This topic describes billing for SAE, including free trials, pay-as-you-go, and resource plans. It also provides methods and examples to help you estimate your costs.
Cost calculation method
Single application
First, let's look at how to calculate costs for the basic scenario of running a single application in SAE. The cost is calculated in the following steps:
Calculate the Raw Resource Usage, which includes VCPU Usage, Memory Usage, and Disk Usage. Resource usage duration is calculated in seconds, and any period less than 1 second is rounded up to 1 second.
To calculate CU Usage, SAE converts the Raw Resource Usage (VCPU Usage, Memory Usage, and Disk Usage) into CU Usage (Cost Unit) for billing. The conversion formula is
CU Usage = Raw Resource Usage × CU conversion coefficient. The CU conversion coefficient varies based on the application version (Lightweight Edition, Standard Edition, or Professional Edition) , raw resource type, and server type (Default or HyGon).If you use a resource plan (subscription), the CU usage is offset by your plan. If you use the pay-as-you-go billing method, the unit prices for CU billing are shown in the following table. The prices are for reference only. The actual prices are subject to the commercial offer.
Multiple applications
In more complex scenarios where you run multiple applications , the cost is calculated in the following steps:
Applications of the same edition are billed together, while applications of different editions are billed separately.
For example, if you run both Lightweight Edition and Professional Edition applications, the costs for each edition are calculated and billed separately.
Calculate the Raw Resource Usage, which includes VCPU Usage, Memory Usage, and Disk Usage. Resource usage duration is calculated in seconds, and any period less than 1 second is rounded up to 1 second.
vCPU usage = ∑(Number of instances × CPU cores per instance × Runtime in seconds)Memory usage = ∑(Number of instances × Memory per instance in GB × Runtime in seconds)Disk usage = ∑(Number of instances × (Disk size per instance in GiB - Free disk size of 20 GiB) × Runtime in seconds)
Calculate the total CU Usage.
CU usage = ∑(Usage of each resource type × Corresponding CU conversion coefficient)
If you use a resource plan (subscription), the CU usage is offset by your plan. If you use the pay-as-you-go billing method, the cost is calculated based on the CU unit price.
Total cost = CU usage × CU unit price
Billing methods
You can activate SAE to use the service and enable billing. SAE supports two billing methods: pay-as-you-go and resource plan (subscription).
Additional billable items
If your SAE application integrates with other Alibaba Cloud services, additional fees are incurred for services such as networking, storage, databases, middleware, logging, and observability.
When you delete an SAE application , SAE stops billing for that resource.
However, if your SAE application depends on other services, such as Classic Load Balancer (CLB), these services will continue to incur fees.
To avoid unnecessary expenses, make sure to stop or delete these services when they are no longer needed and confirm their status to prevent further billing.
Service type | Requirements and scenarios | Implementation method | Billing reference |
Network | Your SAE application needs to be accessed from the internet (inbound traffic) | Access the application based on SAE Ingress (gateway routing): | |
Access the application based on SAE Service: | |||
Your SAE application needs to access the internet (outbound traffic) | Configure an Internet NAT gateway for the VPC associated with the SAE application | ||
Use a registry to enable communication between microservice applications | Implement service registration and discovery based on a registry such as Nacos | SAE's built-in Nacos registry is free. | |
Enable internal network communication between applications | Access the application based on SAE Ingress (gateway routing): | ||
Access the application based on SAE Service: | |||
Storage | Enable data persistence for SAE applications | ||
Database | Your SAE application connects to a database service provided by Alibaba Cloud | See the billing documentation for the specific database service | |
Middleware | Your SAE Standard and Professional Edition applications integrate with the microservice administration capabilities of MSE | Professional Edition: Microservice administration is free. Standard Edition: Microservice administration requires separate activation and is billed. | |
Log | Centrally collect and analyze logs for SAE applications | ||
Observability | Your SAE Standard and Professional Edition applications integrate with the capabilities of ARMS Premium Edition | Professional Edition: ARMS advanced monitoring is free. Standard Edition: ARMS advanced monitoring requires separate activation and is billed. |
View bills
View billing details
Log on to Expenses and Costs and go to the Monthly Billing Overview page to view your monthly consumption. You can switch accounts to view the summarized consumption information of associated RAM users.
Go to the Billing Details page, click the corresponding tab, and then view your consumption.
Billing Records: View the consumption records of your account for each hourly billing cycle. For example, if you use SAE continuously from 00:00 to 24:00 on August 1, 24 consumption records are generated, one for each hour from 00:00 to 24:00.
ImportantSAE bill generation is delayed by approximately 2 hours. For example, you can query the SAE consumption record for the 13:00 to 14:00 period at around 16:00 in the Expenses and Costs console.

Billing Details: You can filter billing details by different Statistic Item and Statistic Period values. The details include product details, consumption type, billable item, price, and deduction information.
 Important
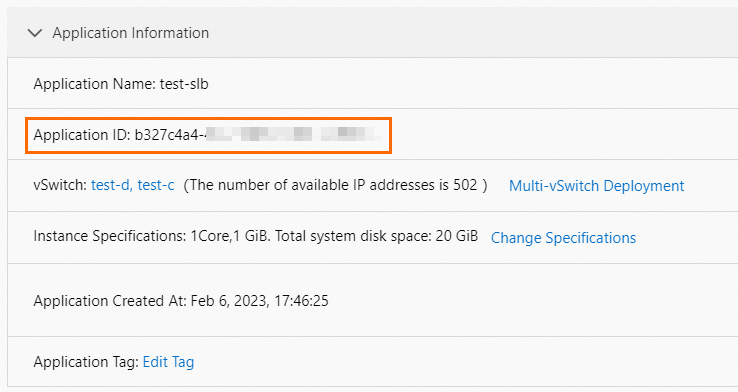
ImportantIn the billing details, the Instance ID corresponds to your Application ID (① and ② in the figure) or Task Template ID. You can view and copy the ID from the application details page or task template details page. Then, on the Billing Details tab, you can search for the bill of a single application or task template by Instance ID (③ in the figure).
The Billable Item (④ in the figure) indicates the billable items for the application or task template. You can reconcile your resource usage based on the billable item.
The following is an example of an Application ID.
View Usage Details: Follow the instructions on the page to download the usage information in CSV format.

View resource plan usage details
Log on to Expenses and Costs. Go to the Usage Details page for resource plans, enter the specific resource instance name, and view the detailed deduction records for the resource plan.
SAE resource plans are of the total decreasing type. During the validity period, the plan's capacity decreases with use until it is exhausted or expires. The remaining amount is calculated as follows: Remaining amount after deduction = Remaining amount before deduction - Deducted amount. The deducted amount is the resource usage of the instance during a specific period.
You can also view the usage of your purchased CU resource plans in the Resource Plan area on the right side of the Overview page.
Billing reconciliation FAQ
How do I reconcile my SAE resource bills?
For more information about reconciliation methods, see View billing details and View resource plan usage details.
After I stop using resources, why does my bill show that SAE is still consuming resources?
Assume that you used SAE resources from 13:00 to 14:00, stopped using them at 14:00, and immediately checked the Billing Records and Billing Details tabs. You find that SAE still has consumption records after 14:00.
This is normal because SAE bill generation is delayed by approximately 2 hours. Therefore, after you stop using SAE resources at 14:00, you can check the Billing Records tab around 16:00 to view the bill details. You can also export detailed data from the View Usage Details tab if needed.
Account deduction order
Credit limit for enterprise users.
Valid coupons in your Alibaba Cloud account.
Valid prepaid cards in your Alibaba Cloud account.
Cash balance in your Alibaba Cloud account.
Balance of your linked Alipay account.
Bank card specified when linking your Alipay account.
Other express payment bank cards linked to your Alipay account.
Yu'e Bao balance of your linked Alipay account (requires you to enable the Yu'e Bao auto-debit feature in Alipay).
The credit limit for enterprise users, valid coupons, and cash balance in your Alibaba Cloud account cannot be used simultaneously.
Overdue payments and renewals
If the available balance in your account, including your Alibaba Cloud account balance and coupons, is insufficient to pay your outstanding bills, your account immediately has an overdue payment.
If you no longer need to use SAE, release the related resources to avoid further charges:
To delete an SAE application, see Delete an application.
If your application integrates with other Alibaba Cloud services, additional fees are incurred for services such as networking, storage, databases, middleware, logging, and observability. Before you delete these resources, make sure to back up any necessary data.
Overdue payments
Overdue duration | Description |
Overdue for less than 7 days | If your account has an overdue payment for less than 7 days (168 hours), your application instances in SAE continue to occupy cloud resources and incur fees, unless they are deleted or stopped. When your SAE service has an overdue payment, the following limits apply.
|
Overdue for more than 7 days | If you fail to pay all outstanding bills within 7 days (168 hours) of the payment becoming overdue, SAE services are stopped. At the same time, the application and task instances that you created in are released, and their data is deleted and cannot be recovered. To ensure that your services are not affected, make your payment promptly. |
View consumption overview
Log on to Expenses and Costs.
On the Account Overview page, you can view the consumption overview.
Renewal policy
Log on to Expenses and Costs.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Payment Details. On the Payment Details page, on the Pending Payment tab, click Pay in the Actions column and follow the on-screen instructions to pay the overdue amount.
