KubeSkoop exporter is a network monitoring tool designed for Kubernetes cloud native environments, which can provide the following functions:
The main differences from common Kubernetes monitoring and observability tools are as follows:
| Functions | Prometheus Node exporter | cAdvisor/Metric API | KubeSkoop exporter |
| By Pod differentiation | No | Yes | Yes |
| Network status monitoring | Yes | No | Yes |
| On-site capture of abnormal events | No | No | Yes |
| Advanced kernel network information | No | Yes | Yes |
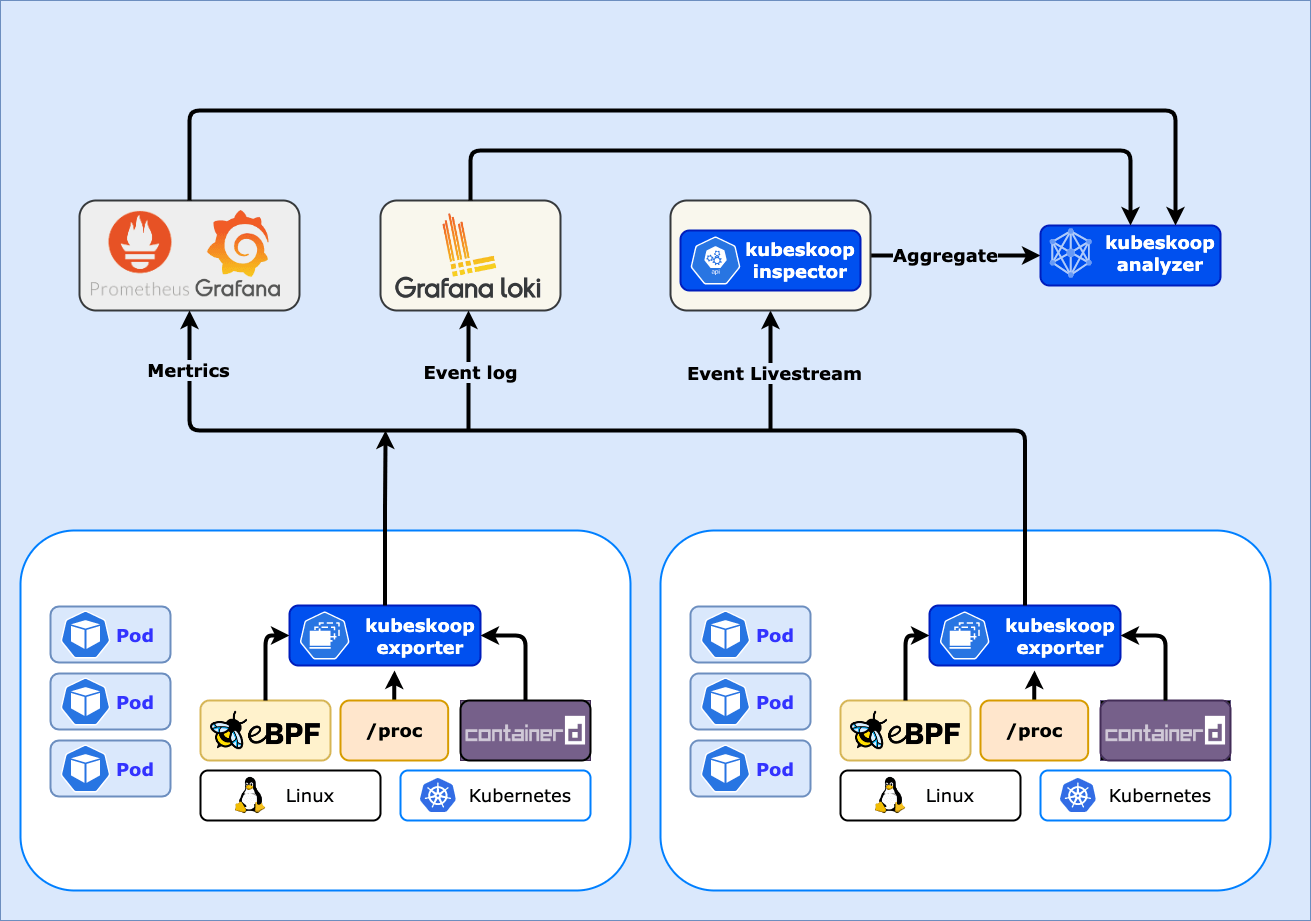
KubeSkoop exporter provides adaptation for Kubernetes network monitoring function. On the nodes, KubeSkoop exporter collects and categorizes a large amount of network-related data. The core principle behind these functions includes:
Regarding how to visualize monitoring data, please refer to KubeSkoop exporter visualization.
KubeSkoop exporter provides Pod-level metric information to reflect environmental changes during instance operation. Metrics are classified into different probes according to their source and user, and their related information is as follows:
| Name | Description | Granularity | Datasource |
| netdev | Exposes network interfaces statistics from /proc/net/snmp. |
pod | procfs |
| io | Exposes process io syscall statistics from /proc/io. |
pod | procfs |
| tcp | Expose tcp basic statistics from /proc/net/tcp
|
pod | procfs |
| softnet | Expose softnet statistics from /proc/net/softnet
|
pod | procfs |
| sock | Expose sock alloc/memory usage statistics | pod | procfs |
| tcpext | Expose tcp extended statistics from /proc/net/netstat
|
pod | procfs |
| udp | Expose udp basic statistics from /proc/net/snmp
|
pod | procfs |
| tcpsummary | Expose tcp diagnosis information | pod | netlink |
| ip | Expose layer3 ip basic statistics from /proc/net/snmp
|
pod | procfs |
| socketlatency | Latency statistics of processing syscall with socket | pod | eBPF |
| net_softirq | Network softirq schedule and processing latency statistic | node | eBPF |
| virtcmdlatency | Virtio-net command processing latency statistic | node | eBPF |
| kernellatency | Latency statistics of processing network packet in kernel stack | pod | eBPF |
| netiftxlat | Network interfaces tc qdisc processing latency statistic | pod | eBPF |
| packetloss | Statistics of packet dropping in kernel stack processing | pod | eBPF |
KubeSkoop exporter provides network-related abnormal events occurring on the nodes. Based on our experience in handling network issues in the long-term, we have summarized several common network troubleshooting problems. They often interfere with normal business operations in the cluster in an unpredictable and occasional manner, lacking effective localization methods. Some of them are as follows:
For network issues that are difficult to quickly reproduce and obtain on-site, KubeSkoop exporter provides eBPF-based operating system kernel context observation capabilities to capture the real-time state of the operating system at the scene of the problem and output it in the form of event logs.
The events supported by KubeSkoop exporter are as follows:
| Name | Description |
| netif_txlat | Expose slow processing events in tc egress qdisc |
| packetloss | Expose packet dropping events in kernel stack processing |
| net_softirq | Expose NET_RX/NET_TX softirq schedule/processing delay |
| socketlatency | Expose high latency of operating socket from user process |
| kernellatency | Expose netfilter/route delay in kernel |
| virtcmdlatency | Expose high latency virtio-net command processing |
| tcpreset | Expose receiving/sending tcp segments with RST flag |
In the information of the event log, relevant information of the event scene can be viewed. Taking the tcp_reset probe as an example, when a Pod receives a normal message on a certain port, KubeSkoop exporter will capture the following event information:
type=TCPRESET_NOSOCK pod=storage-monitor-5775dfdc77-fj767 namespace=kube-system protocol=TCP saddr=100.103.42.233 sport=443 daddr=10.1.17.188 dport=33488 The information in the event is as follows:
For events that require effective operating system kernel stack information, additional protocol stack information of the operating system kernel can be obtained by configuring the switch, which will increase certain costs and obtain more accurate phenomena, for example:
type=PACKETLOSS pod=hostNetwork namespace=hostNetwork protocol=TCP saddr=10.1.17.172 sport=6443 daddr=10.1.17.176 dport=43018 stacktrace:skb_release_data+0xA3 __kfree_skb+0xE tcp_recvmsg+0x61D inet_recvmsg+0x58 sock_read_iter+0x92 new_sync_read+0xE8 vfs_read+0x89 ksys_read+0x5A
668 posts | 55 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native Community - December 11, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - December 11, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - December 11, 2023
Alibaba Container Service - November 15, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - September 28, 2021
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - January 5, 2023

668 posts | 55 followers
Follow ACK One
ACK One
Provides a control plane to allow users to manage Kubernetes clusters that run based on different infrastructure resources
Learn More Container Service for Kubernetes
Container Service for Kubernetes
Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes is a fully managed cloud container management service that supports native Kubernetes and integrates with other Alibaba Cloud products.
Learn More Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Accelerate and secure the development, deployment, and management of containerized applications cost-effectively.
Learn More Managed Service for Prometheus
Managed Service for Prometheus
Multi-source metrics are aggregated to monitor the status of your business and services in real time.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Native Community