This topic describes how to preprocess multi-modal data in AI Search Open Platform.
Scenarios
Multimodal data preprocessing provides solutions for processing unstructured documents and images. The complete process consists of document parsing, image parsing, document slicing, text embedding, and text sparse. You will experience the complete data processing process. All these services require the API service of AI Search Open Platform and will charge based on the actual usage.
Prerequisites
AI Search Open Platform is activated. For more information, see Activate AI Search Open Platform.
The service endpoint and identity authentication information are obtained. For more information, see Query service endpoint and Manage API key.
AI Search Open Platform allows you to call services over the Internet or a virtual private cloud (VPC) and also supports cross-region service calling through VPC. Users in the Germany (Frankfurt) regions can use services in the AI Search Open Platform console by using VPC endpoints.
Development framework for preprocessing multimodal data
To facilitate user access, AI Search Open Platform offers the following development frameworks:
SDK for Java.
SDK for Python.
If your business uses LangChain, select LangChain for development framework.
If your business uses LlamaIndex, select LlamaIndex for development framework.
Step 1: Select services and download the code
In this example, SDK for Python is used as a development framework to build a multi-modal data preprocessing solution.
Log on to the AI Search Open Platform console.
In the top navigation bar, select the Germany (Frankfurt) region.
In the left-side navigation pane, select Scene Center. On the Scene Center page, click Enter in the Multimodal Data Processing Scenario - Data Parsing and Vectorization section.
On the Basic configuration tab of the Scene Development tab, select the services that you want to use from the drop-down lists in the Service Name column. On the Service Details tab, you can view the service details.
NoteIf you want to use an algorithm service in the RAG-based solution by calling an API operation, you must specify the service ID by using the service_id parameter. For example, the ID of the document content parsing service is ops-document-analyze-001.
After you select a service, the service_id parameter in the generated code is modified accordingly. After you download the code to the local environment, you can modify the service_id parameter in the code to call other services.
Service
Description
Document content parsing
Document Content Parsing Service (ops-document-analyze-001): provides a general-purpose document parsing service. You can use this service to extract logical structures, such as titles and paragraphs, from non-structured documents, such as text, tables, and images, to generate structured data.
Image content parsing
Image Content Recognition Service 001 (ops-image-analyze-vlm-001): parses and understands image content and identifies text based on multi-modal LLMs. The parsed text can be used for image retrieval and conversational research scenarios.
Image Text Recognition Service 001 (ops-image-analyze-ocr-001): uses optical character recognition (OCR) capabilities for image text recognition. The parsed text can be used for image retrieval and conversational research scenarios.
Document Slicing
Common Document Slicing Service (ops-document-split-001): provides a general-purpose text slicing service. You can use this service to segment structured data in the HTML, MARKDOWN, and TXT formats based on paragraphs, semantics, and specific rules. You can also extract code, images, and tables from rich text.
Text vectorization
OpenSearch text embedding service -001 (ops-text-embedding-001): provides a text embedding service that supports more than 40 languages. The maximum length of the input text can be 300 tokens, and the dimension of the generated vectors is 1,536.
OpenSearch Universal Text Vectorization Service -002 (ops-text-embedding-002): provides a text embedding service that supports more than 100 languages. The maximum length of the input text can be 8,192 tokens, and the dimension of the generated vectors is 1,024.
OpenSearch text vectorization service-Chinese -001 (ops-text-embedding-zh-001): provides a text embedding service for Chinese text. The maximum length of the input text can be 1,024 tokens, and the dimension of the generated vectors is 768.
OpenSearch text vectorization service-English -001 (ops-text-embedding-en-001): provides a text embedding service for English text. The maximum length of the input text can be 512 tokens, and the dimension of the generated vectors is 768.
Text sparse vectorization
Text sparse embedding converts text data into sparse vectors that occupy less storage space. You can use sparse vectors to express keywords and the information about frequently used terms. You can perform a hybrid search by using sparse and dense vectors to improve the retrieval performance.
OpenSearch text sparse vectorization service-generic (ops-text-sparse-embedding-001): provides a text embedding service that supports more than 100 languages. The maximum length of the input text can be 8,192 tokens.
After you select the services, click After the configuration is completed, enter the code query to view and download the code based on the execution flow when the application calls the data preprocessing solution.
Process | Description |
This process consists of document parsing, image extraction, document chunking, and text embedding. | You can call the main function document_pipeline_execute to perform the following steps. You can specify the document to be processed by using a document URL or Base64-encoded file.
|
On the Code Query tab, click Text Parsing and Vectorization. In the code editor, click Copy Code or Download File to download the code to your device.
Step 2: Test the code in the local environment
After you download the code files to your device, you must specify the parameters in the code. The following table describes the parameters.
Section | Parameter | Description |
AI Search Open Platform | api_key | The API key. For more information about how to obtain the API key, see Manage API keys. |
aisearch_endpoint | The API endpoint. For more information about how to obtain the API endpoint, see Query service endpoint. Note You must remove "http://". You can call API operations over the Internet or a VPC. | |
workspace_name | AI Search Open Platform. | |
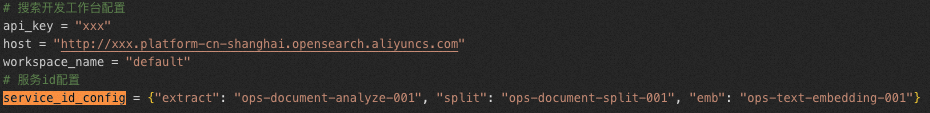
service_id | The service ID. To facilitate code development, you can configure services and specify service IDs separately in the offline.py and online.py files by using the service_id_config parameter.
|
After completing the parameter configurations, you can run the code in Python 3.8.1 or later to test whether the results are correct.
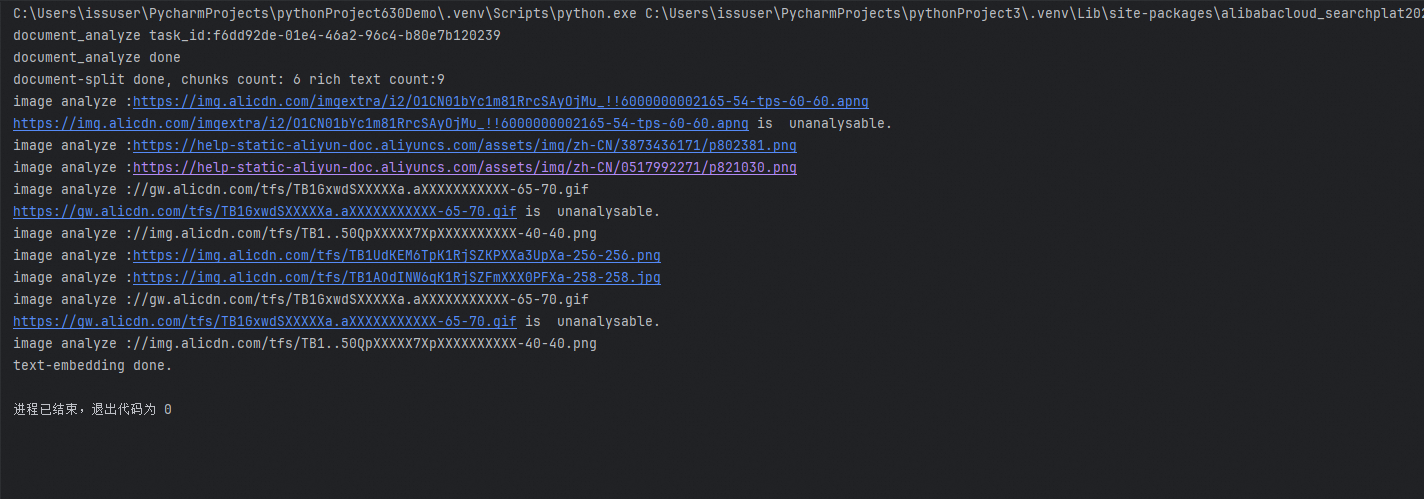
If you preprocess AI Search Open Platform data in the code, the running results are as follows.
Document parsing and embedding files:
# Multi-modal data processing solution
# The following environment requirement is met:
# Python version 3.7 or later is installed.
# The following dependency is installed:
# pip install alibabacloud_searchplat20240529
# AI Search Open Platform configurations
aisearch_endpoint = "xxx.platform-cn-shanghai.opensearch.aliyuncs.com"
api_key = "OS-xxx"
workspace_name = "default"
service_id_config = {"document_analyze": "ops-document-analyze-001",
"split": "ops-document-split-001",
"text_embedding": "ops-text-embedding-001",
"text_sparse_embedding": "ops-text-sparse-embedding-001",
"image_analyze": "ops-image-analyze-ocr-001"}
# Specify the document URL. In this example, the OpenSearch product description document is used.
document_url = "https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/zh/open-search/search-platform/product-overview/introduction-to-search-platform?spm=a2c4g.11186623.0.0.7ab93526WDzQ8z"
import asyncio
from operator import attrgetter
from typing import List
from Tea.exceptions import TeaException, RetryError
from alibabacloud_tea_openapi.models import Config
from alibabacloud_searchplat20240529.client import Client
from alibabacloud_searchplat20240529.models import GetDocumentSplitRequest, CreateDocumentAnalyzeTaskRequest, \
CreateDocumentAnalyzeTaskRequestDocument, GetDocumentAnalyzeTaskStatusRequest, \
GetDocumentSplitRequestDocument, GetTextEmbeddingRequest, GetTextEmbeddingResponseBodyResultEmbeddings, \
GetTextSparseEmbeddingRequest, GetTextSparseEmbeddingResponseBodyResultSparseEmbeddings, \
GetImageAnalyzeTaskStatusResponse, CreateImageAnalyzeTaskRequest, GetImageAnalyzeTaskStatusRequest, \
CreateImageAnalyzeTaskRequestDocument, CreateImageAnalyzeTaskResponse
async def poll_doc_analyze_task_result(ops_client, task_id, service_id, interval=5):
while True:
request = GetDocumentAnalyzeTaskStatusRequest(task_id=task_id)
response = await ops_client.get_document_analyze_task_status_async(workspace_name, service_id, request)
status = response.body.result.status
if status == "PENDING":
await asyncio.sleep(interval)
elif status == "SUCCESS":
return response
else:
print("error: " + response.body.result.error)
raise Exception("document analyze task failed")
def is_analyzable_url(url:str):
if not url:
return False
image_extensions = {'.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.bmp', '.tiff'}
return url.lower().endswith(tuple(image_extensions))
async def image_analyze(ops_client, url):
try:
print("image analyze :" + url)
if url.startswith("//"):
url = "https:" + url
if not is_analyzable_url(url):
print(url + " is unanalysable.")
return url
image_analyze_service_id = service_id_config["image_analyze"]
document = CreateImageAnalyzeTaskRequestDocument(
url=url,
)
request = CreateImageAnalyzeTaskRequest(document=document)
response: CreateImageAnalyzeTaskResponse = ops_client.create_image_analyze_task(workspace_name, image_analyze_service_id, request)
task_id = response.body.result.task_id
while True:
request = GetImageAnalyzeTaskStatusRequest(task_id=task_id)
response: GetImageAnalyzeTaskStatusResponse = ops_client.get_image_analyze_task_status(workspace_name, image_analyze_service_id, request)
status = response.body.result.status
if status == "PENDING":
await asyncio.sleep(5)
elif status == "SUCCESS":
return url + response.body.result.data.content
else:
print("image analyze error: " + response.body.result.error)
return url
except Exception as e:
print(f"image analyze Exception : {e}")
def chunk_list(lst, chunk_size):
for i in range(0, len(lst), chunk_size):
yield lst[i:i + chunk_size]
async def document_pipeline_execute(document_url: str = None, document_base64: str = None, file_name: str = None):
# Generate an AI Search Open Platform client.
config = Config(bearer_token=api_key,endpoint=aisearch_endpoint,protocol="http")
ops_client = Client(config=config)
# Step 1: Parse the document or image.
document_analyze_request = CreateDocumentAnalyzeTaskRequest(document=CreateDocumentAnalyzeTaskRequestDocument(url=document_url, content=document_base64,file_name=file_name, file_type='html'))
document_analyze_response = await ops_client.create_document_analyze_task_async(workspace_name=workspace_name,service_id=service_id_config["document_analyze"],request=document_analyze_request)
print("document_analyze task_id:" + document_analyze_response.body.result.task_id)
extraction_result = await poll_doc_analyze_task_result(ops_client, document_analyze_response.body.result.task_id, service_id_config["document_analyze"])
print("document_analyze done")
document_content = extraction_result.body.result.data.content
content_type = extraction_result.body.result.data.content_type
# Step 2: Split the document.
document_split_request = GetDocumentSplitRequest(
GetDocumentSplitRequestDocument(content=document_content, content_type=content_type))
document_split_result = await ops_client.get_document_split_async(workspace_name, service_id_config["split"],
document_split_request)
print("document-split done, chunks count: " + str(len(document_split_result.body.result.chunks))
+ " rich text count:" + str(len(document_split_result.body.result.rich_texts)))
# Step 3: Perform text vectorization.
# Extract the splitting results. Image splitting uses the image parsing service to extract text.
doc_list = ([{"id": chunk.meta.get("id"), "content": chunk.content} for chunk in document_split_result.body.result.chunks]
+ [{"id": chunk.meta.get("id"), "content": chunk.content} for chunk in document_split_result.body.result.rich_texts if chunk.meta.get("type") != "image"]
+ [{"id": chunk.meta.get("id"), "content": await image_analyze(ops_client,chunk.content)} for chunk in document_split_result.body.result.rich_texts if chunk.meta.get("type") == "image"]
)
chunk_size = 32 # A maximum of 32 vectors can be generated at a time.
all_text_embeddings: List[GetTextEmbeddingResponseBodyResultEmbeddings] = []
for chunk in chunk_list([text["content"] for text in doc_list], chunk_size):
response = await ops_client.get_text_embedding_async(workspace_name,service_id_config["text_embedding"],GetTextEmbeddingRequest(chunk))
all_text_embeddings.extend(response.body.result.embeddings)
all_text_sparse_embeddings: List[GetTextSparseEmbeddingResponseBodyResultSparseEmbeddings] = []
for chunk in chunk_list([text["content"] for text in doc_list], chunk_size):
response = await ops_client.get_text_sparse_embedding_async(workspace_name,service_id_config["text_sparse_embedding"],GetTextSparseEmbeddingRequest(chunk,input_type="document",return_token=True))
all_text_sparse_embeddings.extend(response.body.result.sparse_embeddings)
for i in range(len(doc_list)):
doc_list[i]["embedding"] = all_text_embeddings[i].embedding
doc_list[i]["sparse_embedding"] = all_text_sparse_embeddings[i].embedding
print("text-embedding done.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Run the asynchronous task.
# import nest_asyncio # If you run the code in Jupyter Notebook, uncomment this line of code.
# nest_asyncio.apply() # If you run the code in Jupyter Notebook, uncomment this line of code.
asyncio.run(document_pipeline_execute(document_url))
# asyncio.run(document_pipeline_execute(document_base64="eHh4eHh4eHg...", file_name="attention.pdf")) # You can also use a Base64-encoded file to specify the document to be processed.