In this blog post, we'll explore how to effectively use Snowflake-style IDs on ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL with its snowflake extension. By the end of this guide, you'll understand the essentials of Snowflake IDs and how to implement them in your PostgreSQL environment.
A Snowflake Sequence, or Snowflake ID, is a unique identifier generation system devised by Twitter. This system produces unique, roughly ordered, 64-bit integers that can serve as identifiers across distributed systems. Here's a breakdown of its key characteristics:
● Time-Ordered: Snowflake IDs can be sorted based on when they were created.
● Unique: They ensure uniqueness across distributed systems without requiring coordination.
● Composite Structure: Each ID comprises several components—timestamp, worker ID, and sequence number.
A typical Snowflake ID is a 64-bit integer, structured as follows:
● Timestamp: The upper bits represent the timestamp (in milliseconds since a predetermined epoch), allowing for time ordering of the IDs.
● Node ID: The middle segment denotes a worker or node identifier, preventing conflicts among IDs created by different nodes.
● Sequence Number: The lower bits signify a sequence number, which increases for multiple IDs generated within the same millisecond by the same node. (It's a counter for IDs generated in the same millisecond)
This layered design empowers the generation of unique IDs at a high speed with vast production capability.
Example Representation:
010110101010101010101010101010101010101010 10101 010101010101
|------------ Timestamp -------------| |Node| |Sequence|
Developers frequently opt for Snowflake IDs in PostgreSQL due to the following advantages:
● Better Performance: Avoids database bottlenecks in high-write scenarios
● Time-Ordered: IDs are roughly sortable by creation time, making time-based queries and partitioning more efficient
● Space Efficiency: 64-bit size occupies less space than 128-bit UUIDs
● Index-Friendly: Better for B-tree indexes than random UUIDs
● Human-Readable: Easier to work with than UUIDs while maintaining global uniqueness
Snowflake IDs are especially useful in various scenarios, including:
● Primary Keys: Serve as unique primary keys in databases.
● Log Identifiers: Group logs related to specific transactions or events across multiple services.
● User Accounts: Generate unique identifiers for systems anticipating high volumes of user sign-ups.
● Transaction IDs: Identify transactions for payment systems or order processing.
The snowflake extension simplifies the use of Snowflake IDs on ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL, offering a plug-and-play solution that is easy to implement.
To utilize the snowflake extension, ensure your ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL is running on version 15 to 17 with a minor kernel version of 20250630 or higher.
Implementing the Snowflake Extension
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use the Snowflake extension:
Make sure your ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL is appropriately configured. If you haven't set up an RDS instance, you can provision one.
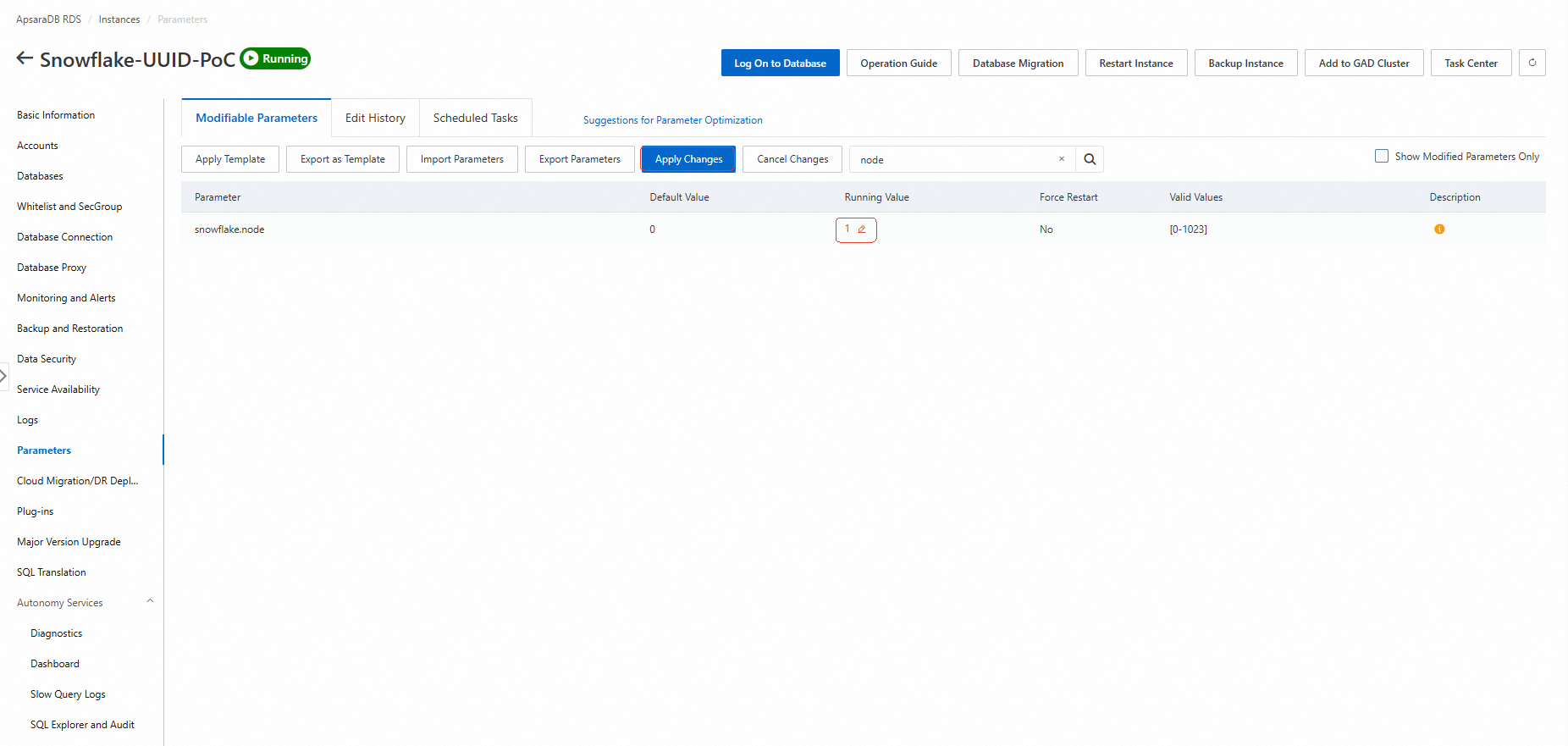
In the RDS console, go to Parameter Settings and update the snowflake.node value to a random number between 1 and 1023. Then, click the "Apply Changes" button to apply the updates immediately without service interruption.
Tip: If you're using multiple ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instances in a distributed system, ensure each instance has a unique snowflake.node value to maintain ID uniqueness. (So, please make sure to set different values for each instance.)
Run the following SQL commands to load the snowflake extension and verify its status:
CREATE EXTENSION snowflake;
\dx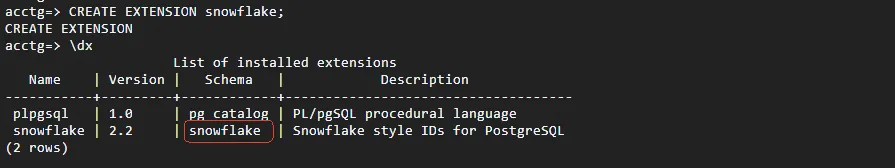
Create tables that utilize Snowflake IDs with the next.val() function. Insert some test data and observe the implementation in action. Here's how to use Snowflake IDs as primary keys:
CREATE TABLE orders (
id bigint PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT snowflake.nextval(),
customer varchar(255),
invoice varchar(50)
);
-- Insert some test data
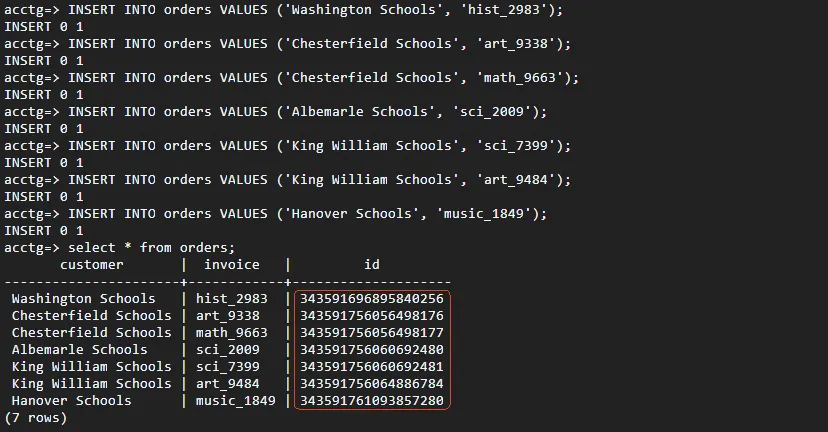
INSERT INTO orders (customer, invoice) VALUES
('Washington Schools', 'hist_2983'),
('Chesterfield Schools', 'art_9338');
SELECT * FROM orders;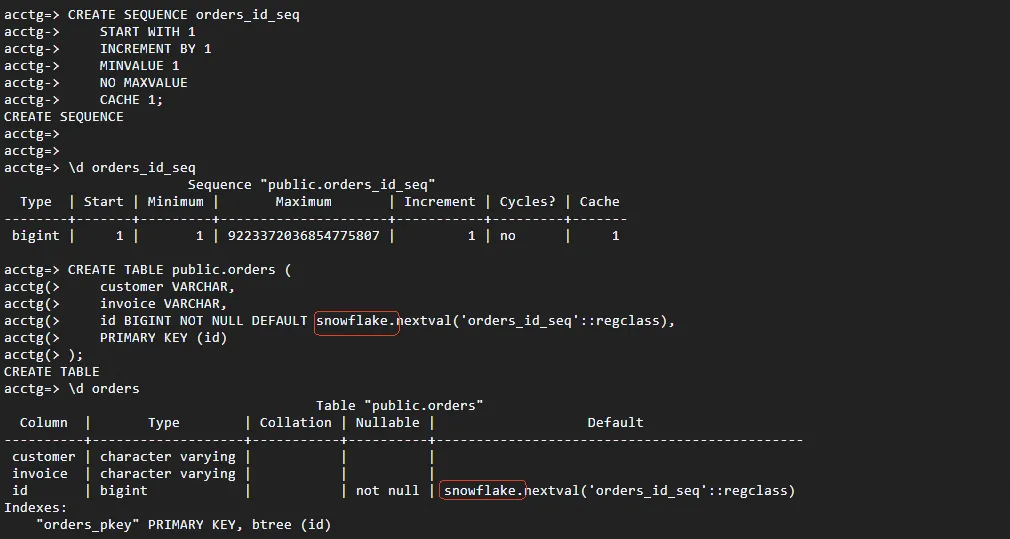
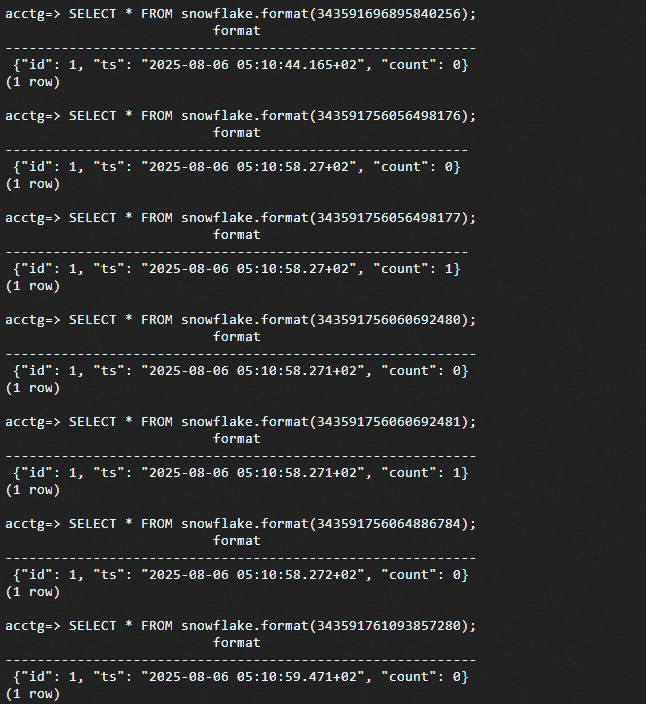
The Snowflake extension provides useful functions beyond basic ID generation:
-- Get details about a Snowflake ID
SELECT snowflake.format(id) FROM orders LIMIT 1;
-- Sample output:
-- {"node": 1, "ts": "2023-10-16 17:57:26.361+00", "count": 0}As shown above, the function snowflake.format(Snowflake ID) returns a JSONB object representing the given Snowflake ID in a human-readable format as below.
{"node": 1, "ts": "2023-10-16 17:57:26.361+00", "count": 0}
Consider Snowflake IDs for these scenarios:
● High-volume inserts: E-commerce order systems, IoT data collection
● Distributed architectures: Microservices, multi-region deployments
● Time-sensitive data: Event logging, financial transactions
● Future-proof systems: Where you might need to merge data from multiple sources
Alternatives to Consider
Before adopting Snowflake IDs, consider these alternatives:
● UUID: Random or version 1 time-ordered UUIDs.
● IDENTITY Columns: PostgreSQL's modern auto-increment.
● Serial/Bigserial Types: Traditional auto-incrementing sequences, simple but centralized.
Each alternative presents its own trade-offs concerning size, randomness, and generation characteristics.
Integrating Snowflake-style IDs within your ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL setup can enhance your application’s scalability and performance, particularly in distributed environments. By leveraging the snowflake extension, you enable easy generation of globally unique identifiers that can optimize your database operations.
Start implementing Snowflake IDs today and experience the benefits that come with distributed, time-ordered ID generation.
[Infographic] Highlights | Database New Features in June 2025
ApsaraDB - September 27, 2025
Alibaba Clouder - July 5, 2019
digoal - December 14, 2018
digoal - April 12, 2019
digoal - April 22, 2021
digoal - January 14, 2019
 ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL
ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL
An on-demand database hosting service for PostgreSQL with automated monitoring, backup and disaster recovery capabilities
Learn More PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn More ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL
ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL
An on-demand database hosting service for MySQL with automated monitoring, backup and disaster recovery capabilities
Learn More ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server
ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server
An on-demand database hosting service for SQL Server with automated monitoring, backup and disaster recovery capabilities
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB