Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) discovers and manages security risks in your cloud assets through automated risk checks, baseline scans, and attack path analysis. This feature identifies security vulnerabilities, such as cloud product configuration errors and server configuration defects, and provides remediation suggestions to address them.
Select an onboarding method
Select an onboarding method based on your security requirements, supported features, and environment type. You can choose between a quick configuration plan and a manual configuration plan.
Comparison item | Quick configuration plan | Manual configuration plan |
Authorization account type | The AccessKey pair of the root user is used only for the initial authorization. | Create an IAM user with least privilege access. |
Supported features | Supports only Host. |
|
Configuration complexity | Simple | Medium |
Plan 1: Quick configuration (Host Assets only)
Step 1: Create authorization credentials for the root user in AWS
The root user's AccessKey pair is used only for the initial authorization. This allows Security Center to automatically create a dedicated IAM user with limited permissions in your AWS account. The username of the IAM user is prefixed with AlibabaSasSubAccount_. After the authorization is successful, you must immediately delete this root user AccessKey pair.
Log on to the AWS console
Log on to the AWS IAM console. On the dashboard, click My Security Credentials.
ImportantOnly the root user can configure Security Credentials.
Create an AccessKey pair
On the My Security Credentials page, configure the settings as instructed, and then click Create access key.
Use case: Select a use case based on your business scenario. If none of the options apply, select Other.
Set description tag (optional): The tag can be up to 256 characters long and can contain letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters: _ . : / = + - @.
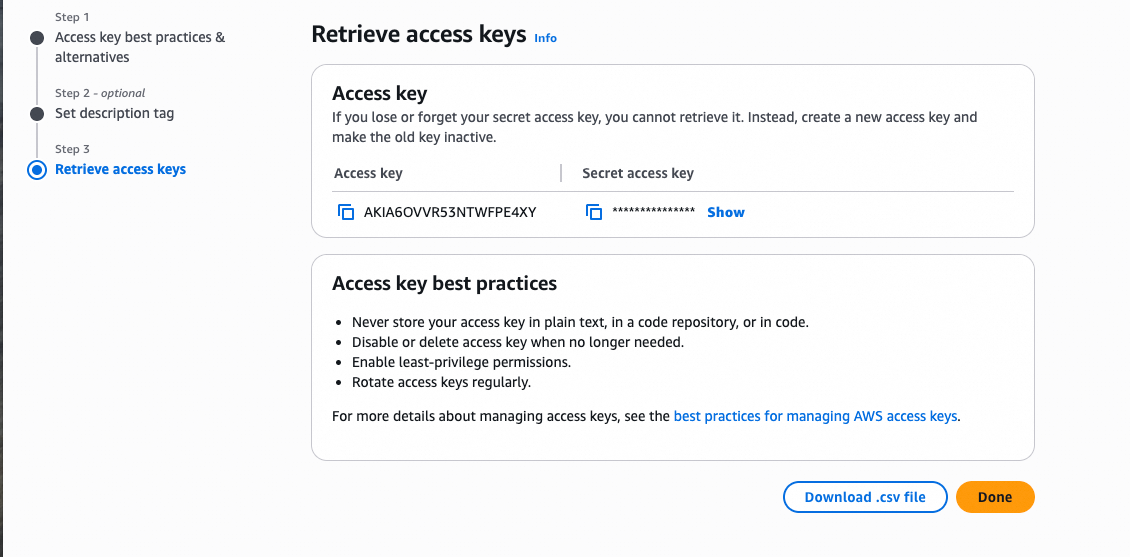
Save the AccessKey pair
After the AccessKey pair is created, go to the Retrieve access key page to view and save the Access key (Access Key ID) and Secret access key.
NoteYou can click Download .csv file to save the AccessKey pair to your computer.
Step 2: Complete the onboarding in Security Center
Go to the authorization page:
You can go to the AWS asset provisioning page in one of the following ways:
Recommended path:
Log on to the Security Center console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . In the upper-left corner of the console, select the region where your assets are located: Chinese Mainland or Outside Chinese Mainland.
On the tab, click Grant Permission, and then select AWS.
Other paths:
On the following pages, find the
 icon in the Multi-cloud Service Access section or a region, and click Provision or Grant.
icon in the Multi-cloud Service Access section or a region, and click Provision or Grant.. You must first switch the region to Outside Chinese Mainland.
Configure provisioning credentials:
In the Add Assets Outside Cloud panel, select Quick Configuration, select the features to provision, and click Next.
On the Submit AccessKey Pair page, enter the credentials that you created in AWS.
Access Key ID and Secret Access Key: Enter the credentials that you created in Step 1: Create authorization credentials for the root user in AWS.
Provisioning Region: Select an available AWS region. The system uses this region to verify asset accessibility.
Domain: Configure this parameter based on the provisioning region. If you use an AWS China proxy, select China. Otherwise, select International.
After you enter the information, click Next. The system automatically verifies the credentials and permissions.
NoteIf the verification fails, see What do I do if the automatic credential and permission verification fails after I enter the AccessKey pair?
Configure the synchronization policy:
Select region: Select the regions of the AWS assets that you want to onboard.
NoteThe synchronized asset data is stored in the data center that corresponds to the region selected in the upper-left corner of the Security Center console.
Chinese Mainland: Data centers are located in the Chinese mainland.
Outside Chinese Mainland: The data center is in Singapore.
Region Management: This option is selected by default. If you select this option, assets in new regions that are added to this AWS account are automatically synchronized. You do not need to add them manually.
Host Asset Synchronization Frequency: Set the interval for automatically synchronizing AWS host (EC2) assets. To disable synchronization, set this parameter to Off.
AK Service Status Check: Set the interval at which Security Center automatically checks the validity of the AccessKey pair for the AWS account. You can set this to Off to disable the check.
After you complete the configuration, click Synchronize Assets. The system automatically synchronizes the host assets from your AWS account to Security Center.
ImportantAfter you complete these operations, Security Center automatically creates an IAM user in AWS for authorization. The username of the IAM user is prefixed with
AlibabaSasSubAccount_. Do not delete or disable the automatically created IAM user or its AccessKey pair. Otherwise, asset provisioning and security monitoring are interrupted.
Step 3: Delete the AWS root user key
After the assets are successfully provisioned, immediately delete the root user's AccessKey pair that was used for the initial authorization to reduce security risks.
Log on to the AWS IAM console as the root user and click My Security Credentials on the dashboard.
In the Access keys section, locate the AccessKey pair used for this authorization. Then, in the Actions column, click Delete and confirm the deletion.
Plan 2: Manual configuration
This plan provisions assets by creating an IAM user with limited permissions in AWS. This method ensures high security and supports all features.
Step 1: Create authorization credentials for a RAM user in AWS
Create an IAM user with least privilege access for Security Center integration and retrieve its AccessKey pair.
For more information, see the AWS official documentation about creating users and adding permissions.
Log on to the AWS console
Log on to the AWS IAM console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Users. On the Users page, click Create user.
Specify user details
User name: Enter an easily identifiable name, such as
aliyun-security-center-user.Provide user access to the AWS Management Console: Do not select this option. This user is for API access only.
Set user permissions
Select Attach policies directly.
Select the permission policies that correspond to the features you plan to use in Security Center.
Feature
AWS policy
Remarks
Host
AmazonEC2ReadOnlyAccessIAMReadOnlyAccessNone
CSPM (CSPM)
ReadOnlyAccessIf you want to perform comprehensive risk detection based on log audits, see Configure AWS service audit logs for CSPM to configure audit logs for related services in AWS.
Agentless Detection
You must manually create a custom policy.
You must create a log delivery pipeline in AWS that consists of CloudTrail, S3, and SQS. For more information, see Create a custom policy for Agentless Detection.

Review and create
Confirm that the user details and permission policies are correct, and then click Create user.
Create and save the AccessKey pair
After the user is created, return to the Users list and click the username to go to the details page.
On the Summary tab, click Create access key. Configure the settings as instructed.
Use case: Select a use case for your business scenario. If none of the options apply, select Other.
Set description tag (optional): Enter a custom tag, such as
for-aliyun-sasc.
Click Create access key. On the Retrieve access key page, copy and save the Access key and Secret access key.
Step 2: Complete the onboarding configuration in Security Center
After creating an API key for the IAM user in AWS, return to the Security Center console to complete the boarding configuration.
Go to the authorization page
NoteFor information about other entry points, see Other entry points.
Log on to the Security Center console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . In the upper-left corner of the console, select the region where your assets are located: Chinese Mainland or Outside Chinese Mainland.
On the tab, click Grant Permission, and then select AWS.
Configure provisioning credentials
In the Add Assets Outside Cloud panel, select Manual Configuration, select the features to provision, and then click Next.
Host: Allows Security Center to automatically discover and synchronize your AWS EC2 host assets.
CSPM: Uses the CSPM feature to scan the configurations of your AWS cloud products to discover and manage configuration risks.
Agentless Detection (supported only in regions Outside Chinese Mainland): Uses the Agentless Detection feature to scan your AWS assets for vulnerabilities and risks.
On the Submit AccessKey Pair page, enter the credentials that you created in AWS.
IAM user Access Key ID and IAM user Secret Access Key: Enter the credentials that you created in Step 1: Create authorization credentials for a RAM user in AWS.
Provisioning Region: Select an available AWS region. The system uses this region to verify asset accessibility.
Domain: Configure this parameter based on the provisioning region. If you use an AWS China proxy, select China. Otherwise, select International.
After you enter the information, click Next. The system automatically verifies the credentials and permissions.
NoteIf the verification fails, see What do I do if the automatic credential and permission verification fails after I enter the AccessKey pair?
Configure audit logs (Optional)
If you want to use the log audit feature of Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), complete the configuration in this step. Otherwise, click Skip.
ImportantBefore you proceed, you must complete all the required configurations in the AWS console. For more information, see Configure AWS service audit logs for CSPM.
AWS Region: Enter the ID of the region where the AWS queue is located. For information about region IDs, see AWS Region IDs.
SQS Queue Name: Enter the name of the SQS queue that you created.
Configure the synchronization policy
On the Policy Configuration page, configure the following settings based on your needs:
Select region: Select the regions that contain the AWS assets that you want to provision.
NoteThe asset data is automatically stored in the data center that corresponds to the region selected in the upper-left corner of the Security Center console.
Chinese Mainland: Data centers located in the Chinese mainland.
Outside Chinese Mainland: The data center is in Singapore.
Region Management: This option is selected by default. When this option is selected, assets in new regions that are added to this AWS account are automatically synchronized, and you do not need to add them manually.
Host Asset Synchronization Frequency: Set the interval for automatically synchronizing AWS host (EC2) assets. To disable synchronization, select Off.
NoteThis parameter is required only if you chose to provision Host.
Cloud Service Synchronization Frequency: Set the interval for automatically synchronizing AWS cloud product configurations. To disable synchronization, select Off.
NoteThis parameter is required only if you chose to provision Cloud Security Posture Management.
AK Service Status Check: Set the interval at which Security Center automatically checks the validity of the AccessKey pair for the AWS account. You can select Off to disable this check.
After you complete the configuration, click Synchronize Assets. The system automatically synchronizes the data from your AWS account to Security Center.
Manage provisioned assets
Host Assets
Go to the page. In the multi-cloud asset provisioning section, click the ![]() icon to view the provisioned AWS hosts. You can perform the following steps to manage the provisioned AWS EC2 hosts and enhance their protection.
icon to view the provisioned AWS hosts. You can perform the following steps to manage the provisioned AWS EC2 hosts and enhance their protection.
For more information, see Host Assets.
Install the client: You can install the Security Center client on an AWS host. When you run the installation command, you must select AWS as the Service Provider. For more information, see Install the client.
Upgrade to a paid edition for protection: The default Free Edition provides only basic security detection. To obtain comprehensive security protection, such as anti-virus, vulnerability remediation, and intrusion prevention, attach a paid edition (Anti-virus Edition or higher) to your AWS hosts. For more information, see Manage security authorizations for hosts and containers.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
In the Security Center console, go to the page. In the All Alibaba Cloud Services navigation pane on the left, click AWS to view your provisioned AWS assets. You can use the following CSPM features for the provisioned AWS assets:
For more information, see Viewing cloud product information.
Perform a configuration risk check: You can check your AWS products for configuration risks. For more information, see Configure and run a cloud platform configuration risk check policy.
Handle risk items: You can view and remediate failed risk check items based on the check results to improve the compliance and security of your cloud assets. For more information, see View and handle failed cloud platform configuration risk check items.
Agentless Detection
In the Security Center console, go to the page. Switch the region to Outside Chinese Mainland. In the Add Multi-cloud Asset area, click the ![]() icon to view the number of imported AWS assets. After the assets are imported, you can use the Agentless Detection feature to scan AWS hosts for items such as vulnerabilities and baselines. For more information, see Agentless Detection.
icon to view the number of imported AWS assets. After the assets are imported, you can use the Agentless Detection feature to scan AWS hosts for items such as vulnerabilities and baselines. For more information, see Agentless Detection.
AWS advanced configuration (for Agentless Detection and CSPM)
Create a custom policy for Agentless Detection
For more information, see the AWS documentation about creating a user and adding permissions.
Log in to the AWS IAM console. On the Policies page, click Create Policy.
In the Policy Editor section, select JSON and paste the following JSON code into the editor.
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "ec2:DeleteSubnet", "ec2:DeleteVpcEndpoints", "ec2:DeleteInternetGateway", "ec2:TerminateInstances", "ec2:StopInstances", "ec2:DeleteSecurityGroup", "ec2:DeleteVpc" ], "Resource": "*", "Condition": { "StringLike": { "ec2:ResourceTag/Name": "alibaba-cloud-security-scan*" } } }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "ec2:DeleteSnapshot" ], "Resource": "*", "Condition": { "StringLike": { "ec2:ResourceTag/Name": "SAS_Agentless*" } } }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "ec2:CopySnapshot", "ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupIngress", "ec2:DescribeInstances", "ec2:CreateImage", "ec2:CreateVpc", "ec2:AttachInternetGateway", "ec2:CopyImage", "ec2:ModifyImageAttribute", "ec2:DescribeSnapshots", "ec2:ModifySubnetAttribute", "ec2:DescribeInternetGateways", "ec2:ModifySnapshotAttribute", "ec2:DescribeInstanceTypeOfferings", "ec2:DescribeAvailabilityZones", "ec2:CreateInternetGateway", "ec2:CreateSecurityGroup", "ec2:DescribeVolumes", "ec2:CreateSnapshot", "ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress", "ec2:RunInstances", "ec2:DetachInternetGateway", "ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups", "ec2:DescribeImages", "ec2:CreateVpcEndpoint", "ec2:CreateSnapshots", "ec2:DescribeVpcs", "ec2:DescribeImageAttribute", "ec2:DescribeVpcEndpoints", "ec2:CreateSubnet", "ec2:DescribeSubnets", "ec2:ModifyVpcEndpoint", "ec2:CreateTags", "ec2:DescribeRouteTables", "ec2:CreateRoute", "ec2:DescribeRegions", "kms:Decrypt", "kms:DescribeKey", "kms:CreateGrant", "kms:ListGrants", "kms:RevokeGrant", "kms:GenerateDataKey", "kms:ReEncrypt*", "iam:GetUser" ], "Resource": "*" } ] }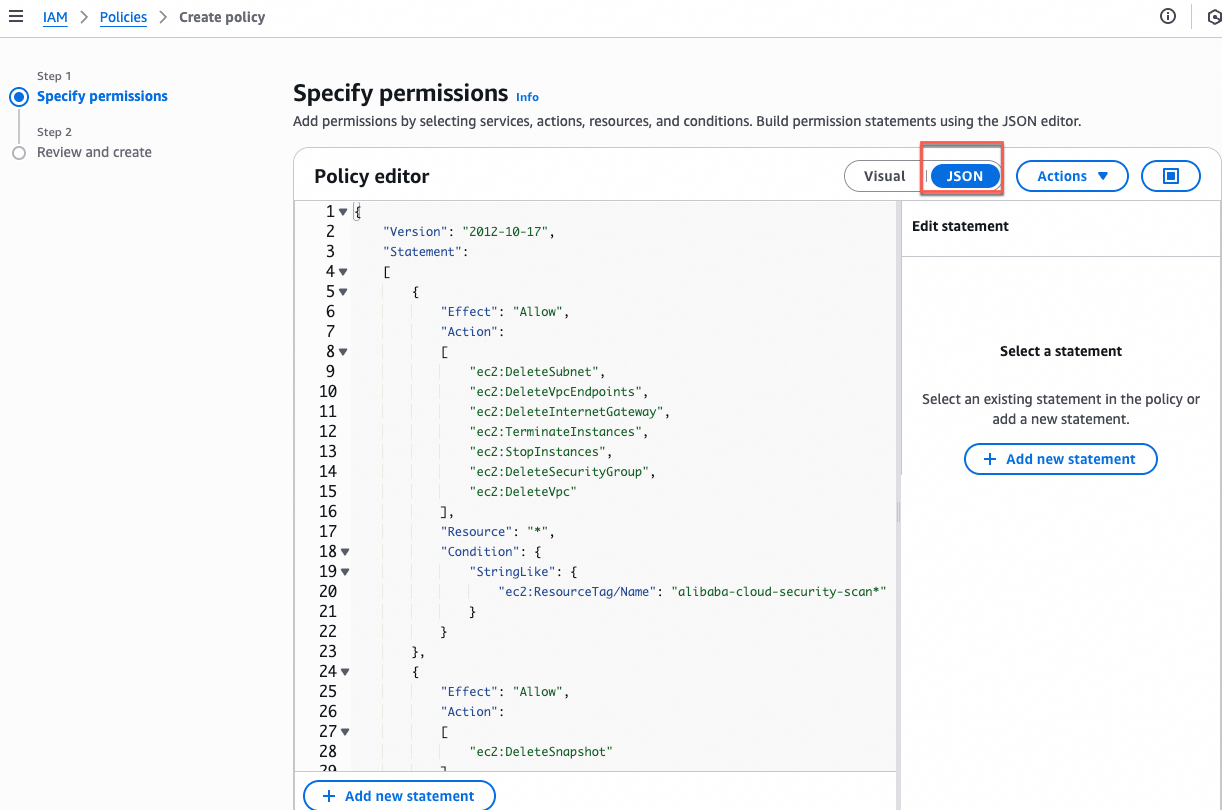
Click Next, enter a name for the policy, such as
AliyunSASC-AgentlessScan-Policy, and click Create Policy.To attach this policy to the AWS RAM user, see Set user permissions.
Configure AWS service audit logs for CSPM
Step 1: Create a CloudTrail trail
In this step, you create a trail in AWS CloudTrail. The trail records and stores all management operations on cloud resources within a specified region. These logs provide the data that is required for CSPM data collection. For more information, see the AWS documentation about creating a trail.
Log on to the AWS CloudTrail console
Log on to the AWS CloudTrail console. In the region selector in the upper-right corner of the console, select the AWS region that you want to monitor.
On the dashboard or in the navigation pane on the left, select Trails and click Create Trail.
Configure trail attributes
On the Choose Trail Attributes page, configure the following settings and click Next.
Trail name: Enter a descriptive name, such as
aliyun-sasc-audit-trail, for easy identification.Storage Location:
ImportantRecord the bucket name for later use.
Create New S3 Bucket: Enter a globally unique bucket name in all lowercase letters.
Use Existing S3 Bucket: In the Trail Log Bucket Name section, click Browse and select the target bucket from the dialog box.
Log File SSE-KMS Encryption: Clear this check box. Use the default Server-Side Encryption with Amazon S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3) to encrypt log files.
Choose log events
On the Choose Log Events page, configure the following settings and click Next.
Event Type: Management events.
API Activity: Read, Write.
Review and create
On the Review and Create page, review the configuration items. If the information is correct, click Create Trail.
Step 2: Create an SQS message queue
This queue receives log file event notifications from an S3 bucket and serves as the target message channel for log delivery. For more information, see the AWS documentation about creating a message queue.
Log on to the AWS SQS console.
Log on to the AWS SQS console, select a region, and then click Create queue.
WarningMake sure that the selected region is the same as the region where you created the CloudTrail trail in the previous step.
Configure queue information
Type: Standard.
Name: Enter an easily identifiable queue name, such as
aliyun-sasc-log-queue.ImportantThis queue name is used to generate its unique ARN and for subsequent access policy configuration. Make sure that you enter it correctly.
Configure the access policy
This is the most critical step. This policy defines who can send messages to this queue and who can read messages from it.
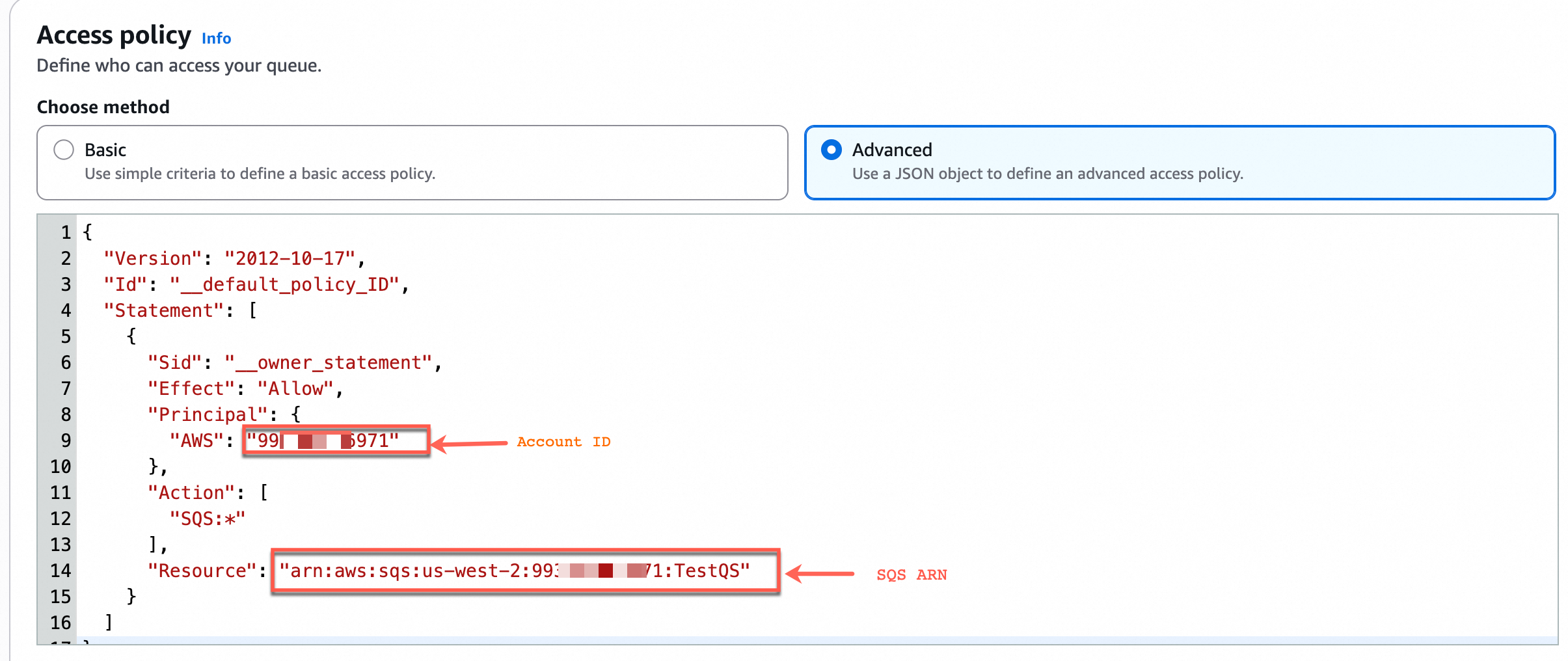
In the Access policy panel, select Advanced.
ImportantRecord the Account ID and Queue ARN from the default policy for later use.
Copy the entire JSON template below and paste it into the policy editor, replacing all existing content.
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Id": "__default_policy_ID", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "__owner_statement", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::${Account ID}:root" }, "Action": "SQS:*", "Resource": "${SQS ARN}" }, { "Sid": "example-statement-ID", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": "s3.amazonaws.com" }, "Action": [ "SQS:SendMessage" ], "Resource": "${SQS ARN}", "Condition": { "ArnLike": { "aws:SourceArn": "arn:aws:s3:*:*:${S3 bucket name}" } } } ] }Important: Replace the placeholders in the template as described in the following table:
Placeholder
How to obtain the value
Example
${Account ID}The Account ID that you saved in the previous step.
99********1${SQS ARN}The SQS ARN that you saved in the previous step.
arn:aws:sqs:ap-northeast-1:123******012:aliyun-sasc-log-queue${S3 bucket name}The name of the S3 bucket that you set when creating a CloudTrail.
NoteYou can log on to the AWS S3 console, find the bucket in the corresponding region, and view its information on the details page.
aws-cloudtrail-logs-123******12-abcdefAfter you replace the placeholders, scroll to the bottom of the page and click Create queue.
Step 3: Create an S3 event notification
In this step, you configure an event notification rule for the S3 bucket. This rule automatically sends a notification to the specified SQS queue when a new log file is generated. For more information, see the AWS documentation about Amazon S3 Event Notifications.
Log in to the AWS SQS console
Log on to the AWS S3 console, select a region, and then click General purpose buckets.
WarningMake sure that the selected region is the same as the region where you created the CloudTrail trail.
On the General purpose buckets tab, locate the S3 bucket that you specified when you created CloudTrail and open its details page.
Configure the event notification
On the Properties tab, in the Event notifications section, click Create event notification. Configure the following settings.
Event types: Select Put.
Destination: Select SQS Queue and specify the queue that you created in Step 2: Create an SQS message queue.
After you complete the configuration, click Save changes.
Step 4: Configure queue access permissions
In this step, you grant the dedicated IAM user for Security Center permission to read notification messages from the SQS queue.
Create an SQS policy:
Log on to the AWS IAM console. On the Policies page, click Create Policy.
Configure the following settings.
Service: SQS.
Effect: Allow.
Read: GetQueueUrl, ReceiveMessage.
Write: Select ReceiveMessage.
For Resources, click Add ARNS. In the Resource ARN field, enter the Queue ARN.
NoteYou can log on to the AWS SQS console, find the queue in the corresponding region, and view its ARN on the details page.
Attach the policy to the IAM user:
To attach the SQS policy that you created to the target IAM user, see Set user permissions.
FAQ
Why can't I see some of my provisioned AWS resources in Security Center?
Region not selected: In the provisioning configuration in Security Center, check whether you have selected the AWS region where the resource is located.
Synchronization latency: Asset synchronization may be delayed after initial provisioning or configuration changes. Wait for the synchronization to complete.
What do I do if the automatic credential and permission verification fails after I enter the AccessKey pair?
Permission issues: The IAM user may have insufficient permissions. Go to the AWS console to modify or add the required permission policies. For more information, see Set user permissions.
Account issues: If you use the quick configuration plan, the AccessKey pair must be generated for the root user. Log on to the AWS console as the root user and create an API access key. For more information, see Step 1: Create authorization credentials for the root user in AWS.
Region issues: The currently selected region may not be available. Switch to another available region or the corresponding domain, and then resubmit.