On behalf of Alibaba Cloud, I participated in the RedisConf 2018. While there, I had an interview with Rui Gu – the creator of the open source Redisson client. The influence Rui Gu has had on the international Redis community and his work on open source left a deep impression on me. The following is the detailed content of our interview.

The people in the picture shown above are Xiazhou from Alibaba Cloud, Rui Gu, Baichen from Alibaba Cloud, and Zexian from Alibaba Group.
As far back as 2004 when I was engaged in industrial automation and industrial IoT work, I have encountered many scenarios that required monitoring and signal processing of a series of pieces of equipment. Such scenarios have very high requirements for real-time processing capabilities, system stability, high availability, and disaster tolerance. Since 2012, when I decided to adopt Redis as a real-time database, I came up with a lot of ideas. Redis and common data structures in programming languages like Java seem similar but are actually quite different. I've always hoped to be able to link the two. Starting from 2013, when Redis was commercialized, this desire of mine became stronger. So I started some related exploration outside of work, and finally decided to adopt the dynamic class form to make Redis data structures operate more like their corresponding Java structures. Nikita, who is far away in Moscow, seemed to have a similar idea. He started practical application development on New Year's Day 2014 and soon made Redisson open source. At the same time, my practice had made some progress and some basic functions were initially realized. However, due to various work issues, coupled with a lack of confidence at that time, progress over the past six months had slowed down. After all, this was a job which no one had ever done before. Unexpectedly, Nikita was facing the same problem, but he had struggled to persist, and had no intention of giving up. Starting from the second half of 2014, I began to notice the Redisson project. After a thorough understanding, I suddenly had a strong resonance: it had the same idea as my practice but a different starting point. So after that, we began to communicate with each other. Finally, at the beginning of 2015, we decided to give up our practice projects and we both joined Redisson. At this point, we were no longer alone on this road.
In the IoT industry, various real-time state values of a set of devices are often used as a business-oriented object, managed by the JVM in memory. If this object is stored in the Redis database as a string, each time a state value is updated, both a serialization and a deserialization are required. At the same time, it is also possible to face the concurrency problem caused by operating different state values of the same object at the same time. The actual application uses the Hash data structure provided by Redis to store this object, in order to effectively avoid such problems. Although the Hash structure of Redis is very similar to the HashMap in Java, the application cannot operate Redis as easy as operating HashMap. And if you have not mastered Redis-related commands, or improperly handle the details, it will eventually cause various problems during operations. Redisson's Map was created to fill the gap between Redis's Hash and Java's HashMap.

Hash operation in Jedis

ConcurrentHashMap in Java
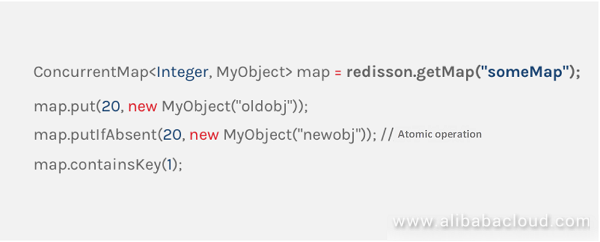
ConcurrentHashMap in Redisson
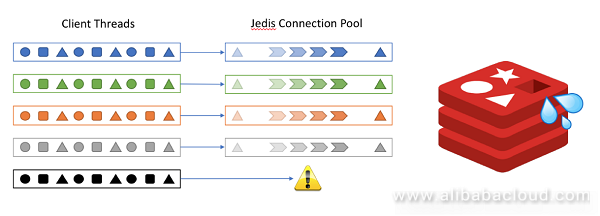
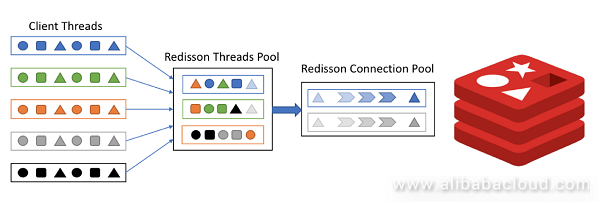
Industrial control and certain IoT scenarios require high real-time processing capabilities and millisecond-level response must be achieved for all signals. Such scenarios also have a feature of high concurrency. Different from scenarios like social networking or e-commerce, such application scenarios basically have no peak/valley traffic and are always operating at peak. Therefore, common peak compensation measures in other scenarios can only increase the burden here. In such a scenario, if you use a client like Jedis which uses a synchronous programming model, you need to ensure that the number of concurrent threads is consistent with the number of connections. Otherwise, an error will occur if available connections cannot be obtained. In contrast, Redisson leverages the Netty asynchronous programming framework, uses an EventLoop thread pool similar to the Redis server-side architecture, and elastically manages connections in a connection pool manner. In the end, the use of a small number of connections can meet the requirements of a large number of threads, and fundamentally ease the competition between threads. Also, the asynchronous operation mode can prevent the data request from blocking the business thread.
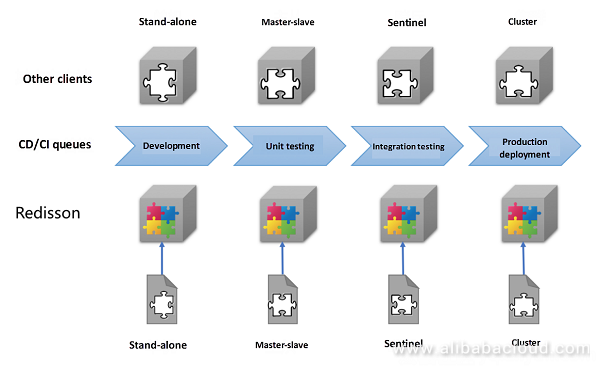
The development of Redis has experienced many technological changes. The official version not only added a lot of useful features during this iteration, but also developed several high availability solutions. At the same time, community and cloud computing vendors have developed a variety of proxy-based high availability solutions based on the official version. By comparison, these solutions have their own advantages and disadvantages, and are applicable for different scenarios. Diverse solutions bring about convenience as well as troubles. Scenarios include, for example, business resizing, switching from simple stand-alone or Master/slave mode to sentinel or cluster mode, migrating from a self-built Redis environment to the cloud, or using different Redis operating modes in different phases during the continuous delivery CD/CI process in the project's different phases. Developers are often required to develop a matching set of usage methods for different high availability scenarios. It makes a project highly coupled to Redis's operation mode and the business code must be modified when Redis's operation mode changes. Redisson provides a convenient file configuration method for this situation and, without modifying the code, supports different Redis operation modes and environments through different JSON, YAML or SpringXML files. This reduces the difficulty of both development and O&M.
For the implementation of Redis distributed locks, there are already a lot of related articles available online. However, almost all related introductions use a simple package based on the setnx command, and few articles analyze the defects of this design. In this era where blogs and codes are casually posted, this situation gives everyone the illusion that Redis distributed locks can only exist in such a simple form, and even if there are defects, they can only be avoided in the code. Think about it, in exchange for business flexibility, is it worth using a slightly more complicated design to make up for its shortcomings? Before talking about redesigning the Redis distributed locks, let's take a look at the shortcomings of the distributed locks which are simply packaged with the setnx command.
When executing the setnx command, the name specified on the business is usually used as the key name, with the time stamp or a random value as the value. Such implementations do not have the capability to track request threads, nor to count the number of reentry attempts, and some implementations even do not have the atomicity of operations. When it comes to business that requires the same lock in multiple places, it is clear that using a lock without reentrant can easily lead to deadlocks. Especially in scenarios with recursive logic, the chance of a deadlock is higher. The Lock object and the synchronized chunk in the Java concurrency tools are reentrant. For those who are familiar with these tools, it is easy to ignore the setnx defect.
In a distributed environment, in order to ensure the activity of the lock and avoid the deadlock caused by application downtime, distributed locks often introduce a expiration time, beyond which they are automatically unlocked. The premise of this design is that the developer has a good grasp of the granularity of this automatic unlock time. Too short may cause the lock to expire before the task completes and too long may cause other nodes to wait a long time before recovery when the application or the service node is down, making it difficult to guarantee the SLA of the service. The design of setnx lacks a renewal mechanism that extends the validity period. It cannot guarantee that the business can be completed before the unlocking, and it cannot ensure that other nodes can quickly restore the business processing when the application or the service node is down.
Everyone more or less knows locks, and each lock has different characteristics due to the difference in the locking strategy. But in general, these locks have two commonalities: one is mutual exclusion and the other is obstruction. Mutual exclusion means that only one thread can get access at any time. Obstruction means that in the case of competition, threads that have not acquired the resource will stop until the resource is successfully acquired or the operation is canceled. It is clear that the setnx command only provides mutual exclusion feature, but does not provide obstruction. Although the spin mechanism can be introduced in the business code for re-acquisition, it is only to transfer the functions that should be implemented in the lock to the business code. It is not a good choice to simplify the implementation of the lock by increasing the complexity of the business code.
Redisson's distributed locks have a feature of thread security while meeting these three basic requirements. Redis's Hash structure is used as the storage unit, the name specified by the service is used as the key, the random UUID and the thread ID are used as the field, and the number of locks is stored as the value. At the same time, the UUID is saved on the client as an instance variable of the lock. When running multiple threads while using the instance of the same lock, using UUID and thread ID as tags still ensure the independence of the operation, and meet the thread security requirements.
When locking, check whether or not the lock exists through a Lua script. If not, create a hash related field, set the expiration time, and return. This indicates that the lock has been successful. If the hash field already exists, check whether or not the random field and the thread ID are consistent. If consistent, the value is incremented and the expiration time is re-updated. This means that the same thread of the same node is successfully locked again, thus ensuring reentrant. If the hash exists and the field and the thread ID are inconsistent, another node or thread already has this lock. So the Lua script returns the current validity of the hash. When the result is returned to the client, if the lock is successful, the renewal is performed via the thread pool according to the set parameter timing, and, finally, the requesting thread is notified to continue the subsequent operation. If the lock is not successful, listen to a pubsub channel suffixed with this key until you receive the unlock message and try again.

When unlocking, check whether or not the lock exists through a Lua script. If not, issue the unlock message and return. If it still exists, check whether or not the tag exists. If not, it means that the lock is not owned by this thread. In this case, the requesting thread will receive an error. If the tag exists, it means that the lock is owned by this thread. In this case, determine after decrementing the tag field if the returned number of locks is greater than 0. If so, the current lock is still valid, and only the number of number of reentry attempts is reduced. On the contrary, this means that it has been completely unlocked, the lock is immediately deleted and the unlock message is issued.
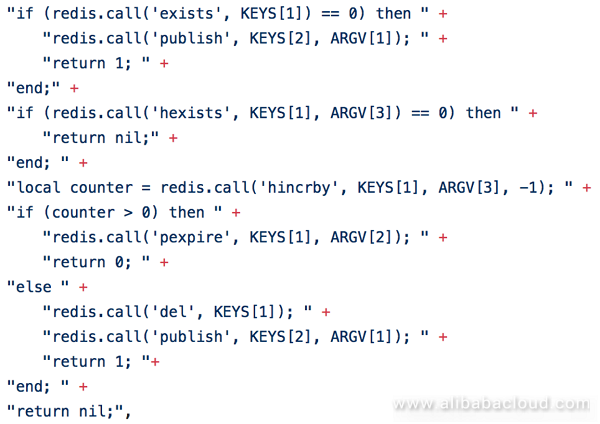
Redisson's reentrant lock solves many of the native shortcomings of setnx locks, but since it is still stored as a single key in a fixed Redis node, it has an automatic expiration time. Although such a design can significantly avoid the impact of client or business node downtime, the drawback is that when the server Redis process or the node is down, it may lead to missing lock information, and such a drawback obviously cannot meet certain scenarios' high availability requirements.
In this case, the Redis creator Salvatore proposed a high availability distributed lock algorithm based on multiple nodes, called RedLock. With this algorithm, the client needs to acquire an independent lock in each of multiple nodes at the same time. Only when most locks are successfully acquired at one time can it be regarded as achieving high availability distributed locks, otherwise it is necessary to release the partially acquired locks, and try again after a random period.
In algorithm design, Salvatore still uses setnx as an example to explain the mutual exclusion feature of distributed locks. In algorithm implementation, Redisson's RedissonRedLock uses the more flexible and convenient reentrant lock mentioned above. Redisson's extension algorithm is the only Java implementation approved on the Redis official website.
Although the Redlock algorithm provides high availability, it is still limited in its applicability under the principle of most visibility. Redisson provides a high availability distributed interlocking RedissonMultiLock based on an enhanced algorithm. This algorithm requires that the client must successfully acquire the locks of all nodes before it is regarded as locking success, which further improves the reliability of the algorithm.
Redisson's development direction determines that it has always been at the forefront of Redis's function expansion and application methods. The most representative one is the local cache function. In 2016, this feature was developed to address a specific enterprise user's pain point. The principle is to sacrifice the client's own memory in exchange for the time spent on the network for frequently obtaining some common data. This function immediately attracted the attention of users after its source was opened up in September of the same year. The emergence of this function accelerates the migration of traditional IT users from other similar platforms to Redis. Its popularity is far beyond Nikita's and my imagination. So every year, enterprise users go to the RedisConf and other similar international exchange conferences and share their use of Redisson and migration process from other platforms to Redis. This trend caught the attention of Redis creator Salvatore. After some face-to-face communication with other users, Salvatore decided to use the client cache function as an important direction for the future development of Redis, and proposed the RESP3 protocol for this purpose. The emergence of RESP3 will provide server-side coordination capabilities for the client cache function. Salvatore also invited the Redisson team as a member of the expert group to participate in the formulation of the Redis client cache standard.
In order to ensure the sustainable development of the Redisson project, and to avoid being unmaintained after a period like some other open source projects, in early 2017, Nikita and I decided to provide additional fee-based consulting services on the basis of the open source project so as to support the normal operation of the project. At the same time, we provide comprehensive enterprise solutions for the special scenarios encountered by large enterprise users. Finally, all these solutions and enterprise SLA support services were packaged as Redisson PRO for enterprise users.

Compared with other clients, although the Redisson project has a short history, it has already gained trust from enterprises in different industries, many of which are leaders in their industries. The most worthy of introduction is following world-class enterprise users:
IBM in the computer industry. I am sure everyone is familiar with IBM, the originator of the PC. It is one of the several companies in the industry that have both strong hardware and software development capabilities. Even so, IBM is willing to use Redisson, this trust is the greatest support to us.
Boeing in the aviation industry. Before they contacted us, it was hard to imagine that Boeing is interested in Redisson. In fact, in addition to aircraft, Boeing is also the world's largest provider of flight chart and mobile electronic flight bag. Almost every airline company is one of Boeing's users. Redisson provides a solid foundation for their online flight navigation service.
American International Group (AIG) in the insurance industry. Founded in 1919 in Shanghai, China, AIG is the first Western company to bring the concept of insurance to the Chinese. They now have operations in more than 130 countries and regions around the world. Although in the financial crisis of 2008, the sudden collapse of the stock price made AIG enter the public view, it is still an international large-scale enterprise with 99 years of history and total assets of more than USD $600 billion. After a long period of research by the AIG team, Redisson was used to support its numerous financial and insurance businesses.
S&P Global in the financial industry. When it comes to the financial crisis, I have to mention the world's leading financial analysis agency Standard & Poor's. It is one of the three major credit rating organizations recognized by the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and provides investors with credit ratings, investment research and consulting services. It is well known in the industry, and the famous S&P 500 index is created and maintained by it. Standard & Poor's not only provides external ratings for listed companies, but also provides ratings for national governments. It flatly lowered the US government's rating in 2011 and adjusted its outlook to negative, which immediately triggered violent fluctuations in the financial industry. But even such a powerful organization has become a user of Redisson, and uses it for analysis and processing of complex financial data.
Interactive Viewing Experience for the World Cup Using Redis
Alibaba Cloud Community - January 30, 2024
Alibaba Clouder - December 19, 2018
ApsaraDB - June 22, 2021
Alex - January 22, 2020
ApsaraDB - June 13, 2022
Alibaba Clouder - April 18, 2018
 IoT Platform
IoT Platform
Provides secure and reliable communication between devices and the IoT Platform which allows you to manage a large number of devices on a single IoT Platform.
Learn More IoT Solution
IoT Solution
A cloud solution for smart technology providers to quickly build stable, cost-efficient, and reliable ubiquitous platforms
Learn More ApsaraDB for Redis
ApsaraDB for Redis
A key value database service that offers in-memory caching and high-speed access to applications hosted on the cloud
Learn More LedgerDB
LedgerDB
A ledger database that provides powerful data audit capabilities.
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB