In data analysis, custom SQL enables the creation of data tables with complex logic or models. It also supports parameter passing to accommodate more sophisticated and variable analysis scenarios.
Prerequisites
You have obtained the data. For more information, see Connect to a data source.
Limits
API data sources do not support custom SQL.
Enter SQL code
You can add custom SQL using one of the following methods:
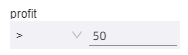
Navigate to the custom SQL page.
Entry 1: On the data source page, click Create Dataset By SQL in the upper-right corner.
Entry 2: On the dataset editing page, select the data source in the left panel. If there is no data table on the canvas, click Click To Create A Dataset Using SQL Code on the canvas or Create table by SQL code in the left panel.

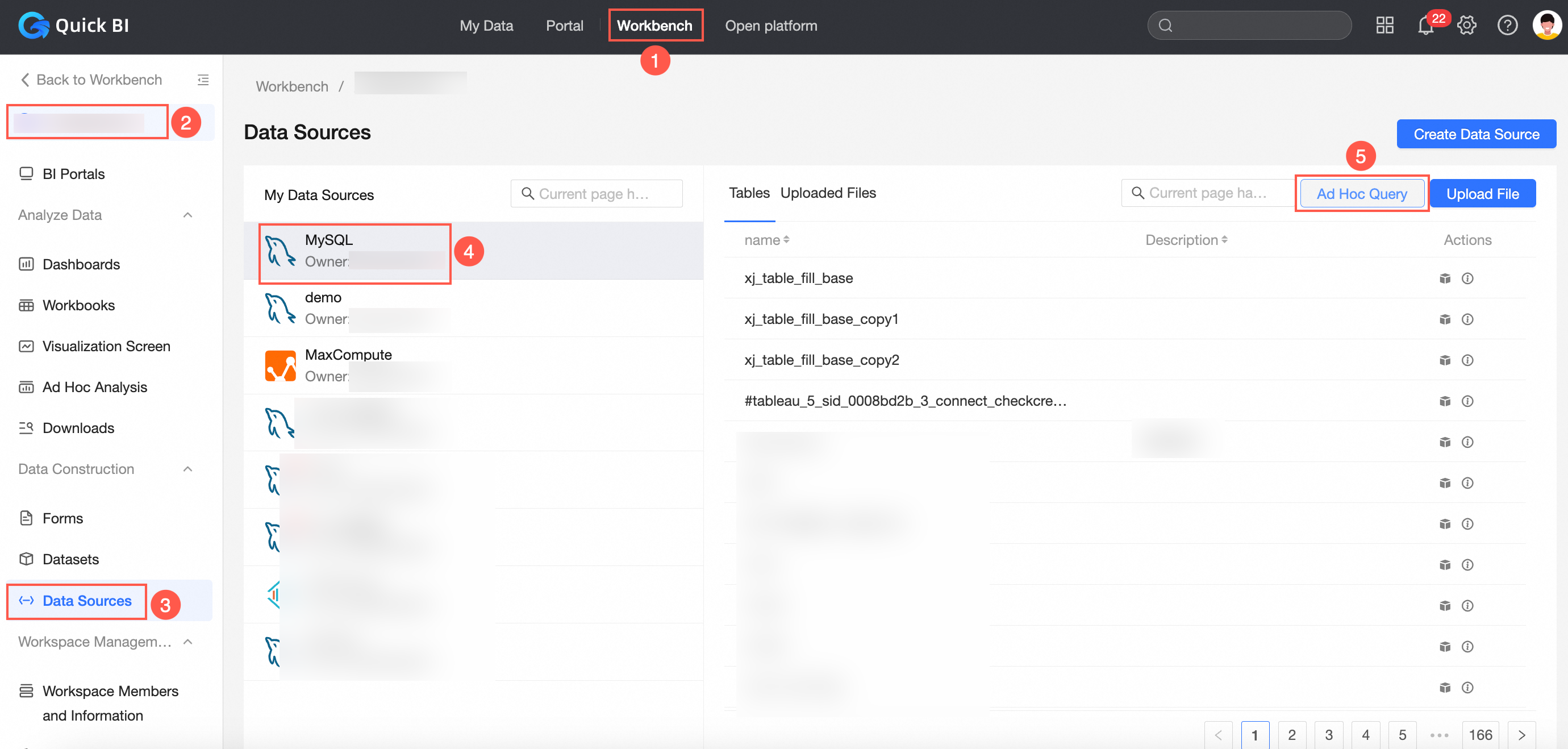
After entering the SQL code, click Run.
Sample SQL statement:
SELECT report_date, order_level, shipping_type, area, price, order_number from company_sales_record where $expr{report_date :report_date} and $expr{order_level :order_level} and $expr{order_number :order_number}After a successful run, you can preview the results on the Run Result tab.

Click Confirm Edit to save the dataset created with the custom SQL statement.
Modify SQL code
You can modify the SQL code using one of the following three methods:
Click the
 icon to the right of the target table.
icon to the right of the target table. 
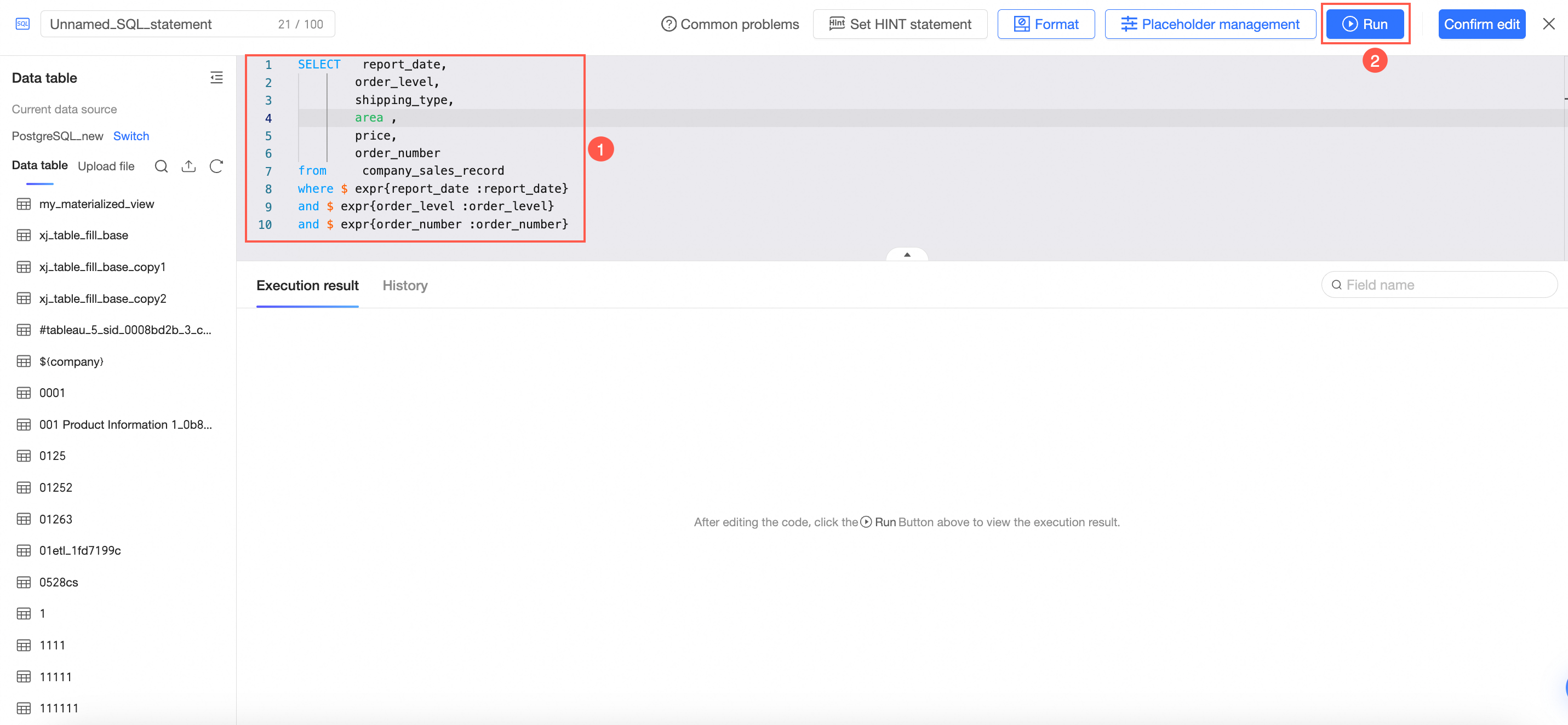
Click the target table on the canvas. In the Table Details section below, click Edit Code.

Click the
 icon to the right of the target table and select Edit Code.
icon to the right of the target table and select Edit Code.
SQL syntax
Custom SQL for datasets primarily supports query statements. INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE syntax are not supported in custom SQL statements, nor are stored procedures.
The SQL query syntax follows the database syntax of the data source being used. For example, if the data source uses MySQL, the custom SQL should be written according to MySQL query statements. Some special database syntax is not supported in Quick BI, such as find() and findone() in MongoDB. In custom SQL, you need to use SELECT statements to query data.
When adding comments in custom SQL, you can use the format "--" + space + comment.

Sample SQL statement:
SELECT area, -- area price -- price from company_sales_recordWhen joining multiple tables in custom SQL, you need to pay attention to the use of table aliases and field aliases, as different databases may have different syntax for writing aliases.
There is no limit to the number of rows in custom SQL for datasets, but the custom SQL character length cannot exceed 65,536 characters. If necessary, you can split and optimize the custom SQL logic, or create multiple datasets separately and then perform join queries.
Dataset SQL is executed in the database, and the result data is returned to Quick BI. The query wait time is 5 minutes. If data is not returned after 5 minutes, a timeout error will occur.
If a query timeout error occurs before the 5-minute limit, common causes include timeout settings on user-side network devices such as SLB, or firewall network blocking policies that cause query interface requests to be intercepted.
Placeholders
Quick BI allows for parameter passing using placeholders. This feature enables flexible data analysis during report viewing and data analysis by passing placeholder values to SQL through a query control. Quick BI supports both value and expression placeholders, which you can configure as needed.
Type | Description | Scenarios | Format |
Value placeholder | You can pass a value or a set of values through the query control on the dashboard. Note If the placeholder indicates a date value, you must specify the date format to determine the format of the input value. | Applicable to most scenarios where parameters need to be passed. |
|
Expression placeholder | You can pass a condition through the query control on the dashboard. | When users can freely modify the filter method in the filter conditions on the dashboard, you need to use an expression placeholder to pass the entire filter condition to SQL. For example, in the following dashboard, users can set |
|
Configuration method
Compose SQL to meet business requirements and incorporate placeholders.
On the SQL code editing page, click Placeholder Management.

In the Placeholder Management panel, configure the placeholders as shown and click OK.
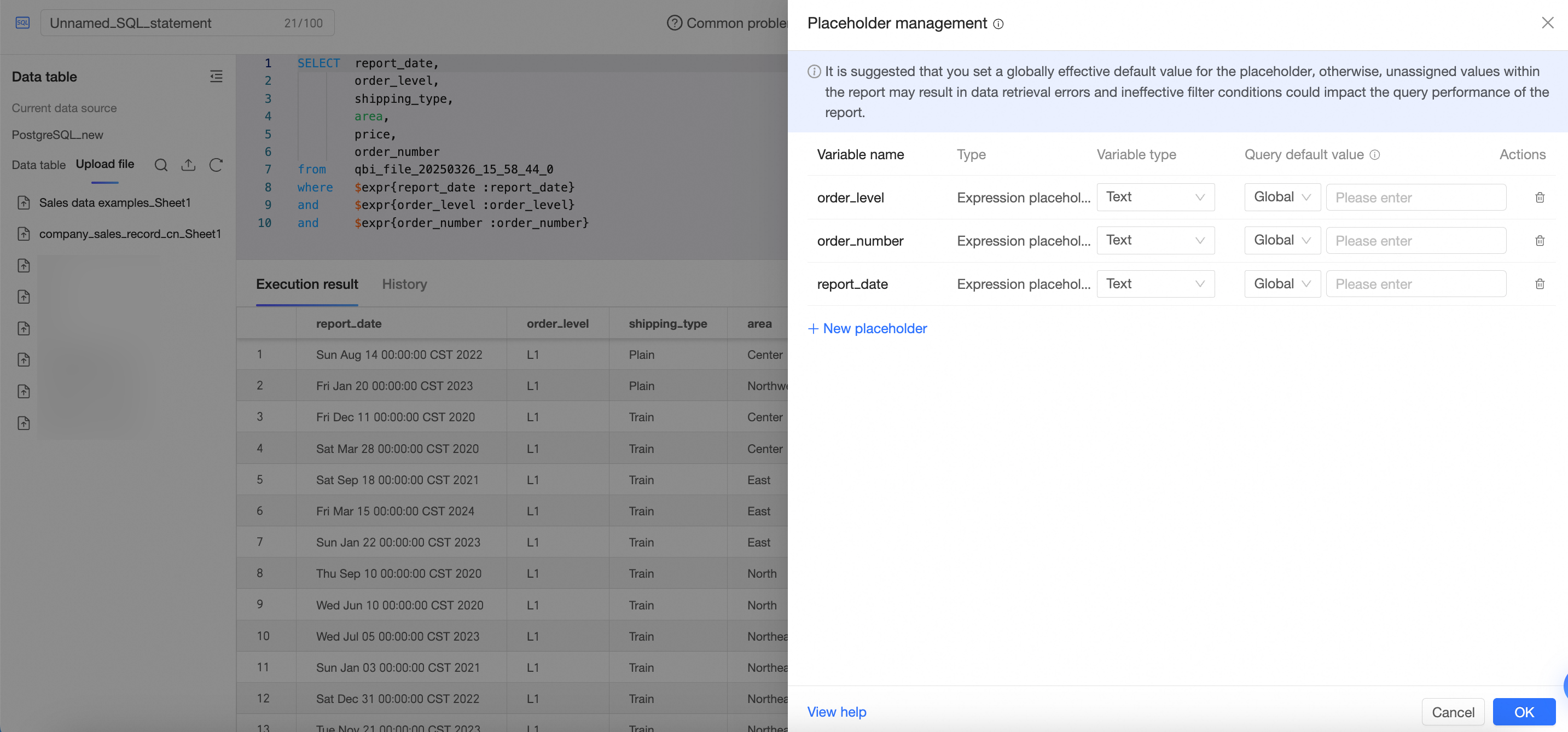
For configuration items, see Create a dataset.
NoteIf a placeholder is used after the select statement, you must assign a globally effective default value.
For instance, when creating a dataset, include the placeholder "profit_range" after the select statement as follows:
SELECT report_date, order_level, shipping_type,price,order_number,area, case when profit_amt< ${profit_range} then'Loss' when profit_amt> ${profit_range} then'Profitable' else 'Flat' end 'order_level' from company_sales_record where $expr{report_date :report_date} and $expr{order_level :order_level} and $expr{order_number :order_number}Without a default value, the code will not run correctly.

Set the query default value for "profit_range" in Placeholder Management.

After setting the default value, the code will run correctly, as shown:

Click Save to store the dataset.

In the top menu bar, click the
 icon or click the
icon or click the  icon and select Create Dashboard.
icon and select Create Dashboard.
On the dashboard editing page, add query conditions and bind placeholders.
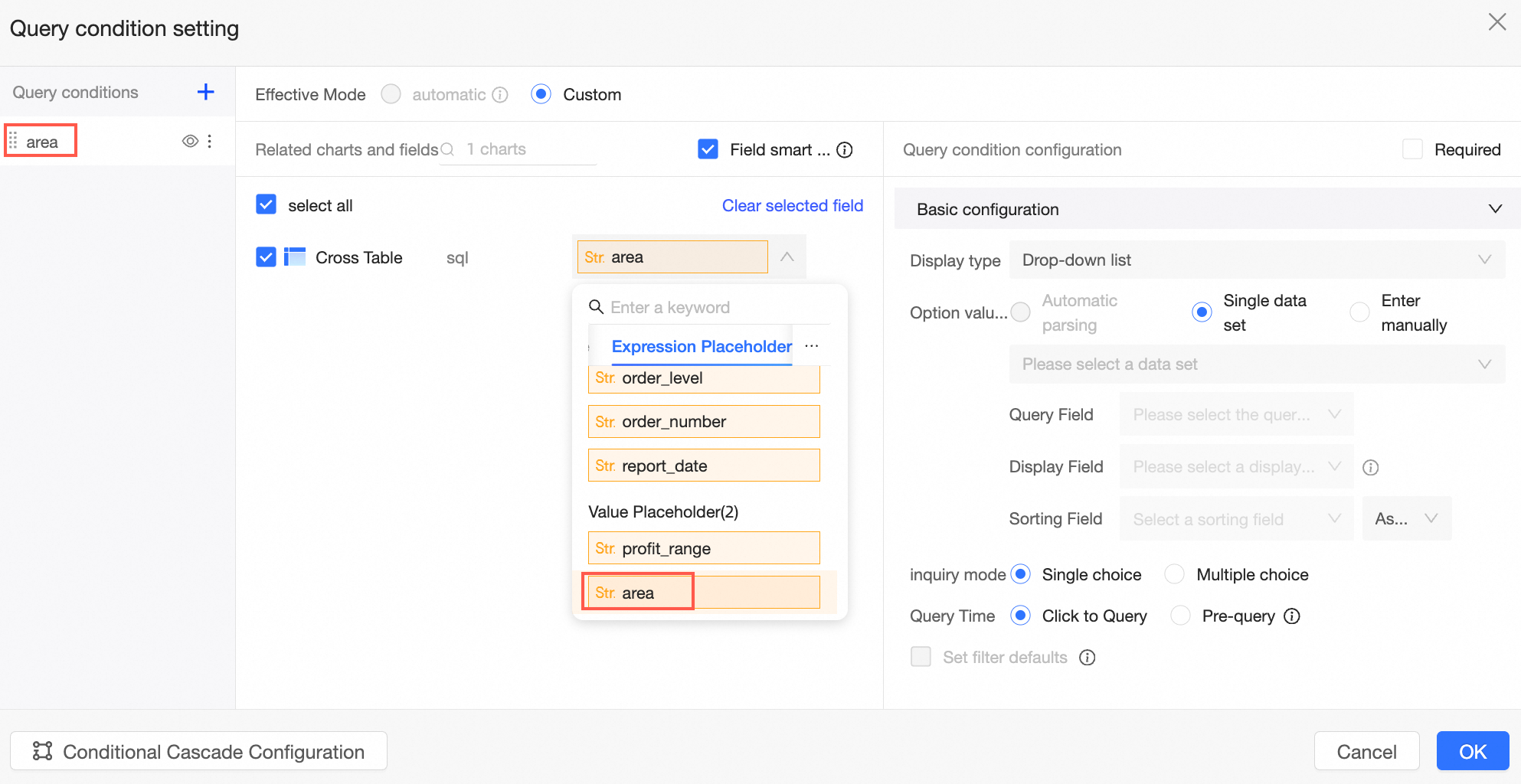
For instance, to set query conditions, use a drop-down single selection to filter area, bind the SQL placeholder, and pass in one value.
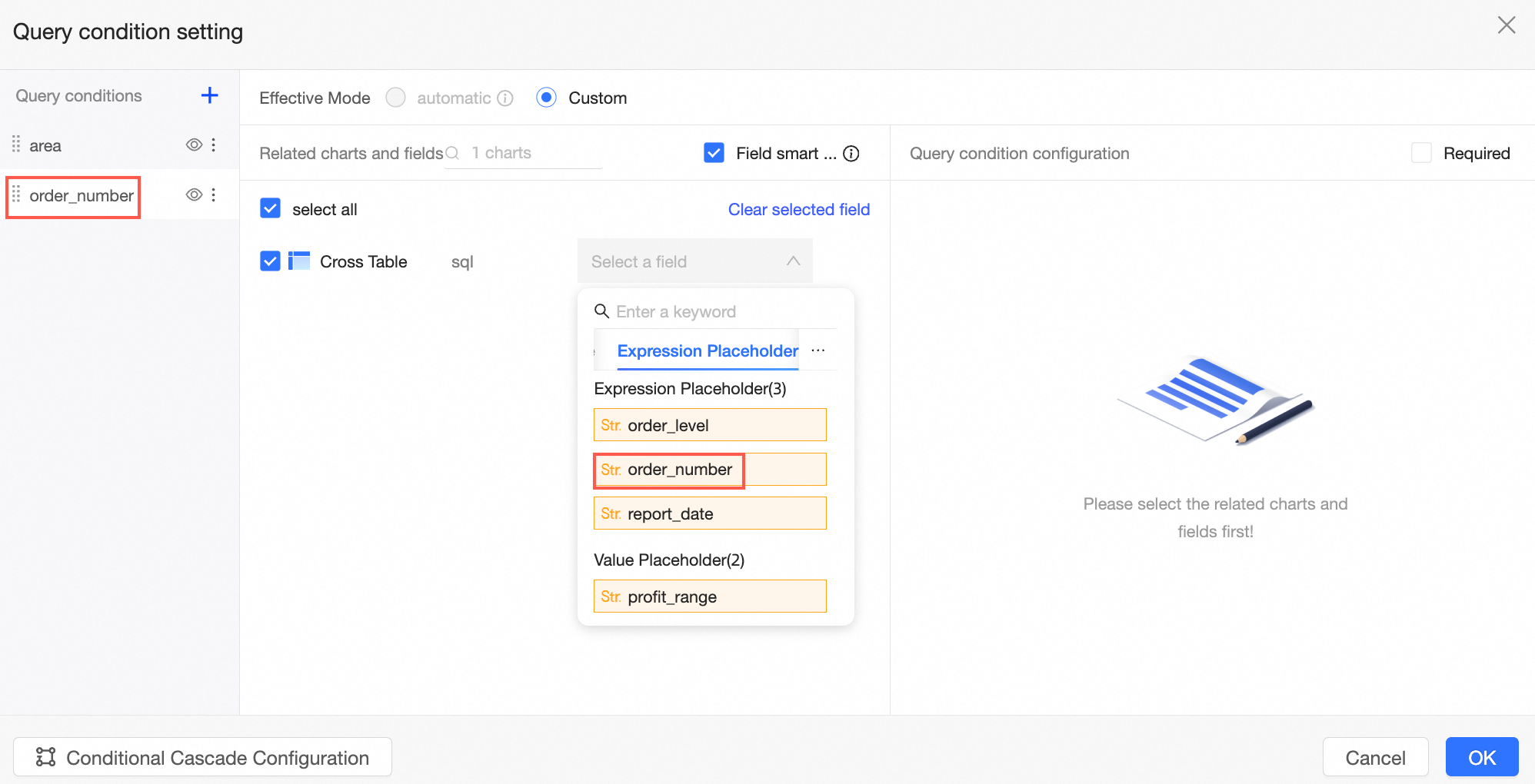
Use text filtering to filter order_number, bind the SQL parameter, and pass in a condition.
When the dashboard is queried, it will transmit the specified content to the value and expression placeholders based on the query conditions.
For example, the dashboard query conditions are illustrated below.

The corresponding SQL is as follows:
SELECT * FROM company_sales_record WHERE area = 'North' AND order_number > 100An example of using placeholders is as follows:
SELECT * FROM tablename WHERE area in ('$val{area_ph}') -- Text type, multiple selection AND name = '$val{name_ph}' -- Text type, single selection AND number = $val{number_ph} -- Numeric type AND report_date > '$val{report_date_ph.get(0)}' -- Date type, obtain the start date of the date range control AND report_date < '$val{report_date_ph.get(1)}' -- Date type, obtain the end date of the date range control
For scenarios where placeholders are applied, refer to Placeholders.
Compatible with historical writing:
Historical writing of value placeholders (original placeholders): ${placeholder_name}
Historical writing of expression placeholders (original parameters): ${physical_field_name:parameter_name}