Audience filtering is the main way to generate a audience.
What is audience?
A audience in Quick Audience is essentially a list of specified multiple users. The list contains the user's QAID.
The QAID that Quick Audience generates for the user when the user data stored in the audience file is imported to Quick Audience. When you use a group of users, Quick Audience can map all the ID types contained in the user data based on the user's QAID, and then use the currently required ID type.
Different from the full users in the original data table, the audience is generally generated after filtering from the full users for specific purposes or to meet specific conditions.
Example 1: You want to send text messages to a group of users. If you have a list of their mobile phone numbers, you can use Upload Audience to save them as a group. Then, you can conduct SMS Marketing to the group.
Example 2: If you want to send SMS greetings to users who celebrate their birthdays this month, you can import the user tags table of all users. The table contains the mobile phone numbers and birthdays. Then, you can filter the users who celebrate their birthdays this month into a group of users by Tag Filtering and conduct SMS Marketing to them.
audiences can be used for many purposes, such as Insight Analysis, Marketing Content Sending, and pushing to Data Bank, Damengpan, or Kafka.
Type of audience filtering method
To generate audience from the imported data, you mainly filter the audience that meets specific conditions. There are multiple ways to filter audience, depending on the data table and the type of model generated from the data table:
Tag Filtering: filters audience based on user tags, including user attributes and custom tags. The relationship between multiple tag filtering conditions can be AND, OR. For example, province=Zhejiang province and gender=female are selected.
AIPL Model Filter: filters audience based on AIPL models. You can filter users by AIPL model type or forwarding status.
Filter by type: Select users in the cognition, I interest, P purchase, and L loyalty stages to join the audience.
Filter by Flow Status: Select users whose AIPL model phase has changed. For example, users who have changed from the cognitive phase to the P purchase phase to join the audience.
RFM Model Filter: allows you to filter audience by RFM model. For example, you can filter high-value users.
Behavior filtering: filters audience whose behavior or order records meet the requirements based on user behavior data and order details data. For example, the group of people who purchased product A from offline stores in the last 30 days.
Metric Filter: The imported statistics table is used to filter out audience who meet the specified metric and dimension requirements. For example, audience whose mobile devices are in a city and have logged in to the app at least once in the last seven days.
Audience Intersection: A new audience is generated by calculating the sum (intersection), or (merge), and difference of an existing audience.
Cross Filtering: You can use a combination of the preceding methods to obtain the final audience by calculating the sum, the sum, the sum, or the difference between the results of the preceding audience filtering.
If one or more audience pass and, or, or are poor with other audience filtering methods to generate new groups, they will be classified as audience intersection instead of cross-filtering.
FAQ
In addition to audience filtering, what are other audience generated methods?
A: In addition to passing audience filtering, support:
Audience is generated for each selected tag value based on text or multi-value tags. For more information, see Select Audience Based on Tag Values.
You can upload a user ID in the CSV or TXT format to audience. For more information, see Upload Audience.
Generate audience by reading the user ID data table from the analysis source. For more information, see Create Audience from Analysis Source.
You can use the Duplicate audience feature to obtain a new audience that is the same as the original audience. For more information, see Duplicate Audience.
When you perform user analysis, you can create a new audience or add them to an existing audience. For more information, see User Analysis.
When you perform a self-service analysis, you can select a graph or data in a report to select audience. For more information, see Self-service Analysis.
Within seven days after you run a non-automated SMS, email, or push marketing task, you can create audiences who send the specified results on the task details page. For more information, see SMS Marketing Tasks Management, Email Marketing Tasks Management, and PUSH Marketing Tasks Management.
Within seven days after the execution of components such as text and SMS in automated marketing, you can save the users who have been sent or failed to be sent as audience in the Action Analysis panel. For more information, see View The Execution of Campaign.
When you view an analysis report, you can select audience by selecting graphs or data in the report. For more information, see Analysis Dashboard Select Audience.
What is the sum (cross), or (combination) and difference in the audience filtering operation?
Answer: They are three common ways of set operations:
And: and, both conditions are met, which is equivalent to the intersection operation, which is to take the overlapping parts of the two sets and then deduplicate them.
Or: Alternatively, only one of the conditions needs to be met, which is equivalent to the union operation, which is to merge the two sets and then deduplication.
Difference: a difference set operation that removes the part of the previous set from the next set.
As shown in the following figure, the two circles R and S are the original data set, and the shaded part is the result after the operation. 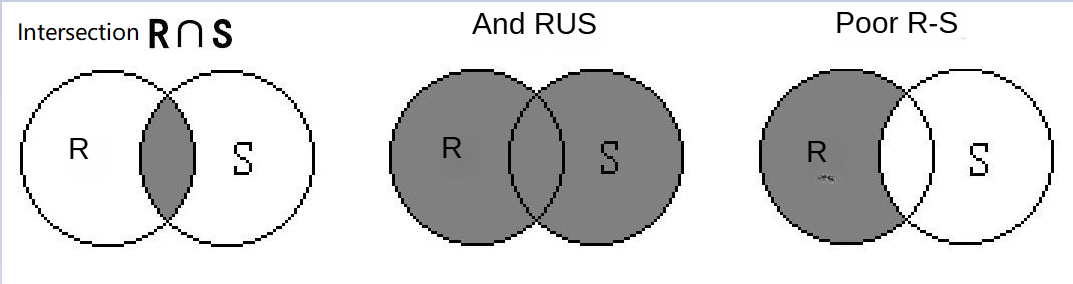
recommend reading
User Insight FAQ
Audience Management, Audience Push, Audience Analysis, Self-service Analysis, Audience Marketing, and Automatic Audience Marketing