TairTS is a time series data structure developed on top of Redis modules. This data structure provides low-latency and high-concurrency in-memory read and write access, supports fast filtering and aggregate queries, and offers both storage and computing capabilities. TairTS simplifies the processing of time series data and significantly improves performance.
Overview of TairTS
Compared with RedisTimeSeries, TairTS provides a richer set of features:
Multi-timeline aggregate queries by using pkeys. Pkeys have an extra hash layer.
For example, you can create multiple skeys named after metric names and device IDs in the foo pkey, such as temperature:1, pressure:1, and distance:1. You can then run the EXTS.S.MRANGE command provided by TairTS to retrieve custom monitoring data such as skeys that have a device ID of 1. If you want to implement a similar feature using RedisTimeSeries, you must insert many aggregate queries into business logic code.
Figure 1. Comparison between TairTS and RedisTimeSeries
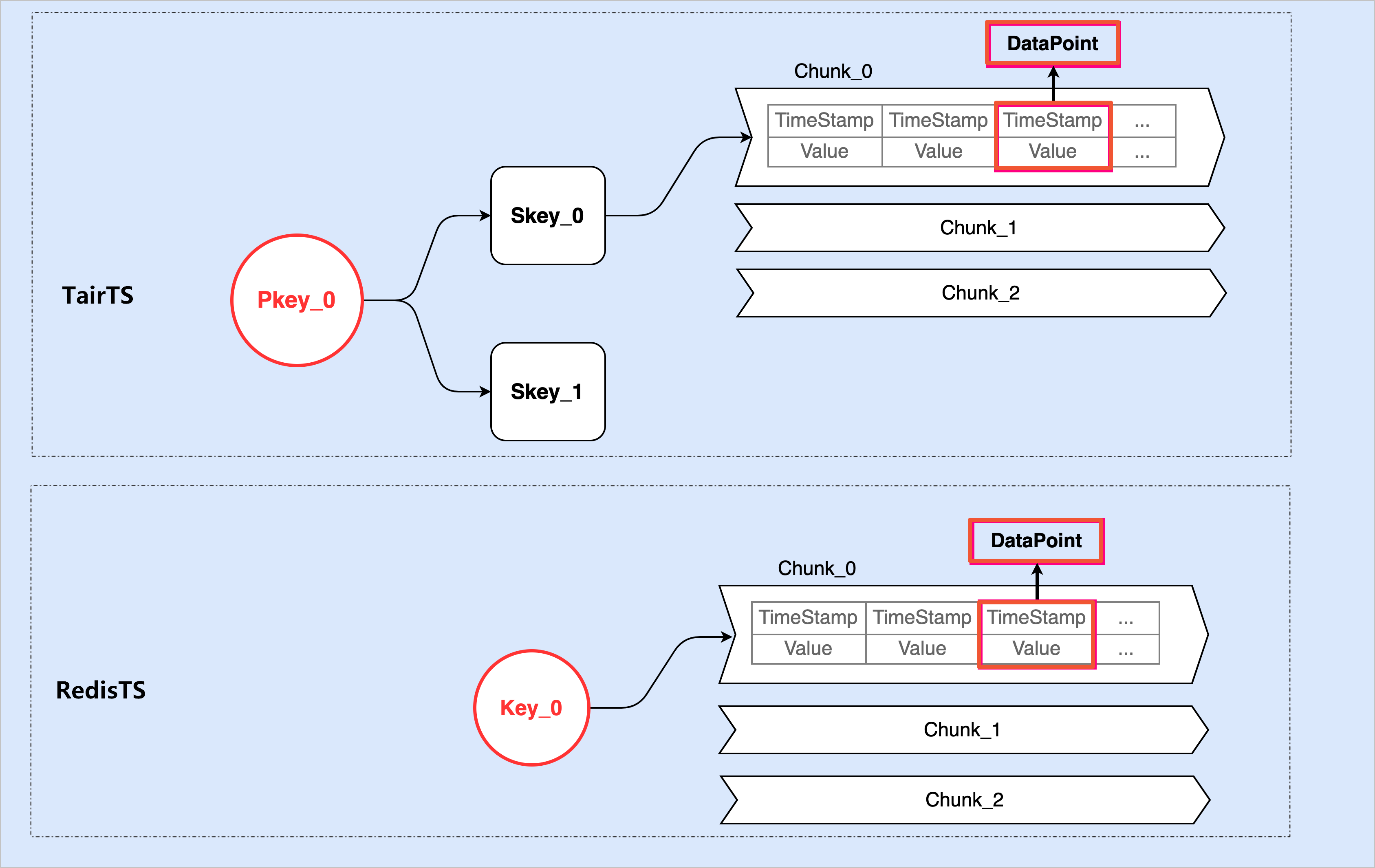
The following section describes the structure of TairTS data:
Pkey: a piece of TairTS data that indicates a set of timelines. A pkey consists of multiple skeys.
Skey: a timeline. An skey consists of multiple chunks that have a fixed capacity. You can attach one or more different labels to each skey. Then, skeys can be filtered by label.
Chunk: a data chunk. A chunk can store multiple datapoints.
The capacity of each chunk is customizable. If compression is not enabled, a chunk can store up to 256 datapoints. However, if compression is enabled, a chunk can store more than 256 datapoints.
Chunks are the smallest expiration units. A chunk is deleted after all datapoints in the chunk expire.
Datapoint: a piece of time series data that includes a timestamp and a DOUBLE-type value.
Aggregate queries in scenarios such as downsampling, attribute filtering, batch query, and the use of multiple numerical functions. This feature integrates batch query and aggregation into a single command to reduce network interaction and provide single-digit millisecond response time.
Update and accumulation of historical time series data.
Support for timeline-level TTL setting ensures that each timeline can automatically scroll according to a time window.
Efficient Gorilla compression algorithm and specific storage to significantly reduce costs.
Typical scenarios
Storage and computing of monitored data
Data analytics based on time windows
Data analytics and processing for IoT
Caching of hot news
Per-second monitoring for application performance management (APM)
Risk control in throttling scenarios
Best practices
Preparations
The instance that you want to manage is a Tair DRAM-based instance.
If the instance is a DRAM-based instance that is compatible with Redis 5.0, the minor version of the instance must be 1.7.20 or later.
The latest minor version provides more features and higher stability. We recommend that you update the instance to the latest minor version. For more information, see Update the minor version of an instance. If your instance is a cluster instance or read/write splitting instance, we recommend that you update the proxy nodes in the instance to the latest minor version to ensure that all commands can be run as expected.
Usage notes
The TairTS data that you want to manage is stored on the Tair instance.
TairTS supports real-time, high-concurrency writes and queries but provides limited storage capacity. We recommend that you specify TTL for TairTS data to ensure that expired data is deleted in a timely manner.
Breaking changes:
On July 22, 2024, the 24.7.0.0 version of Tair DRAM-based instances that are compatible with Redis 6.0 was released. This version introduces a new parameter called ts-auto-del-empty-skey-enable, which is set to yes by default. This indicates that when all data points in an skey expire, the skey is automatically deleted. However, in versions prior to 24.7.0.0 of Tair DRAM-based instances that are compatible with Redis 6.0, skeys whose data points expire are not deleted by default.
Before you use TairTS on a Tair DRAM-based instance that is compatible with Redis 6.0, we recommend that you upgrade the instance to version 24.7.0.0 or later, and confirm and manually adjust the ts-auto-del-empty-skey-enable parameter settings. This can prevent any potential impact on your business due to the change in default behavior.
Command list
Table 1. TairTS commands
Type | Command | Syntax | Description |
Basic write operations |
| Creates a TairTS pkey. If a pkey with the same name already exists, the pkey cannot be created. | |
| Creates an skey in a specified pkey. If the pkey does not exist, it is automatically created. If an skey with the same name already exists, the skey cannot be created. Note You can specify parameters for the skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression. | ||
| Modifies the metadata of a specified skey. Only the DATA_ET time value can be modified. | ||
| Inserts a data point into a skey. If the pkey or skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The parameters for the skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created. | ||
| Inserts a data point into multiple skeys of a pkey. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created. | ||
| Inserts a data point into an skey. If the data point that you want to insert has a positive value, the inserted value is added to the value of the last data point that exists in the skey. If the data point has a negative value, the inserted value is subtracted from the value of the last data point that exists in the skey. If the pkey or skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The default initial value is 0. The parameters for the skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created when the skey does not already exist. | ||
| Inserts a data point into multiple skeys of a pkey. If the data point that you want to insert has a positive value, the inserted value is added to the value of the last data point that exists in each skey. If the data point has a negative value, the inserted value is subtracted from the value of the last data point that exists in each skey. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The default initial value is 0. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created when the skey does not already exist. | ||
| Deletes an skey from a pkey and all data points in the skey. | ||
Basic read operations |
| Queries the value of the latest data point in a specified skey. | |
| Queries the metadata of a specified skey. The metadata includes the number of data points, the timestamp and value of the latest data point, and the label information of the skey. | ||
| Queries the skeys that meet specified filter conditions in a pkey. | ||
Aggregate operations |
| Queries the number of data points that exist in a skey during a specified time range. The time range is a closed interval. | |
| Queries the number of data points that meet specified filter conditions in multiple skeys during a specified time range. The time range is a closed interval. | ||
| Aggregates data points in a pkey that meet specified filter conditions. If you specify one or more skeys for aggregation, the skeys are first aggregated in the same manner as when the EXTS.S.MRANGE command is used. Then, pkeys are aggregated based on the skey aggregation results. | ||
Concurrent write operations |
| Modifies the value of a data point in a specified skey. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created. | |
| Modifies the values of multiple data points in a specified skey at a time. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created. | ||
| Modifies the value of a data point in a specified skey. You can specify an increment or a decrement by which to modify the value. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The default initial value is 0. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created when the skey does not already exist. | ||
| Modifies the values of multiple data points in a specified skey at a time. You can specify an increment or a decrement by which to modify the values. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created when the skey does not already exist. | ||
General-purpose operations |
| Deletes one or more TairTS keys. |
The following list describes the conventions for the command syntax used in this topic:
Uppercase keyword: indicates the command keyword.Italic text: indicates variables.[options]: indicates that the enclosed parameters are optional. Parameters that are not enclosed by brackets must be specified.A|B: indicates that the parameters separated by the vertical bars (|) are mutually exclusive. Only one of the parameters can be specified....: indicates that the parameter preceding this symbol can be repeatedly specified.
EXTS.P.CREATE
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(1) |
Command description | Creates a TairTS pkey. If a pkey with the same name already exists, the pkey cannot be created. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.CREATE
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(1) |
Command description | Creates an skey in a specified pkey. If the pkey does not exist, it is automatically created. If an skey with the same name already exists, the skey cannot be created. Note You can specify parameters for the skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.ALTER
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(1) |
Command description | Modifies the metadata of a specified skey. Only the DATA_ET time value can be modified. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.ADD
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(1) |
Command description | Inserts a data point into a skey. If the pkey or skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The parameters for the skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.MADD
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(n), where n indicates the number of skeys. |
Command description | Inserts a data point into multiple skeys of a pkey. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.INCRBY
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(1) |
Command description | Inserts a data point into an skey. If the data point that you want to insert has a positive value, the inserted value is added to the value of the last data point that exists in the skey. If the data point has a negative value, the inserted value is subtracted from the value of the last data point that exists in the skey. If the pkey or skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The default initial value is 0. The parameters for the skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created when the skey does not already exist. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Run the Sample command: Sample output: If the |
EXTS.S.MINCRBY
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(n), where n indicates the number of skeys. |
Command description | Inserts a data point into multiple skeys of a pkey. If the data point that you want to insert has a positive value, the inserted value is added to the value of the last data point that exists in each skey. If the data point has a negative value, the inserted value is subtracted from the value of the last data point that exists in each skey. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The default initial value is 0. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created when the skey does not already exist. |
Options |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.DEL
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(1) |
Command description | Deletes an skey from a pkey and all data points in the skey. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.GET
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(1) |
Command description | Queries the value of the latest data point in a specified skey. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.INFO
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(1) |
Command description | Queries the metadata of a specified skey. The metadata includes the number of data points, the timestamp and value of the latest data point, and the label information of the skey. |
Options |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.QUERYINDEX
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(n), where n indicates the maximum number of sets involved in filter conditions. |
Command description | Queries the skeys that meet specified filter conditions in a pkey. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.RANGE
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(n), where n indicates the number of chunks to which the data points belong. |
Command description | Queries the number of data points that exist in a skey during a specified time range. The time range is a closed interval. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.MRANGE
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(n), where n indicates the number of chunks to which the data points belong. |
Command description | Queries the number of data points that meet specified filter conditions in multiple skeys during a specified time range. The time range is a closed interval. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.P.RANGE
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(n), where n indicates the number of chunks to which the data points belong. |
Command description | Aggregates data points in a pkey that meet specified filter conditions. If you specify one or more skeys for aggregation, the skeys are first aggregated in the same manner as when the EXTS.S.MRANGE command is used. Then, pkeys are aggregated based on the skey aggregation results. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.RAW_MODIFY
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(1) |
Command description | Modifies the value of a data point in a specified skey. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.RAW_MMODIFY
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(n), where n indicates the number of skeys. |
Command description | Modifies the values of multiple data points in a specified skey at a time. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
EXTS.S.RAW_INCRBY
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(1) |
Command description | Modifies the value of a data point in a specified skey. You can specify an increment or a decrement by which to modify the value. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The default initial value is 0. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created when the skey does not already exist. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Run the Sample command: Sample output: If the |
EXTS.S.RAW_MINCRBY
Item | Description |
Syntax |
|
Time complexity | O(n), where n indicates the number of data points. |
Command description | Modifies the values of multiple data points in a specified skey at a time. You can specify an increment or a decrement by which to modify the values. If the pkey or an skey does not exist, the pkey or skey is automatically created. The parameters for an skey, such as the expiration time and whether to enable compression, take effect only if the skey is automatically created when the skey does not already exist. |
Parameter |
|
Output |
|
Example | Sample command: Sample output: |
Index filtering syntax
Skeys can be filtered by label. The following syntax is used for filter conditions.
When you specify a filter condition, you can use one or more of the following commands and you must use one of the EQ, CONTAINS, and LIST_MATCH logics.
Filter command | Description | Logic |
| The label L equals V. | EQ (equals) |
| The label L is not NULL, which indicates that the skey contains label L. | CONTAINS |
| The label L is v1, v2, or another value. | LIST_TMATCH |
| The label L does not equal V. | NOEQ (equals) |
| The label L is NULL, which indicates that the skey does not contain label L. | NOCONTAINS |
| The value of label L does not match any of the values in the list, such as v1 or v2. | LIST_NOTMATCH |
Aggregation syntax
In aggregation operations, data that exists during an interval specified by the timeBucket parameter is aggregated. The following aggregation types are supported.
MAX: returns the maximum value.MIN: returns the minimum value.AVG: returns the average value.SUM: returns the sum of all values.FIRST: returns the first value.LAST: returns the last value.RANGE: returns the range from the minimum value to the maximum value.COUNT: returns the number of values.STD.P: returns the population variance.STD.S: returns the sample variance.VAR.P: returns the population standard deviation.VAR.S: returns the sample standard deviation.
FAQ
Q: Why is the default value of CHUNK_SIZE relatively small in some Tair DRAM-based instances that are compatible with Redis 5.0?
A: Starting with version 25.2.0.0, CHUNK_SIZE is set to 256 by default. In previous versions, CHUNK_SIZE is set to 32 by default.