Considerations
You must first delete a large amount of data: The OPTIMIZE TABLE command does not effectively reduce tablespace usage unless you first delete a large amount of data using the DELETE statement.
Temporary increase in disk usage: When you run the OPTIMIZE TABLE command, MySQL creates a temporary table to store the reorganized data. This causes a temporary increase in disk usage. After the operation is complete, the temporary table is deleted and the disk usage returns to normal.
Table and index statistics may not change after the release: The disk space is released, but the table statistics in MySQL are not refreshed promptly. For more information, see Why does the disk space of my ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance remain unchanged after I run the OPTIMIZE TABLE command?.
Performance impact and peak-hour risks: In ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL 5.7 and 8.0, the OPTIMIZE TABLE command is run using the online DDL method, which supports concurrent DML operations. However, running this command on a large table may cause I/O and buffer resource usage to burst. This can lead to table locking or resource contention. During peak hours, the instance may even become unavailable or monitoring may be interrupted. Therefore, you should run this command during off-peak hours to avoid affecting your services.
Use the command line
Connect to an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance from a client.
Use the DELETE statement to delete unwanted data as needed.
Run the OPTIMIZE TABLE command to release the tablespace.
OPTIMIZE TABLE <$Database1>.<Table1>,<$Database2>.<Table2>;
Note <$Database1> and <$Database2> represent database names. <Table1> and <Table2> represent table names.
When you run the OPTIMIZE TABLE statement on a table that uses the InnoDB engine, the following message is returned. This message indicates that the statement is run successfully. You can ignore this message. Make sure that "ok" is returned in the status. For more information, see OPTIMIZE TABLE Statement.
Table does not support optimize, doing recreate + analyze instead
Use DMS
Log on to an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance using DMS.
In the navigation pane on the left, find the target instance and click the instance ID. Double-click the destination database. Right-click a table and select Batch Operations.
Select the tables for which you want to release space, and then choose .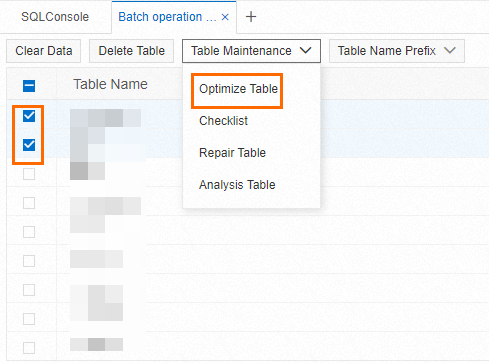
In the dialog box that appears, confirm that the information is correct and click Confirm.
FAQ
Why does the disk space of my ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance remain unchanged after I run the OPTIMIZE TABLE command?
Problem description
You follow an official ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL tutorial to delete a large amount of data using the DELETE command and then run the OPTIMIZE TABLE command to reclaim tablespace. Immediately after, you query the DATA_FREE field in information_schema.tables and find that the value is not updated. You might conclude that the disk space was not released and the operation was ineffective.
Cause
The disk space is actually released. The issue occurs because the MySQL table statistics information is not refreshed promptly. This issue is common in ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL 5.6, 5.7, and 8.0 instances that run a minor engine version earlier than 20250531. In these versions, running the OPTIMIZE TABLE command does not automatically update table and index statistics information. As a result, the DATA_FREE value in information_schema.tables is not updated and cannot accurately reflect the actual space usage. For more information, see Bug #117426: optimize table does not update table and index stats.
Solutions
Recommended solution: Upgrade the minor engine version to 20250531 (for MySQL 8.0)
This issue is fixed in ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL 8.0 minor engine version 20250531. This upgrade fixes an issue where the OPTIMIZE TABLE command does not update the table status. After you run the OPTIMIZE TABLE command, the statistics information is automatically refreshed, and the DATA_FREE value correctly reflects the actual space usage.
Temporary workaround: Force a refresh of statistics information (for scenarios where you cannot upgrade in the short term) If you cannot upgrade your database version in the short term, you can run the ALTER TABLE table_name ENGINE=InnoDB; command on a table on which the OPTIMIZE TABLE command has been executed. This command forcibly rebuilds the table and updates the statistics information. After the command is executed, the DATA_FREE value in information_schema.tables correctly displays the released space.
Why is disk space not released in my ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance after I run the DELETE command?
In ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, the DELETE statement only marks record locations or data pages as reusable. It does not change the disk file size. As a result, the tablespace is not immediately reclaimed. This behavior creates fragmentation that consumes instance storage space.
Two solutions are available: native DDL operations and DMS lock-free schema evolution. Before you use either solution, ensure that the instance has enough free space. This prevents the instance from being locked if its storage becomes full.
Use commands to manage fragmentation: Run DDL operations, such as OPTIMIZE TABLE or ALTER TABLE <table_name> ENGINE=InnoDB;, to reorganize table data and the index schema. This releases fragmented space.
Important Run native DDL commands during off-peak hours to prevent metadata locks from blocking other operations. For more information, see Considerations.
Use DMS lock-free schema evolution: To avoid metadata locks, use DMS lock-free schema evolution to reclaim fragmented table space.
Why is disk space not released in my ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance after I run the TRUNCATE or DROP command?
In ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, if disk space is not released after you execute a TRUNCATE or DROP operation, follow these steps:
Confirm space release logic
After you execute the TRUNCATE or DROP command, confirm whether the space is released by monitoring the disk usage of the instance. Typically, a decrease in disk usage reflects the proportion of the deleted table's size relative to the total instance space.
Avoid relying on outdated information
If you check the table size using information_schema.tables or the RDS console (), the tablespace might appear unchanged because of data update latency. Therefore, you should use disk usage as the primary metric.
Impact of asynchronous deletion
If the instance has an asynchronous deletion feature enabled, such as Alibaba Cloud's Purge Large File Asynchronously feature, the space that the table files occupy is not released immediately. Instead, a background process gradually cleans up the space. You must wait for this asynchronous process to complete. The disk space is released only after the process finishes.
