This topic describes how to configure BGP dynamic routing, virtual border routes (VBRs), and IPsec-VPN connections to encrypt and transmit private traffic over Express Connect circuits.
Background information
Before you start, we recommend that you learn about how private traffic is encrypted and transmitted over Express Connect circuits. For more information, see Encrypt Express Connect traffic.
Use scenarios
The following figure shows a use scenario. An enterprise owns a data center in Hangzhou and has a VPC deployed in the China (Hangzhou) region. Applications are deployed on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances in the VPC. To expand businesses, the enterprise wants to connect the data center to the cloud. To meet security compliance requirements, the enterprise needs to use Express Connect circuits and transit routers to exchange data between the data center and VPC through private connections. In addition, to prevent data breaches and data tampering, the enterprise wants to encrypt data before transmitting the data to Alibaba Cloud over the Express Connect circuit.
The data center is connected to the VPC by using an Express Connect circuit. In this scenario, the enterprise can create a private IPsec-VPN connection between the customer gateway device and transit router and then encrypt the traffic that traverses the IPsec-VPN connection to ensure data security.

Network design
If you want to design the networks of your data center and network instances, make sure that their networks do not overlap.
Routing mechanism
To encrypt and transmit private traffic over Express Connect circuits, make sure that the data center and VPC preferably exchange data through the private IPsec-VPN connection instead of the Express Connect circuit. To meet this goal, the following routes are added in this example:
For traffic from the VPC to the data center:
The transit router can learn routes pointing to the data center from the VBR and private IPsec-VPN connection. By default, the routes learned from the VBR have higher priorities. Consequently, traffic from the VPC to the data center is preferably forwarded over the Express Connect circuit and therefore cannot be encrypted.
To avoid this issue, different subnet masks are used when the data center CIDR block is advertised in this example. When the customer gateway device advertises the data center CIDR block to the VBR, make sure that its mask length is short. When the customer gateway device advertises the data center CIDR block to the private IPsec-VPN connection, make sure that its mask length is long.
For example, the CIDR block of the data center is 192.168.0.0/16. The client CIDR block connected to the VPC is 192.168.20.0/24. In this case, advertise the data center CIDR block 192.168.0.0/16 to the VBR and advertise the client CIDR block 192.168.20.0/24 to the private IPsec-VPN connection. This way, the routes that the transit router learns from the private IPsec-VPN connection have higher priorities. Traffic from the VPC to the client in the data center is preferably encrypted and transmitted over the private IPsec-VPN connection.
For traffic from the data center to the VPC:
The data center can learn routes pointing to the VPC from the VBR and private IPsec-VPN connection. In this example, routing policies are configured on the transit router side to adjust the route priorities in order to ensure that traffic from the data center to the VPC is preferably transmitted over the private IPsec-VPN connection.
This ensures that the data center and VPC can still exchange data through the Express Connect circuit and transit router when the private IPsec-VPN connection is closed. However, the data is not encrypted in this case.
Basic subnetting
Network item | Subnetting | IP address |
VPC |
|
|
VBR | 10.0.0.0/30 |
|
Data center | Client CIDR block: 192.168.20.0/24 | Client IP address: 192.168.20.6 |
CIDR block of the customer gateway device:
|
|
Subnetting for BGP dynamic routing
The CIDR block of the BGP tunnel must fall within 169.254.0.0/16. The mask of the CIDR block must be 30 bits in length. The CIDR block cannot be 169.254.0.0/30, 169.254.1.0/30, 169.254.2.0/30, 169.254.3.0/30, 169.254.4.0/30, 169.254.5.0/30, 169.254.6.0/30, or 169.254.169.252/30. The two tunnels of an IPsec-VPN connection must use different CIDR blocks.
Resource | Tunnel | BGP tunnel CIDR block | BGP IP address | BGP local ASN |
IPsec-VPN connection | Tunnel 1 | 169.254.10.0/30 | 169.254.10.1 | 65534 |
Tunnel 2 | 169.254.20.0/30 | 169.254.20.1 | ||
Customer gateway device | Tunnel 1 | 169.254.10.0/30 | 169.254.10.2 | 65530 |
Tunnel 2 | 169.254.20.0/30 | 169.254.20.2 |
Prerequisites
A VPC is created in the China (Hangzhou) region and applications are deployed on the ECS instances in the VPC. For more information, see Create a VPC with an IPv4 CIDR block.
The customer gateway device supports the IKEv1 and IKEv2 protocols for establishing private IPsec-VPN connections. To check whether the gateway device supports the IKEv1 and IKEv2 protocols, contact the gateway vendor.
Procedure
Step 1: Connect the data center to the VPC by using an Express Connect circuit and transit router
Step a: Deploy an Express Connect circuit
Deploy an Express Connect circuit to connect the data center to Alibaba Cloud.
Apply for an Express Connect circuit.
Apply for an Express Connect circuit in the China (Hangzhou) region. For more information, see Requesting Classic Mode or Overview of hosted connections. In this example, a dedicated connection over an Express Connect circuit is created.
Create a VBR.
Log on to the Express Connect console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Virtual Border Routers (VBRs).
In the top navigation bar, select the China (Hangzhou) region.
Make sure that the VBR and Express Connect circuit are deployed in the same region.
On the Virtual Border Routers (VBRs) page, click Create VBR.
In the Create VBR panel, set the following parameters and click OK.
The following table describes only some of the parameters. Other parameters use the default values. For more information, see Create and manage VBRs.
Parameter
Description
Name
In this example, VBR is used.
Physical Connection Information
In this example, Dedicated Physical Connection is selected, and the Express Connect circuit that you deployed is selected.
VLAN ID
0 is used in this example.
Alibaba Cloud Side IPv4 Address
In this example, 10.0.0.1 is entered.
Data Center Side IPv4 Address
In this example, 10.0.0.2 is entered.
IPv4 Subnet Mask
In this example, 255.255.255.252 is used.
Configure a BGP group for the VBR.
On the Virtual Border Routers (VBRs) page, click the ID of the VBR.
On the details page, click the BGP Groups tab.
On the BGP Groups tab, click Create BGP Group, set the following parameters, and click OK.
The following table describes only the relevant parameters. For more information, see Configure BGP.
Name: Enter VBR-BGP.
Peer ASN: Enter the ASN of the customer gateway device, which is 65530.
Local ASN: Enter the BGP ASN of the VBR, which is 65534.
Configure a BGP peer for the VBR.
On the VBR details page, click the BGP Peers tab.
On the BGP Peers tab, click Create BGP Peer.
In the Create BGP Peer panel, set the following parameters and click OK:
BGP Group: Select VBR-BGP.
BGP Peer IP Address: Enter the IP address of the BGP peer. In this example, the IP address 10.0.0.1 is entered. This is the IP address of the interface that the customer gateway device uses to connect to the Express Connect circuit.
Configure BGP routing on the customer gateway device.
NoteIn this example, the software Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) 9.19.1 is used to describe how to configure a Cisco firewall. The commands may vary with software versions. Consult the documentation or your vendor based on your actual environment during operations. For more information, see Configure local gateways.
The following content contains third-party product information, which is only for reference. Alibaba Cloud does not make guarantees or other forms of commitments for the performance and reliability of third-party products, or the potential impacts of operations performed by using these products.
ciscoasa> enable Password: ******** # Enter the password for entering the enable mode. ciscoasa# configure terminal # Enter the configuration mode. ciscoasa(config)# Verify that the interfaces are configured and enabled on the Cisco firewall. In this example, the following interface configurations are used: ciscoasa(config)# show running-config interface ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 # The interface that connects to the VBR. nameif VBR # The name of the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface. security-level 0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252 # The IP address of the GigabitEthernet0/0 interface. ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 #The interface that connects to the data center. nameif private # The name of the GigabitEthernet 0/2 interface. security-level 100 #Make sure that the security level of the interface connecting to the data center is lower than that of the interface connecting to Alibaba Cloud. ip address 192.168.50.215 255.255.255.0 #The IP address of the GigabitEthernet0/2 interface. ! interface GigabitEthernet0/3 #The interface that connects to the private IPsec-VPN tunnel 1. nameif VPN-IP1 #The name of the GigabitEthernet0/3 interface. security-level 0 ip address 192.168.10.136 255.255.255.0 #The private IP address of the GigabitEthernet0/3 interface. ! interface GigabitEthernet0/4 #The interface that connects to the private IPsec-VPN tunnel 2. nameif VPN-IP2 #The name of the GigabitEthernet0/4 interface. security-level 0 ip address 192.168.40.159 255.255.255.0 #The private IP address of the GigabitEthernet0/4 interface. ! #Configure prefix-list and route-map. prefix-list VBR permit 192.168.0.0/16 route-map VBR permit 10 match ip address prefix-list VBR #Configure BGP routing. router bgp 65530 # Enable BGP and configure the ASN of the data center. 65530 is used in this example. bgp router-id 10.0.0.1 # Enter the ID of the BGP router. In this example, 10.0.0.1 is used. address-family ipv4 unicast neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 65534 #Establish a peering connection to the VBR. neighbor 10.0.0.2 activate # Activate the BGP peer. neighbor 10.0.0.2 route-map VBR out #Advertise only routes pointing to large CIDR blocks to the VBR. network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 #Advertise the CIDR block of the data center. We recommend that you use a short subnet mask. exit-address-family ! #Add a route that points to the client in the data center. route private 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 192.168.50.216ImportantTo advertise the data center CIDR block to the VBR, we recommend that you use a short subnet mask. This way, the data center CIDR block that the transit router learns from the private IPsec-VPN connection is more specific than the advertised one and the route has a higher priority.
Step b: Configure a transit router
After the data center connects to Alibaba Cloud through the Express Connect circuit, you need to configure a transit router to exchange data between the data center and VPC.
In the Create CEN Instance dialog box, click Create CEN Only, enter a name, and use the default settings for other parameters.
Create an Enterprise Edition transit router.
Create a transit router in the China (Hangzhou) region to connect the VBR and VPC. Use the default settings for other parameters.
Create a VPC connection.
On the CEN details page, click the tab. Find the transit router in the China (Hangzhou) region and click Create Connection in the Actions column.
On the Connection with Peer Network Instance page, configure the following parameters and click OK to connect the VPC to the transit router.
The following table describes only some of the parameters. Other parameters use the default values. For more information, see Use an Enterprise Edition transit router to create a VPC connection.
Parameter
Description
Instance Type
Select Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Region
Select China (Hangzhou).
Attachment Name
Enter VPC-Attachment.
Network Instance
Select your VPC.
VSwitch
Select the vSwitches that are deployed in the zones of the transit router.
In this example, vSwitch 2 and vSwitch 3 are selected. If the region has multiple zones, choose at least two zones and select one vSwitch in each zone. We recommend that you select idle vSwitches.
Advanced Settings
In this example, the default settings are used. All advanced features are enabled.
Click Create More Connections to return to the Connection with Peer Network Instance page.
Create a VBR connection.
On the Connection with Peer Network Instance page, configure the following parameters and click OK to connect the VBR to the transit router. The following table describes only some of the parameters. Other parameters use the default values. For more information, see Connect a VBR to a transit router.
Parameter
Description
Instance Type
Select Virtual Border Router (VBR).
Region
Select China (Hangzhou).
Attachment Name
VBR-Attachment is entered in this example.
Network Instance
VBR is selected in this example.
Advanced Settings
In this example, the default settings are used. All advanced features are enabled.
Step c: Test the connectivity
After you complete the preceding configuration, the data center is connected to the VPC. You can perform the following steps to test the connectivity.
Make sure that you are familiar with the security group rules for the ECS instances in the VPC and the access control rules for the client in the data center. Make sure that the rules allow the ECS instances in the VPC to communicate with the client in the data center. For more information, see View security group rules and Add a security group rule.
The access control rules for the data center must allow ICMP messages and access from the VPC. The security group rules for the ECS instances must allow ICMP messages and access from the CIDR block of the data center.
Connect to ECS 1 in the VPC. For more information, see Connection method overview.
Run the ping command to ping a client in the data center.
ping <the IP address of a client in the data center>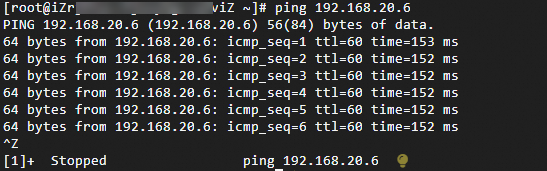
As displayed in the preceding figure, if ECS 1 can receive the response, the data center and VPC are connected.
Step 2: Encrypt the dedicated connection over the Express Connect circuit
After the data center is connected to the VPC, you can create a private IPsec-VPN connection between the customer gateway device and transit router, and configure routes to encrypt and transmit traffic over the private IPsec-VPN connection between the data center and VPC.
Step a: Create a private IPsec-VPN connection
Add the CIDR block 10.10.10.0/24 for the transit router. For more information, see Transit router CIDR blocks.
A gateway IP address will be allocated from the transit router CIDR block to create a private IPsec-VPN connection. The transit router CIDR block must not overlap with the CIDR blocks of the data center and VPC used for communication.
Create two customer gateways to register the two VPN IP addresses and BGP ASN of the customer gateway device with Alibaba Cloud.
- Log on to the VPN gateway console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Customer Gateway page, click Create Customer Gateway.
In the Create Customer Gateway panel, set the following parameters and click OK.
The following table describes only some of the parameters. Other parameters use the default values. For more information, see Customer gateway.
Customer Gateway 1
Name: Enter Customer-Gateway1.
IP Address: Enter one of the VPN IP addresses of the customer gateway device, which is 192.168.10.136.
ASN: Enter the BGP ASN of the customer gateway device, which is 65530.
Customer Gateway 2
Name: Enter Customer-Gateway2.
IP Address: Enter the other VPN IP address of the customer gateway device, which is 192.168.40.159.
ASN: Enter the BGP ASN of the customer gateway device, which is 65530.
Create an IPsec-VPN connection.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the IPsec Connections page, click Bind CEN.
Configure parameters and click OK. The following table describes the parameters.
The following table describes only the key parameters. The default values are used for the other parameters. For more information, see Create and manage dual-tunnel connections.
Parameter
IPsec-VPN connection
Name
Enter IPsecConnection.
Region
Select the region of the transit router to attach.
The IPsec-VPN connection is created in the same region as the transit router.
Gateway Type
Select Private.
Bind CEN
Select Same Account.
CEN Instance ID
In this example, the CEN instance that connects the data center and VPC is selected.
The system displays the instance ID and CIDR block of the transit router that is created by the CEN instance in the current region. The IPsec-VPN connection will be attached to the transit router.
Transit Router
The system automatically displays the transit router of the CEN instance in the current region.
Routing Mode
Destination Routing Mode is selected in this example to control traffic routing.
Enable BGP
Enable BGP.
Local ASN
Enter the BGP ASN of the IPsec-VPN connection, which is 65534.
Tunnel 1
Customer Gateway
Select Customer-Gateway1.
Pre-Shared Key
fddsFF111**** is used in this example.
ImportantThe pre-shared key of the IPsec-VPN connection must be the same as the pre-shared key of the peer gateway device. Otherwise, the IPsec-VPN connection cannot be established.
Encryption Configuration
Use the default values of parameters except for the following parameters.
Set the DH Group parameter in the IKE Configurations section to group14.
Set the DH Group parameter in the IPsec Configurations section to group14.
NoteYou need to select encryption parameters based on the on-premises gateway device to ensure that the encryption configurations for the IPsec connection are the same as those for the on-premises gateway device.
BGP Configuration
Tunnel CIDR Block: Enter 169.254.10.0/30.
Local BGP IP address: Enter 169.254.10.1.
Tunnel 2
Customer Gateway
Select Customer-Gateway2.
Pre-Shared Key
fddsFF222**** is used in this example.
Encryption Configuration
Use the default values of parameters except for the following parameters.
Set the DH Group parameter in the IKE Configurations section to group14.
Set the DH Group parameter in the IPsec Configurations section to group14.
NoteYou need to select encryption parameters based on the on-premises gateway device to ensure that the encryption configurations for the IPsec connection are the same as those for the on-premises gateway device.
BGP Configuration
Tunnel CIDR Block: Enter 169.254.20.0/30.
Local BGP IP address: Enter 169.254.20.1.
Advanced Configuration
In this example, the default settings are used. All advanced features are enabled.
On the details page of the IPsec-VPN connection, you can find that the gateway IP addresses are used to create private IPsec-VPN connections to the customer gateway device.
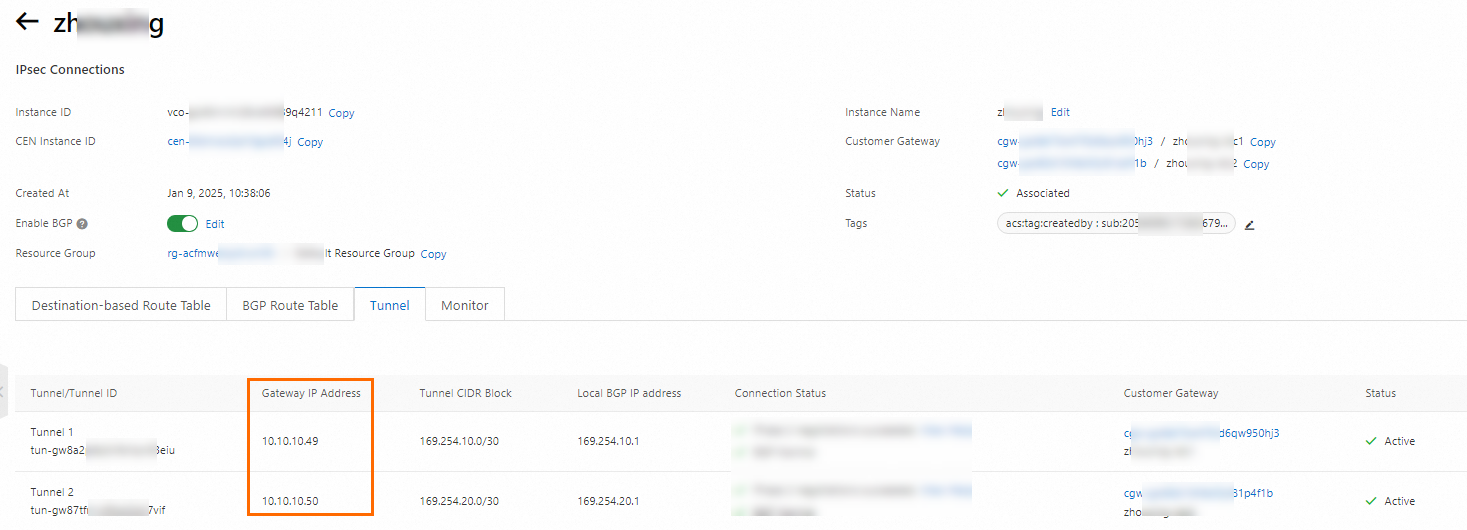
On the IPsec Connections page, find the IPsec-VPN connection that you create and click Generate Peer Configuration in the Actions column.
The configurations of the IPsec peer refer to the VPN configurations that you need to add when you create the IPsec-VPN connection. In this example, you need to add the VPN configurations to the gateway device of the data center.
In the IPsec Connection Configuration dialog box, copy and save the configurations to an on-premises machine. The configurations are required when you configure the gateway device of the data center.
Configure the customer gateway device.
After you create an IPsec-VPN connection, you need to add VPN configurations on the customer gateway device so that private IPsec-VPN connections can be established between Alibaba Cloud and the customer gateway device.
After you complete the configuration, the customer gateway device can establish private IPsec-VPN connections to Alibaba Cloud. However, BGP peers are not created. You can check the connection status on the details page of the IPsec-VPN connection. If private IPsec-VPN connections are not created, troubleshoot accordingly. For more information, see Self-service diagnostics.
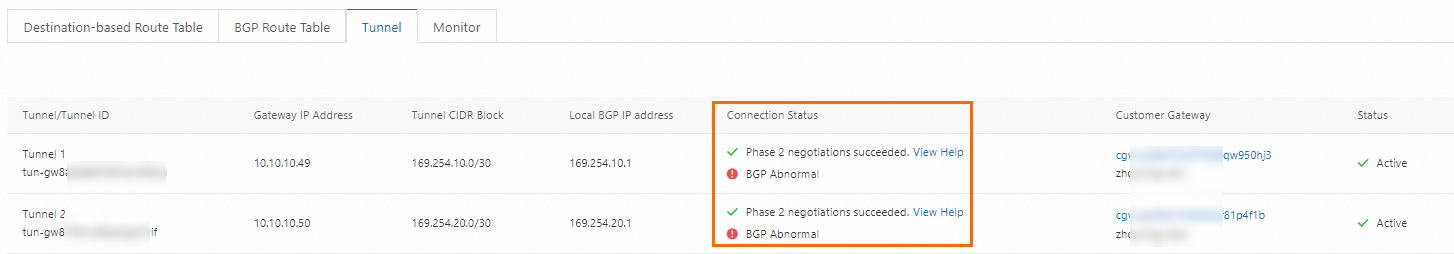
Step b: Configure routes
After private IPsec-VPN connections are created, data is still transmitted over the Express Connect circuit between the data center and VPC. In addition, the data is not encrypted. You need to add routes to encrypt and transmit the data over the private IPsec-VPN connections.
Add BGP routing configurations on the customer gateway device.
#Configure prefix-list and route-map. prefix-list VPN permit 192.168.10.0/16 prefix-list VPN permit 192.168.20.0/16 prefix-list VPN permit 192.168.40.0/16 route-map VPN permit 10 match ip address prefix-list VPN #Configure BGP to create a BGP peer between the customer gateway device and the IPsec-VPN connection. router bgp 65530 address-family ipv4 unicast neighbor 169.254.10.1 remote-as 65534 #Specify the BGP peer, which is the IP address of Tunnel 1 on the Alibaba Cloud side. neighbor 169.254.10.1 activate # Activate the BGP peer. neighbor 169.254.10.1 route-map VPN out #Advertise only specific routes to Tunnel 1. neighbor 169.254.20.1 remote-as 65534 #Specify the BGP peer, which is the IP address of Tunnel 2 on the Alibaba Cloud side. neighbor 169.254.20.1 activate # Activate the BGP peer. neighbor 169.254.20.1 route-map VPN out #Advertise only specific routes to Tunnel 2. maximum-paths 5 # Increase the number of ECMP route entries. network 192.168.10.0 mask 255.255.255.0 #Advertise the data center CIDR block, which must be more specific than the data center CIDR block advertised to the VBR. network 192.168.20.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 192.168.40.0 mask 255.255.255.0 exit-address-familyImportantTo advertise the data center CIDR block to the private IPsec-VPN connections, make sure that the CIDR block is more specific than the one advertised to the VBR. This way, routes that the transit router learns from the private IPsec-VPN connections to transmit traffic to the data center have higher priorities.
Add custom routes for the transit router.
After you add the preceding routes, the private IPsec-VPN connections will be interrupted. In this case, you need to add specific routes pointing to the VPN IP addresses of the customer gateway device to the route table of the transit route, and set the next hops to the VBR to recreate the private IPsec-VPN connections.
On the Route Table tab of the CEN console, click the Route Entry tab and click Add Route Entry.
In the Add Route Entry dialog box, configure the parameters and click OK. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
CIDR block 1
CIDR block 2
Destination CIDR
Enter one of the VPN IP addresses of the customer gateway device, which is 192.168.10.136/32.
Enter the other VPN IP address of the customer gateway device, which is 192.168.40.159/32.
Whether it is a black hole route
Select No.
Next Hop Connection
Select VBR-Attachment.
Create a routing policy for the route table of the transit router.
The data center learns CIDR blocks pointing to the VPC from the VBRs and the private IPsec-VPN connections. To ensure that traffic destined for the VPC is routed to the private IPsec-VPN connections, you must create a routing policy for the transit router. This way, the priority of the CIDR blocks advertised by the VBRs is lower than the priority of the CIDR blocks advertised by the private IPsec-VPN connections.
Log on to the CEN console.
On the Instances page, find the CEN instance and click its ID.
On the details page, find the transit router in the China (Hangzhou) region and click its ID.
On the details page of the transit router, click the Route Table tab and click Route Maps.
On the Route Maps tab, click Add Route Map. Set the following parameters and click OK:
The following table describes only the key parameters. The default values are used for the other parameters. For more information, see Route map overview.
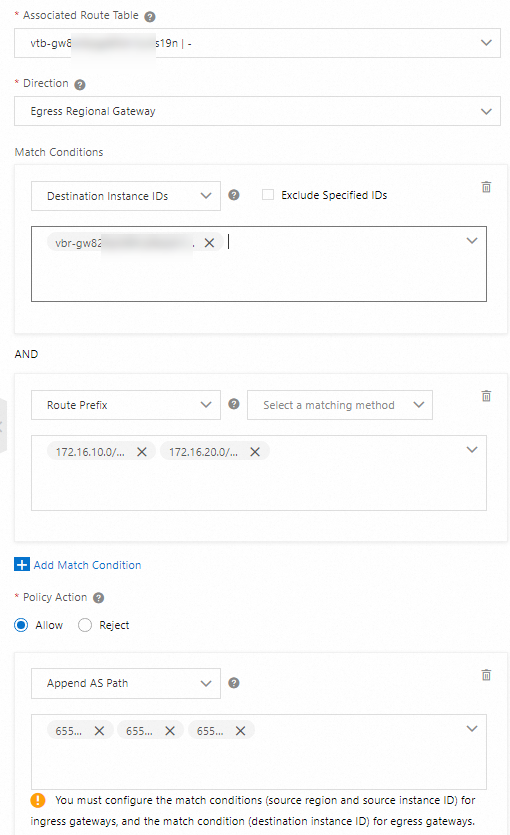
Parameter
Routing policy
Policy Priority
Enter 30.
Associated Route Table
Use the default value.
Direction
Select Egress Regional Gateway.
Match Conditions
Destination Instance IDs: The ID of the VBR is selected.
Route Prefix: Enter 172.16.10.0/24 and 172.16.20.0/24, and select Exact Match.
Policy Action
Select Allow.
Add Action Object
In this example, Prepend AS Path is selected and 65525, 65526, and 65527 are specified. This reduces the priority of the VPC CIDR block that the VBR advertises to the data center.
Create another routing policy for the route table of the transit router to forbid the private IPsec-VPN connections to propagate routes pointing to the VPN IP addresses of the customer gateway device to the data center. This prevents routing loops.
Policy Priority: Enter 40.
Associated Route Table: Use the default value.
Direction: Select Egress Regional Gateway.
Match Conditions:
Destination Instance IDs: The ID of the VBR is selected.
Route Prefix: Enter the VPN IP addresses 192.168.10.136/32 and 192.168.40.159/32, and select Exact Match.
Policy Action: Select Reject.
Step c: Verify the encryption setting
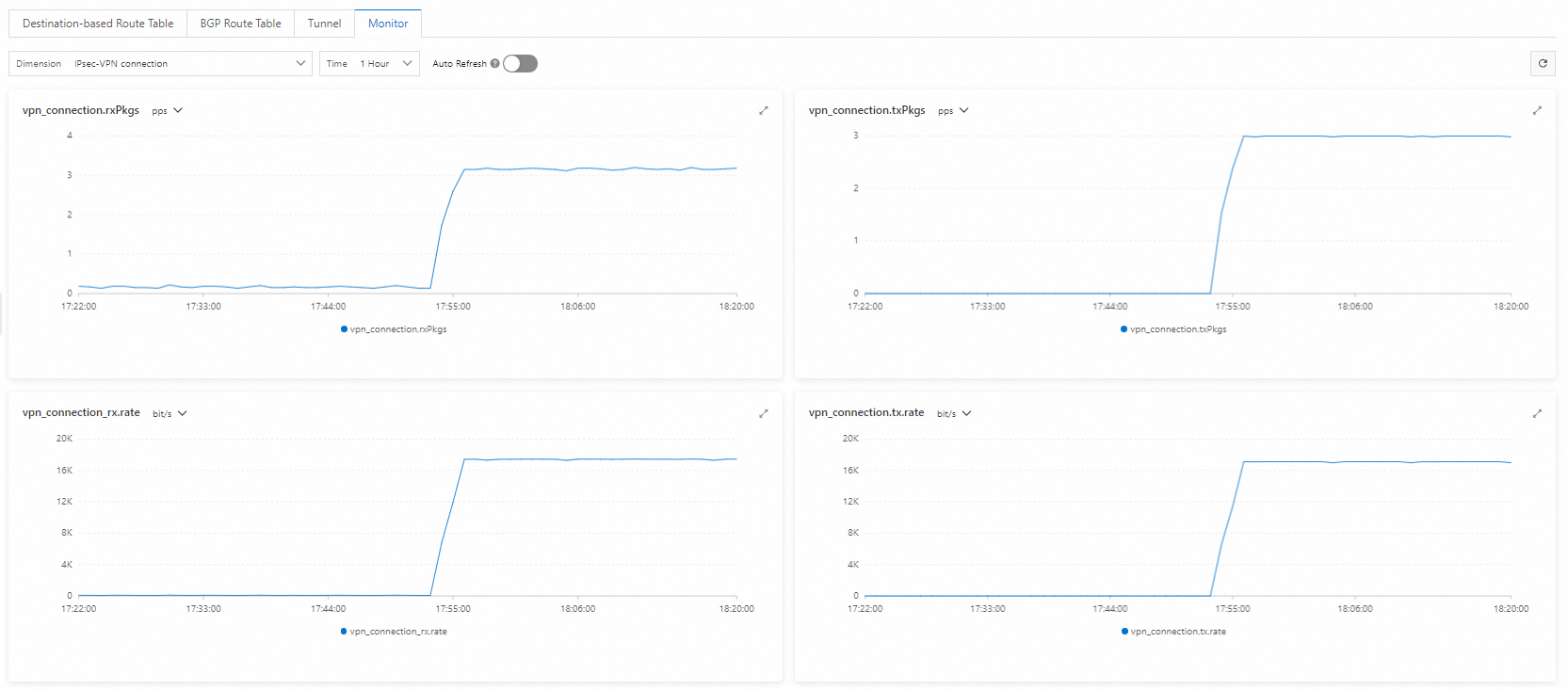
After you complete the configuration, if you can view the data transfer details on the details page of the IPsec-VPN connection, traffic is encrypted.
Connect to ECS 1 in the VPC. Run the ping command to ping a client in the CIDR block of the data center.
ping <IP address of a client in the data center> -s 1000 -c 10000-s 1000: Send 1,000 bytes.-c 10000: Continuously send 10,000 requests.
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the top navigation bar, select the China (Hangzhou) region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the IPsec Connections page, find the IPsec-VPN connection that you created and click its ID.
Go to the details page of the IPsec-VPN connection to view the details of data transfer.