ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL provides two methods to upgrade the major database version. You can upgrade the database version directly in the console. You can also purchase a new ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance that runs a later version and use a Data Transmission Service (DTS) data migration task to migrate data from the original instance to the new one. This process indirectly upgrades the database version.
ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL does not support direct downgrades of the database version from the console. You can purchase an RDS instance that runs an earlier version and use DTS to migrate data from the instance with the later version to the instance with the earlier version. After you verify that the migration is successful, you can release the instance with the later version.
Select an upgrade method
Both Method 1: Directly upgrade the database version in the console and Method 2: Upgrade the database version using DTS support upgrades for all major MySQL versions. This includes upgrades from MySQL 5.5 to 5.6, 5.6 to 5.7, and 5.7 to 8.0. Before you upgrade the database, select a suitable upgrade method based on the following information:
If your instance belongs to one of the following four categories and its configuration meets the corresponding requirements, use Method 1: Directly upgrade the database version in the console.
NoteServerless instances do not support direct upgrades from the console. You must use Method 2: Upgrade the database version using DTS.
Cluster Edition (ESSD and premium performance disk)
Group replication restriction: You cannot upgrade Cluster Edition instances that use MySQL Group Replication (MGR).
Database proxy restriction (if applicable): The minor version of the database proxy must be 1.13.41 or later.
Instance status restriction: The instance must be in the Running state. The primary and secondary nodes must be healthy and have no replication delay.
Engine restriction: The database and all its tables must use the InnoDB storage engine.
The instance must not use a phased-out instance type.
High-availability Edition (ESSD and premium performance disk)
Database proxy restriction (if applicable): The minor version of the database proxy must be 1.13.41 or later.
Instance status restriction: The instance must be in the Running state. The primary and secondary nodes must be healthy and have no replication delay.
Engine restriction: The database and all its tables must use the InnoDB storage engine.
The instance must not use a phased-out instance type.
High-availability Edition (premium performance local disk)
Encryption restriction: The transparent data encryption (TDE) feature must be disabled. After TDE is enabled, it cannot be disabled. If TDE is enabled on your instance, you must use Method 2: Upgrade the database version using DTS.
Database proxy restriction (if applicable): The minor version of the database proxy must be 1.13.41 or later.
Instance status restriction: The instance must be in the Running state. The primary and secondary nodes must be healthy and have no replication delay.
Table quantity restriction: The number of tables cannot exceed 1 million.
Engine restriction: The database and all its tables must use the InnoDB storage engine.
Instance type restriction: The database version after the upgrade must support the original instance types of the primary and read-only instances. The instances must not use a phased-out instance type. For more information, see Primary ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance types.
Basic Edition (ESSD and premium performance disk)
Instance status restriction: The instance must be in the Running state.
Engine restriction: The database and all its tables must use the InnoDB storage engine.
The instance must not use a phased-out instance type.
If your instance does not belong to one of the preceding four categories or if TDE is enabled, use Method 2: Upgrade the database version using DTS.
If your instance belongs to one of the preceding four categories but its configuration does not meet the requirements, you can modify the configuration as described in the following table. Then, you can use either Method 1: Directly upgrade the database version in the console or Method 2: Upgrade the database version using DTS.
Problem
Solution
The instance is in a state other than Running, such as Restarting.
Wait for the current task to complete before you upgrade the database version.
The number of tables on a High-availability Edition instance with a premium performance local disk exceeds 1 million.
Delete redundant tables before the upgrade.
Some databases or tables do not use the InnoDB engine.
Run the
ALTER TABLE <table_name> engine=InnoDB;command to switch to the InnoDB engine.The instance uses a phased-out instance type.
Upgrade the instance type before you upgrade the database version. For more information, see Change instance configurations.
The minor version of the database proxy does not meet the requirements.
Upgrade the minor version of the database proxy to 1.13.41 or later. For more information, see Upgrade the minor engine version of a database proxy.
The storage type of the instance is standard SSD.
First, upgrade the standard SSD to an enterprise SSD (ESSD), and then upgrade the database version.
To upgrade the major database version of other database engines, see the following topics:
Method 1: Directly upgrade the database version in the console
Preparations
Understand the differences and benefits of the new version
Upgrade from 5.6 to 5.7: For information about feature differences, see Appendix 4: Feature differences between MySQL 5.7 and MySQL 5.6. For information about the benefits of the upgrade, see Appendix 2: Benefits of upgrading from MySQL 5.6 to MySQL 5.7.
Upgrade from 5.7 to 8.0: For information about feature differences, see Appendix 3: Feature differences between MySQL 8.0 and MySQL 5.7. For information about the benefits of the upgrade, see Appendix 1: Benefits of upgrading from MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0.
Understand the upgrade process and its impact
Version span restriction: You cannot upgrade across major versions. By default, the instance is upgraded to the latest minor version of the target major version. For example, you cannot directly upgrade an instance from MySQL 5.6 to MySQL 8.0. You must first upgrade it to MySQL 5.7, and then to MySQL 8.0.
Downgrade restriction: You cannot directly downgrade the version from the console. You can purchase an RDS instance that runs an earlier version and use DTS to migrate data from the instance with the later version to the instance with the earlier version. After you verify that the migration is successful, you can release the instance with the later version.
Upgrade process for instances with premium performance local disks: The system first upgrades the secondary node. After the upgrade is complete, a primary/secondary failover occurs. Then, the system upgrades the original primary node. The upgrade process causes a service interruption of 15 seconds. We recommend that you perform the upgrade during off-peak hours.
Upgrade process for instances with ESSDs: The system creates a new node and performs the upgrade on the new node. After the upgrade on the new node is complete, connections are switched to it. The upgrade process causes a service interruption of 15 seconds. We recommend that you perform the upgrade during off-peak hours.
Check the instance and database configurations
Check for reserved keywords: Check user-defined functions to make sure they do not use any reserved keywords.
Check full backups: Check whether a successful full data backup was created in the last week. If not, perform a full data backup.
Check the automatic reconnection mechanism: During the database upgrade, RDS performs an instance switchover. We recommend that you perform the upgrade during off-peak hours or ensure that your application has an automatic reconnection mechanism. For more information about the impact of an instance switchover, see Impact of an instance switchover.
Check the available storage space: Make sure you have enough free disk space before the upgrade. We recommend reserving at least 10 GB.
Adjust the log cleanup policy: Increase the retention period and the maximum storage usage percentage for local logs. For more information, see Modify the local log policy.
Back up instance parameters: To ensure the stability and performance of the new MySQL version, RDS deprecates some parameters from the old version. You can no longer view or modify these parameters after the upgrade. Before you perform a major version upgrade, back up the modification records of relevant parameters for future operations and audits.
For upgrades from 5.6 to 5.7 or from 5.7 to 8.0, you must perform the following additional checks:
Upgrade from 5.6 to 5.7
Check full-text indexes and version information: For databases on RDS for MySQL 5.6 instances with a minor version earlier than 20221130, full-text indexes are created in the system tablespace. Upgrading to version 5.7 might damage the tablespace. If your instance runs an earlier minor version, first upgrade it to the latest minor version of RDS for MySQL 5.6, and then upgrade the major database version. For more information, see the FAQ.
Upgrade from 5.7 to 8.0
Check feature compatibility: If the stored procedures, triggers, views, or functions in your database use features that are not supported by MySQL 8.0, modify them before the upgrade. Otherwise, the upgrade will fail.
Check system table dependencies: Check if your services depend on MySQL 5.7 system tables (tables in the sys, mysql, information_schema, and performance_schema databases). Some system tables in MySQL 5.7 are changed during the upgrade to 8.0. For example, tables might be removed, renamed, or have their schemas altered. If your services depend on these tables, they may encounter errors.
Check data type compatibility: RDS for MySQL 8.0 no longer supports some data types from older versions. If a table contains fields with data types that are not supported in MySQL 8.0, you must resolve this issue by running
REPAIR TABLEor by performing a logical export and import before the upgrade. For more information, see Preparing Your Installation for Upgrade.Check
commentvalues: Minor versions of MySQL 8.0 from 20221231 onward introduce theloose_upgrade_clear_invalid_commentparameter. When this parameter is set toON(the default value), garbled characters in the comments of tables, fields, and indexes are automatically cleared during the upgrade to prevent failure. Therefore, before the upgrade, check if thecommentvalues in your database tables contain garbled characters. If they do, thecommentwill be cleared.Check stored procedures: If the stored procedures or functions in your database contain garbled characters, correct them before the upgrade to prevent failure.
Check time data types from MySQL 5.5 and earlier: If your database contains tables with time data types from MySQL 5.5 or earlier, rebuild the tables before upgrading to MySQL 8.0 to prevent failure.
Run the following SQL statements to check if your database instance contains tables with time data types from MySQL 5.5 or earlier:
# Show old time data types. SET SESSION show_old_temporals= ON; # Query for tables that contain old time data types. SELECT TABLE_NAME, COLUMN_NAME, COLUMN_TYPE FROM information_schema.columns WHERE COLUMN_TYPE IN ("time /* 5.5 binary format */ ", "timestamp /* 5.5 binary format */", "datetime /* 5.5 binary format */ ");If a table contains time data types from MySQL 5.5 or earlier, you can run the following command to rebuild the table schema:
# Rebuild the table. ALTER TABLE <table_name> FORCE;
Pre-upgrade testing and simulation
Syntax testing: Before the upgrade, create a new RDS instance with the later version to test for syntax compatibility. This helps avoid issues where syntax or features from the earlier version are not supported after the upgrade.
Upgrade simulation: Before the upgrade, clone the original instance and use the cloned instance to test the upgrade. After you confirm that all features work as expected, upgrade the original instance.
Post-upgrade notes
Restore an instance to the old version: You can use a cloud disk backup from the old version to restore an instance to that version. This is not supported for instances with premium performance local disks.
Restore an instance to the new version: You cannot use backup sets from the old version to restore an instance to the new version. To perform a restoration, use a backup set created after the instance was upgraded.
Procedure
Select an upgrade method based on the upgrade scenario:
Upgrade method | Upgrade scenario |
Perform a pre-check and then upgrade |
|
Direct upgrade |
|
Perform a pre-check and then upgrade
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region where your instance is located. Then, click the instance ID.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Major Version Upgrade to go to the Upgrade Check page.
From the Select upgrade version drop-down list, select the target version number and click Create upgrade check report. For more information about the report, see Description of the major version upgrade check report.
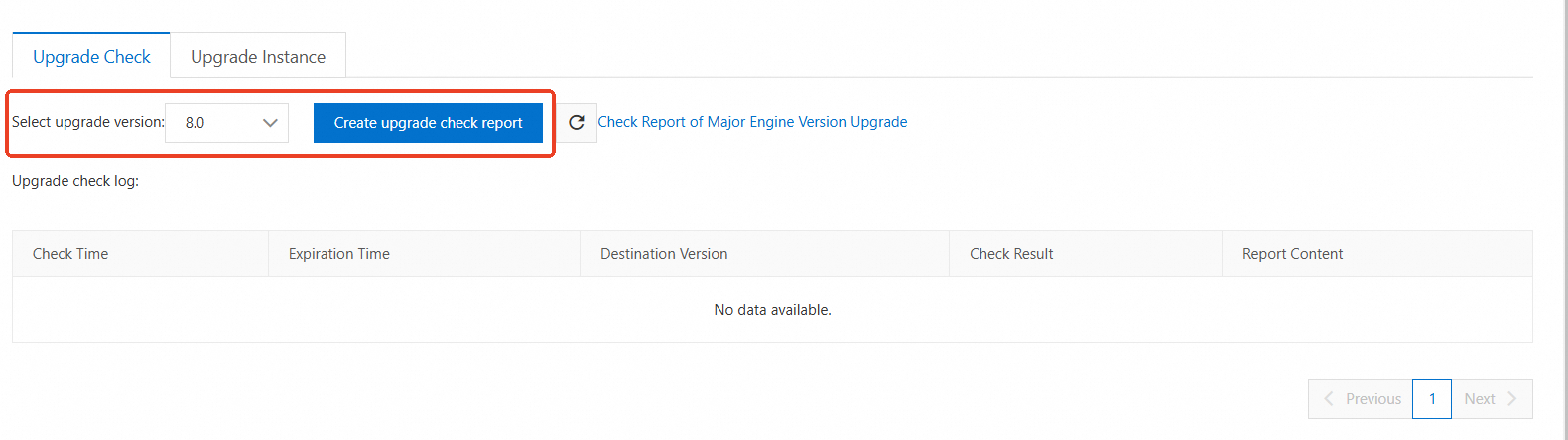
After the check is complete and you confirm that there are no risks, switch to the Upgrade Instance tab.
From the Select upgrade version drop-down list, select the target version number and click Upgrade Instance.
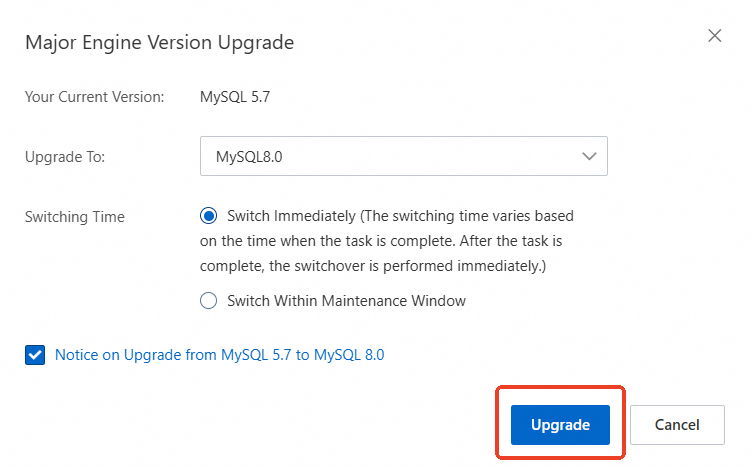
In the Major Engine Version Upgrade dialog box, confirm the target version, select a Switching Time, and click Upgrade.
Direct upgrade
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region where your instance is located. Then, click the instance ID.
In the section, click Upgrade Major Engine Version.
 Note
NoteIf this option is not available, check whether your instance meets the upgrade requirements.
In the dialog box that appears, select Switch Immediately or Switch Within Maintenance Window, and then click Yes.
Switch Immediately: Starts the upgrade immediately.
Switch Within Maintenance Window: Performs the upgrade within the specified maintenance window. You can also click Settings next to Maintenance Window to quickly change the maintenance window.
NoteDuring the upgrade, the instance status is Migrating Version.
Method 2: Upgrade the database version using DTS
For instances that do not support a direct upgrade from the console, you can create a new instance with a later database version. Then, use a DTS data migration task to migrate data from the original instance to the new one. This indirectly upgrades the database version. This process involves the following steps:
Example: You have a MySQL 5.7 instance with TDE enabled, which cannot be directly upgraded from the console. In this case, you can create a new instance that runs MySQL 8.0, migrate the data from the original instance to the new one, and finally release the original instance. This indirectly upgrades the database version.
After a cross-version data migration, test for compatibility and monitor the instance for a period of time. After you confirm that everything is normal, release the original instance.
Appendix 1: Benefits of upgrading from MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0
Improves security and provides greater flexibility in account management.
Supports the creation and management of resource groups.
Enhances the features of the InnoDB storage engine.
Adds support for new character sets, data types, syntax, new backup locks, and optimizer_switch flags.
Enhances JSON and XML functionality.
Enhances the features of the optimizer.
Improves replication performance.
Supports the creation of multi-valued indexes and derived condition pushdown optimization.
Supports reading MySQL grant tables.
Supports resource allocation control.
Appendix 2: Benefits of upgrading from MySQL 5.6 to MySQL 5.7
Adds features such as password management, account locking, and encrypted connections to improve database security.
Supports Online DDL operations, such as renaming an index using RENAME INDEX.
Improves the scalability of the InnoDB engine and the performance of temporary tables for faster data loading.
Supports JSON.
Supports Index Condition Pushdown (ICP) for partitioned tables and new InnoDB spatial indexes.
Optimizes most parsers, optimizers, and cost models to improve database maintainability, scalability, and performance.
Expands the range of supported character sets, including the GB18030 character set specified by the Chinese national standard.
Provides the ngram full-text parser plugin, which supports Chinese, Japanese, and Korean.
Optimizes source dump threads to reduce lock contention and increase source throughput.
Significantly reduces replication delay.
Adds the sys system database, which provides multiple metrics and reduces storage usage, significantly improving database usability.
Appendix 3: Feature differences between MySQL 8.0 and MySQL 5.7
The following table lists only some of the important differences between MySQL 8.0 and 5.7. For more information about other differences, see MySQL Release Notes.
Feature | 5.7 | 8.0 |
GRANT ... IDENTIFIED BY PASSWORD syntax | Supported | Not supported |
PASSWORD() function | Supported | Not supported |
FLUSH QUERY CACHE and RESET QUERY CACHE syntax | Supported | Not supported |
Parameters for the SQL_MODE system variable: DB2, MAXDB, MSSQL, MYSQL323, MYSQL40, ORACLE, POSTGRESQL, NO_FIELD_OPTIONS, NO_KEY_OPTIONS, NO_TABLE_OPTIONS | Supported | Not supported |
Default automatic sorting for GROUP BY syntax | Support | Not supported |
Syntax that contains the EXTENDED or PARTITIONS keyword | Supported | Not supported |
Encryption functions such as ENCODE(), DECODE(), and ENCRYPT() | Supported | Not supported |
Functions related to spatial analysis | Supported | Not supported |
Functions that previously accepted WKB string or geometry arguments but no longer accept geometry arguments | Supported | Not supported |
Parsing \N as NULL | Support | Not supported |
PROCEDURE ANALYSE() function | Supported | Not supported |
Creating partitioned tables using the NDB storage engine | Supported | Not supported |
Compressing temporary tables using the InnoDB storage engine | Supported | Not supported |
JSON_APPEND() function | Supported | Not supported |
Support for placing table partitions in a shared tablespace | Supported | Not supported |
ALTER TABLE ... UPGRADE PARTITIONING syntax | Supported | Not supported |
Appendix 4: Feature differences between MySQL 5.7 and MySQL 5.6
The following table lists only some of the important differences between MySQL 5.7 and 5.6. For more information about other differences, see MySQL Release Notes.
Feature | 5.6 | 5.7 |
CREATE...AS SELECT in GTID mode | Support | Not supported |
Using temporary tables in transactions in GTID mode | Supported | Not supported |
Specifying a partition key in a partitioned table | Supported | Not supported |
ENGINE_NO_CACHE syntax | Supported | Not supported |
Invisible Indexes | Support | Not supported |
UPDATE non_affected_rows INSERT syntax | Supported | Not supported |
Proxy-related commands | Uses the SET command method | Uses the Call Procedure mode |
TokuDB, Sphinx, RocksDB, and Memory engines | Supported | Not supported |
str_ord() function | Supported | Not supported |
raiseerror() function | Supported | Not supported |
OPTIMIZE TABLE table ASYNC | Support | Not supported |
ENGINE_NO_CACHE | Supported | Not supported |
INFORMATION.TABLE_UTILIZATION table | Support | Not supported |
The requesting_thd_id and blocking_thd_id columns in the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_LOCK_WAITS table | Supported | Not supported |
INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_RSEG table | Supported | Not supported |
INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_IO_STATUS table | Supported | Not supported |
Column compression feature | Supported | Not supported |
Query Plan Cache | Supported | Not supported |
Limit + Union syntax | Parentheses are not required. | Parentheses are required. |
SHOW FULL PROCESSLIST syntax | In MySQL 5.7, the memory and query_memory columns are removed from the result. | |
max_statement_time and max_execution_time | In MySQL 5.7, max_statement_time is removed, and only max_execution_time is retained. | |
RDS_SQL_MAX_AFFECTED syntax | In MySQL 5.7, you can no longer use RDS_SQL_MAX_AFFECTED to limit the number of records affected by a single UPDATE or DELETE statement. Use the rds_sql_max_affected_rows variable instead. | |
Concurrency performance optimization adjustments | In MySQL 5.7, the following parameters are no longer supported for concurrency control:
| |
Adjustments to connection count variables | The following variables are removed in MySQL 5.7:
| |
Replication-related adjustments |
| |
Log-related adjustments | MySQL 5.7 error log adjustments:
| |
Old time data types ( | Before version 5.6.4, old time data types did not support microseconds. | Time data types support microsecond precision. Important During an upgrade from 5.6 to 5.7, the system detects and rebuilds tables that contain fields with old time data types. This slows down the upgrade process. |
Appendix 5: Feature differences between MySQL 5.5 and MySQL 5.6
The following table lists only some of the important differences between MySQL 5.5 and 5.6. For more information about other differences, see MySQL 5.6 Reference Manual.
Feature | MySQL 5.5 | MySQL 5.6 |
Full-text index | Not supported | Supported |
InnoDB online DDL | Not supported | Partially supported |
REDO | Supports a maximum of 4 GB | Supports a maximum of 512 GB |
Dirty page flushing | Single-threaded | Uses a separate flushing thread |
Purge | Single-threaded | Multi-threaded |
EXCHANGE PARTITION | Not supported | Supported |
Explicit partition selection in DML | Not supported | Supported |
INFORMATION_SCHEMA | MySQL 5.6 provides more information about the buffer pool and more metadata about tables, indexes, and fields. | |
PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | Performance Schema in MySQL 5.6 adds more monitoring information and viewing formats. | |
Replication | Replication enhancements and changes in MySQL 5.6 include the following:
Important After an RDS for MySQL instance is upgraded from 5.5 to 5.6, it automatically switches to GTID-based replication mode. | |
Optimizer | MySQL 5.6 enhances the optimizer with features including the following:
| |
Not supported | Supported | |
Not supported | Supported | |
Not supported | Supported | |
Not supported | Supported | |
Not supported | Supported | |
FAQ
Q: Why does an instance switchover occur during the upgrade? Are there other serious risks?
A: To ensure service stability, instances with premium performance local disks are upgraded by first upgrading the secondary node and then performing a switchover. Instances with ESSDs are upgraded by creating a new node and then performing a switchover. There are no other serious risks. For more information about the impact of a primary/secondary failover, see Impact of a primary/secondary failover.
Q: Are the primary and secondary nodes upgraded at the same time?
A: When you upgrade a high-performance local disk, the secondary instance is upgraded first, followed by the primary instance.
Q: How do I upgrade a Basic Edition instance that runs MySQL 5.7 with standard SSDs?
A: You cannot directly upgrade this type of instance. To upgrade a Basic Edition instance that runs MySQL 5.7 with standard SSDs, you must first change the storage type from standard SSD to ESSD, and then upgrade the database version.
Q: Is the parameter template retained after the database version is upgraded?
A: It depends. If the instance uses a system parameter template before the upgrade, it is automatically switched to the corresponding system parameter template for the new version. For example, an instance using the MySQL_InnoDB_5.7_High-availability_Performance parameter template is switched to the MySQL_InnoDB_8.0_High-availability_Performance parameter template after an upgrade from MySQL 5.7 to 8.0. However, if the instance uses a custom parameter template, the parameter template is not retained after the upgrade.
Q: Can I modify the instance during the database version upgrade?
A: No, you cannot. You can perform other operations on the instance only after the upgrade is complete.
Q: Does the database version support automatic upgrades?
A: No, it does not. Automatic major version upgrades are not supported.
Q: Can I downgrade the database version?
A: No, you cannot directly downgrade the version from the console. To downgrade, you can purchase an instance with an earlier version and use DTS to migrate data from the instance with the later version to the new instance. After the migration is complete, you can release the instance with the later version. For more information, see Data migration between RDS instances.
Q: When I upgrade an RDS for MySQL instance from 5.6 to 5.7 or from 5.7 to 8.0, the upgrade fails. It shows the message "The current instance has a full-text index and its minor version is earlier than 20221130. Please upgrade the minor version before deleting and rebuilding the full-text index" or "The current instance contains a full-text index built in the system tablespace. Please delete and rebuild the corresponding full-text index before proceeding with the upgrade." What is the cause and solution?
A: The cause and solution are as follows:
Cause
Due to a historical issue in MySQL, when you create a full-text index on an early version of MySQL 5.6, it is built in the system tablespace. When you upgrade to version 5.7 or 8.0, a full-text index in the system tablespace might cause tablespace corruption. Therefore, you must resolve this issue before the upgrade to prevent data corruption and inaccessibility.
NoteThis issue was fixed in RDS for MySQL 5.6 version 20221130. Full-text indexes are now built in a separate tablespace.
Solution
ImportantFull-text indexes on earlier versions of RDS for MySQL 5.6 are created in the system tablespace. Therefore, make sure that the version you are upgrading from is RDS for MySQL 5.6 20221130 or later before you upgrade to RDS for MySQL 5.7. If you are using an earlier version, upgrade to the latest version of RDS for MySQL 5.6 first.
Based on the table name in the prompt, delete the full-text index that was built in the system tablespace.
# Delete the full-text index. ALTER TABLE $table_name DROP INDEX $fts_name;Re-create the full-text index.
# Re-create the full-text index. ALTER TABLE $table_name ADD FULLTEXT INDEX $fts_name;After you create the index, you can run the following SQL statement to check the full-text indexes on the current instance. The statement returns any full-text indexes that are built in the system tablespace. If the query returns an empty result, the upgrade from RDS for MySQL 5.6 to RDS for MySQL 5.7 will not fail due to this issue.
# Query for full-text indexes built in the system tablespace. SELECT NAME FROM information_schema.INNODB_SYS_TABLES WHERE TABLE_ID IN ( SELECT CONV(SUBSTRING_INDEX(SUBSTRING_INDEX(NAME, '_', -4),'_', 1),16,10) FROM INNODB_SYS_TABLES WHERE NAME LIKE '%fts_00000000%' AND SPACE = 0);
Q: When I upgrade an RDS for MySQL instance from 5.7 to 8.0, the error
267 - Illegal mix of collations (utf8mb4_general_ci,IMPLICIT) and (utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci,IMPLICIT) for operation '='is reported. How do I handle this?A: Check the character set and collation in MySQL. If you are using utf8mb4_general_ci, run the following SQL statements to change it to utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci.
# Modify the character set and collation of the database. ALTER DATABASE database_name CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci; # Modify the character set and collation of the table. ALTER TABLE table_name CONVERT TO CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci; # Modify the character set and collation of the field. ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE column_name column_name type CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;If you create a table with the utf8mb4_general_ci collation in MySQL 5.7 and then upgrade to MySQL 8.0, the system uses utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci as the default collation. If you run a query that compares a column that uses utf8mb4_general_ci with a column that uses utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci, MySQL cannot process the two different collations, which results in an error.
Q: Is the transient connection time during a major version upgrade always 15 seconds, regardless of whether there are read-only instances?
A: Yes, it is. We recommend that you perform the upgrade during off-peak hours.
Related API operations
API operation | Description |
Upgrades the major database version of an RDS instance. |