Quick BI supports single-table models and multi-table models. Multiple tables can be associated or merged. This topic describes how to build a model.
Before you start
You have created a dataset. For more information, see Create a dataset.
Background information
Association
Quick BI supports LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN, INNER JOIN, and FULL JOIN operations. The following example uses a student table and a course score table to describe the four join methods for building models.

The preceding figure shows only the principles of the JOIN operations. When you join tables, the original columns of the tables that you join are retained.
Merging
Quick BI supports merging between data tables. The following example uses provincial sales data to describe three scenarios of table merging.

Limits
You can join tables from different data sources only in Quick BI Enterprise Standard.
To join or merge tables from different data sources, you must enable the Quick engine extraction acceleration feature. You can go to the Data Source Function Item List to view the data sources that support the extraction acceleration feature.
MySQL data sources do not support Full Outer Join.
You can configure a maximum of five layers (five association nodes) for table association. There is no limit on the number of associations in each layer.
You can merge a maximum of five tables.
In API data sources, only data sources in extraction mode can be associated and merged. Direct connection mode supports only single-table modeling.
Select a data source and a data table
When you create a dataset by using Procedure of Entry 4, the data table of the current data source is selected by default. You can manually modify the data source. For other entries, you need to manually select a data source and a data table.
After you select a data source, you can move the pointer over a data table in the data table list on the left side and click the
 icon on the right side to view the details of the data table.
icon on the right side to view the details of the data table.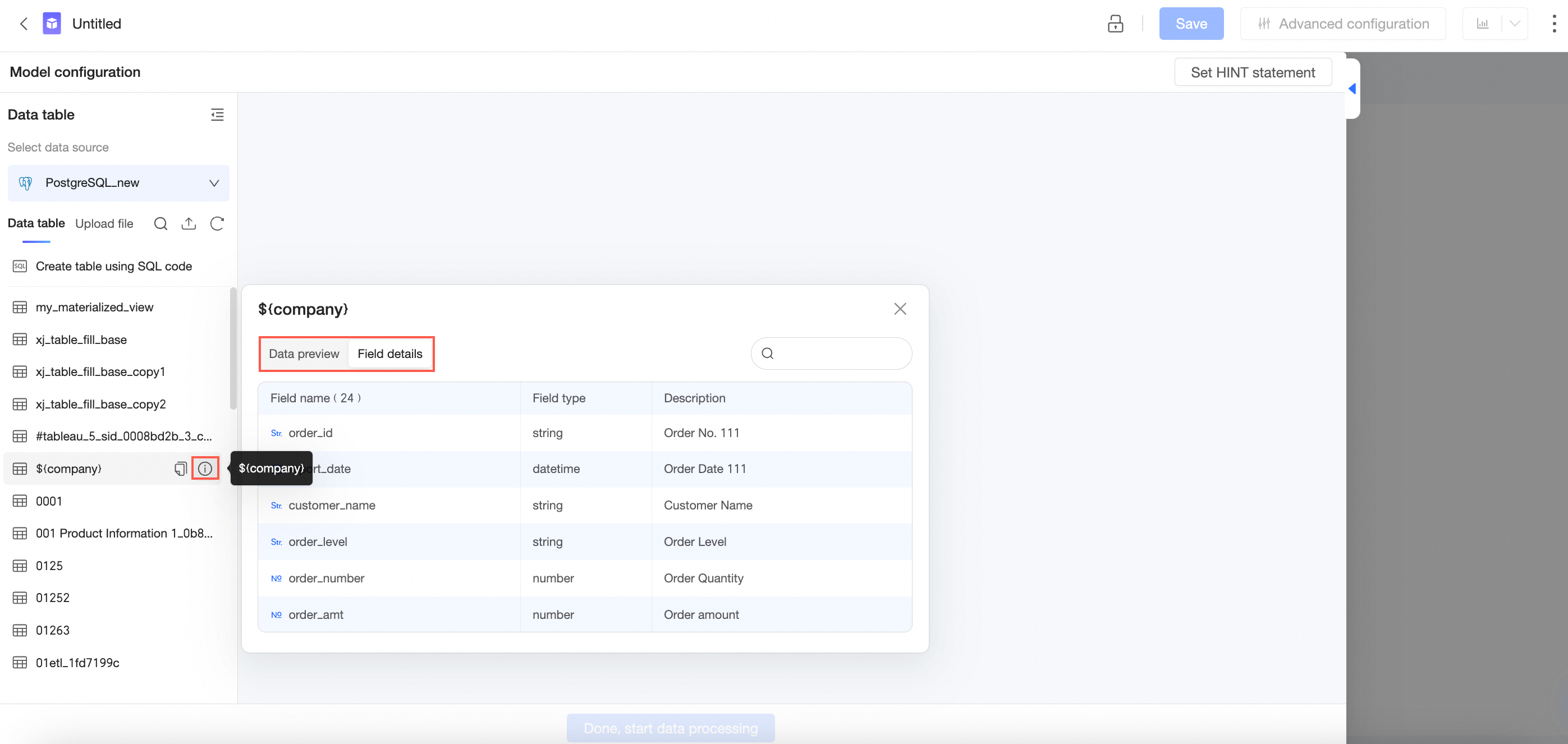
You can move the pointer over a data table and click the
 icon to copy the name of the data table.
icon to copy the name of the data table.Double-click a data table or drag it to the canvas. You can also use Use Custom SQL Statement to Create a Dataset to create a table.
After you select a data table, you can view Table Details.
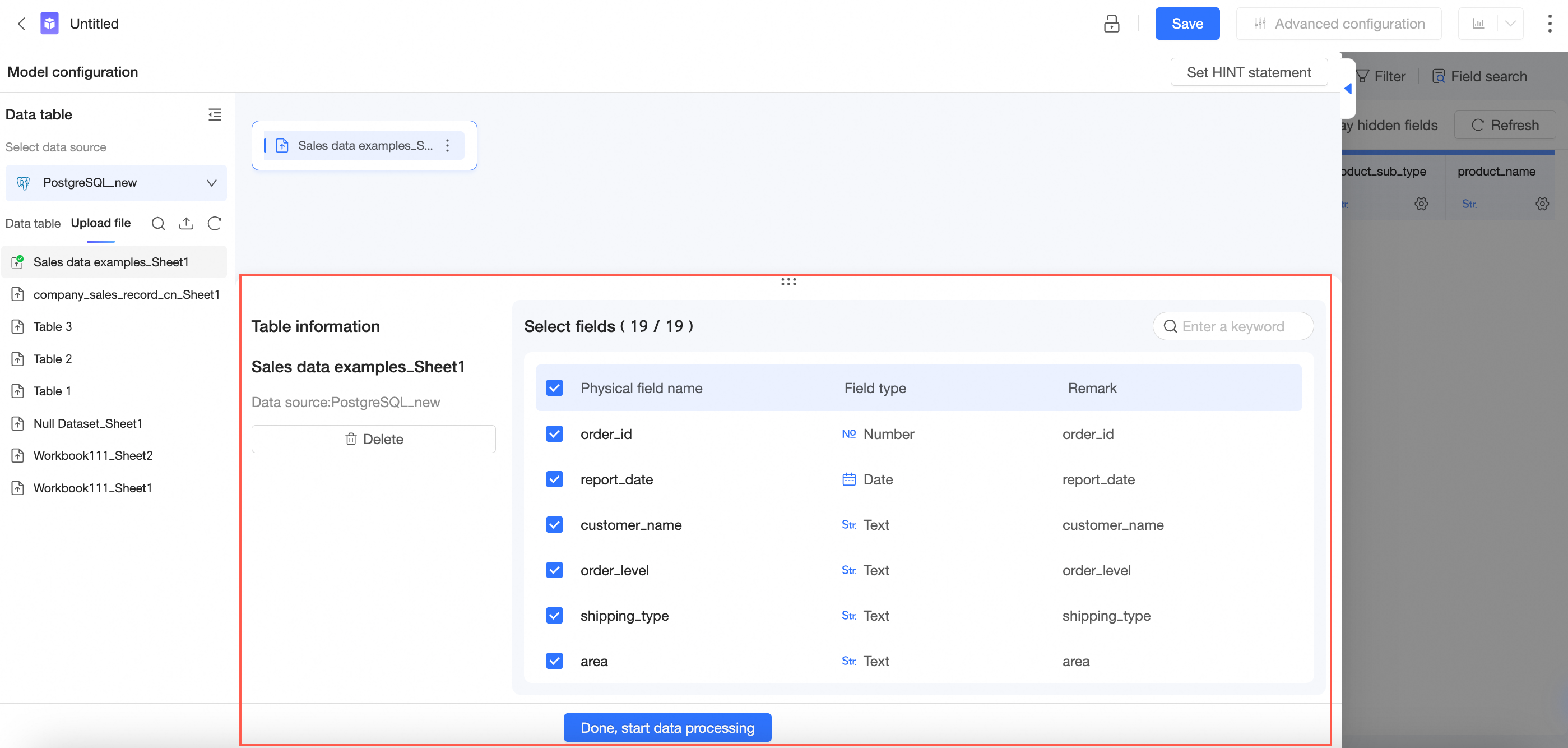
On the Table Details page, you can select fields.
When you no longer need a data table, you can delete it.
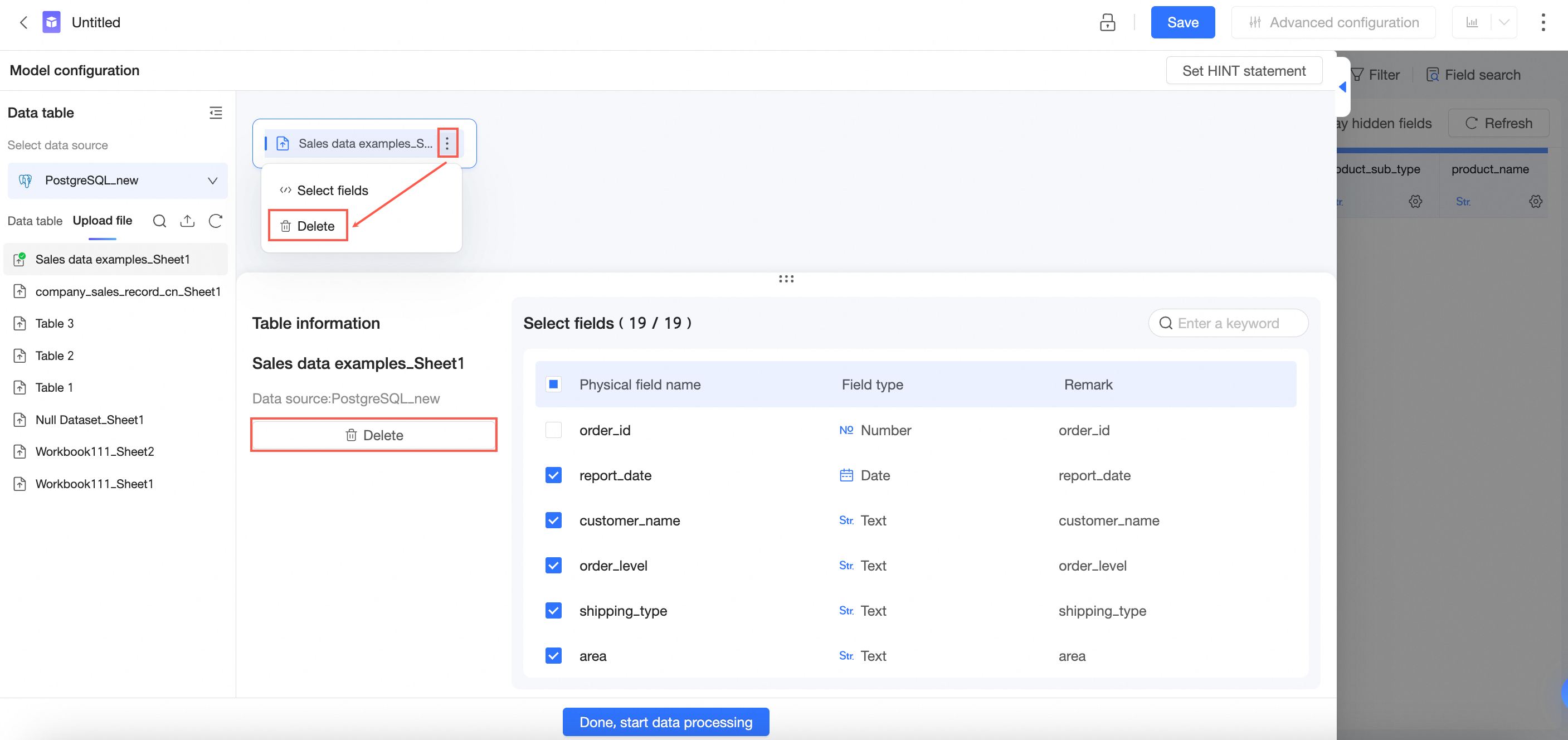
Association
Procedure
Select a data source.
Select or create tables to associate.
You can associate a data table with a data table, associate a data table with a table created by using SQL code, associate a table created by using SQL code with a data table, or associate a table created by using SQL code with a table created by using SQL code.
NoteFor information about how to edit SQL code, see Use Custom SQL Statement to Create a Dataset.
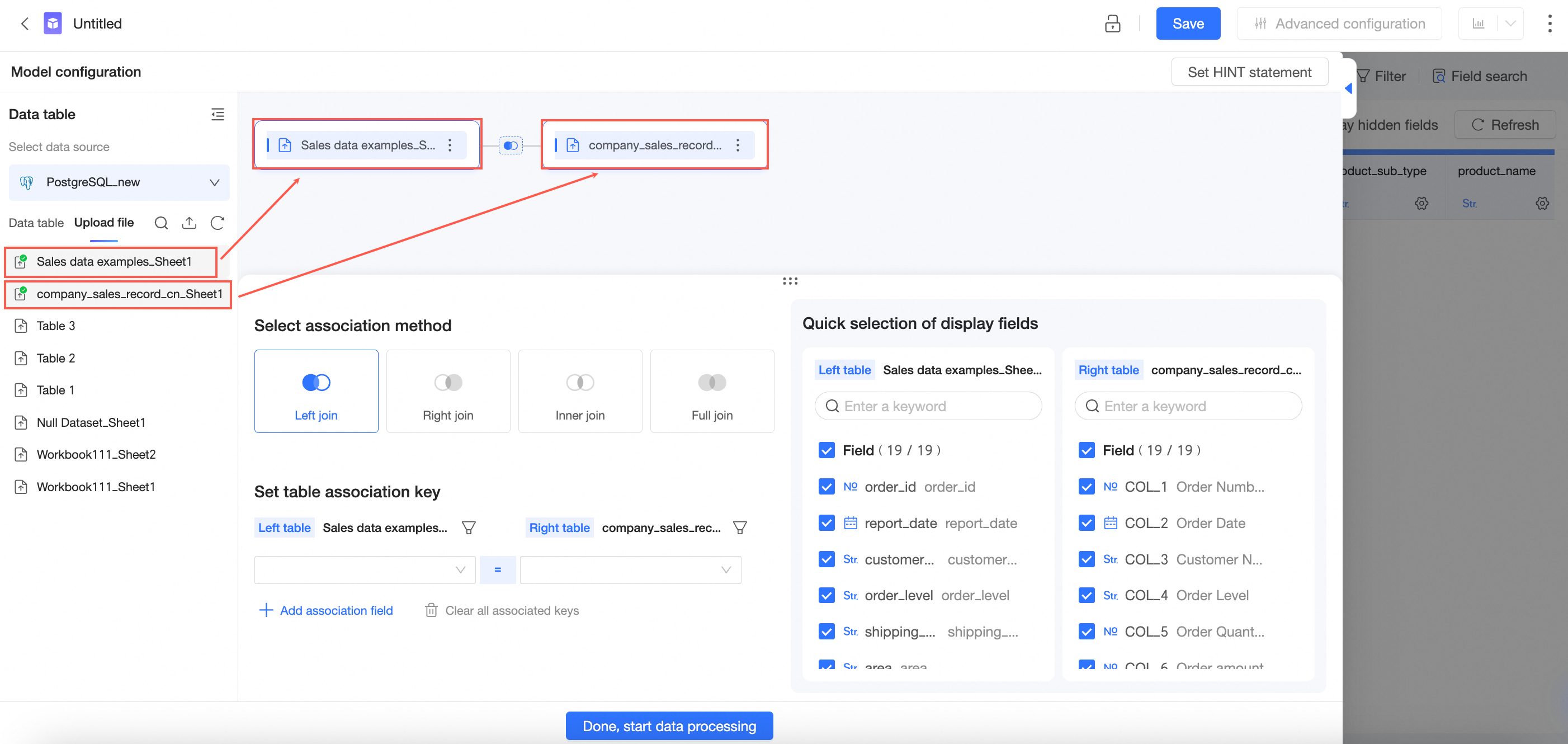
Associate a data table with a data table
On the dataset edit page, follow the steps that are shown in the following figure to drag tables to the canvas.
Associate a data table with a table created by using SQL code
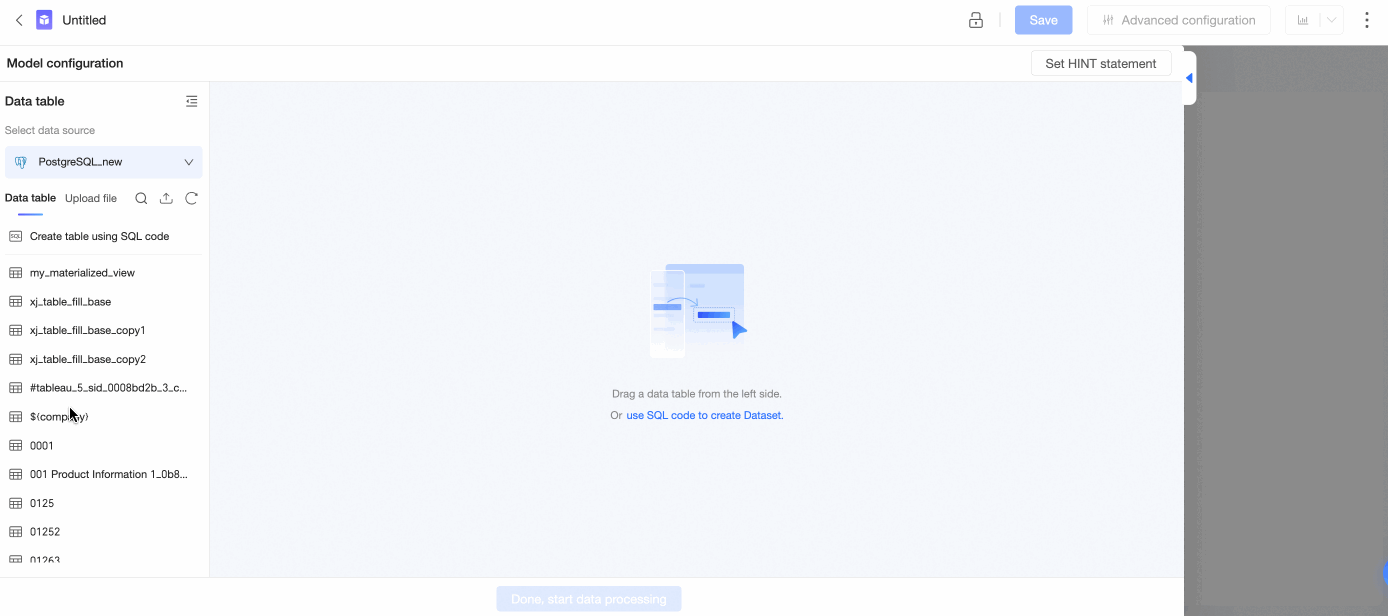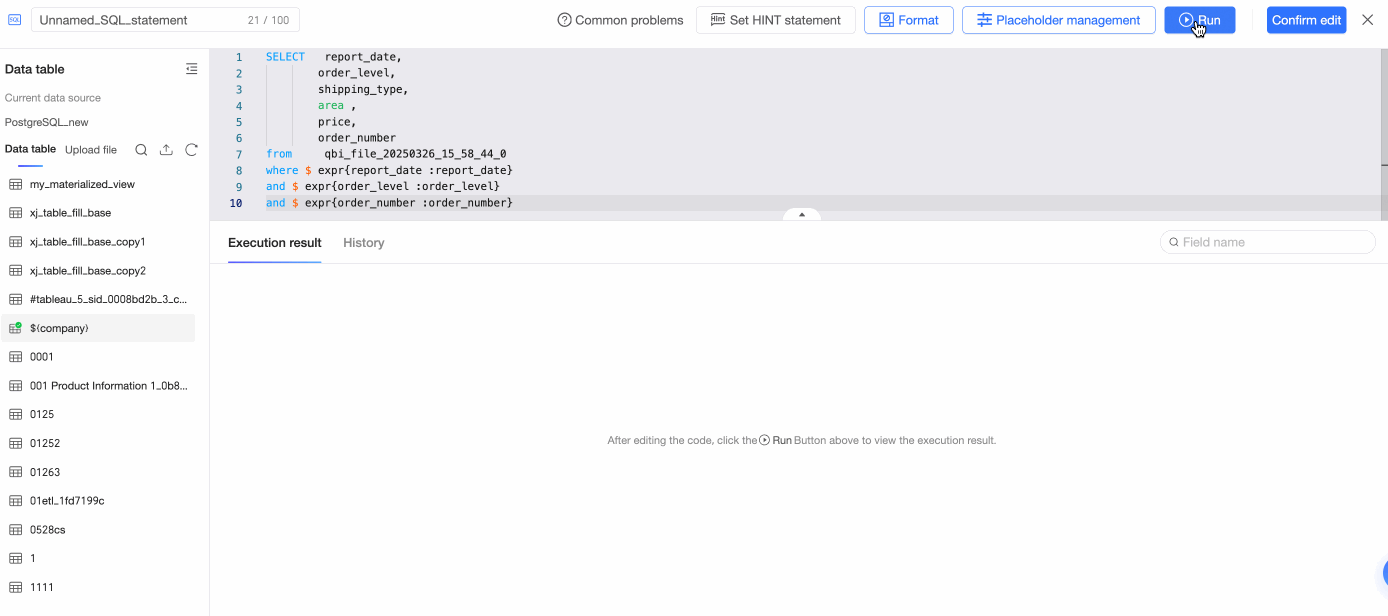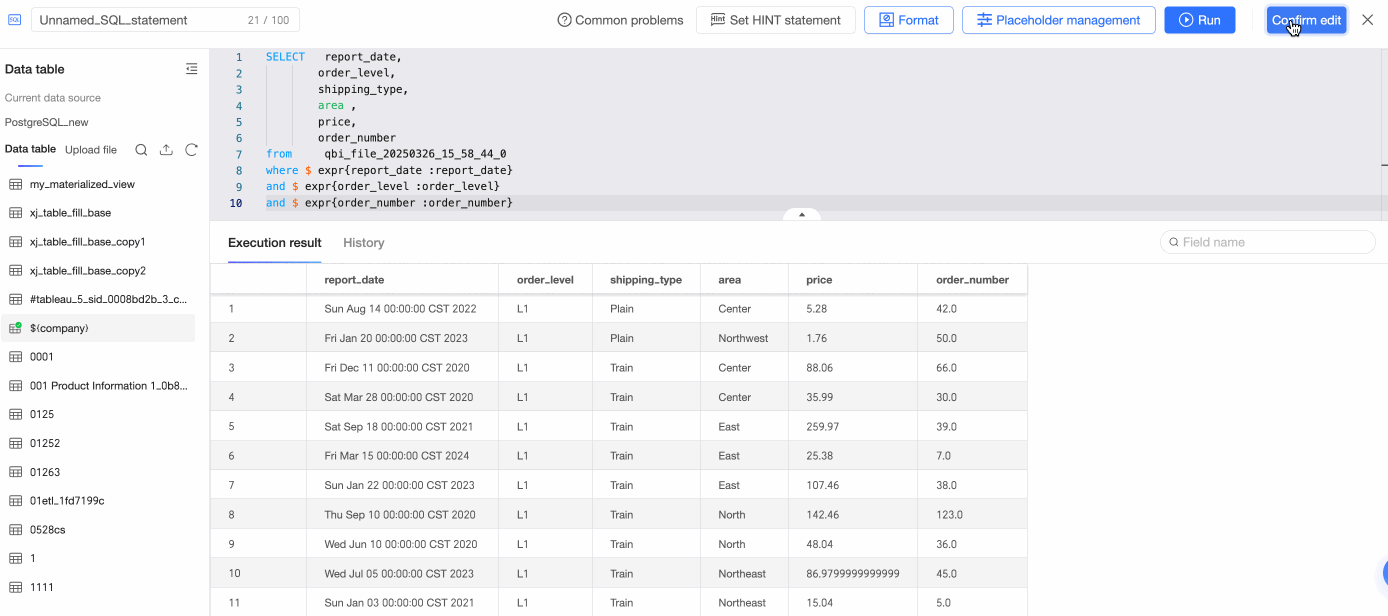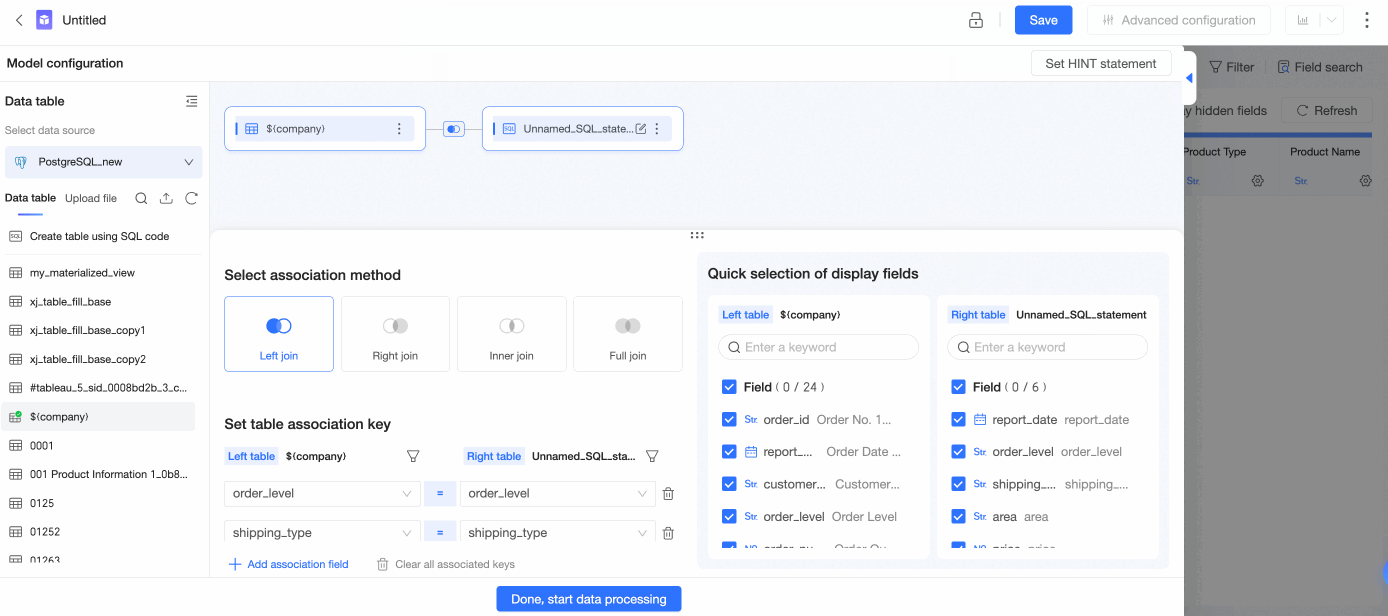
Double-click a data table or drag it to the canvas.
Double-click Create Table by Using SQL Code or drag it to the canvas.
On the SQL code editing page, enter SQL statements, click Run, and confirm the edits to create the table.
Associate a table created by using SQL code with a data table
Click Use SQL Code to Create a Dataset, enter SQL statements, click Run, and confirm the edits to create the table.
Double-click a data table or drag it to the canvas.
Associate a table created by using SQL code with a table created by using SQL code
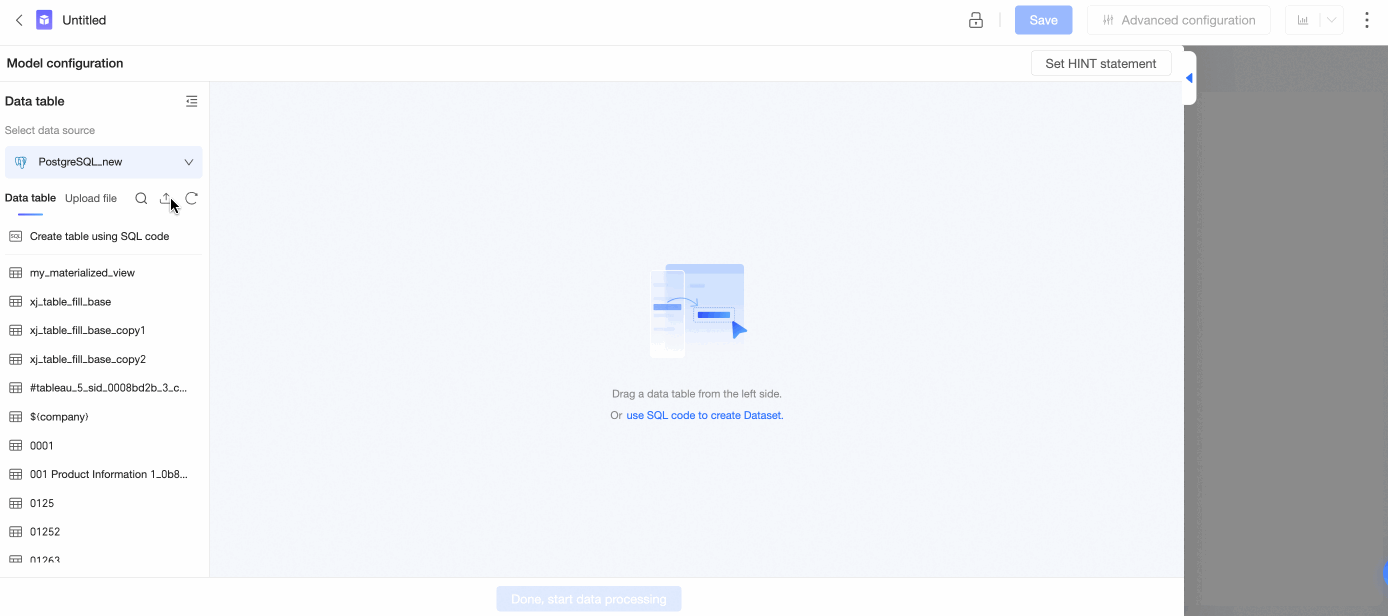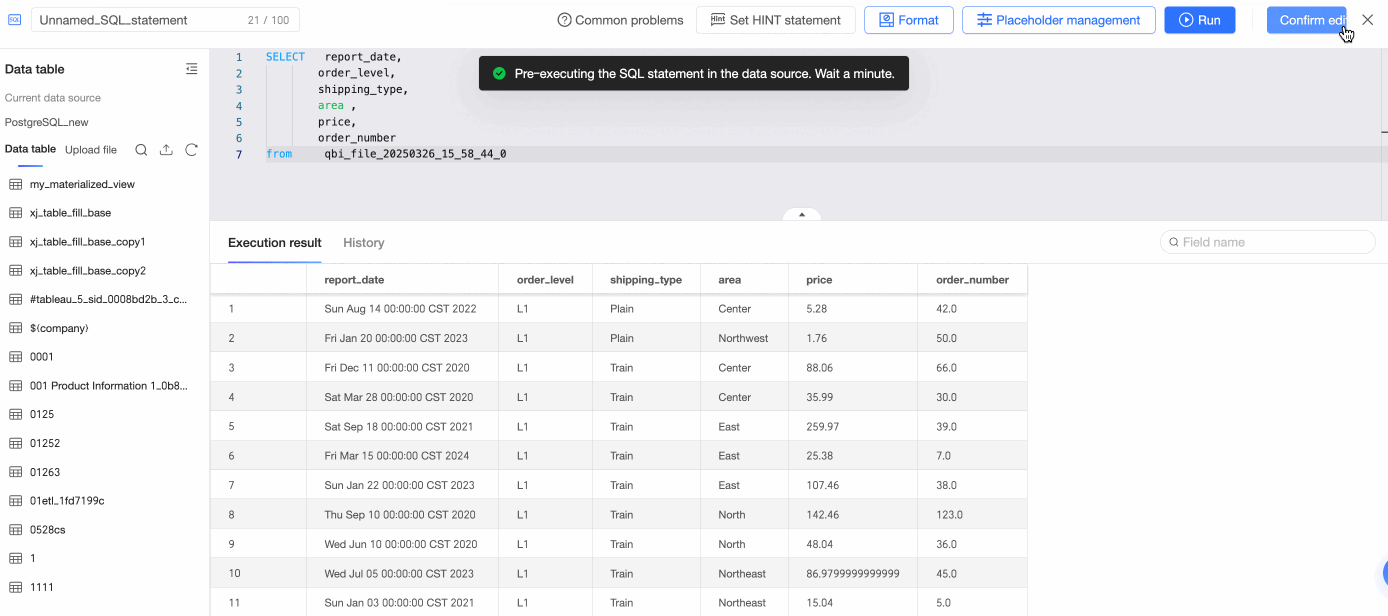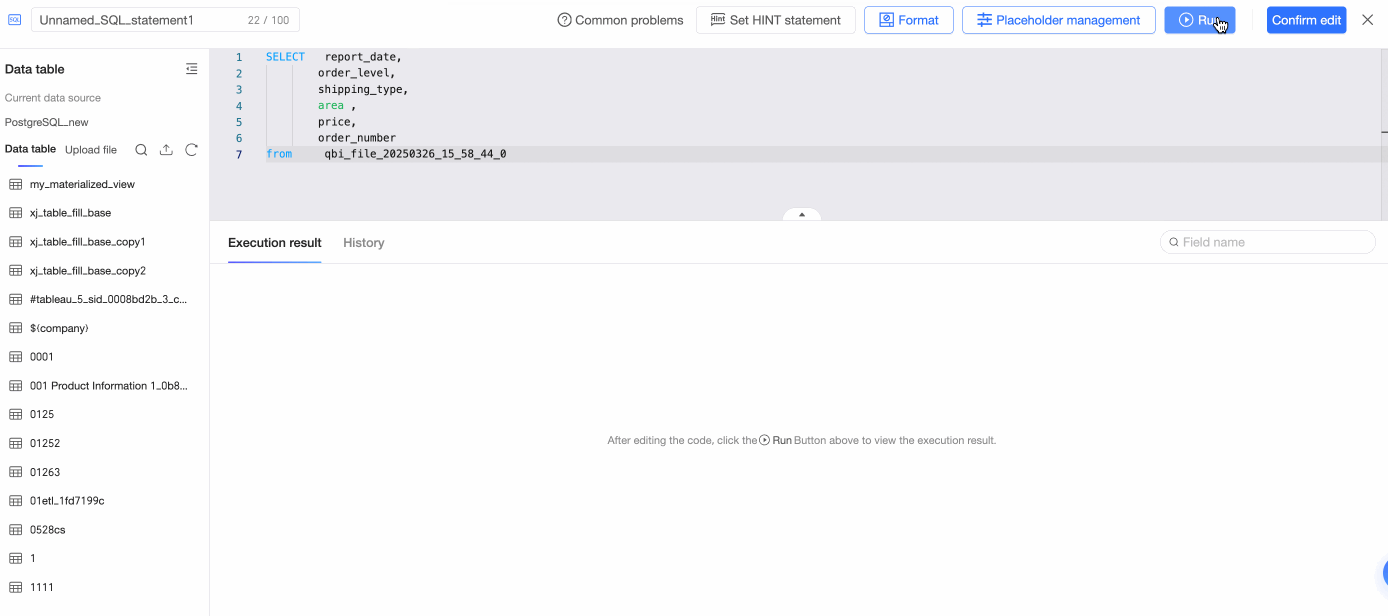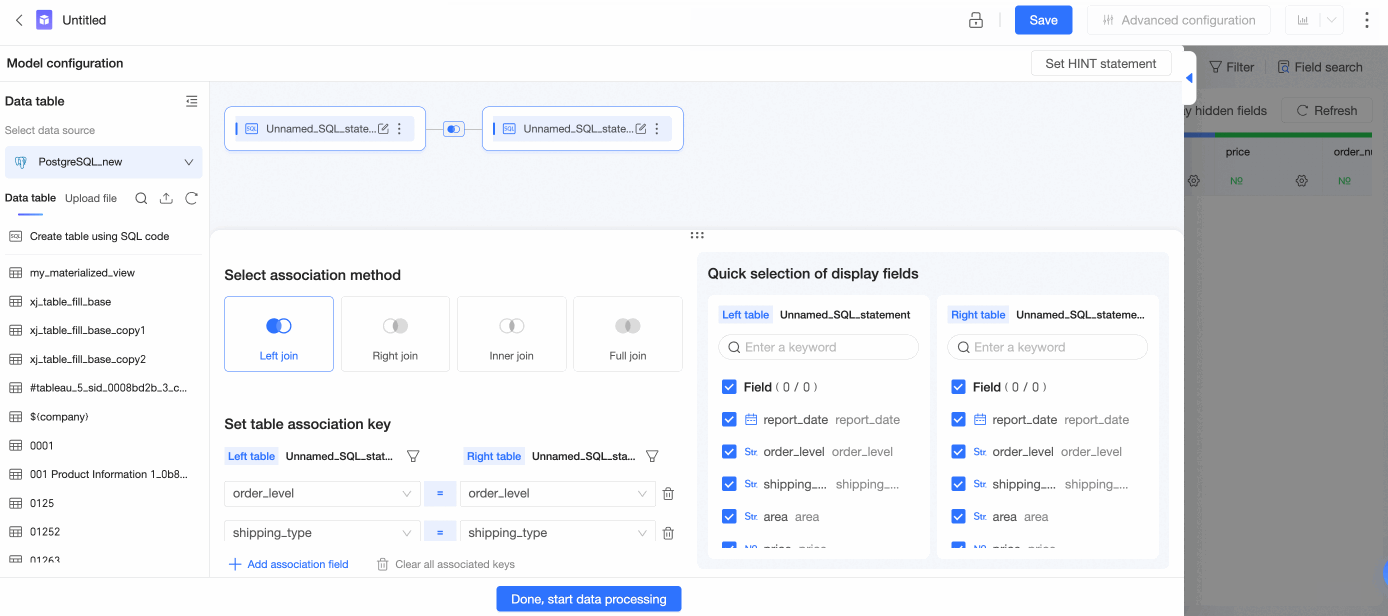
Click Use SQL Code to Create a Dataset, enter SQL statements, click Run, and confirm the edits to create the table.
Double-click Create Table by Using SQL Code or drag it to the canvas.
On the SQL code editing page, enter SQL statements, click Run, and confirm the edits to create the table.
You can select fields based on your business requirements.
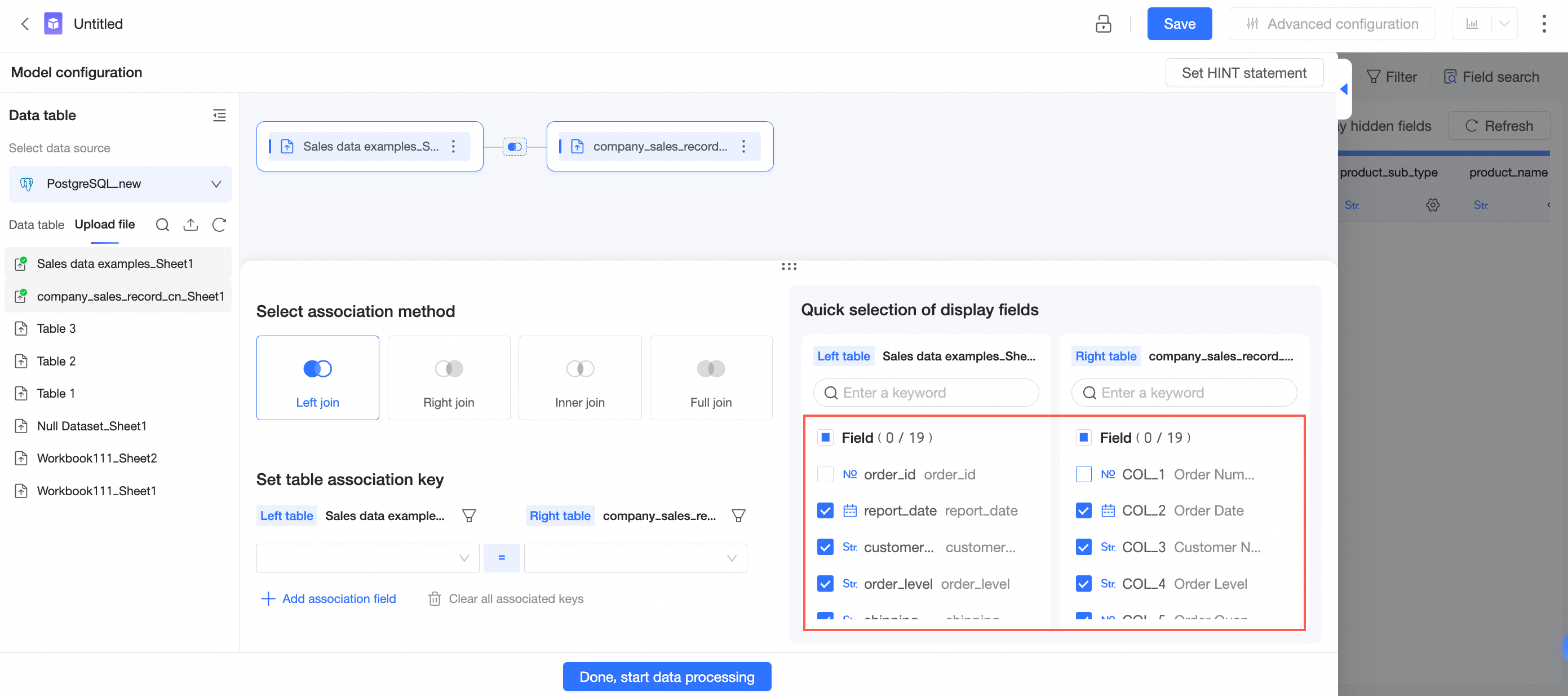
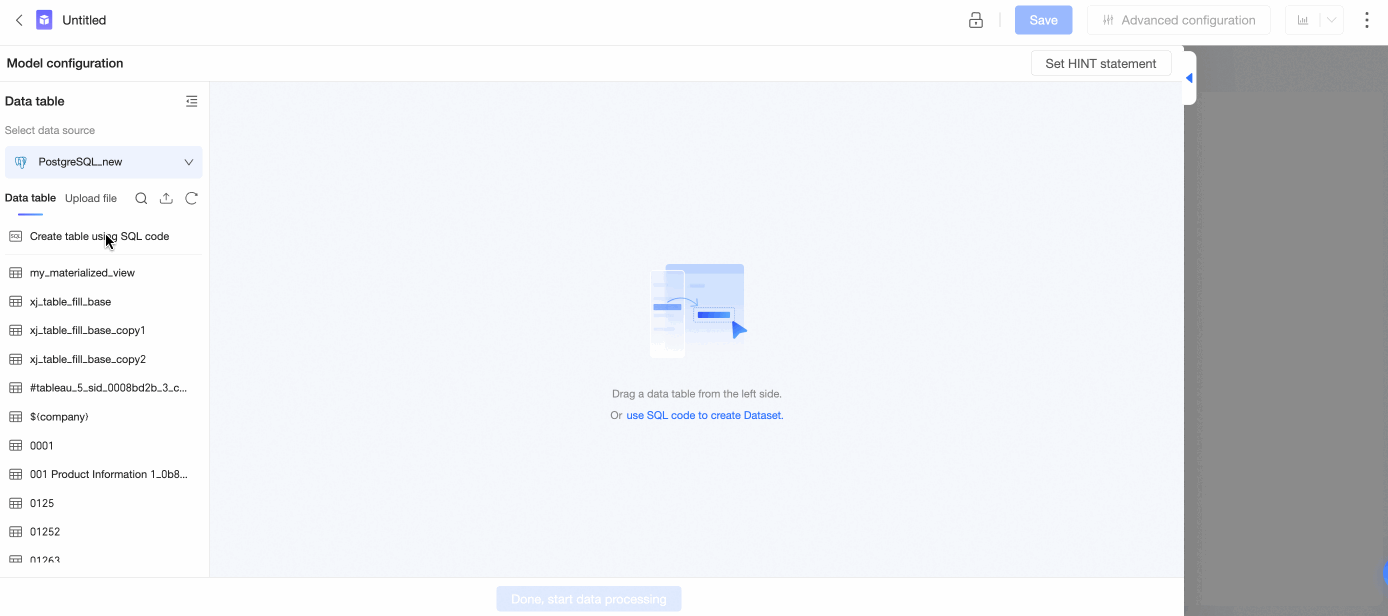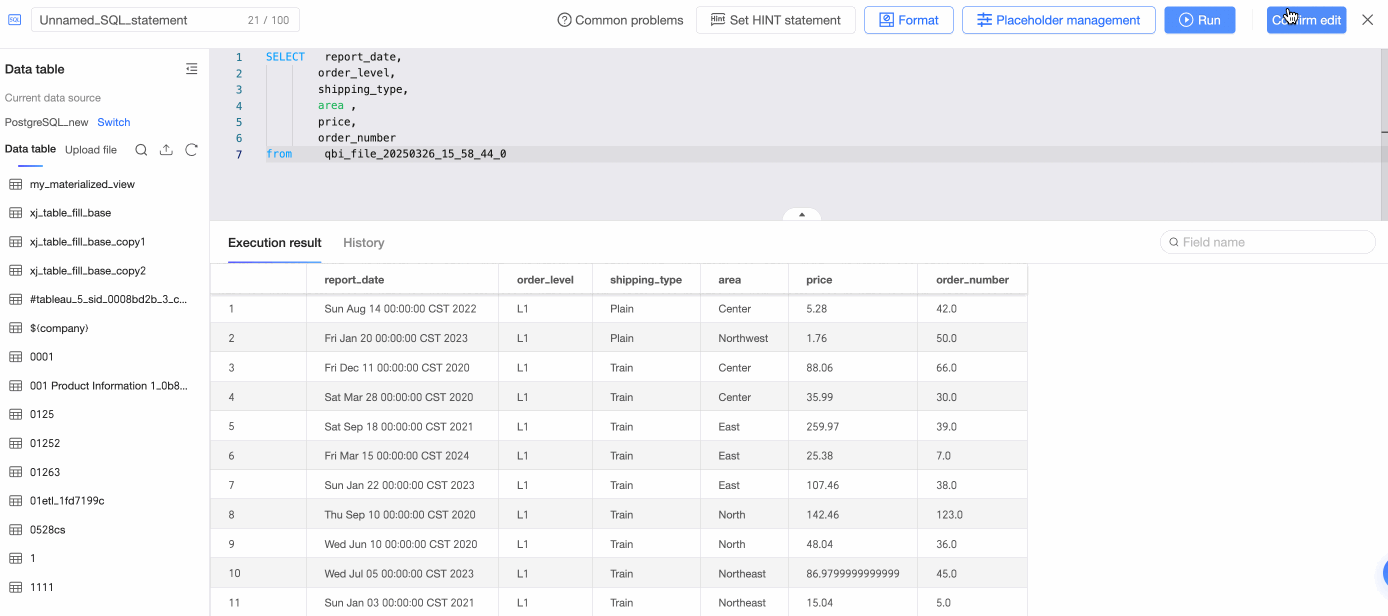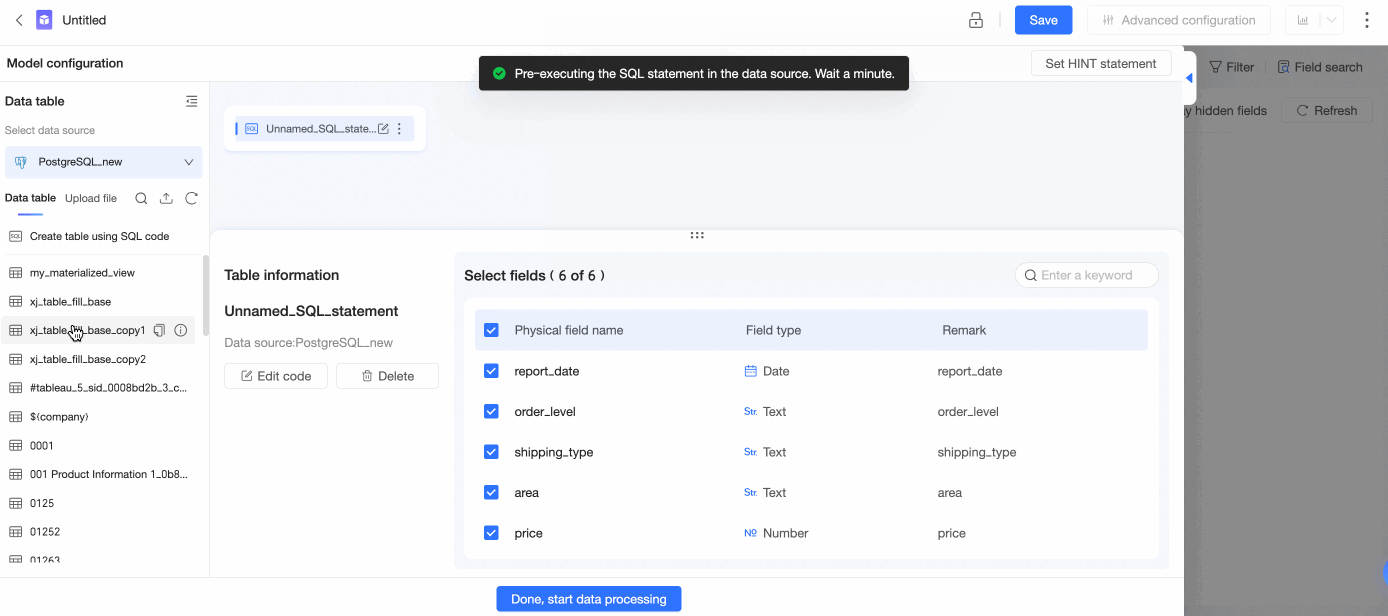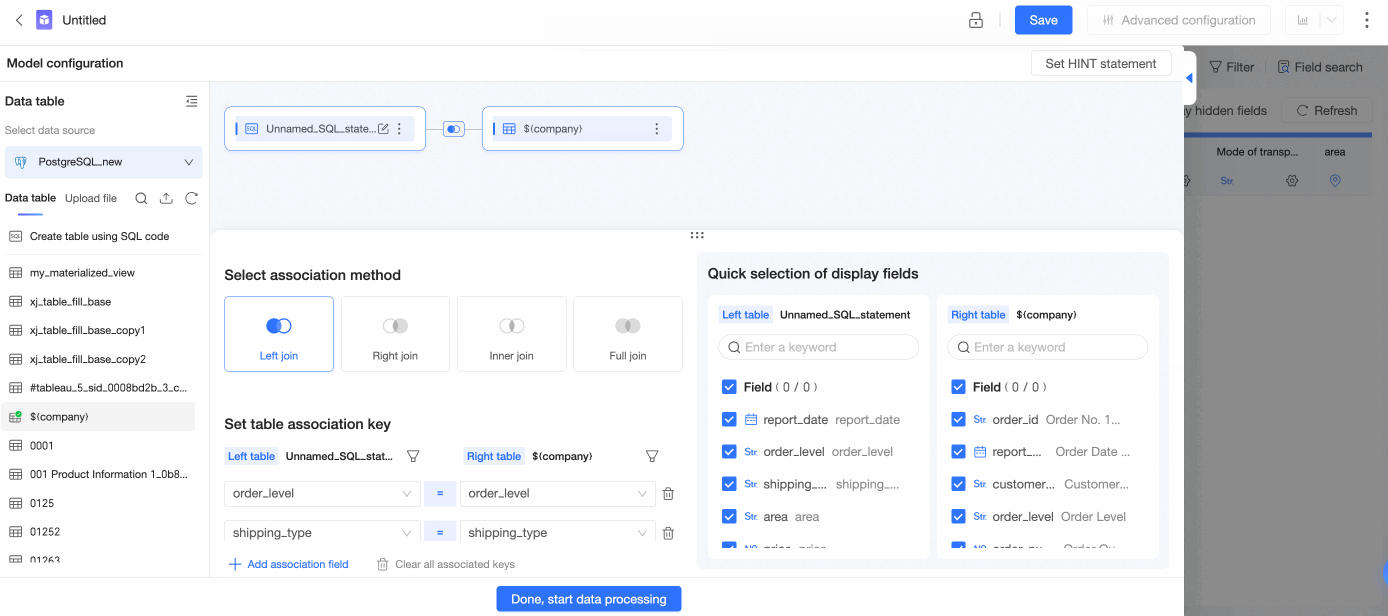
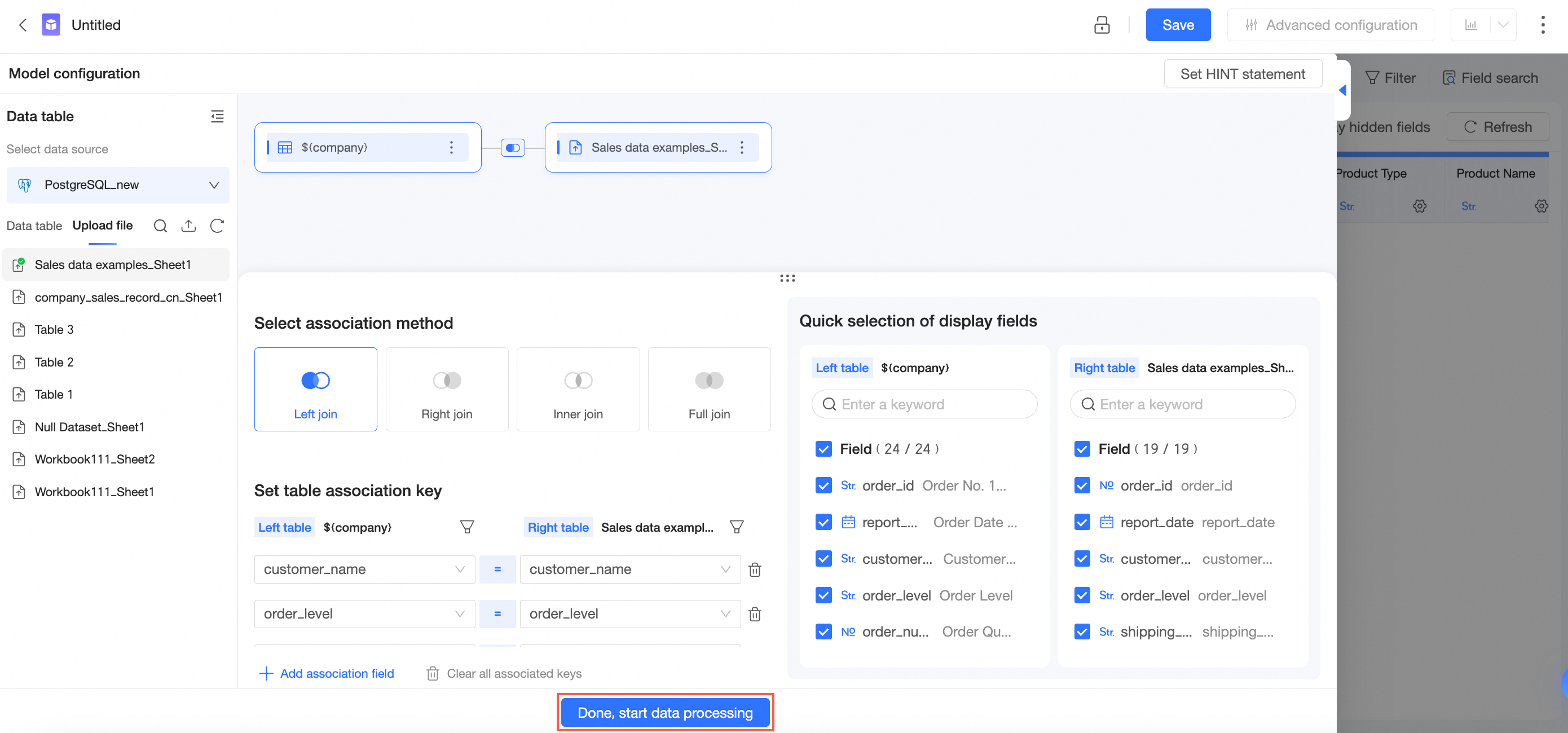
In the Add Association Relationship panel, configure data association by following the steps in the following figure.
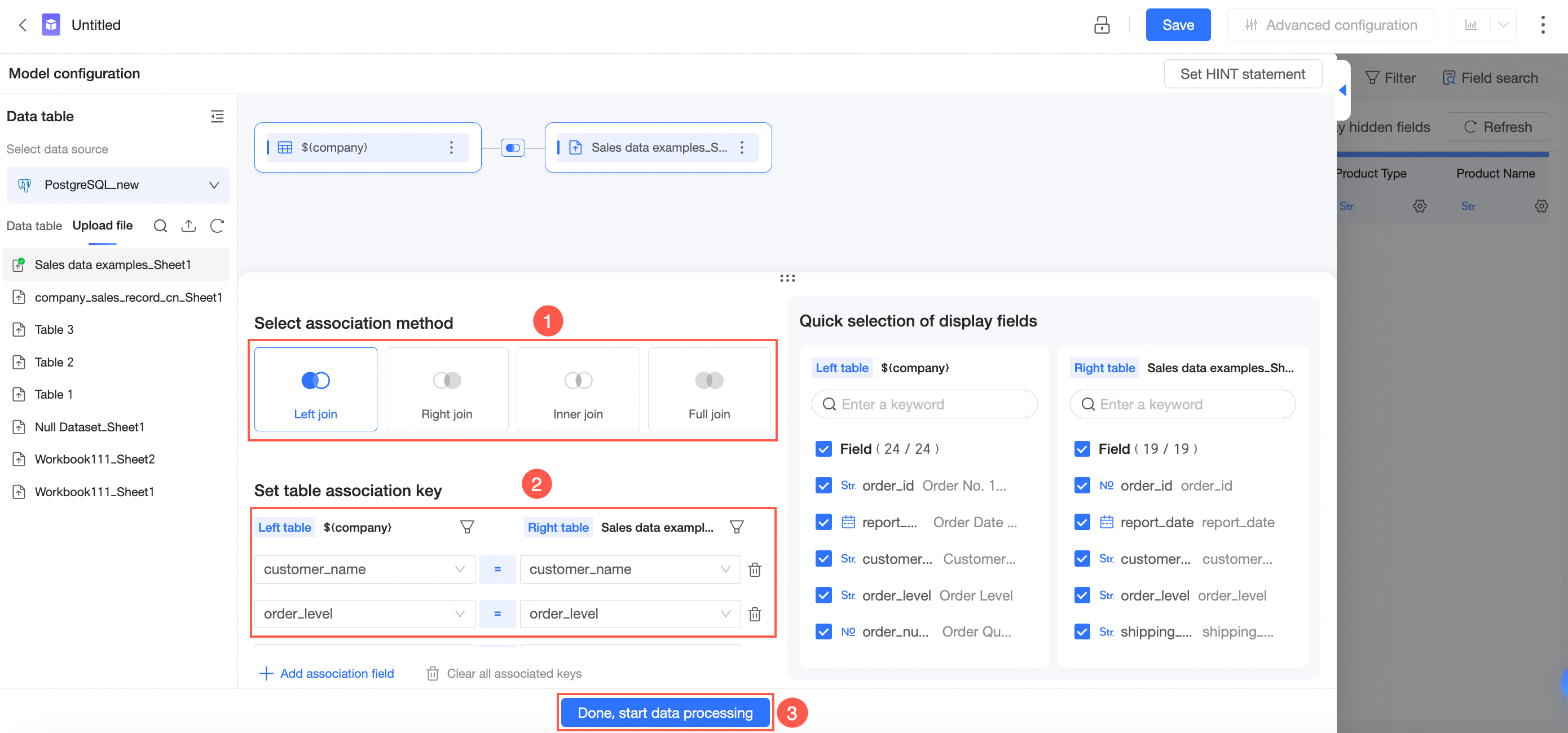
Select Left Join, Right Join, Inner Join, or Full Join as the association method.
NoteMySQL does not support Full Outer Join.
Set association keys.
The association symbol is set to "=" by default. You can change it to "≠", ">", ">=", "<", or "<=".
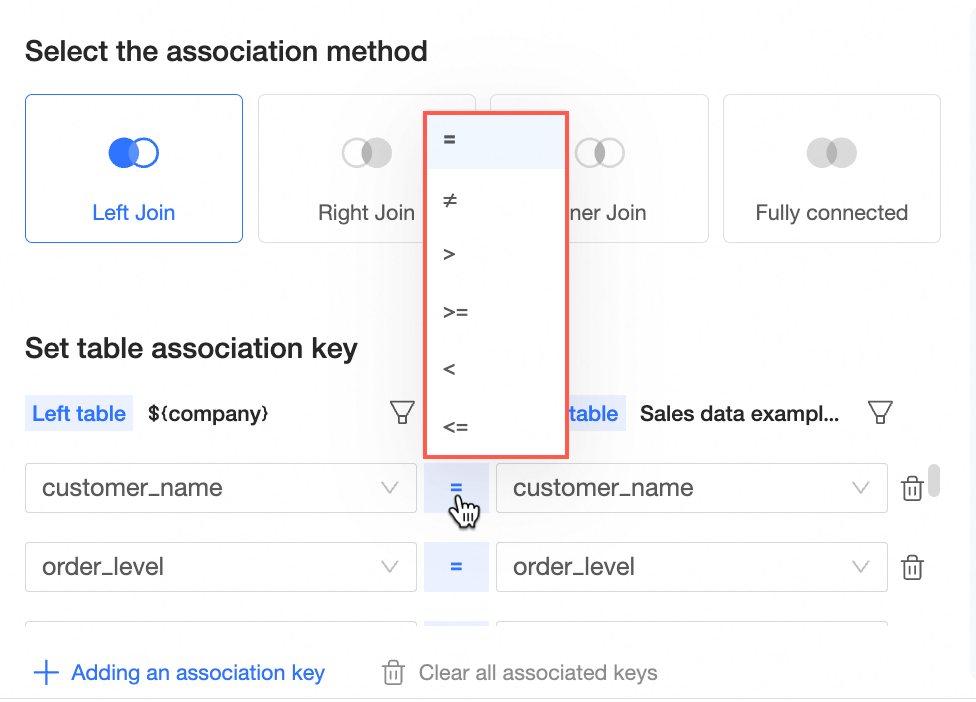
You can click Add Association Key to add multiple association keys.
You can delete association keys.
You can clear all association keys.
Click Complete and Start Data Processing to complete the configuration and go to the data processing page.
 On the data processing page, you can click Model Configuration on the left side or click Source Table -> Model Details to go to the Model Configuration page again. For information about operations on the data processing page, see Create a dataset.
On the data processing page, you can click Model Configuration on the left side or click Source Table -> Model Details to go to the Model Configuration page again. For information about operations on the data processing page, see Create a dataset.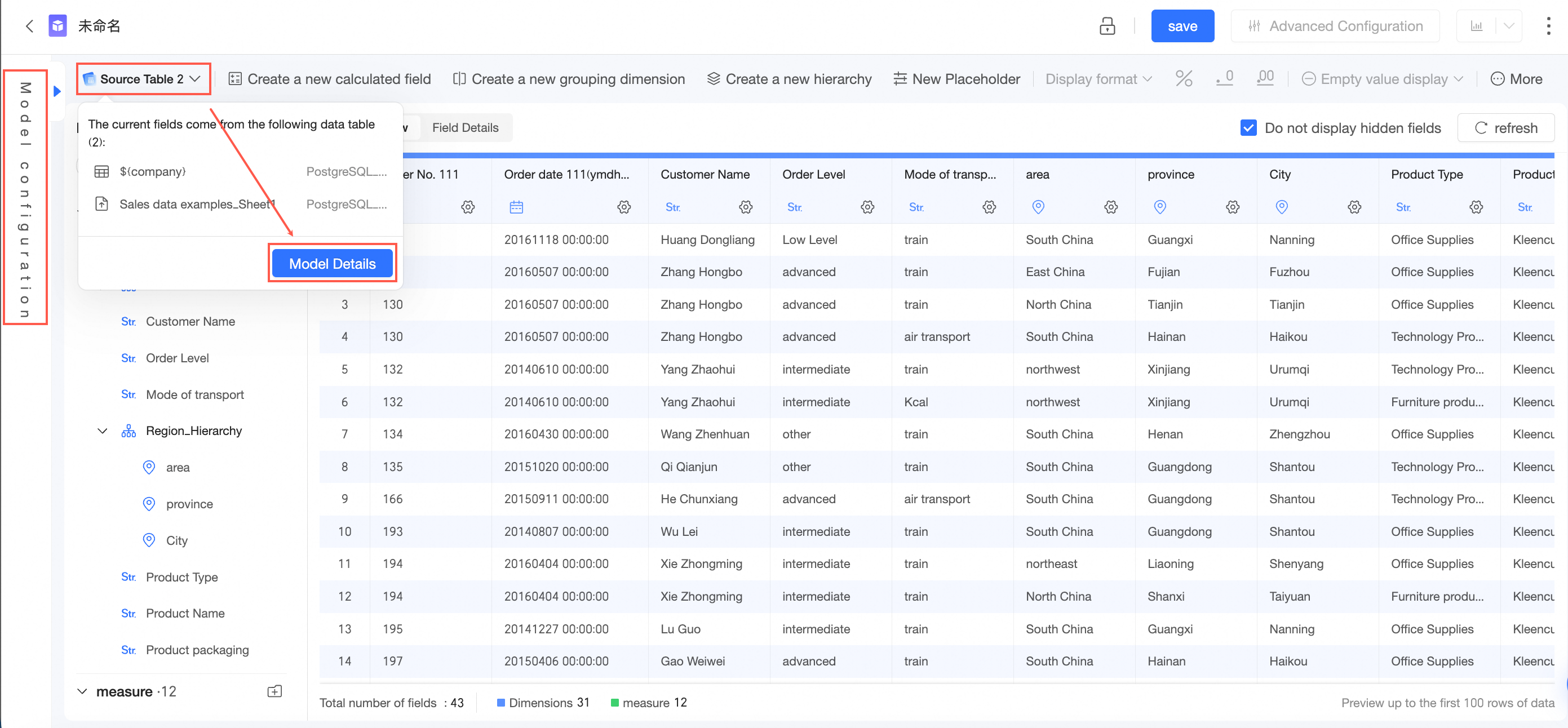 You can click the association icon on the canvas to view the association relationship.
You can click the association icon on the canvas to view the association relationship.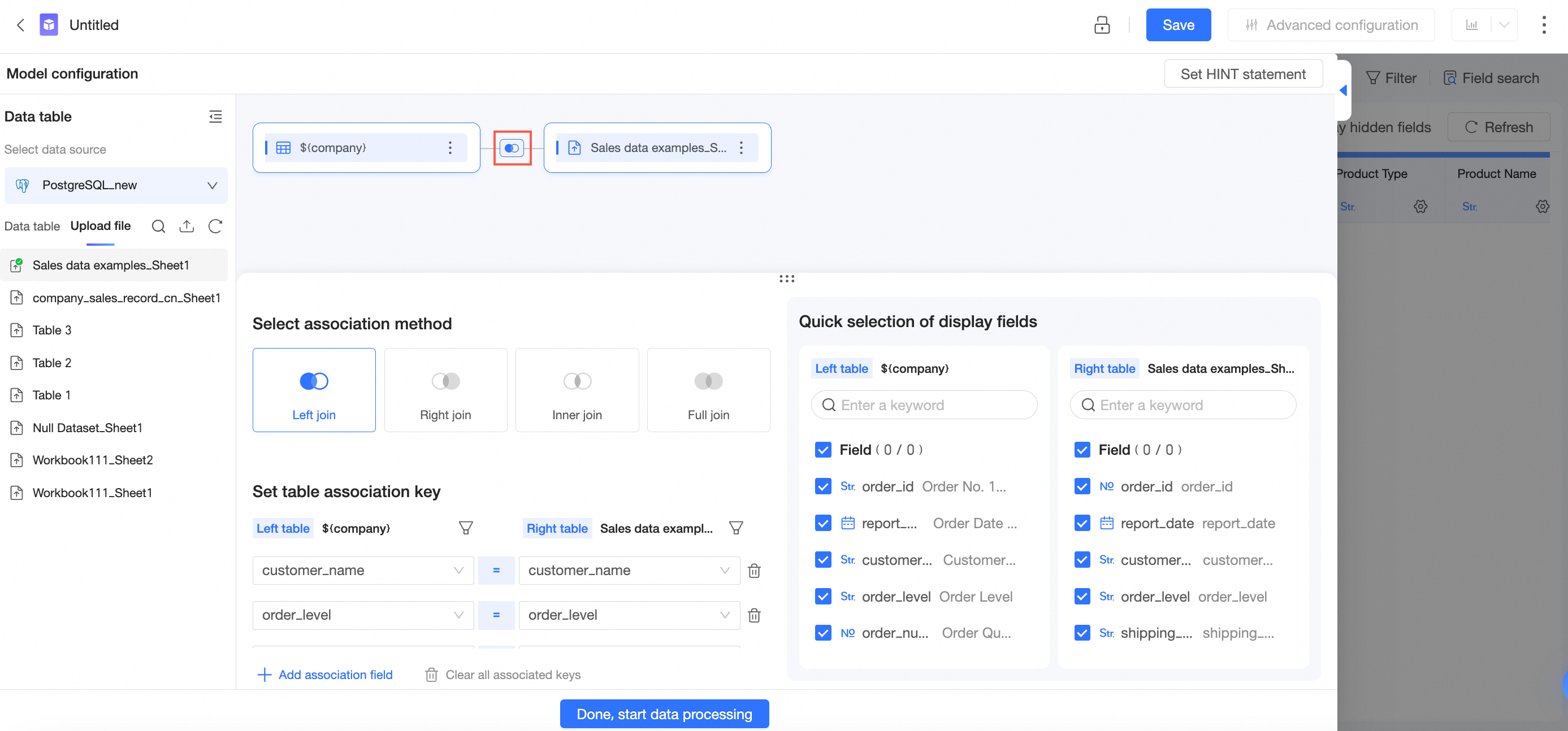 If you do not need a node, you can click the
If you do not need a node, you can click the  icon on the right side of the node and select Delete.
icon on the right side of the node and select Delete.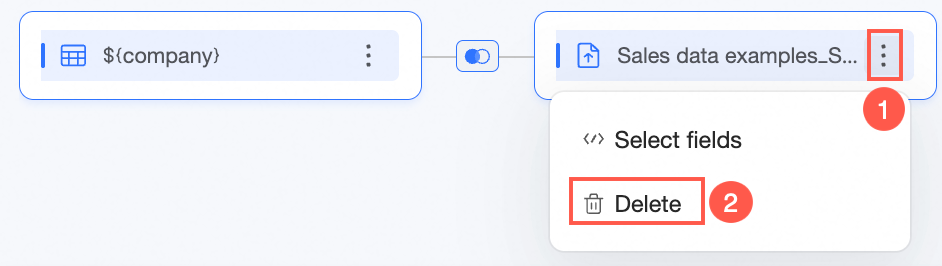 Note
NoteYou can delete only the last node of a model.
Custom join condition
When you configure a custom join condition, you can create a custom formula as a field that you want to associate with the custom join condition.
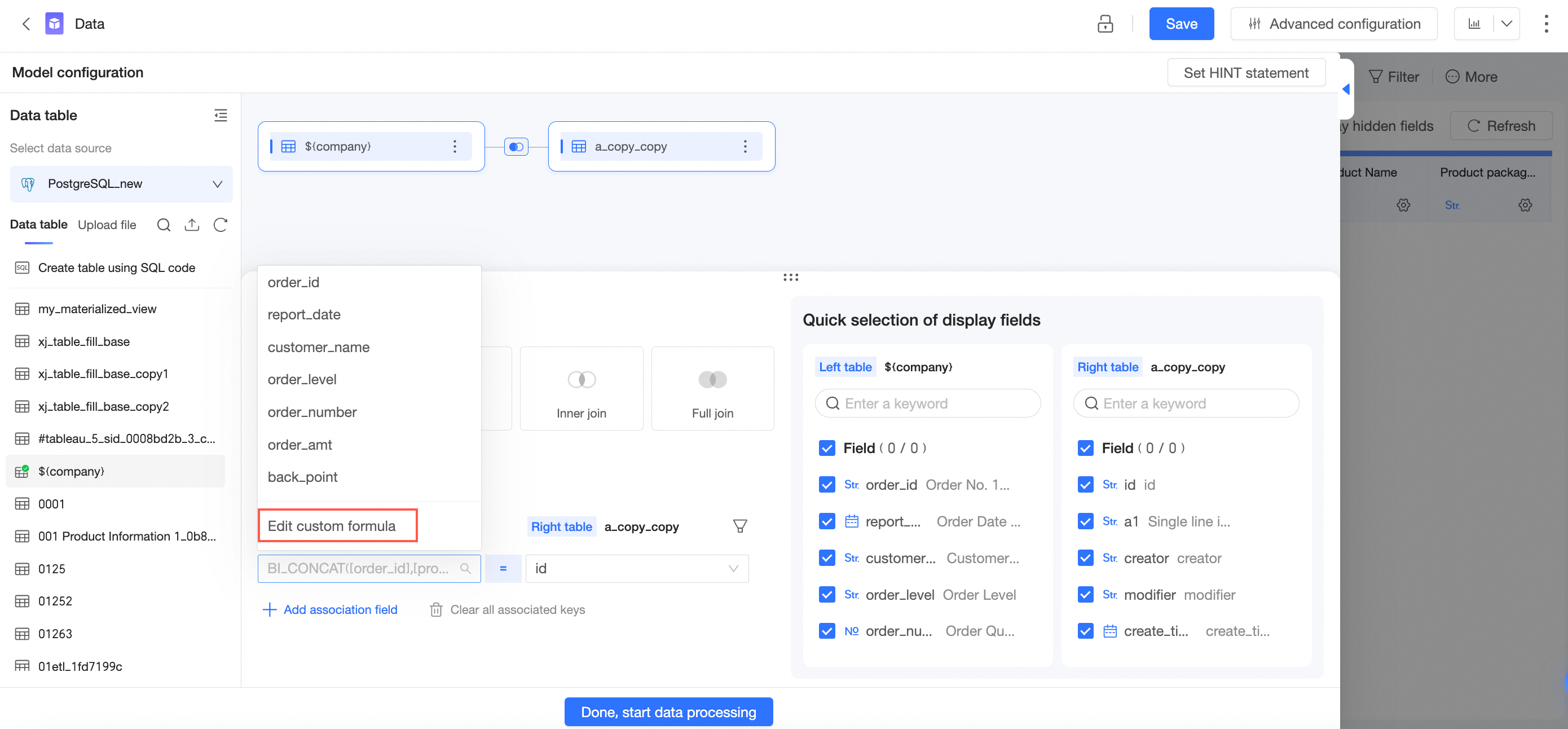
When you select an association field, select Create Custom Calculation from the drop-down list.
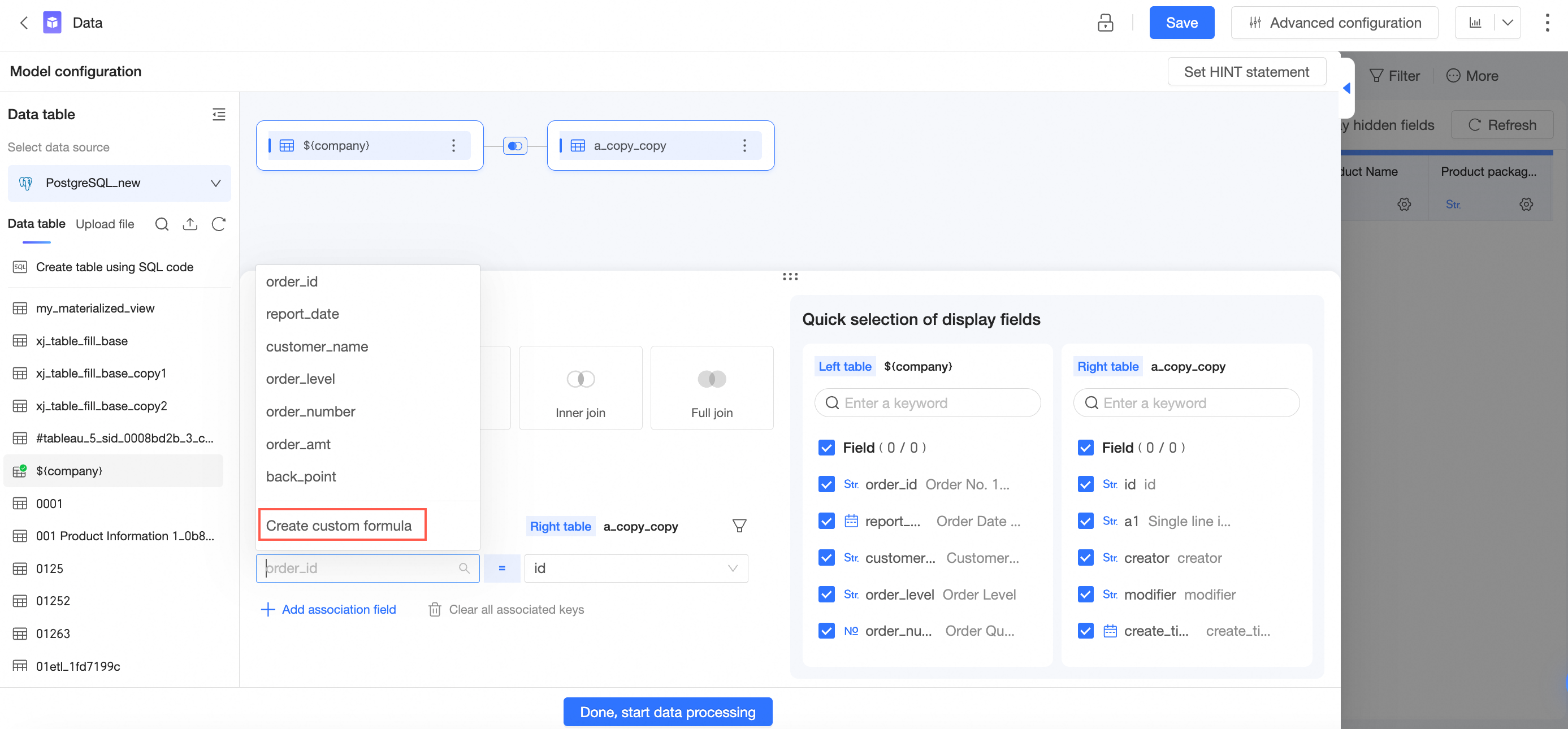
Enter a field expression and click OK.
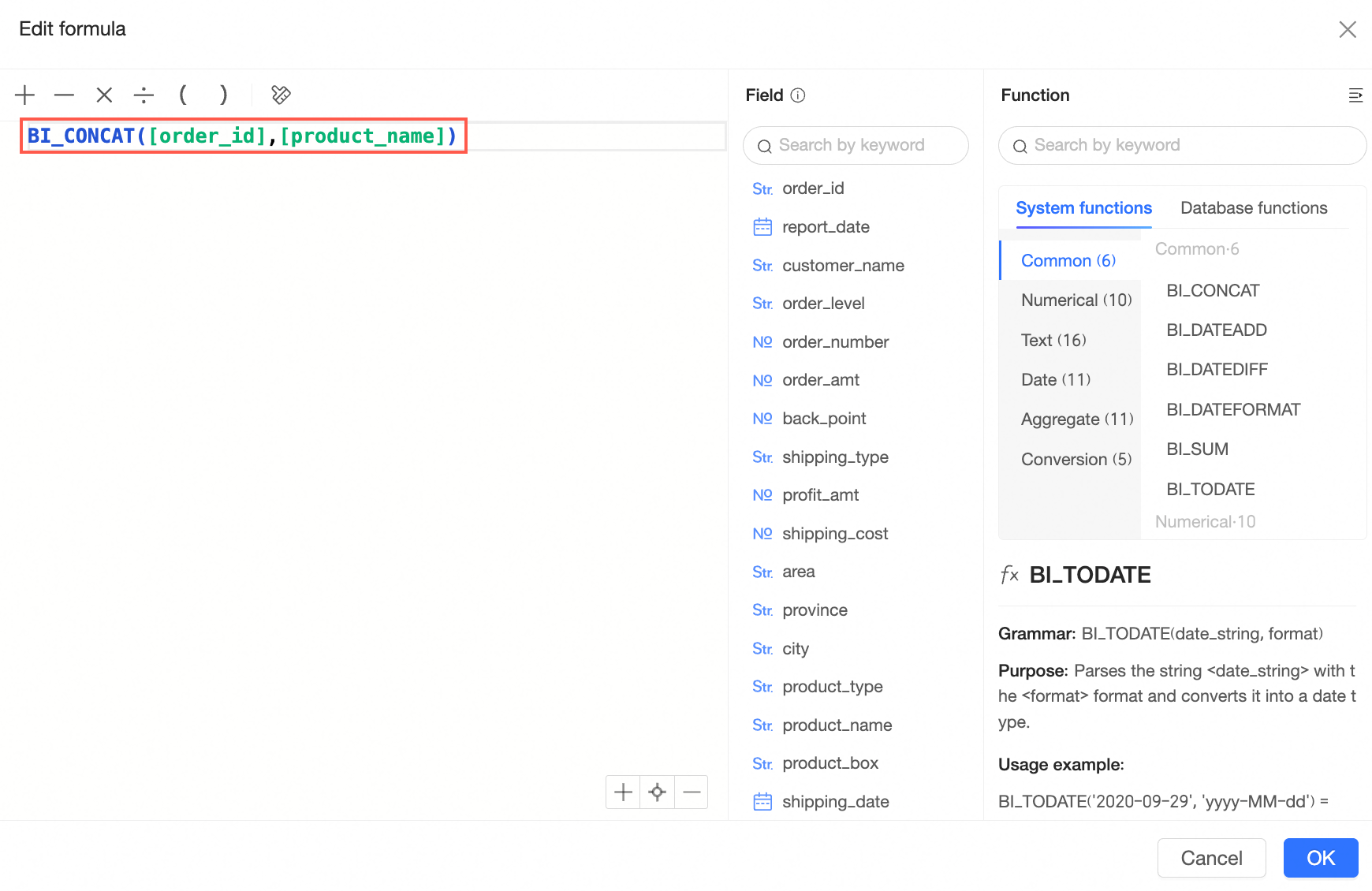
Click OK. You can see the newly created field expression in the association field.
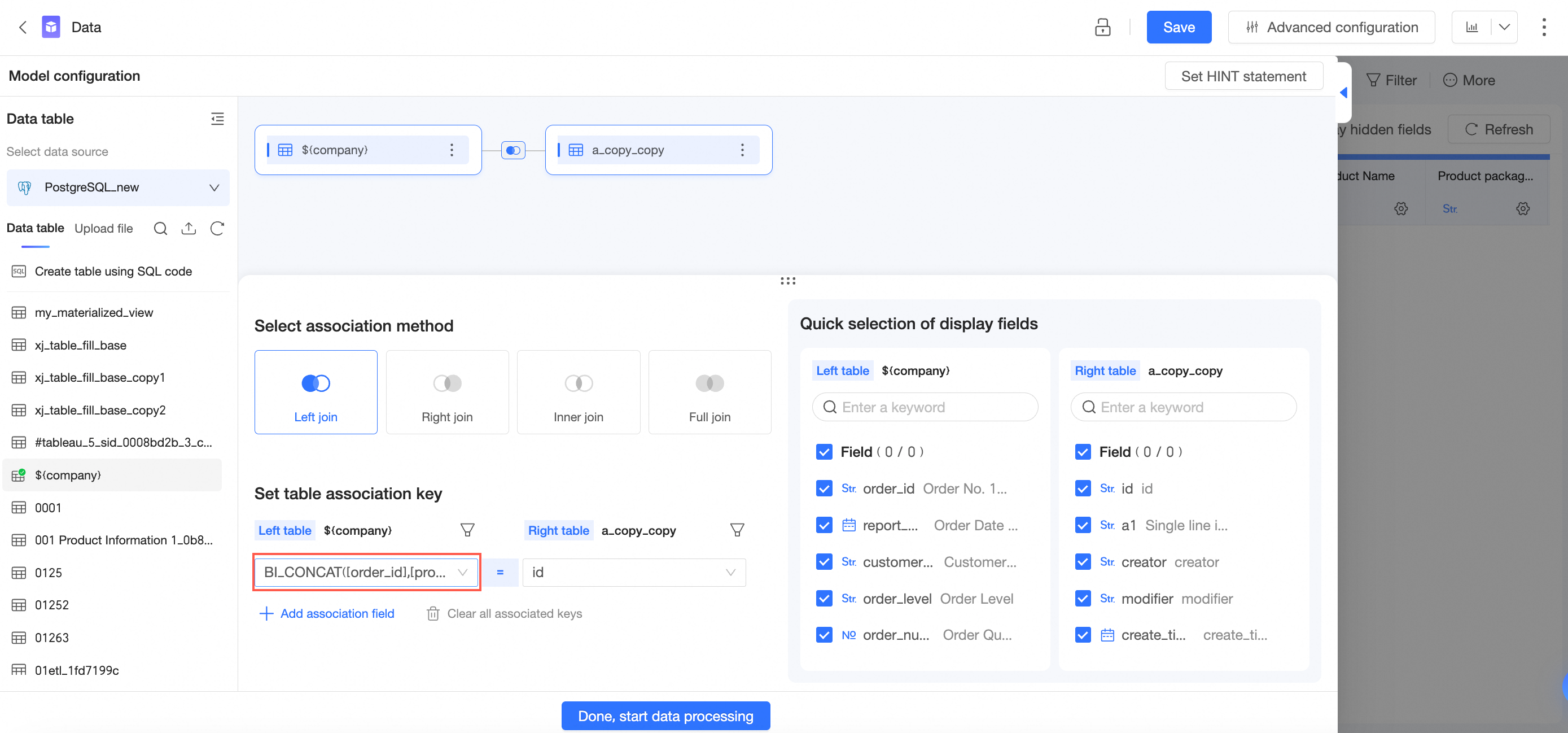
You can also edit the custom calculation.
Filter before association
When you associate tables, you can create filter conditions for each of the two tables. The filter operations are performed before the association.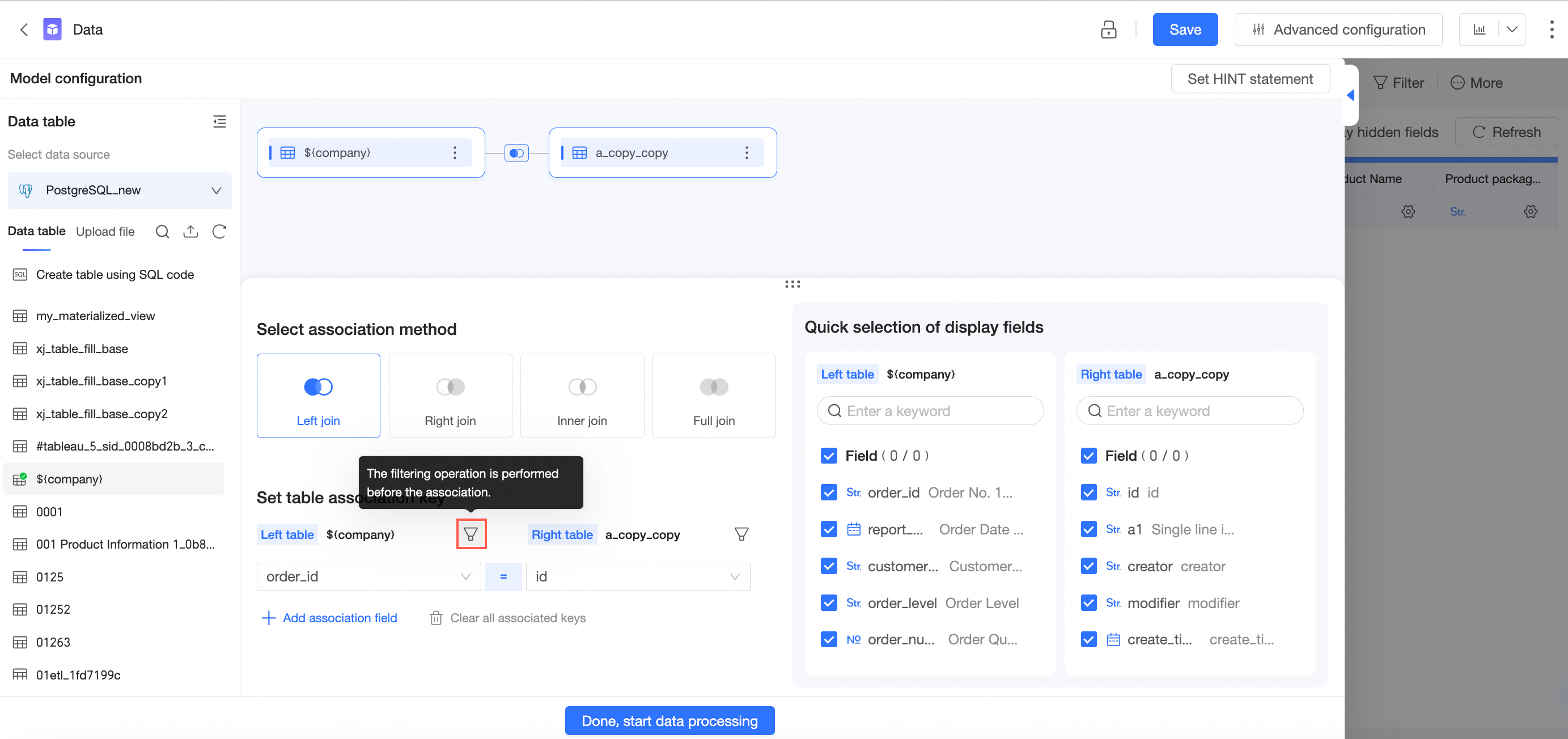
Click the
 icon on the right side of the table that corresponds to the association field.
icon on the right side of the table that corresponds to the association field.Set filter conditions.
Click OK to complete the configuration of the filter conditions before association.
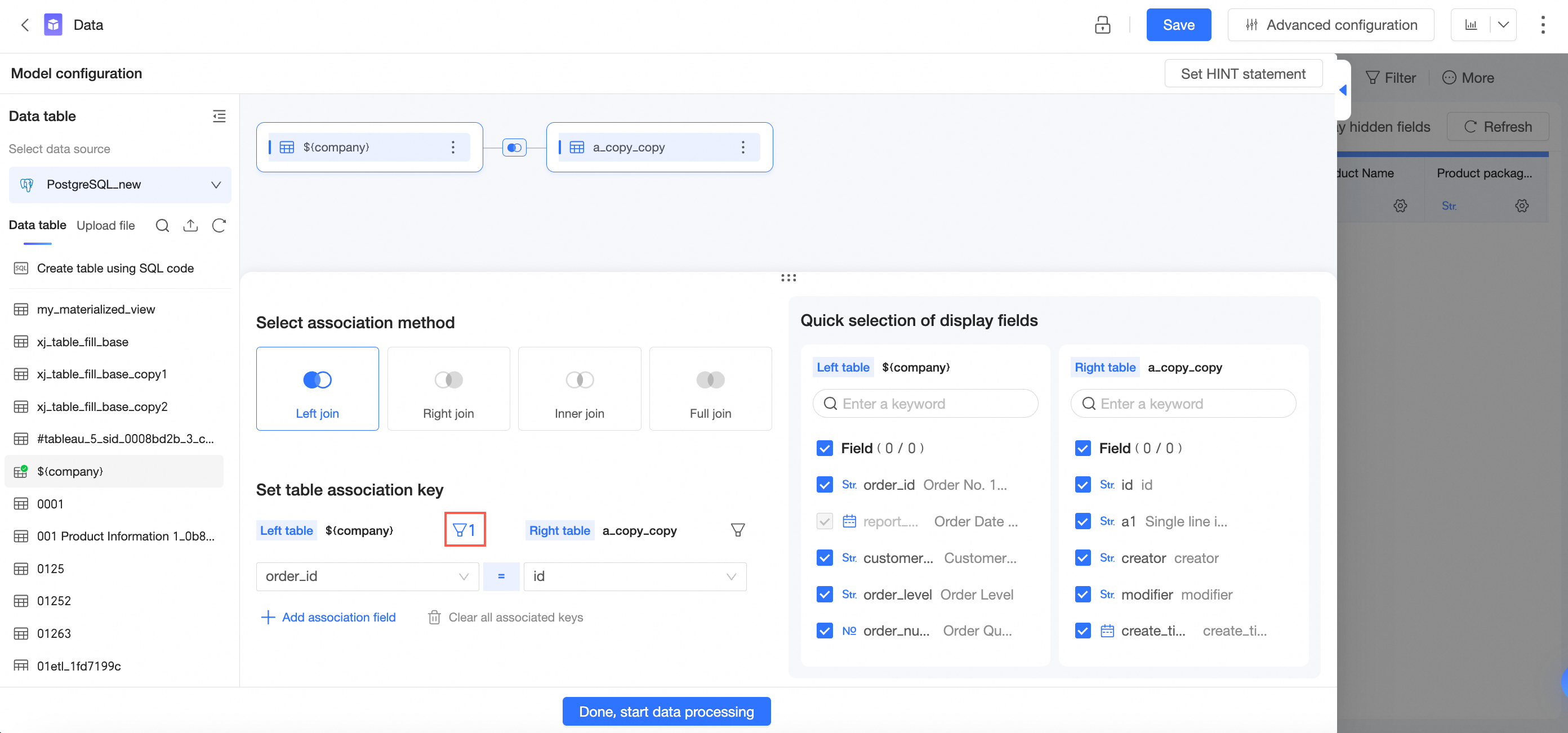
Cross-source association
When the data tables that you need to use are stored in different data sources, you can associate multiple tables from different data sources on the dataset edit page to form a model for data analytics. To configure a whitelist, perform the following steps:
You can join tables from different data sources only in Quick BI Enterprise Standard.
To join tables from different data sources, you must enable the Quick engine extraction acceleration feature. You can go to the Data Source Function Item List to view the data sources that support the extraction acceleration feature.
In the data table list on the dataset edit page, find the data table of the target database and drag it to the canvas.
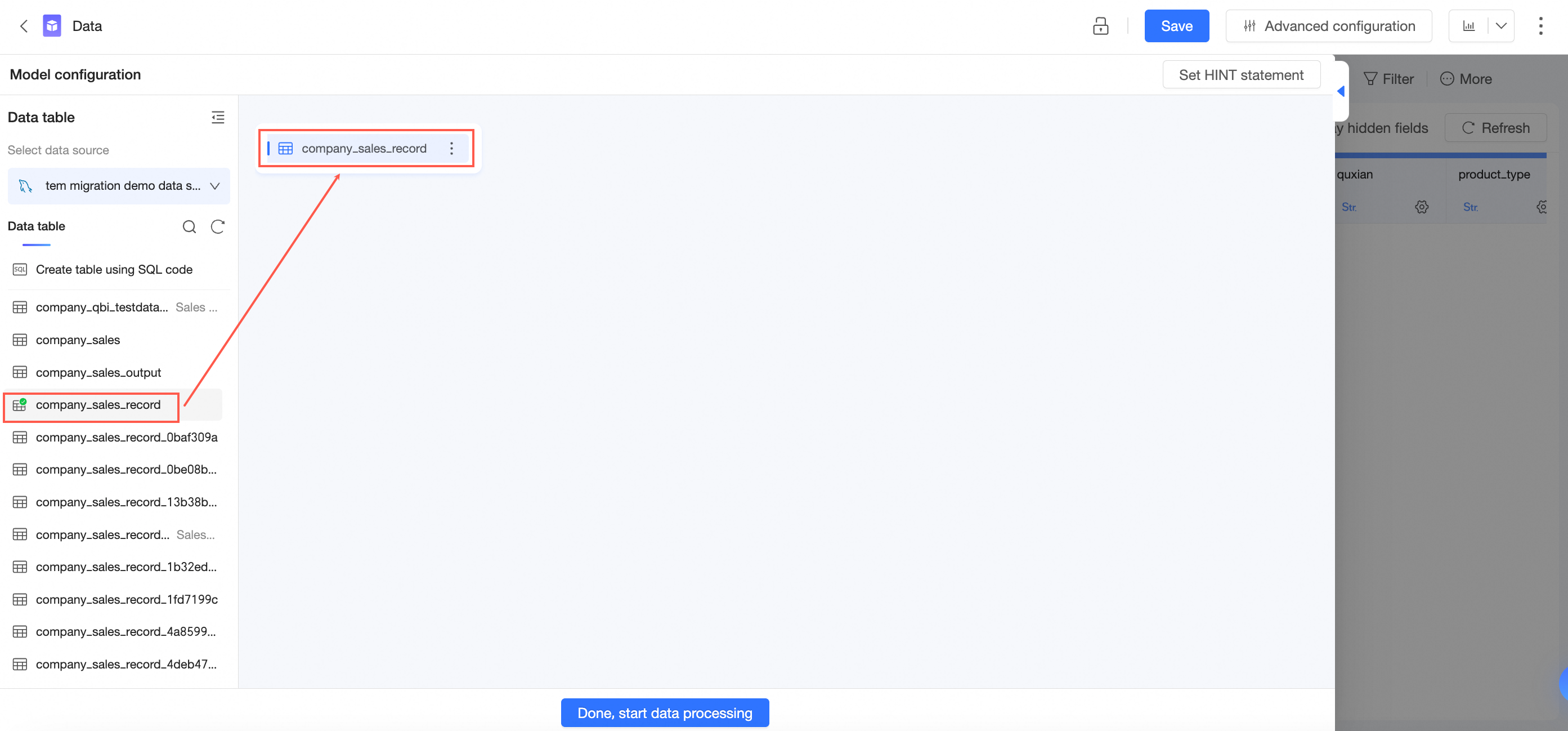
Switch the data list to another target database, find the required data table, and drag it to the canvas.
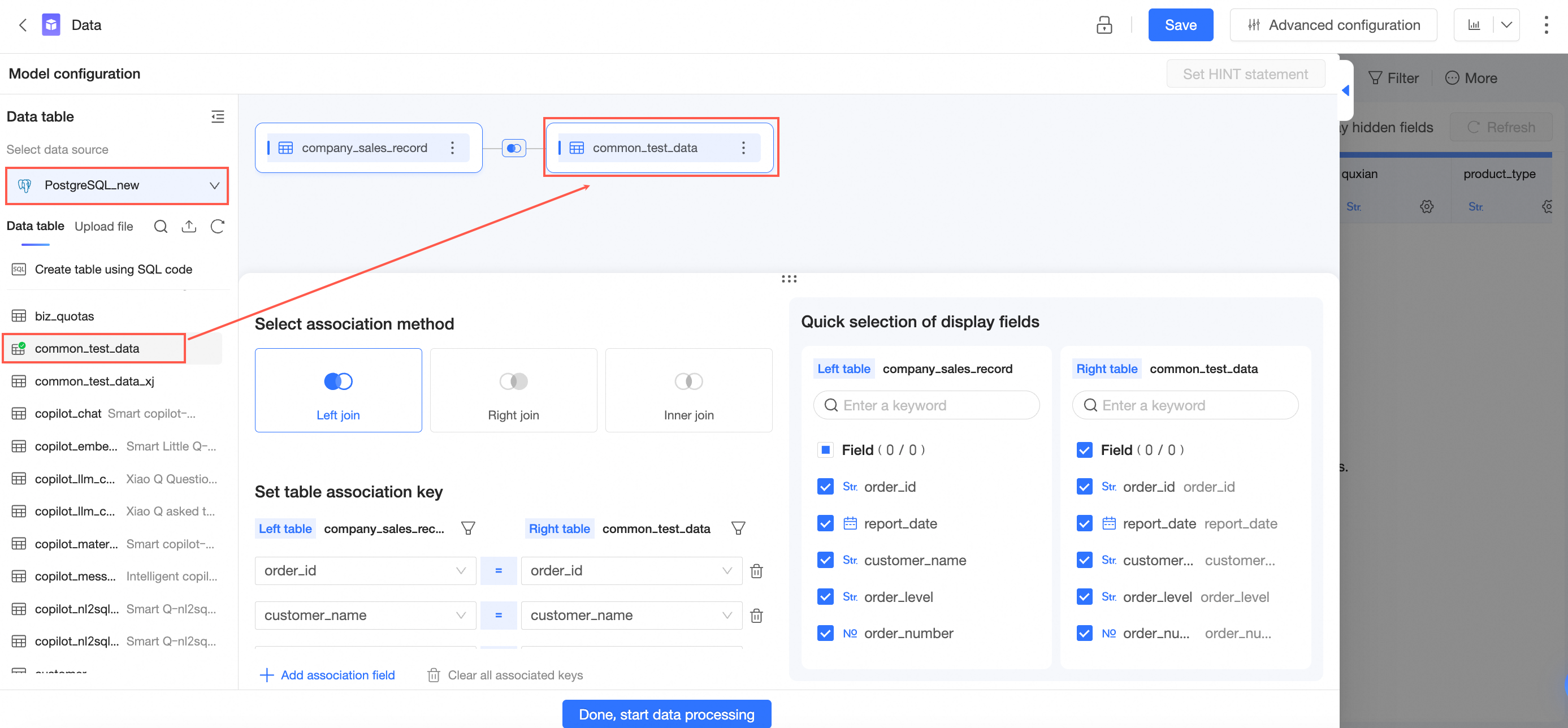
Configure the association relationship between the data tables based on your requirements. For more information, see Add Association Relationship in this topic. After you complete the configuration, save the current dataset.
Click Advanced Configuration in the toolbar at the top of the page.
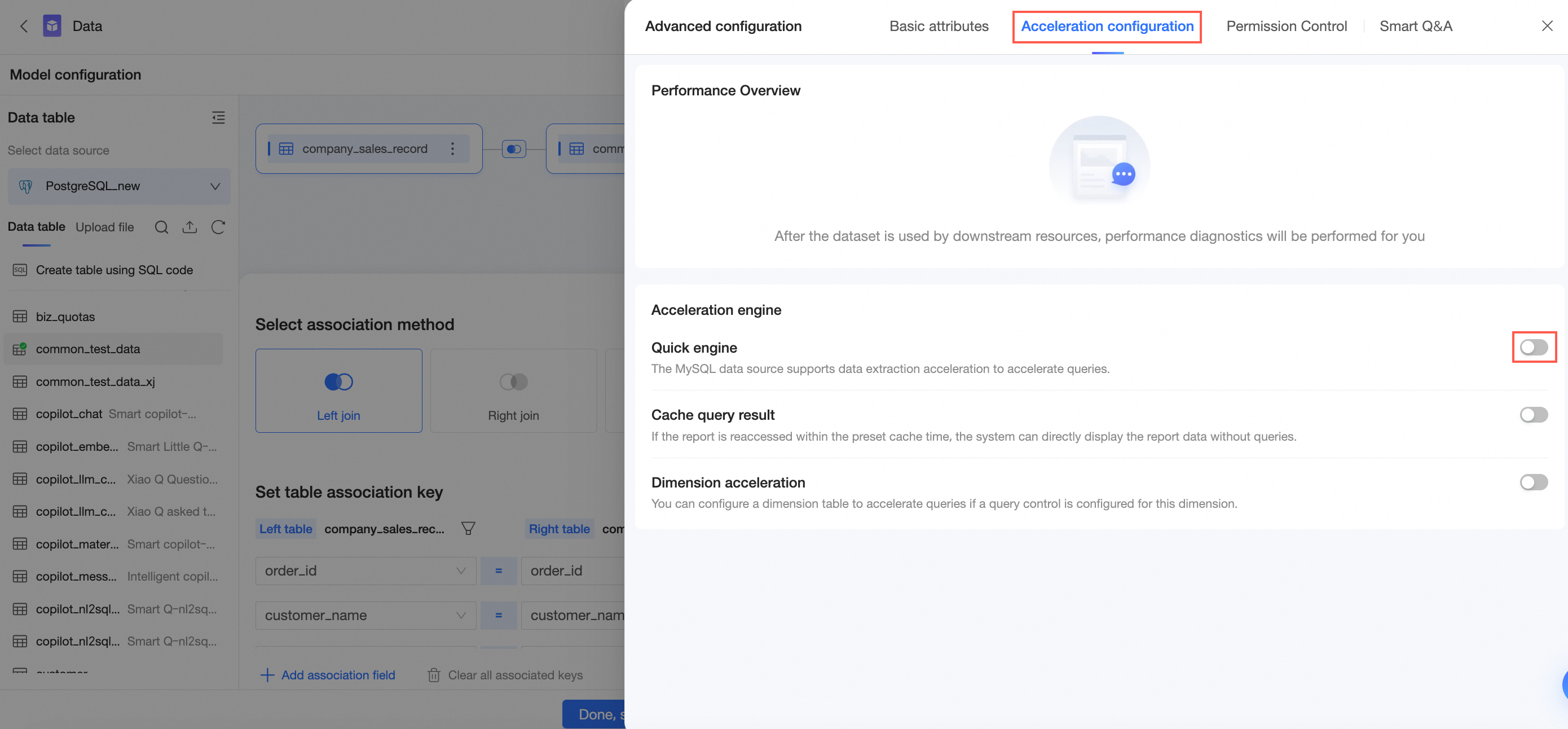
Click Acceleration Configuration to go to the acceleration configuration page and turn on Quick Engine.
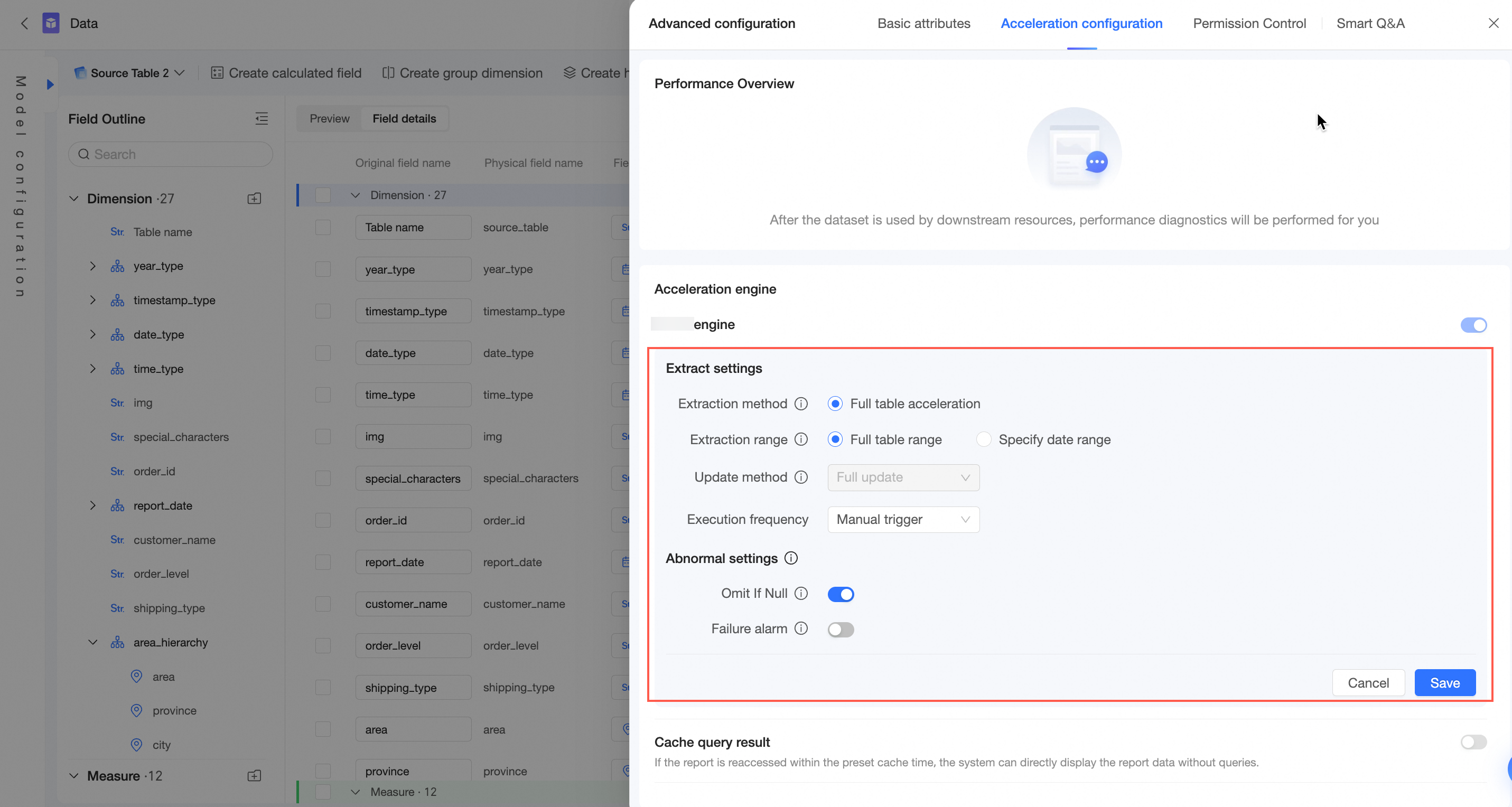
After you turn on Quick Engine, you need to configure the following parameters. For information about the configuration, see Configure Quick Engine.
Click Save to complete the extraction acceleration configuration.
Merging
Data merging is used to configure the summarization and integration of information from different data sources or data tables into a single dataset for better analysis, processing, or reporting.
After tables are merged, they can be associated as a whole. When you associate merged results, Custom Calculation and Filter Before Association are not supported.
Procedure
Select a data source.
Select or create tables to merge.
You can merge a data table with a data table, merge a data table with a table created by using SQL code, merge a table created by using SQL code with a data table, or merge a table created by using SQL code with a table created by using SQL code.
NoteFor information about how to edit SQL code, see Use Custom SQL Statement to Create a Dataset.
You can merge a maximum of five tables.
The following example shows how to merge a data table with a table created by using SQL code:
Double-click a data table or drag it to the canvas.
Drag Create Table by Using SQL Code to the lower part of the table to be merged.
On the SQL code editing page, enter SQL statements, click Run, and confirm the edits to create the table.
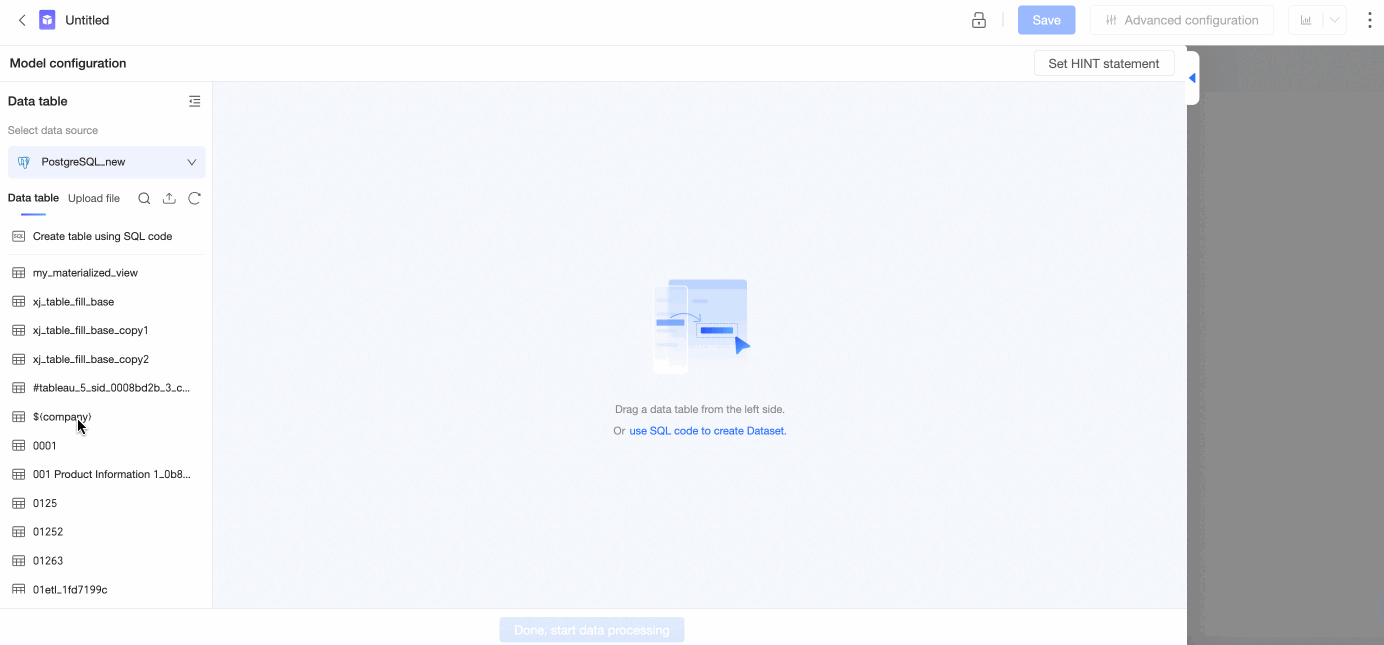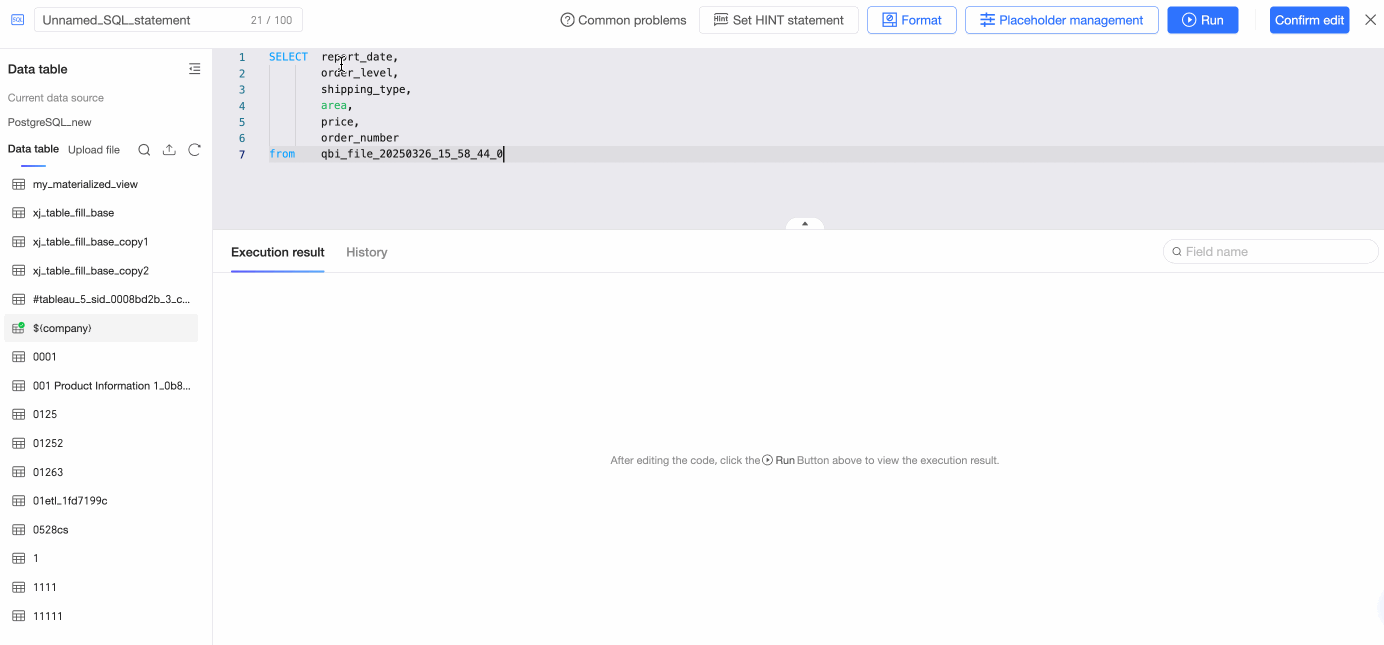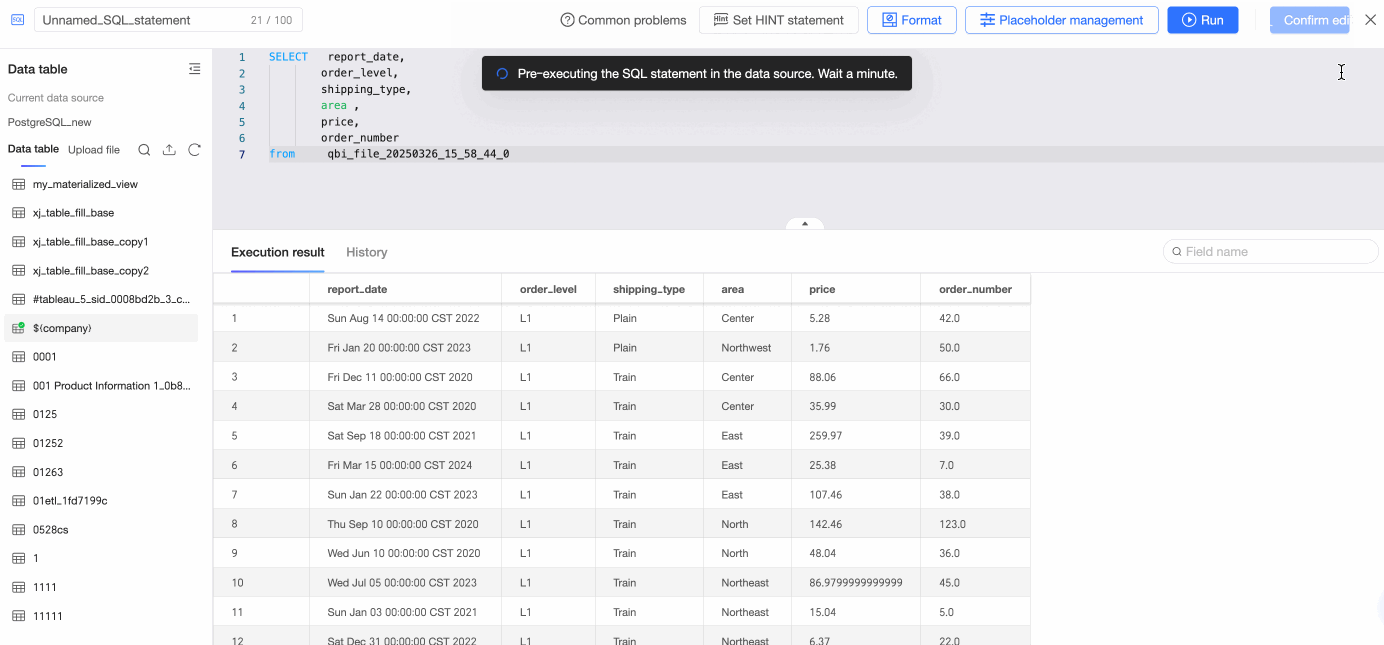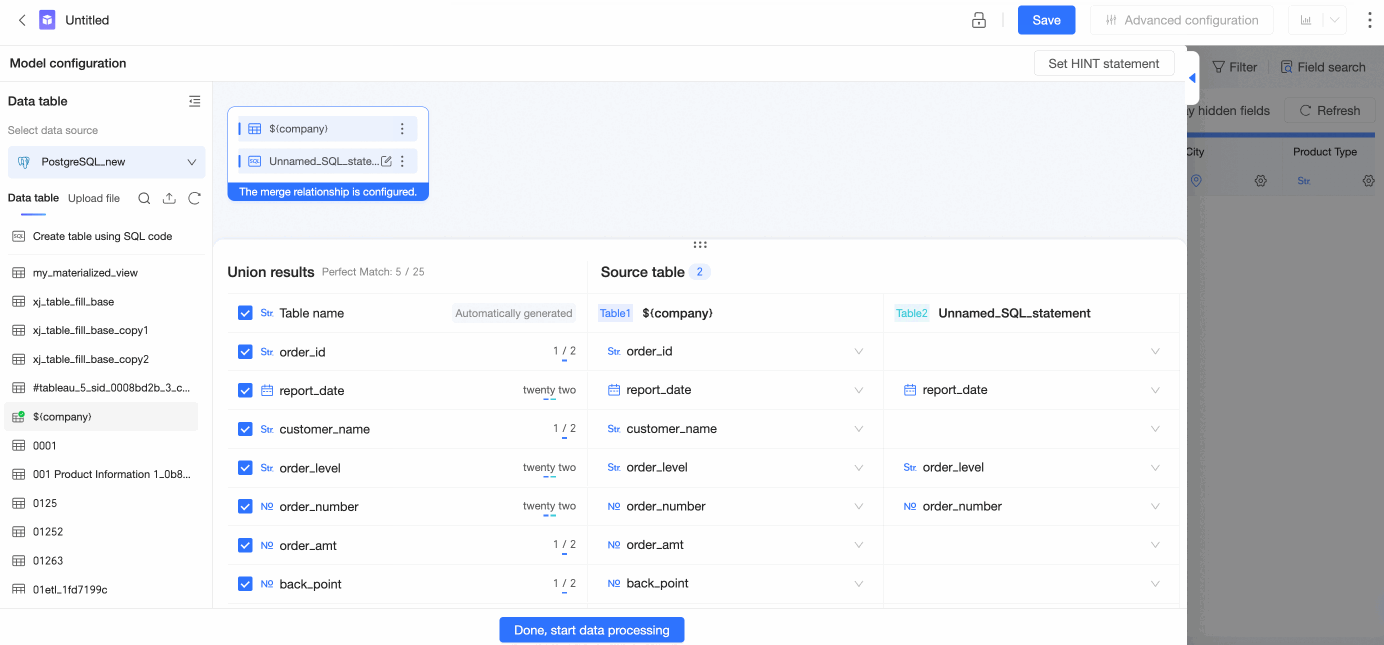
Configure table merging relationship.
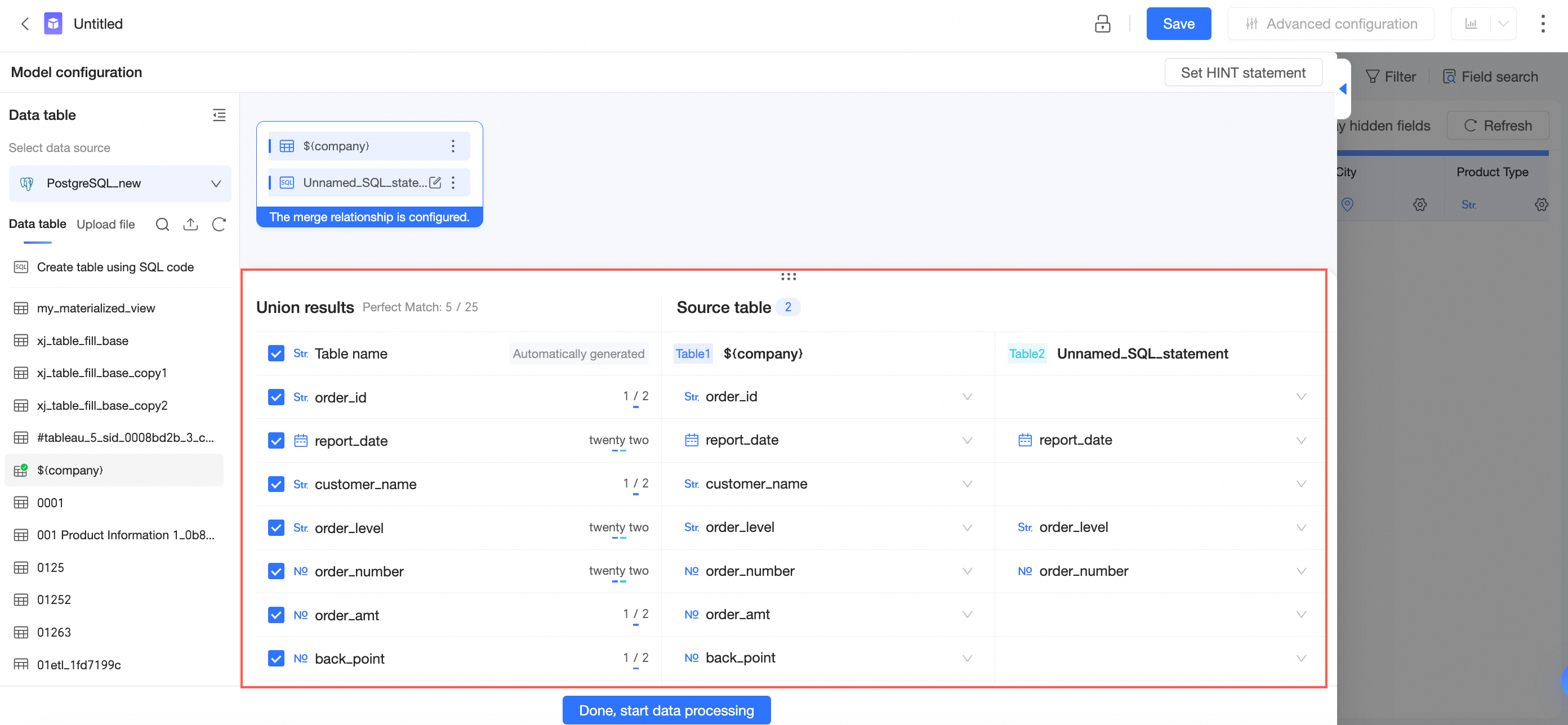
Fields with the same name and type are automatically matched.
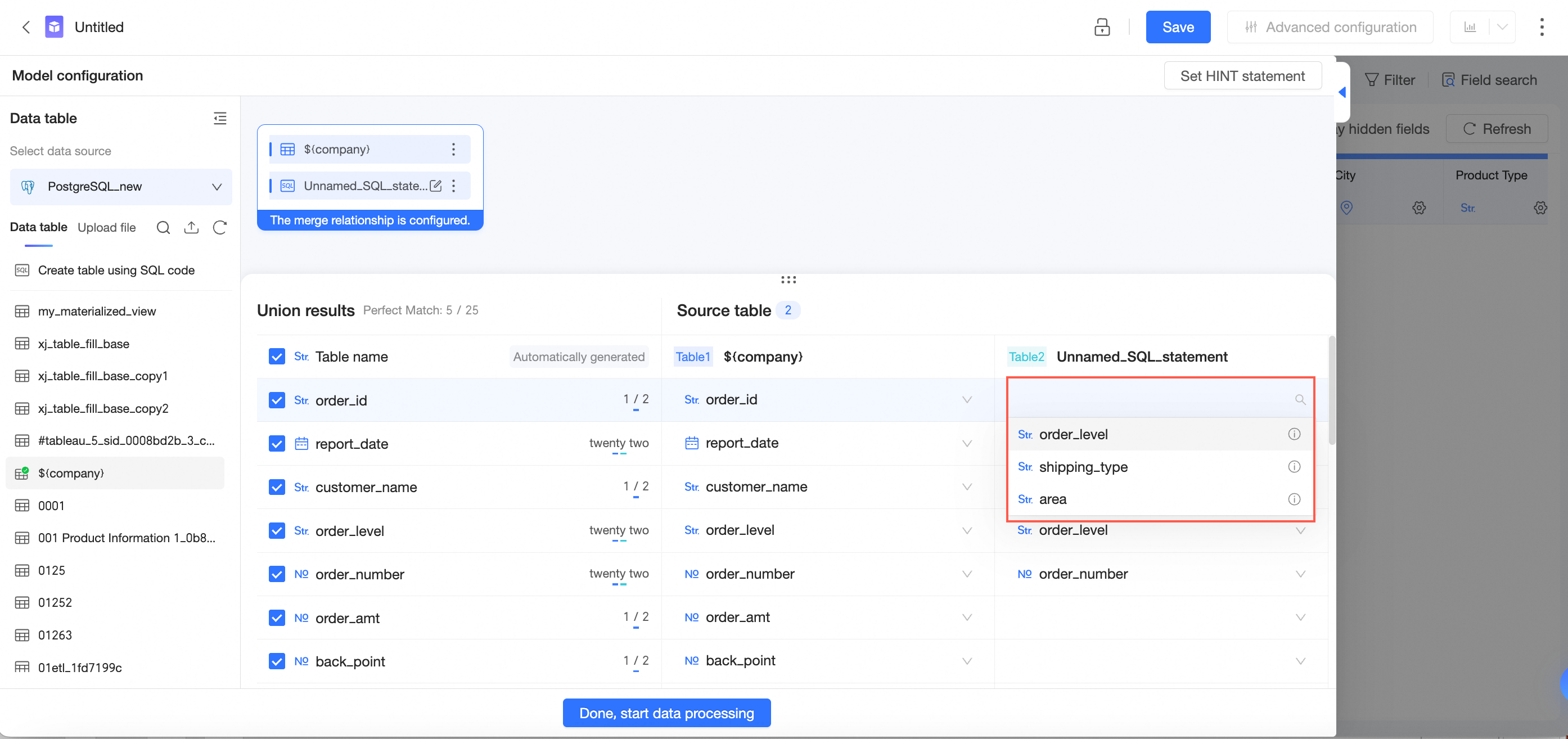
You can click a field box and select a field from the drop-down list to manually adjust field matching.
NoteThe drop-down list displays only fields of the same type.
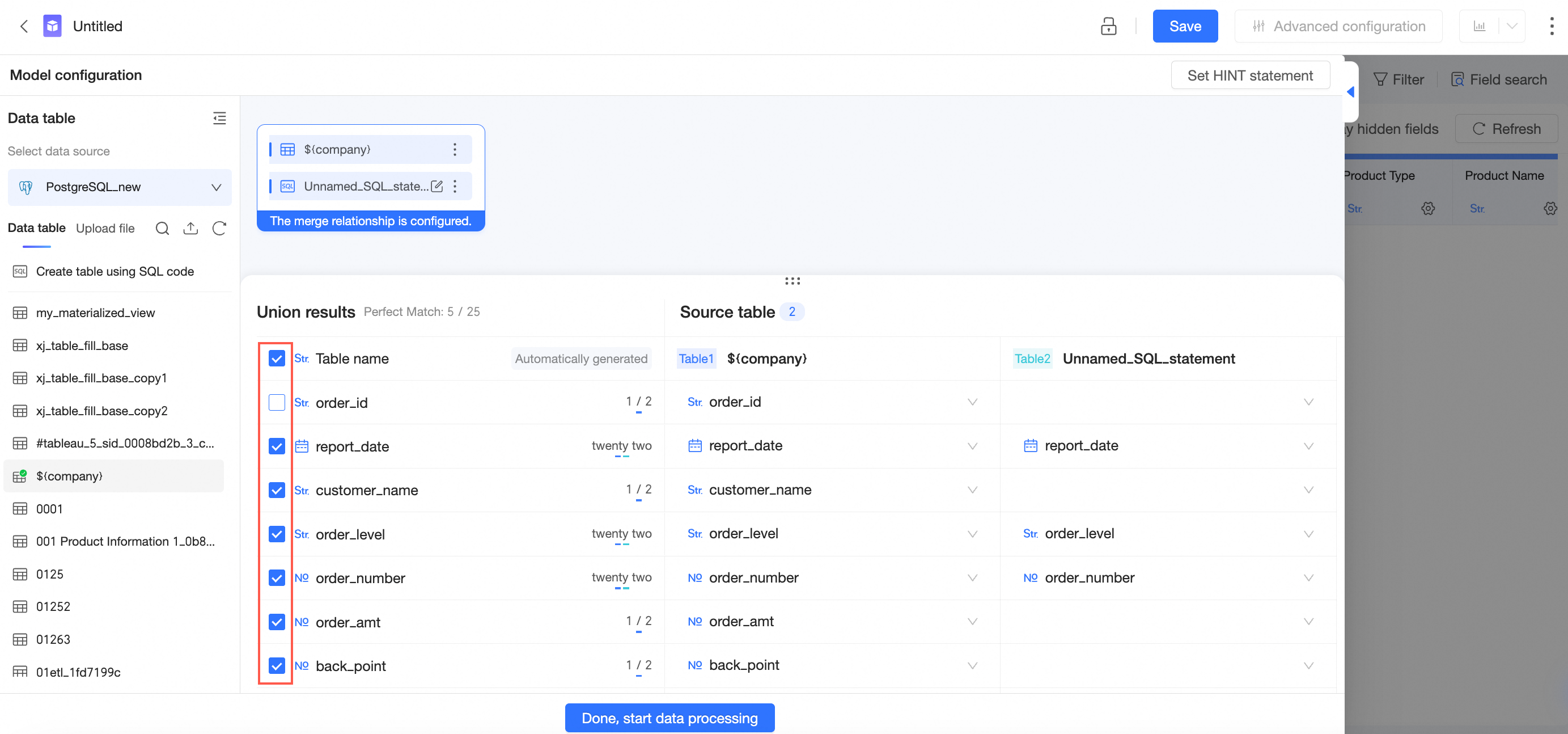
You can select fields based on your business requirements.
After you configure the table merging relationship, click Complete and Start Data Processing to complete the configuration and go to the data processing page.
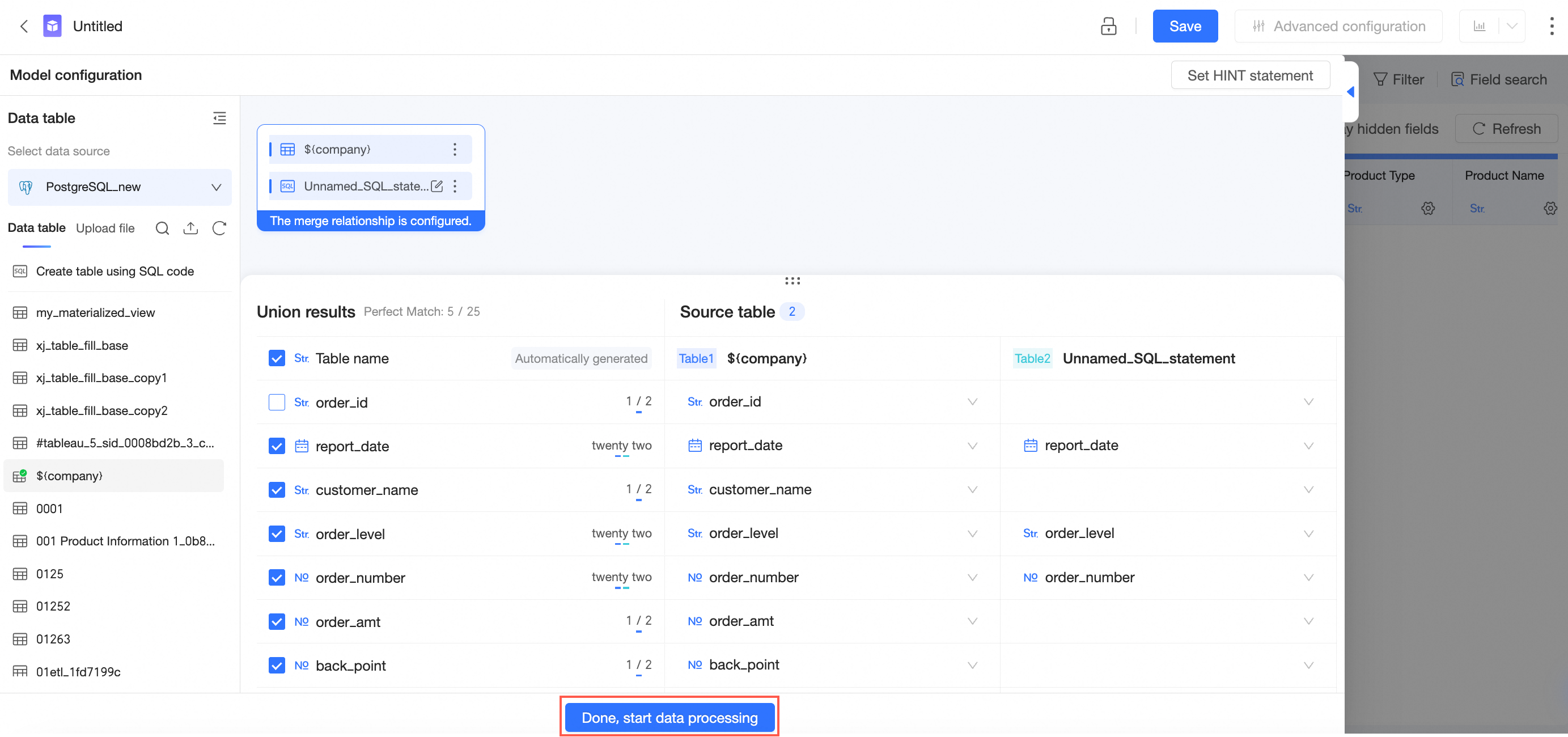
For information about operations on the data processing page, see Create a dataset.
Cross-source merging
When the data tables that you need to use are stored in different data sources, you can merge multiple tables from different data sources on the dataset edit page to form a model for data analytics. To configure a whitelist, perform the following steps:
You can merge tables from different data sources only in Quick BI Enterprise Standard.
To merge tables from different data sources, you must enable the Quick engine extraction acceleration feature. You can go to the Data Source Function Item List to view the data sources that support the extraction acceleration feature.
In the data table list on the dataset edit page, find the data table of the target database and drag it to the canvas.

Switch the data list to another target database, find the required data table, and drag it to the canvas.
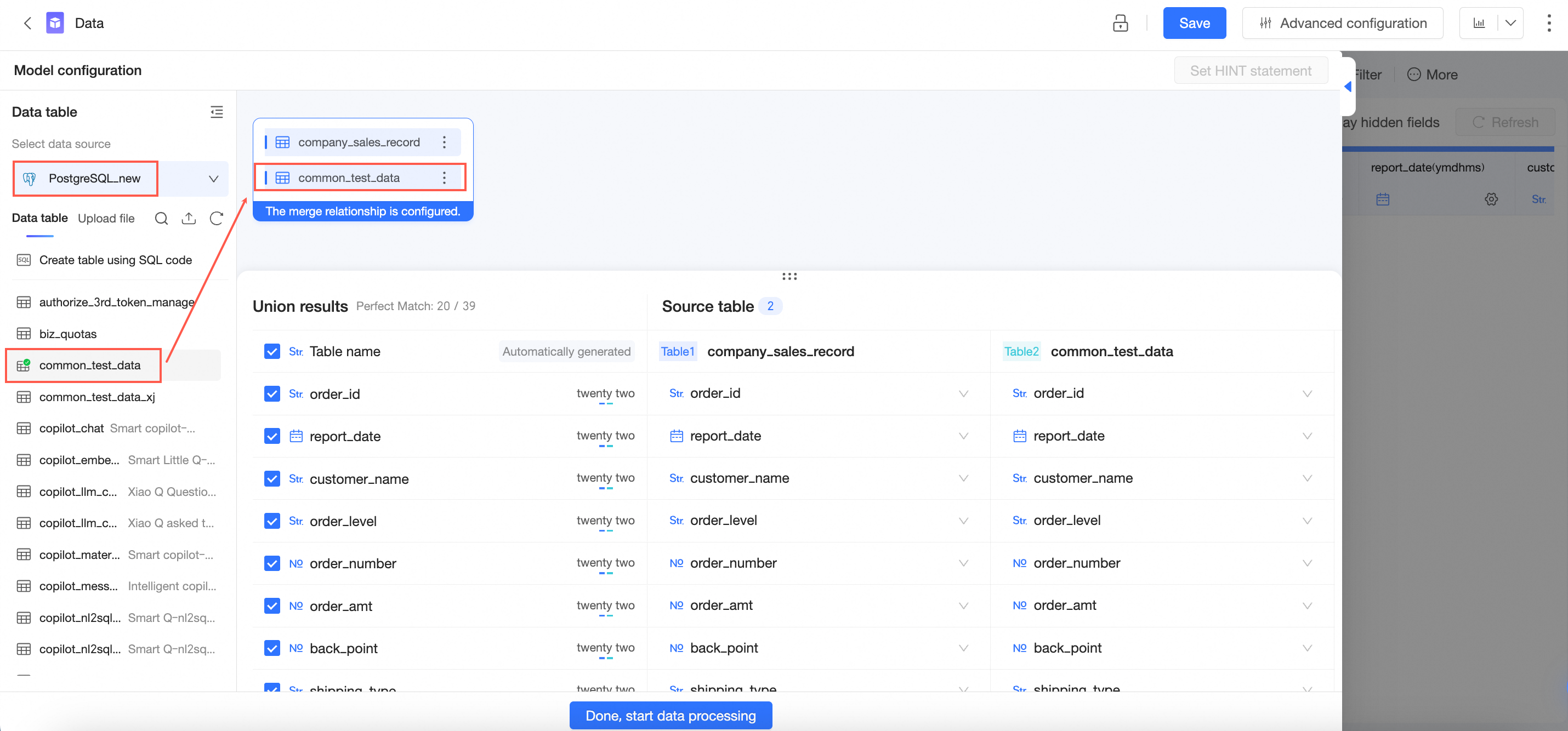
Configure the merging relationship between the data tables based on your requirements. For more information, see Configure table merging relationship in this topic. After you complete the configuration, click Complete and Start Data Processing to go to the data processing page, and save the current dataset.
Click Advanced Configuration in the toolbar at the top of the page.

Click Acceleration Configuration to go to the acceleration configuration page and turn on Quick Engine.

After you turn on Quick Engine, you need to configure the following parameters. For information about the configuration, see Configure Quick Engine.

Click Save to complete the extraction acceleration configuration.
Switch data tables
When you need to use other data tables, you can switch data tables on the table details page. You can switch to a data table from the same data source or a data table from another data source.
Notes
Currently, you cannot switch data tables for the following data sources:
Data sources created by using custom SQL statements
File data sources in exploration spaces
API data sources
DingTalk table data sources
Lark spreadsheet data sources
Lark multidimensional table data sources
When you switch data tables, fields with the same name are automatically matched. Make sure that the fields in the destination table are consistent with those in the source table.
If the data source type of the destination table is different from that of the source table, check whether the calculated fields are correct after you switch the data tables. If you have configured extraction acceleration, reset it.
Procedure
On the Table Details page, click Switch Data Table.
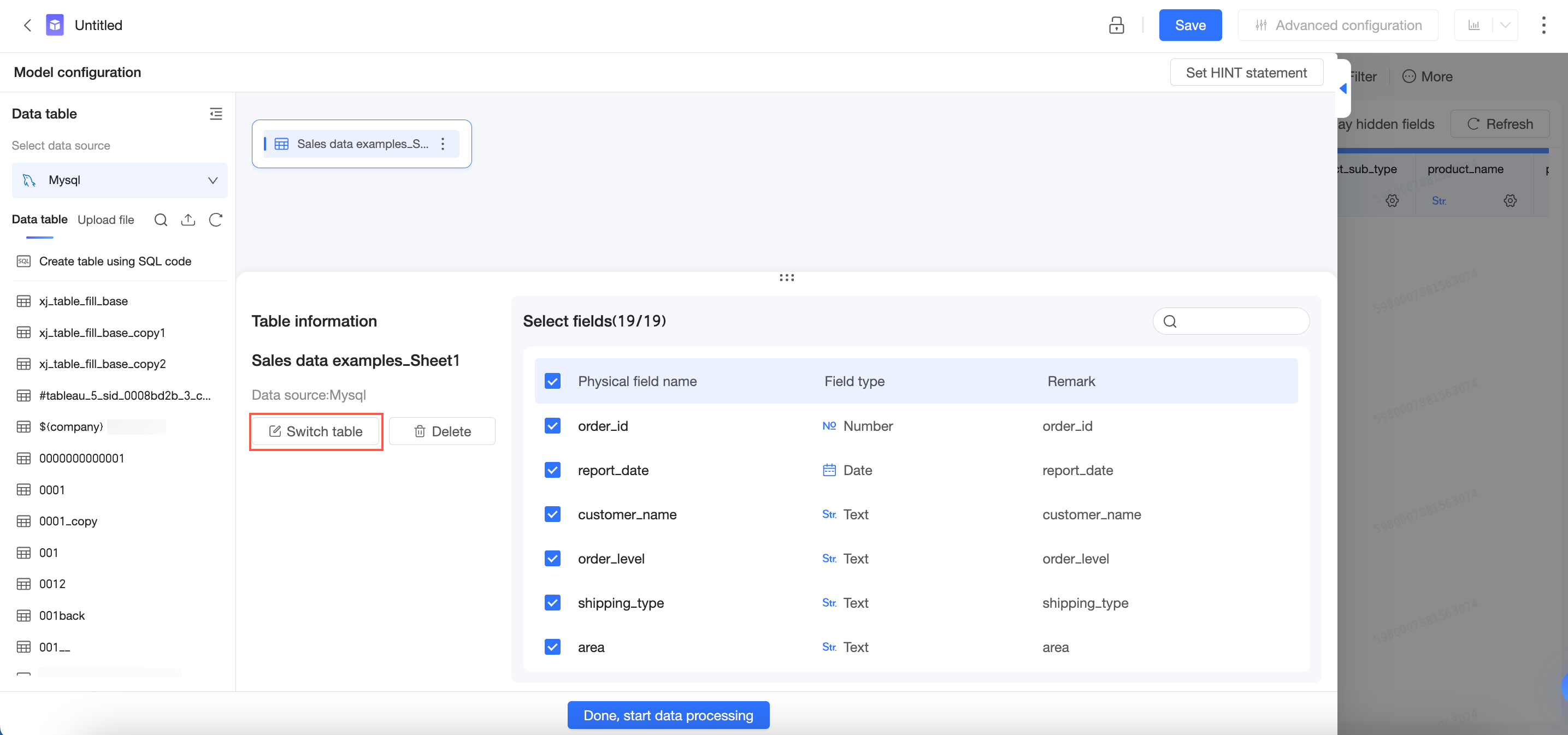
On the Switch Data Table page, select a data source and a data table.
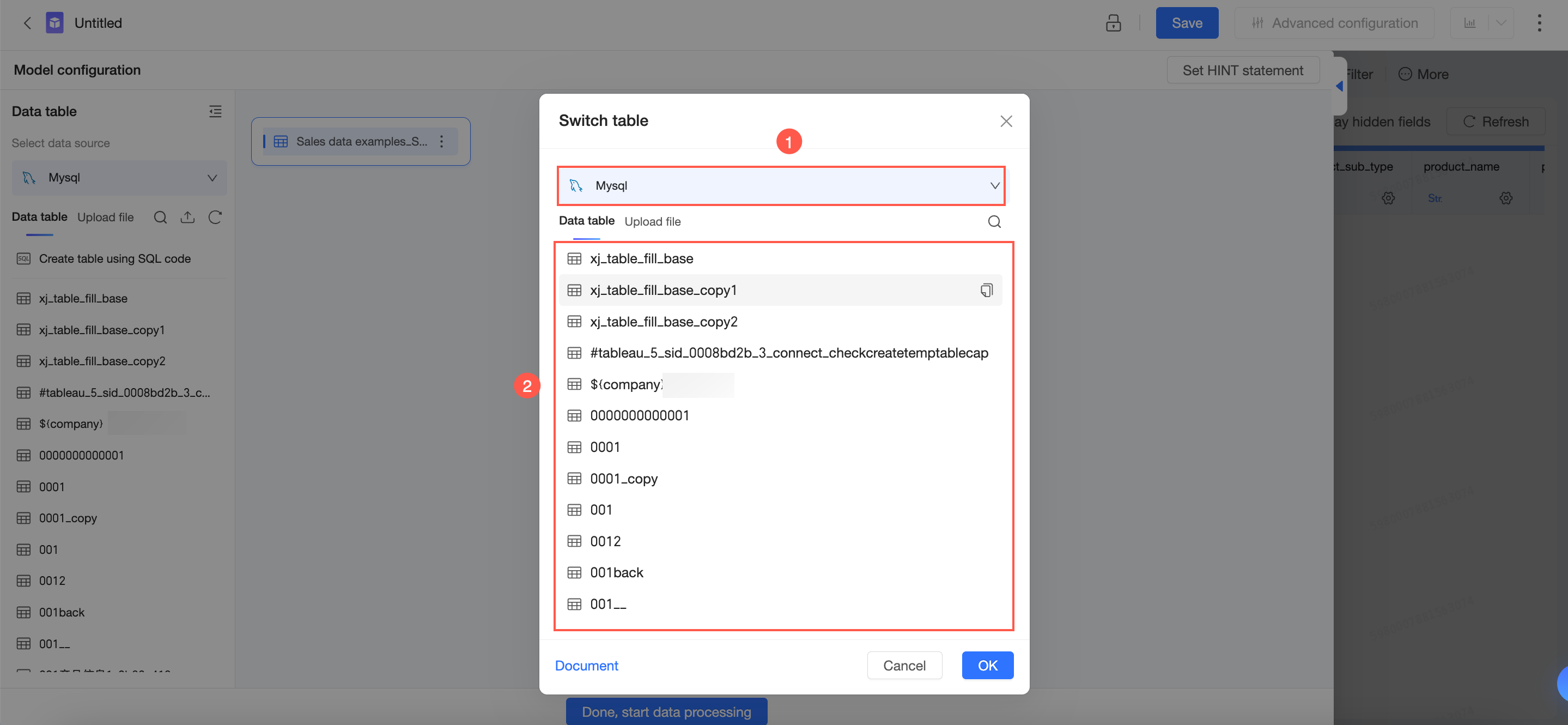
Click OK.
In the dialog box that appears, click OK to switch the data source.