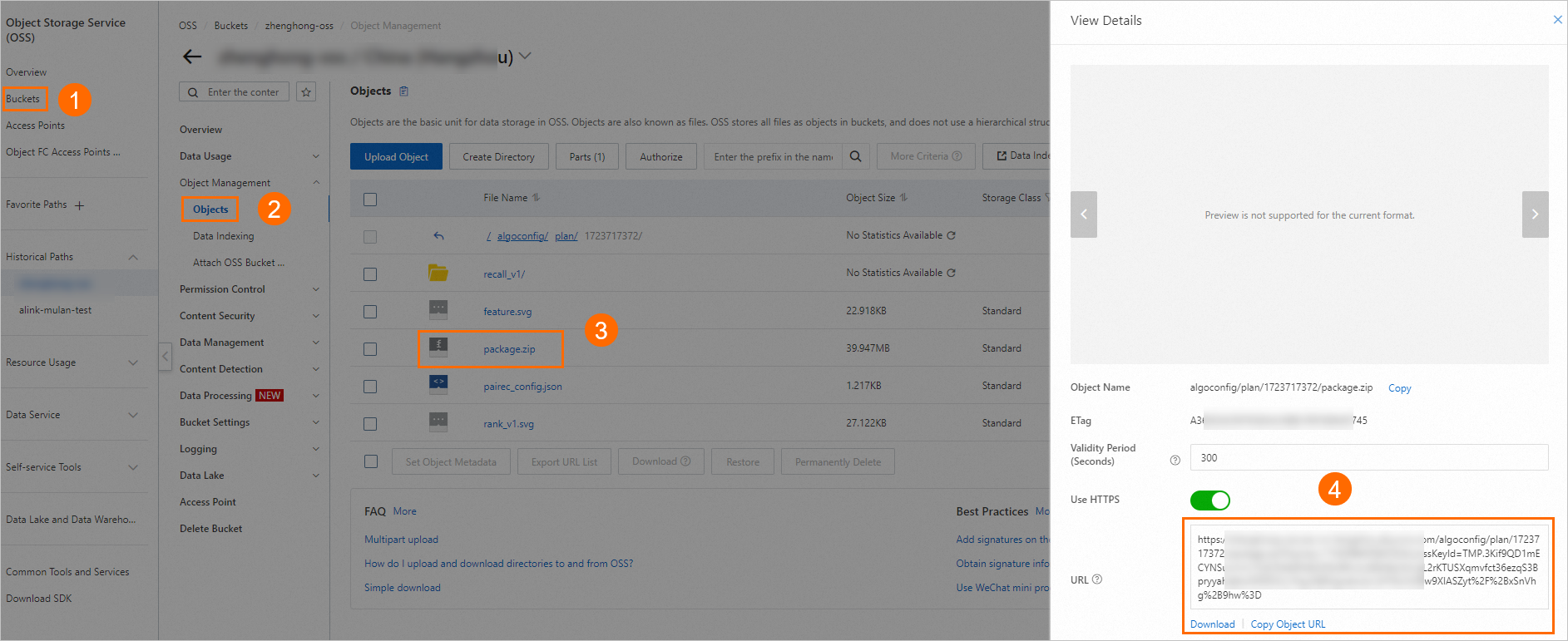
7. Freeze nodes
This topic uses demo data. After the data backfill is complete, freeze the tasks in the Operation Center (the three nodes from Step 2.2) to prevent them from being scheduled and run daily.
Go to the DataWorks Operation Center. Choose Periodic Task O&M > Periodic Tasks. Search for the name of the node that you created, such as rec_sln_demo_user_table_v1. Select the target node (Workspace.Node Name) and choose Pause (Freeze).