Quick BI provides the Quick Engine to improve dataset performance. The Quick Engine supports four computing modes: direct connection, extraction acceleration, query cache, and dimension value acceleration. This topic describes how to configure the Quick Engine.
Prerequisites
You have connected to the target data source. For more information, see Connect to a data source.
Limits
Only users with the developer user type who have permission to create or edit datasets in a workspace can use the acceleration configuration feature.
Incremental updates are not supported for cross-source datasets.
Incremental updates are not supported for manually triggered acceleration tasks.
If a dataset contains placeholders, only accelerated placeholders support Quick Engine extraction acceleration. Other types of placeholders do not support offline extraction acceleration.
Direct connection mode
The direct connection mode is the default query mode for the Quick Engine. In this mode, all queries are sent to the underlying database or data warehouse for execution. All databases that you connect to Quick BI support this mode.
Log on to the Quick BI console.
On the Quick BI home page, follow the steps in the figure to go to the dataset editing page.

On the dataset editing page, create a dataset. For more information, see Create a dataset.

After you save the dataset, data analytics queries that are created based on this dataset use the direct connection mode by default.
Extraction acceleration
A high number of queries in direct connection mode or a large data volume can increase the database load. This can slow down queries and affect the efficiency of dashboard displays and data analytics. To address this, you can use the extraction acceleration feature of the Quick Engine. Extraction acceleration has the following features:
Periodically extracts data into the Quick Engine. This mode is typically suitable for offline data, such as data with daily granularity.
Supports incremental and full extraction, which includes two modes: full table acceleration and pre-computation.
Provides free extraction storage:
The Premium Edition provides 2 GB of extraction acceleration storage.
The Professional Edition provides 10 GB of extraction acceleration storage.
A single dataset cannot exceed 100 million rows of data.
You can scale out the extraction acceleration storage for the Premium and Professional editions as follows:
Capacity expansion must be purchased in 5 GB units ($1000/year), with a maximum expansion of 100 GB.
If you upgrade from the Premium Edition to the Professional Edition after scaling out, the paid storage capacity remains unchanged, and the free storage increases from 2 GB to 10 GB.
Extraction acceleration is supported only in the Premium and Professional editions. For a list of supported data sources, see Data source feature list. Acceleration dependencies are supported only in the Professional Edition.
When you configure extraction acceleration for MaxCompute, the data source connects over the internet, which may incur additional download fees from MaxCompute. To prevent this, you can go to the data source settings and modify the database address.
Steps to configure extraction acceleration
An organization administrator enables the extraction acceleration feature.
Log on to the Quick BI console.
Follow the steps shown in the figure to turn on the Extraction Acceleration switch.

Click the
 icon to set the dataset extraction limit.Note
icon to set the dataset extraction limit.NoteYou can set a maximum number of rows for a single dataset to optimize task execution. This setting applies to all datasets in the organization. If the number of rows exceeds the specified maximum value, the extraction task fails. A single dataset can have a maximum of 100,000,000 rows.

A data developer enables and uses the extraction acceleration feature in the target dataset.
On the Quick BI home page, follow the steps in the figure to go to the dataset management page.

In the dataset list, select the target dataset and click Acceleration Configuration.

In the Acceleration Engine section, turn on the Quick Engine switch and configure the following parameters:

Extraction Settings
Configuration Item
Description
Extraction Method
Two computing modes are supported: Full Table Acceleration and Pre-computation.
Full Table Acceleration: The system extracts the full data and performs accelerated computation.
After you enable this mode, all queries can be accelerated. This mode has high requirements for extraction storage. If you have sufficient extraction storage, select Full Table Acceleration.
Pre-computation: The system extracts partial data and performs accelerated computation.
After you enable this mode, the system pre-calculates the results of high-frequency queries. When a user accesses the report, the results can be returned quickly. For example, for a partitioned ODPS table, you can select the pre-computation method to extract only a part of the data. This saves extraction storage and improves analysis efficiency.
Execution Frequency
Two methods are supported: Manual Trigger and Scheduled Acceleration.
Select Manual Trigger. Data extraction and acceleration are performed only after you manually trigger the task.
Select Scheduled Acceleration and configure a time. Data extraction and acceleration are performed on a monthly, weekly, daily, or hourly basis.
Extraction Scope
You can extract data from a Full Table Scope or a Specified Date Range.
Full Table Scope: The entire table is updated using a full update.
Specified Date Range Update: You can set the Date Field, Date Range, and Update Method to customize the date range you want to accelerate. The Quick engine will only retain data within the selected date range, such as the last 365 days. This saves storage capacity.

Date Field
When the extraction scope is Specified Date Range Update, you can set the Date Field. The date field and its format must be consistent with the field format in the database.

Date Range
When the extraction scope is Specified Date Range Update, you can set the Date Range. T represents the latest partition time of the data extracted on the current day. The current day is T-0, yesterday is T-1, and the day before yesterday is T-2.

Update Method
When the extraction scope is Full Table Scope, the default update method is Full Update, which cannot be changed. When the extraction scope is Specified Date Range Update, you can set the update method to Full Update or Incremental Update.
Full Update: Each acceleration task fully extracts all data within the selected range.
Incremental Update: The initial task fully extracts data from the selected range. Subsequent tasks incrementally update the latest N partitions of data.
Update Scope Preview
When the extraction scope is Specified Date Range Update, you can preview the update scope.
If the Update Method is Full Update, the update scope preview shows a full update.

If the Update Method is Incremental Update, the update scope preview shows Historical Data and Incremental Update.

Number of Partitions for Incremental Update
When the Update Method is Incremental Update, you can set the number of partitions for the incremental update. Make sure the number of partitions for the incremental update is within the specified date range.
Extract Calculated Fields
Select this check box to extract calculated fields. This option is selected by default.
Dependency Settings
You can customize the dependencies of tables in the dataset. You must specify the date field, date format, and offset of the dependent table. The update is triggered only after the dependency conditions are met.
NoteIf you turn off the 'Ignore Empty Extractions' option, acceleration tasks that extract zero rows are marked as 'Failed'. In this case, you cannot configure acceleration dependencies.
If you enable acceleration dependencies and the input data is not updated, the Quick Engine polls the status of the input data every 10 minutes for up to 2 hours.
Turn on the acceleration dependency switch.

Click the plus sign (+) on the right to add the required configurations.

Configuration Item
Description
Dependent Table
Select a table from the current dataset. You can also search for a table.

Move the mouse pointer over the table name to view the corresponding data source name.

Date Field
Select a date field from the current table.

Date Format
You can select YYYY, YYYYMM, YYYY/MM, YYYY-MM, YYYYMMDD, YYYY-MM-DD, or YYYY/MM/DD.
Offset
Set the data timestamp for the polling task to check. The range is from T-0 to T-10000.
Click the plus sign (+) on the right to add more dependencies.

You can delete dependency settings.

Exception Settings
NoteIf an acceleration task fails, the system automatically retries it 3 times at 1-hour intervals.
Configuration Item
Description
Ignore Empty Extractions
If you enable this option, the status of tasks that extract zero rows is set to "Successful".
If you disable this option and a task extracts zero rows, the task status is set to "Failed". This can trigger a failure alert, and you need to promptly check the status of the input data generation.
Failure Alert
When a task fails, you can configure the reception method and recipients for alerts.
The supported reception method is Mailbox.
Recipients: You can select multiple recipients at a time. Recipients must be Alibaba Cloud accounts within the same organization.
If a recipient's name is grayed out, it means the account does not have a mailbox set. Make sure the recipient has configured a mailbox. For information about how to configure a mailbox, see Configure a recipient's mailbox.
Click Save. The Quick Engine acceleration configuration is complete.
You can perform the following operations on the dataset: Data Backfill (①), Accelerate Now (②), View Logs (③), or Modify Configuration (④).

Configuration Item
Description
Data Backfill
When the dataset structure changes, the system automatically synchronizes the latest structure to the Quick engine to ensure the accuracy of data backfill. You can flexibly set the data range for backfill in the engine to Full Backfill or Specified Range.
Full Backfill: Purges the current data and re-extracts it.
Specified Range backfill: Supports flexible settings. You can add multiple date ranges.

Accelerate Now
Immediately runs acceleration for the corresponding dataset.
View Logs
View the logs of the corresponding dataset, including time, status, and duration.

Modify Configuration
Modify the original configuration of the Quick engine. The changes take effect after you click Save.
When a task is running or pending, you can click Stop Task.

Organization administrators and workspace administrators manage acceleration tasks. For more information, see Manage extraction acceleration tasks.
Data analysts create reports and analyze data.
After the configuration is complete, you can create reports and perform data analytics, such as creating an ad hoc analysis.
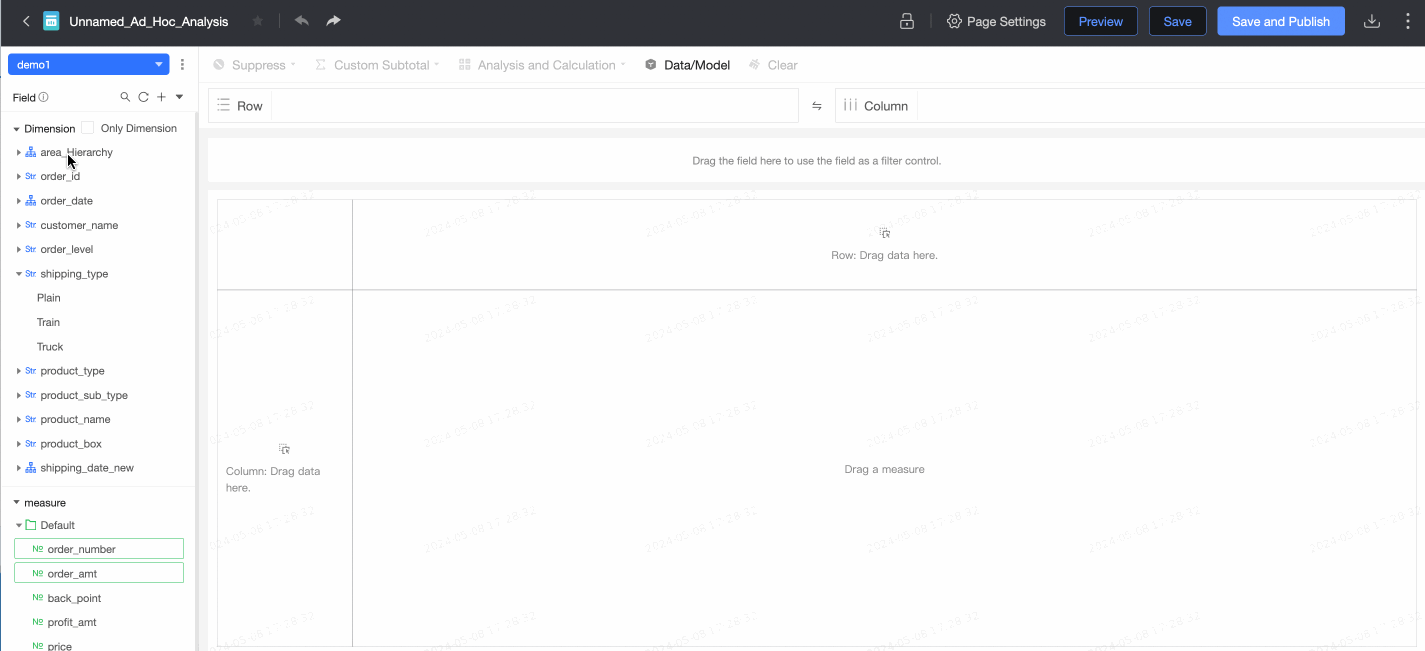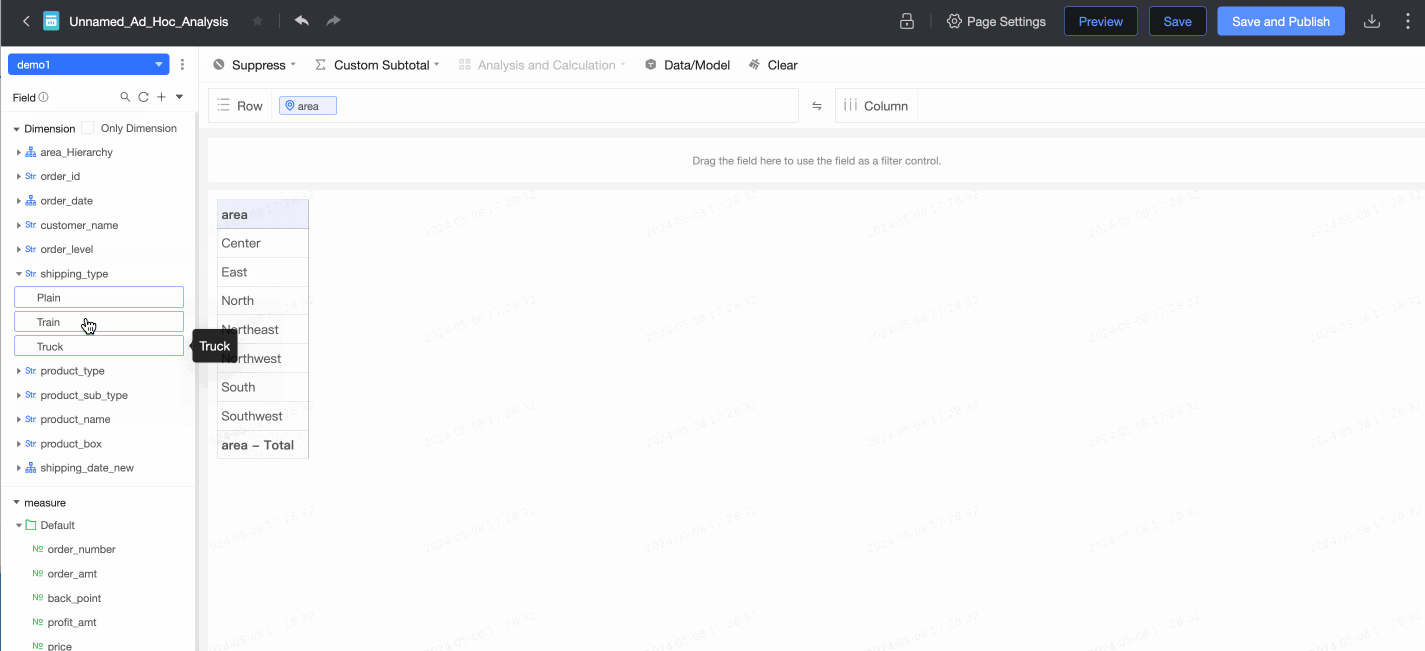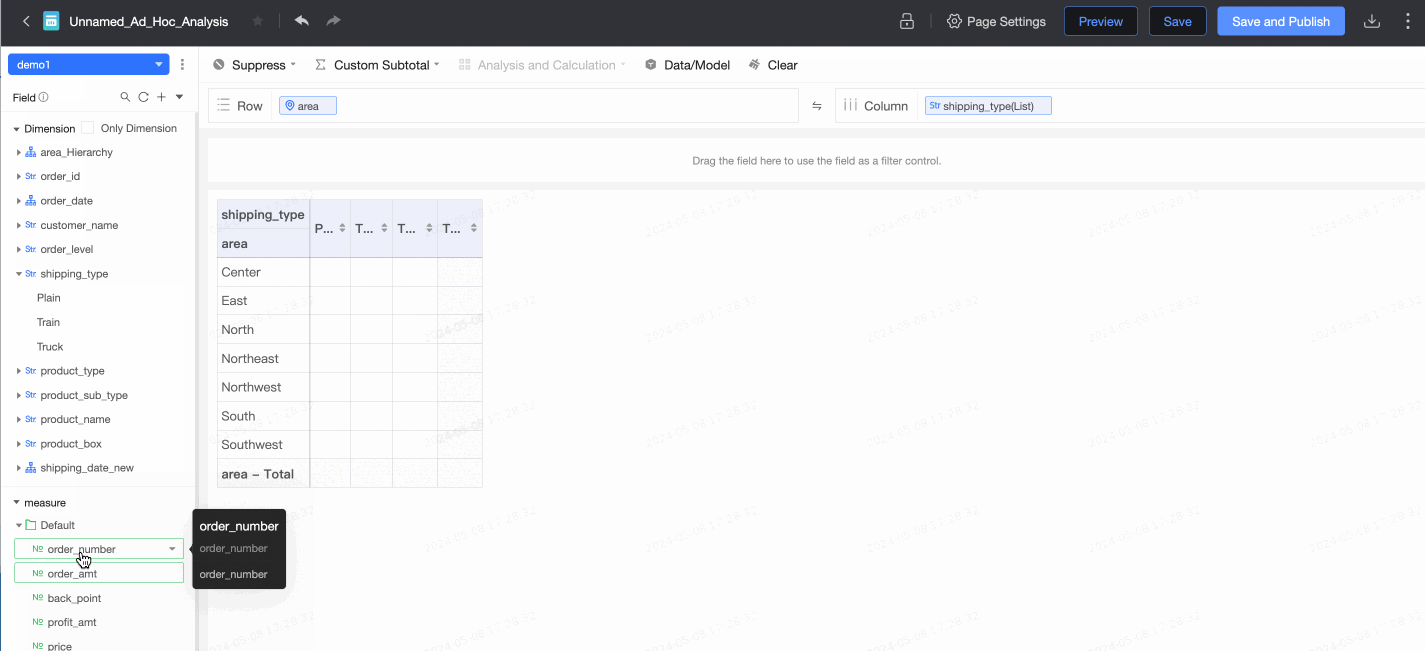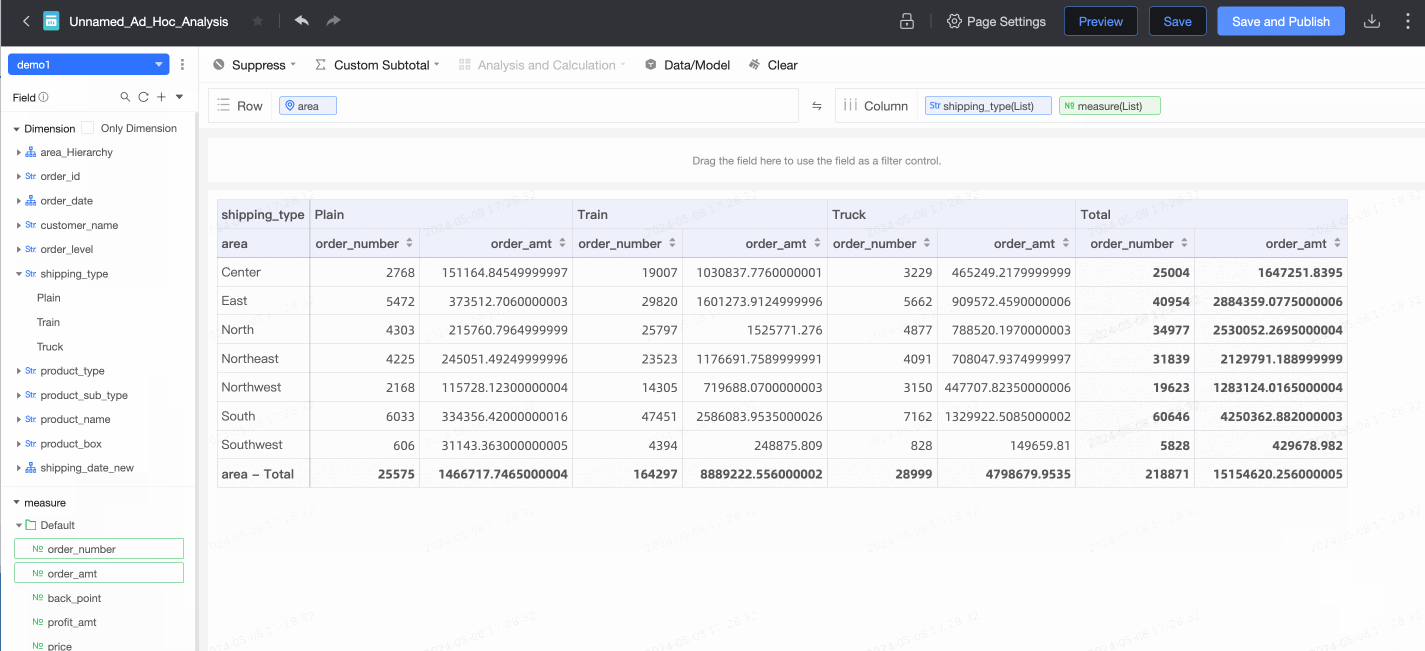
For more information, see Create an ad hoc analysis.
Manage extraction acceleration tasks
Organization-level extraction acceleration management interface
After an organization administrator enables the acceleration engine, they can view all datasets that have the Quick Engine enabled, check the running status of tasks, and manage these tasks centrally.
Overview
Displays the workspace name and owner of all datasets that have the Quick Engine enabled. Click the
 icon to View Details.
icon to View Details.
On the View Details page, you can view the datasets that have the Quick Engine enabled in the corresponding workspace. You can also perform the following operations: View Logs, Stop Task, Accelerate Now, Data Backfill, Modify Configuration, and Disable Extraction Acceleration.

View Logs
Click View Logs to view the logs of the corresponding dataset, which include the time, status, and duration of the task.

Stop Task
This operation stops the current dataset's extraction acceleration task and purges the data extracted in the current cycle.

Accelerate Now
Click Accelerate Now to run the acceleration task for the corresponding dataset. You can also click Stop Task while the task is running.

Data Backfill
Click Data Backfill and select a data range of Full Backfill or Specified Range.

Full Backfill: Purges the current data and re-extracts all data.
Specified Range: Allows you to flexibly set and add multiple date ranges for backfilling.

Click OK. The data in the specified range is backfilled for the dataset. You can also click Stop Task while the task is running.

Modify Configuration
Click Modify Configuration to go to the editing page for the dataset, where you can modify its Quick Engine configuration.

Disable Extraction Acceleration
This operation purges all historical data that was extracted for the dataset.
Switch workspace
On the workspace details page, click the Switch button next to the workspace name to switch to another workspace.

Running List
Acceleration engine resources are shared within an organization, and all running tasks occupy these resources. This page displays all running and pending tasks in the organization, which allows the organization administrator to manage them.
You can search by entering a dataset name.

You can filter running tasks by selecting Task Status, Creator, and Workspace.

You can Stop Task and Modify Configuration.

Failed List
This page displays all failed tasks in the organization, which allows the organization administrator to manage them.
You can search by entering a dataset name.

You can filter failed tasks by selecting Task Status, Creator, and Workspace.

You can Rerun Task, View Logs, and Modify Configuration.

Workspace-level extraction acceleration management interface
On the workspace-level extraction acceleration page, a workspace administrator can manage datasets that have the Quick Engine enabled within the workspace and adjust the running status of tasks. You can go to the workspace-level extraction acceleration page as shown in the figure.

You can search by entering a dataset name.

You can filter dataset tasks by selecting Task Status and Creator.

You can View Logs, Stop Task, Accelerate Now, Data Backfill, Modify Configuration, and Disable Extraction Acceleration.
Extraction acceleration FAQ
If the remaining storage in the organization is insufficient for the current dataset's extraction acceleration, will the task fail?
No, it will not. Even if the available storage is insufficient, Quick BI ensures that the acceleration task completes successfully. You are not charged for the extra usage.
Why does the storage space occupied by some datasets decrease after the extraction task is complete?
After an extraction task is complete, the Quick Engine continuously performs intelligent storage optimization. It automatically compresses the data to help you save storage space.
Does the Quick Engine support automatic retries?
Yes, it does. If a task fails, the system automatically retries it twice at 1-hour intervals.
Query cache
The dataset caching mechanism can speed up report access and reduce database pressure. For example, after you enable the cache for a dataset, if a report has already been accessed, the system can display the report data directly for subsequent access requests within the specified cache validity period without running a new query.
Result caching is a widely used and effective way to accelerate data queries. You can configure a query cache for datasets that have repeated queries within a certain period, large query data volumes, slow query speeds, or poor database query performance. This feature is especially useful for scenarios with many repeated queries, such as dashboard displays, because it can significantly improve query performance and relieve database query bottlenecks. However, the query result cache is not suitable for scenarios where data is updated frequently and reports must display real-time data.
When you enable the query result cache, you can configure different cache validity periods. For example, if the data is not updated on an hourly basis, you can select a 12-hour validity period.
The dataset cache feature is supported only in the Premium and Professional editions. It is available for all data sources that can connect to Quick BI.
Log on to the Quick BI console.
On the Quick BI home page, follow the steps in the figure to go to the dataset management page.

In the dataset list, select the target dataset and configure the cache validity period.

You can choose to Follow Global Cache Policy or Customize the cache validity period.
When you create a new dataset, the cache configuration defaults to following the global cache policy. For more information about how to configure the global cache policy, see Global cache configuration.

You can also customize the cache policy for each dataset.

Configuring a cache validity period specifies how long the cache is valid. Supported cache validity periods are 1 minute, 5 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, 4 hours, 8 hours, 12 hours, and 24 hours.
After the specified cache validity period expires, the cache becomes invalid. At this point, a query triggered on the report page creates a new cache. Subsequent identical SQL queries then retrieve data from the new cache.
The cache is at the dataset granularity. Purging the cache purges all cached chart data associated with that dataset. After the specified cache validity period expires, all chart caches for that dataset are purged.
Within the cache validity period, if the underlying data is updated and the report must display the latest data, you can manually purge the result cache before querying. This ensures that the latest data is retrieved from the database.
Click Save. The query cache takes effect.
Purge cache
Automatic cache purge.
The cache automatically becomes invalid after the configured cache validity period expires.
Manual cache purge.
Purge a single dataset cache.
On the acceleration configuration page, click the Purge Cache button to the right of Query Result Cache to purge the query result cache.

Purge the cache in batches.
On the dataset list page, select the check boxes for the datasets whose caches you want to purge. Then, click the Purge Cache button to purge the caches in a batch.

Dataset cache FAQ
Why do two charts in the same dashboard show inconsistent data even though they use the same dataset fields and query conditions?
This can happen if the dataset has caching enabled and the two charts were added at different times. After the first chart is configured, subsequent queries load cached data as long as the cache is valid and the query conditions remain unchanged. If a user adds a new chart after the underlying database data has been updated, the first chart does not reflect this update because its query conditions have not changed. The new chart, however, loads the latest data when it is configured. This leads to inconsistent query results between the two charts. To resolve this, you can disable the cache configuration or manually purge the dataset cache.
If I enable the global cache, will it apply to existing historical datasets?
Yes, it will. After you enable the global cache, it applies to all existing datasets. The global cache is also enabled automatically for any new datasets you create.
The data in the database table used by my Quick BI report has been updated, but the report does not reflect the changes. Why?
Report data comes from a dataset. First, confirm whether the dataset data has been updated. If it has not, check whether the dataset is configured with a result cache or extraction acceleration. If a result cache or extraction acceleration is configured, dataset queries retrieve data from the cache or accelerated extraction first, instead of connecting directly to the database.
Solutions
Disable the query result cache. This forces all queries to use a direct database connection, which maintains data consistency.
Manually purge the dataset result cache. The next query will retrieve the latest data from the database and cache it.
Set a reasonable automatic cache purge time based on your business data update frequency to ensure that queries retrieve the latest data.
Rerun the extraction acceleration task or disable extraction acceleration, and then refresh the dataset preview.
A dataset that used to load data in real time now requires me to click 'Purge Cache' to display the latest data. Why?
This can happen if your organization administrator has enabled the global cache setting, which causes datasets without specific acceleration settings to be cached. To resolve this, you can ask the organization administrator to disable the global cache setting, or you can customize the cache policy in the dataset's cache configuration.
Where is the dataset cache data stored?
The cache stores query results on the in-memory servers of Quick BI.
Dimension value acceleration
If certain dimension fields are frequently used in query controls and ad hoc analyses, you can configure dimension value acceleration for these high-frequency fields. For example, to query transaction details based on customer name and product name, you must configure dimension value acceleration for the customer name and product name fields in the Order Details table.
Assume that these two fields exist in the database tables customer_info and product, and are named user_name and product_name, respectively.
After you configure acceleration, data queries are faster because Quick BI only needs to query the value of user_name in customer_info and the value of product_name in product, instead of performing an aggregate query on the Order Details table.
The dimension value acceleration feature is supported only in the Premium and Professional editions. It is available for all data sources that can connect to Quick BI.
Log on to the Quick BI console.
On the Quick BI home page, follow the steps in the figure to go to the dataset management page.

In the dataset list, follow the steps in the figure to select the target dataset and configure dimension value acceleration.

After you enable dimension value acceleration, assume the target dataset is Order Details. To query transaction details on a dashboard based on customer name and product name, you must configure dimension value acceleration for these two fields.

Assume that the customer name and product name fields are in the database tables customer_info and product, respectively. The corresponding field names are
user_nameandproduct_name. In this case:Dataset Dimension: Customer Name and Product Name, respectively.
Configuration Table: customer_info and product, respectively.
The fields in the configuration table are
customerandproduct_name, respectively.
Global cache configuration
Organization administrators of the Premium and Professional editions can configure a global cache policy. The global cache is disabled by default for new organizations.
You can go to the global cache configuration page as shown in the figure.

If you select Enable for the global cache (①), you can set the Interval for returning cached results for identical queries (②) and the Automatic purge time (③).
 Note
NoteThe interval for returning cached results for identical queries can be set to 1 minute, 5 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, 4 hours, 8 hours, 12 hours, or 24 hours.
The automatic purge time is every half hour.
Click Update Configuration to save the configuration.