This topic describes the background information, principles, and best practices for designing resource groups.
Background information
As the number of cloud resources of your enterprise increases, you must manage the cloud resources by category at the earliest opportunity to improve resource management efficiency, reduce O&M risks, and reduce unnecessary costs.
Resource groups allow you to manage cloud resources within an Alibaba Cloud account by category. Each resource must belong to a resource group and can belong to only one resource group. Resource groups provide the following benefits for resource management:
Improve management efficiency: After you classify your resources into different resource groups, you can deploy resources, monitor resources, and manage permissions on the resources by resource group. For example, if you want to grant permissions on only resources of a specific project group to members of the project group, you can create a resource group for the project group, transfer the resources of the project group to the resource group, and then grant permissions on the resource group to the members. This way, the members have permissions on only the resources in the resource group, instead of permissions on all resources of the related account. If the resources of the resource group change, you do not need to modify permission configurations for the members. This can reduce the maintenance costs of permission configurations.
Reduce O&M risks: If you classify your resources into resource groups, each resource must belong to a resource group and can belong to only one resource group. Therefore, you do not need to be concerned about risks that may be caused by management of the same resource in different resource groups. For example, if you want to perform an O&M operation to modify the names of multiple resources at a time by resource group, you do not need to be concerned about conflicts that may be caused by different O&M operations performed on the same resource.
Principles for designing resource groups
When you design resource groups, we recommend that you perform the following steps: resource group planning, standard execution, and check and evaluation. You must abide by the principles of each step during the design.

Mutual exclusivity: When you plan resource groups, you must make sure that the classification dimensions are mutually exclusive. For example, you can classify resources by department, project, function, and resource deployment environment. This can ensure that a resource belongs to only one resource group from the business perspective. For example, the classification dimensions Project A and Project A in Production Environment do not conform to the mutual exclusivity principle. If a resource needs to be used in multiple business systems, you can follow the sharing principle to design resource groups.
Comprehensiveness: When you plan resource groups, you must make sure that all your resources can be classified into appropriate resource groups. You must also take into account the development and change of your subsequent business. This can prevent risks and additional costs that are caused by adjustment of resource groups due to inappropriate classification dimensions. We strongly recommend that you do not classify your resources into the default resource group. The default resource group is generated by the system and cannot be deleted. The resources of an Alibaba Cloud account that are not classified are added to the default resource group. We recommend that you use custom resource groups to classify resources.
Sharing: If some resources need to be shared by multiple projects or business systems, you can create a dedicated resource group to store these resources and specify a resource group name that can be distinguished from the names of other resource groups. For example, your enterprise has two business systems and the business systems use the same virtual private cloud (VPC). You need to create a resource group for each project of your enterprise and create a dedicated resource group to store shared resources. This way, the VPC can be classified into the dedicated resource group.
Principle of least privilege: When you perform authorization by resource group, you must abide by the principle of least privilege. For example, an enterprise has multiple business systems, and each business system is deployed in multiple environments. The enterprise plans resource groups by business system instead of deployment environment, and performs authorization by resource group. As a result, the RAM users that use the resources of the development environment may have permissions on resources of the production environment, which may cause security and stability issues for the business systems in the production environment.
Standard naming: Names of resource groups must be simple, adhere to a specific standard, and are relevant to your business. This helps you easily identify and manage the resource groups. For example, the resource group name Project A in Production Environment conforms to the standard naming principle. The resource group name Production Environment does not conform to the standard naming principle because the name does not have a definite business system meaning.
Timely adjustment: If existing classification dimensions of resource groups cannot meet the requirements of your business development, you must adjust the classification dimensions at the earliest opportunity to prevent risks and additional costs that may arise from business development. For example, you classify the resources of your enterprise into different resource groups by department. As the business develops, each department in your enterprise will have multiple business systems. As a result, classification by department cannot meet your requirements of permission isolation. To resolve this issue, you must classify the resources of your enterprise by business system and adjust the permissions of RAM identities on resource groups.
Timely clearing: If specific resource groups are no longer required, you must delete the resource groups at the earliest opportunity to reduce management costs. For example, you classify the resources of your enterprise into different resource groups by project and you create resource groups such as Project A and Project B. If Project A is no longer required, you must transfer the resources of Project A to another resource group or release the resources of Project A and delete Project A at the earliest opportunity to reduce management costs.
Best practices
An Internet enterprise has two online business systems and deploys the online business systems in the testing environment and production environment to meet the requirements of continuous iteration and development of service features. The two business systems use multiple types of cloud resources in the environments. In addition to the business department, the enterprise also has finance, O&M, and compliance audit departments. These departments have different requirements for cloud resource management. The following descriptions provide details:
Business department: hopes that only members of a business system can access the resources of the business system. The business department also hopes to identify the resources that are used by each business system in an efficient manner and hopes to separately monitor and manage resources used by each business system.
Finance department: hopes to understand the resource fees of the entire enterprise and the resource fees of each business system.
O&M department: hopes to perform efficient O&M on resources. The O&M department needs to perform O&M operations on resources used by two business systems based on different standards. For example, the O&M department needs to perform an exception inspection on resources used by Business System A at 02:00 every early morning to identify the resources that require O&M at the earliest opportunity.
Compliance audit department: requires that the compliance of all cloud resources of the enterprise be audited and all resources comply with laws and regulations, industry standards, and the compliance requirements of the enterprise. However, due to different compliance standards for resources used by the business systems, the compliance audit department hopes to implement differentiated compliance audit.
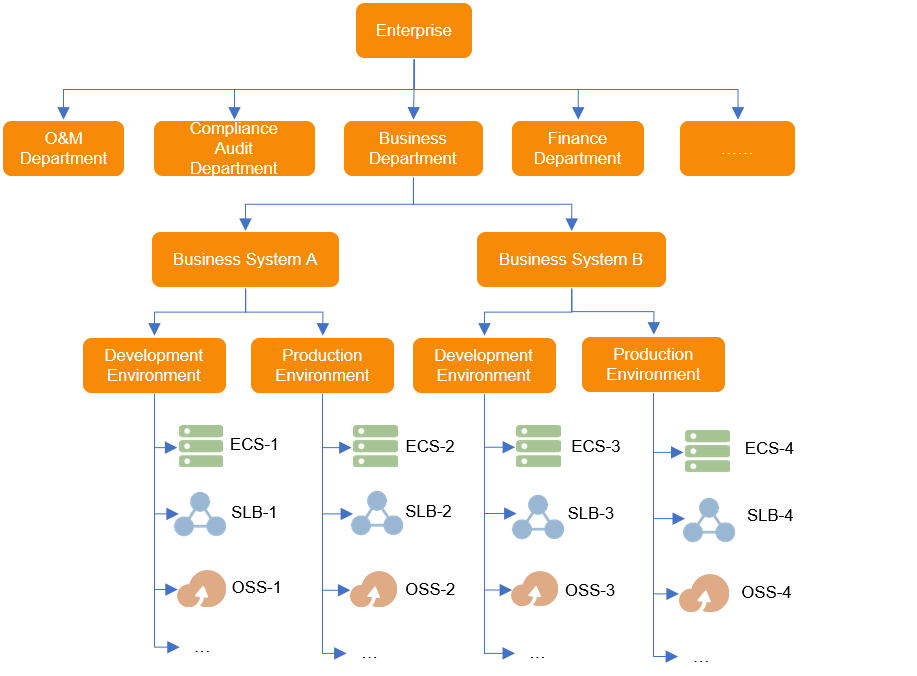
To meet the preceding requirements, the enterprise designs resource groups from the business system and environment dimensions at the same time and creates the following resource groups: Business System A in Development Environment, Business System A in Production Environment, Business System B in Development Environment, and Business System B in Production Environment. In addition, the enterprise grants permissions on the resource groups to related functional personnel.
After the enterprise classifies all resources into resource groups, the requirements of different functional personnel for resource management are met.
Department/Personnel | Requirement | Implementation | References |
Permission administrator | Fine-grained access control | The permission administrator uses RAM to grant different permissions on the resource groups to different personnel to implement fine-grained access control. | |
Business department | Resource search and management | The business development personnel can identify resources that are used by a specific business system by using Resource Center to search for resources by resource group. | |
Differentiated resource monitoring | The business development personnel create application groups from resource groups in CloudMonitor and configure differentiated monitoring settings for resources used by different business systems based on monitoring standards for the business systems. | ||
Finance department | Cost management and allocation | The financial personnel use cost centers to allocate costs by resource group and can obtain the resource fees of each business system. | |
O&M department | Differentiated resource O&M | The O&M personnel determine resources that require O&M by resource group and use O&M tools such as CloudOps Orchestration Service (OOS) and Resource Orchestration Service (ROS) to implement differentiated O&M by resource group. | |
Compliance audit department | Differentiated compliance audit | The audit personnel determine resources that require auditing by resource group and create different audit rules for the resource groups based on different standards in Cloud Config to implement differentiated compliance audit. | Use resource groups and Cloud Config to audit compliance of resources based on multiple standards |