Realtime Compute for Apache Flink can integrate with Key Management Service (KMS) to encrypt and decrypt sensitive data (such as database passwords) configured for your Flink workloads, thereby ensuring data security. This topic describes how to encrypt and decrypt database passwords with KMS in a JAR deployment that reads data from an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL database.
Background information
KMS is an all-in-one platform that supports simplified, reliable, secure, and compliant credential management and data encryption. KMS provides cryptographic API operations that enable you to encrypt and decrypt data in a simplified manner, which frees you from complicated and abstract cryptography. Furthermore, KMS offers automatic key rotation, which enhances data security and reduces the effort of key management. For more information, see Benefits of Key Management Service in the KMS documentation.
In real-time computing scenarios, Flink often needs to connect to data sources (Kafka, MySQL, etc) to access sensitive data. The traditional practice of hardcoding sensitive data or storing it in configuration files can lead to significant security challenges. By integrating with KMS, Flink can retrieve encrypted information and decrypt it on demand to protect against plaintext credential exposure.
The solution's architecture is as follows:

Prerequisites
-
The on-premises development environment is set up.
-
Development tools including IntelliJ IDEA are installed and properly configured.
-
Maven 3.6.3 or later is installed.
-
-
A Realtime Compute for Apache Flink workspace is created. For more information, see Create a workspace.
-
An ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance is created. For more information, see Step 1: Create an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance and configure databases.
-
A KMS instance is created and enabled, and a default KMS key is created. For more information, see Purchase and enable a KMS instance and Manage a key.
NoteThe ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance and the KMS instance must reside in the same virtual private cloud (VPC) as the Realtime Compute for Apache Flink workspace. If they do not reside in the same VPC, you must establish network connections among them. For more information, see the How do I access other services across VPCs? and How do I access the Internet?
(Optional) Step 1: Make preparations
Prepare an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL data source.
Run a JAR deployment with unencrypted data
Step 2: Encrypt a plaintext password with KMS
KMS encrypts the plaintext password flink_rds_password@123. The encrypted password is a2V5LWh6ejY3YTJmZTY5ejR2NTlpOHE1MC03d3ozYWU1anlzC6NLoC0JHHEXTJ4P/4iVOe/B+eniv8EcaviQDzZWWNPedOYkoFFYWA==.
To obtain the KMS encryption key, use any of the following methods:
Method 1: Call the KMS Encrypt operation on OpenAPI portal
-
Go to Alibaba Cloud OpenAPI Portal. Choose the target region.
-
Set KeyId and Plaintext.
-
Click Initiate Call.
-
View the ciphertext.
For more information, see Encrypt.
Method 2: Call the KMS Encrypt operation from IntelliJ IDEA
-
Enable Internet access to KMS keys. For more information, see Access KMS instance keys over the Internet.
KMS keys are only accessible through the VPC network by default.
-
Configure the
ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_IDandALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRETenvironment variables. For instructions on how to obtain the AccessKey pair, see How do I view the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret?. -
In the target IntelliJ IDEA project, create a class file named EncryptFlink.
-
Copy and paste the following code snippet to the EncryptFlink class file. Remember to modify the values of the configuration options to match your specific setup.
package org.example; import com.aliyun.kms20160120.models.EncryptResponse; import com.aliyun.kms20160120.models.EncryptResponseBody; import com.aliyun.tea.*; public class EncryptFlink { /** * <b>description</b> : * <p>Use your AccessKey pair to initialize the client.</p> * @return Client * * @throws Exception */ public static com.aliyun.kms20160120.Client createClient() throws Exception { // If the project code is leaked, the AccessKey pair may be leaked, compromising the security of all resources within your account. The following sample code is provided only for reference. com.aliyun.teaopenapi.models.Config config = new com.aliyun.teaopenapi.models.Config() // Required. Make sure that the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID environment variable is configured. .setAccessKeyId(System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID")) // Required. Make sure that the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variable is configured. .setAccessKeySecret(System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")); // Specify an endpoint. For more information, visit https://api.aliyun.com/product/Kms. config.endpoint = "kms.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com"; return new com.aliyun.kms20160120.Client(config); } public static void main(String[] args_) throws Exception { java.util.List<String> args = java.util.Arrays.asList(args_); com.aliyun.kms20160120.Client client = EncryptFlink.createClient(); com.aliyun.kms20160120.models.EncryptRequest encryptRequest = new com.aliyun.kms20160120.models.EncryptRequest() .setPlaintext("flink_rds_password@123") .setKeyId("key-hzz67ab1ff4e750h****"); com.aliyun.teautil.models.RuntimeOptions runtime = new com.aliyun.teautil.models.RuntimeOptions(); try { // Write your own code to display the response of the API operation if necessary. EncryptResponse encryptResponse = client.encryptWithOptions(encryptRequest, runtime); EncryptResponseBody body = encryptResponse.getBody(); System.out.println(body.getCiphertextBlob()); } catch (TeaException error) { // Handle exceptions with caution in actual business scenarios and do not ignore the exceptions in your project. In this example, error messages are simply printed for demonstration purposes. // The error message. System.out.println(error.getMessage()); // The URL for troubleshooting. System.out.println(error.getData().get("Recommend")); com.aliyun.teautil.Common.assertAsString(error.message); } catch (Exception _error) { TeaException error = new TeaException(_error.getMessage(), _error); // Handle exceptions with caution in actual business scenarios and do not ignore the exceptions in your project. In this example, error messages are simply printed for demonstration purposes. // The error message. System.out.println(error.getMessage()); // The URL for troubleshooting. System.out.println(error.getData().get("Recommend")); com.aliyun.teautil.Common.assertAsString(error.message); } } }Option
Description
Example
config.endpoint
The endpoint of your KMS instance.
kms.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com
Plaintext
The plaintext password to encrypt.
flink_rds_password@123
KeyId
The KMS key ID.
key-hzz67ab1ff4e750h****
-
Add the following dependencies to the POM.xml file.
<dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun</groupId> <artifactId>kms20160120</artifactId> <version>1.2.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun</groupId> <artifactId>tea</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency> -
Run the EncryptFlink class file to obtain the ciphertext.
Step 3: Add the KMS decryption code to your program
Procedure
-
Create a decryption utility class file.
-
In IntelliJ IDEA, create a class file named KmsUtil under the target project folder.
-
Copy and paste the following code snippet to the KmsUtil class file. Remember to modify the values of the configuration options to match your specific setup.
package org.example; import com.aliyun.kms20160120.Client; import com.aliyun.kms20160120.models.DecryptRequest; import com.aliyun.teaopenapi.models.Config; public class KmsUtil { public static String decrypt(String ak, String sk, String ciphertext) throws Exception { Client client = new Client(new Config() .setAccessKeyId(ak) .setAccessKeySecret(sk) .setEndpoint("kst-hzz67ab1e****f7hle9ab.cryptoservice.kms.aliyuncs.com") .setCa("-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\n" + "MIIDuzCCAqOgAwIBAgIJA*****--\n")); return client.decryptWithOptions( new DecryptRequest().setCiphertextBlob(ciphertext), new com.aliyun.teautil.models.RuntimeOptions() ).getBody().getPlaintext(); } }Option
Description
Example
Endpoint
The VPC endpoint of your KMS instance.
kst-hzz67ab1e****f7hle9ab.cryptoservice.kms.aliyuncs.com
Ca
The CA certificate.
Download the KMS instance's CA certificate to your device in the KMS console. For more information, see Create access credentials.
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\n" + "MIIDuzCCAqOgAwIBAgIJA*****--\n
-
-
Modify the JavaDemo file.
-
Write code to retrieve an AccessKey pair and decrypt encrypted data.
Replace the value of encryptedPassword with the ciphertext you obtained in Step 2.
// Parse parameters to get the AccessKey pair. final ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args); String ak = params.get("akid"); String sk = params.get("aksecret"); // Decrypt the encrypted password. String encryptedPassword = "a2V5LWh6ejY3YTJmZTY5ejR2NTlpOHE1MC03d3ozYWU1anlzC6NLoC0JHHEXTJ4P/4iVOe/B+eniv8EcaviQDzZWWNPedOYkoFFYWA=="; String decryptedPassword = KmsUtil.decrypt(ak, sk, encryptedPassword); -
Change the plaintext password to the newly added variable.
For example,
.password("flink_rds_password@123")is changed to.password(decryptedPassword).
-
-
Modify the pom.xml file
-
Set mainClass to
org.example.JavaDemo. -
Add KMS dependencies.
<dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun</groupId> <artifactId>kms20160120</artifactId> <version>1.2.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun</groupId> <artifactId>tea</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency> -
(Optional) Change the value of artifactId to KmsJavaDemo.
This will help you distinguish the two JARs.
-
-
Build the JAR.
The KmsJavaDemo-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar file will appear under the target directory.
Complete code demo
KmsJavaDemo
package org.example;
import com.ververica.cdc.connectors.mysql.source.MySqlSource;
import com.ververica.cdc.debezium.table.RowDataDebeziumDeserializeSchema;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.DataTypes;
import org.apache.flink.table.data.RowData;
import org.apache.flink.table.runtime.typeutils.InternalTypeInfo;
import org.apache.flink.table.types.DataType;
import org.apache.flink.table.types.logical.LogicalType;
import org.apache.flink.table.types.logical.RowType;
import org.apache.flink.table.types.utils.TypeConversions;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.utils.ParameterTool;
public class JavaDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
// Parse parameters to get the AccessKey pair.
final ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args);
String ak = params.get("akid");
String sk = params.get("aksecret");
// Decrypt the encrypted password.
String encryptedPassword = "a2V5LWh6ejY3YTJmZTY5ejR2NTlpOHE1MC03d3ozYWU1anlzC6NLoC0JHHEXTJ4P/4iVOe/B+eniv8EcaviQDzZWWNPedOYkoFFYWA==";
String decryptedPassword = KmsUtil.decrypt(ak, sk, encryptedPassword);
// Build a deserializer.
DataType dataType =
DataTypes.ROW(
DataTypes.FIELD("id", DataTypes.INT()),
DataTypes.FIELD("username", DataTypes.STRING()),
DataTypes.FIELD("age", DataTypes.INT()));
LogicalType logicalType = TypeConversions.fromDataToLogicalType(dataType);
InternalTypeInfo<RowData> typeInfo = InternalTypeInfo.of(logicalType);
RowDataDebeziumDeserializeSchema deserializer =
RowDataDebeziumDeserializeSchema.newBuilder()
.setPhysicalRowType((RowType) dataType.getLogicalType())
.setResultTypeInfo(typeInfo)
.build();
// Configure the data source (com.ververica.cdc.connectors.mysql.source.MySqlSource).
MySqlSource<RowData> mySqlSource =
MySqlSource.<RowData>builder()
.hostname("rm-bp****2ye09w72zjq.mysql.rds.aliyuncs.com")
.port(3306)
.databaseList("school") // Specify the database.
.tableList("school.student") // Specify the table.
.username("flink_rds_user")
.password(decryptedPassword)
// Initialize data in the RowData structure.
.deserializer(deserializer)
.build();
// Integrate the external data source into the Flink DataStream program
// Do not use a watermark strategy.
DataStreamSource<RowData> mySQLSource = env.fromSource(mySqlSource, WatermarkStrategy.noWatermarks(), "MySQL Source");
// Write to stdout.
mySQLSource.print();
// Execute the program.
env.execute("MySQL CDC Test");
}
}
POM.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>KmsJavaDemo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>Flink MySQL CDC Demo</name>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<flink.version>1.17.1</flink.version>
<flink-cdc.version>2.4.2</flink-cdc.version>
<log4j.version>2.17.1</log4j.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<! -- Flink core dependencies (Set the scope to provided when packaging the program) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-java</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-streaming-java</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-table-api-java-bridge</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Realtime Compute for Apache Flink's MySQL CDC connector -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.ververica</groupId>
<artifactId>ververica-connector-mysql</artifactId>
<version>1.17-vvr-8.0.4-1</version>
<! -- Comment out the following line for local execution -->
<!-- <scope>provided</scope> -->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-table-runtime</artifactId>
<version>1.17.1</version> <! -- The version should be consistent with the Flink version you specified earlier -->
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-core</artifactId>
<version>1.17.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-table-common</artifactId>
<version>1.17.1</version> <! -- The version should be consistent with the Flink version you specified earlier -->
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<! -- Log dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.17.1</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>kms20160120</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>tea</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<! -- Compiler plug-in -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.13.0</version> <! -- Patch version -->
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<! -- Plug-in for building a fat JAR -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<artifactSet>
<excludes>
<exclude>org.apache.flink:force-shading</exclude>
<exclude>com.google.code.findbugs:jsr305</exclude>
<! -- Retain logging dependencies -->
<!-- <exclude>org.slf4j:*</exclude> -->
<!-- <exclude>org.apache.logging.log4j:*</exclude> -->
</excludes>
</artifactSet>
<filters>
<filter>
<artifact>*:*</artifact>
<excludes>
<exclude>META-INF/*.SF</exclude>
<exclude>META-INF/*.DSA</exclude>
<exclude>META-INF/*.RSA</exclude>
<exclude>META-INF/MANIFEST.MF</exclude> <! -- Add a key filter -->
</excludes>
</filter>
</filters>
<transformers>
<transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.ManifestResourceTransformer">
<mainClass>org.example.JavaDemo</mainClass>
</transformer>
<transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.ServicesResourceTransformer"/> <! -- Add a necessary transformer -->
</transformers>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Step 4: Deploy the new JAR and start the deployment
-
Upload the new JAR.
-
Log on to the management console of the Realtime Compute for Apache Flink.
-
Find the target workspace and click Console in the Actions column.
-
In the left-side navigation pane, click Artifacts.
-
Click Upload Artifact and select the JAR to upload.
KmsJavaDemo-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar built in step 3 is uploaded in this example.
-
-
Create a JAR deployment.
-
In the left-side navigation pane, choose . In the upper-left corner of the Deployments page, choose Create Deployment > JAR Deployment.
-
In the Create Deployment dialog box, configure the parameters of the deployment:
Parameter
Description
Example
Deployment Mode
The mode that you want to use to deploy the JAR deployment. Select Stream Mode.
Stream Mode
Deployment Name
Enter the name of the JAR deployment.
kmsjavademo
Engine Version
The engine version that will be used by the deployment.
We recommend that you use an engine version labelled RECOMMENDED or STABLE because they are more reliable and performant. For more information, see Release notes and Engine versions.
vvr-8.0.11-flink-1.17
JAR URI
Choose the uploaded JAR.
NoteIn Realtime Compute for Apache Flink that uses VVR 8.0.6 or later, access to Object Storage Service (OSS) buckets is restricted to the bucket bound to the workspace at its creation.
KmsJavaDemo-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
Entry Point Class
The entry point class of the JAR application. If you do not specify a main class for the JAR, enter a standard directory in the Entry Point Class field.
-
Entry Point Main Arguments
Enter the arguments you want to pass to the main method.
To protect your AccessKey pairs, we recommend that you configure the AccessKey pair by using variables. For more information, see Variable management. In this example, akid and aksecret are variable names.
For instructions on how to obtain the AccessKey pair, see How do I view the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret?.
--akid ${secret_values.akid} --aksecret ${secret_values.aksecret}
Deployment Target
The destination in which the deployment is deployed. Select the desired queue or session cluster from the drop-down list. For more information, see Manage queues and the "Step 1: Create a session cluster" section of the Debug a deployment topic.
ImportantDo not use session clusters for production. Session clusters do not support monitoring metrics, monitoring and alerting, or Autopilot. For more information, see Debug a job.
default-queue
For more information, see Deploy a job.
-
Click Deploy.
-
-
Start a deployment.
On the Deployments page, find the kmsjavademo deployment, and click Start in the Actions column. In the Start Job panel, select Initial Mode, and click Start.
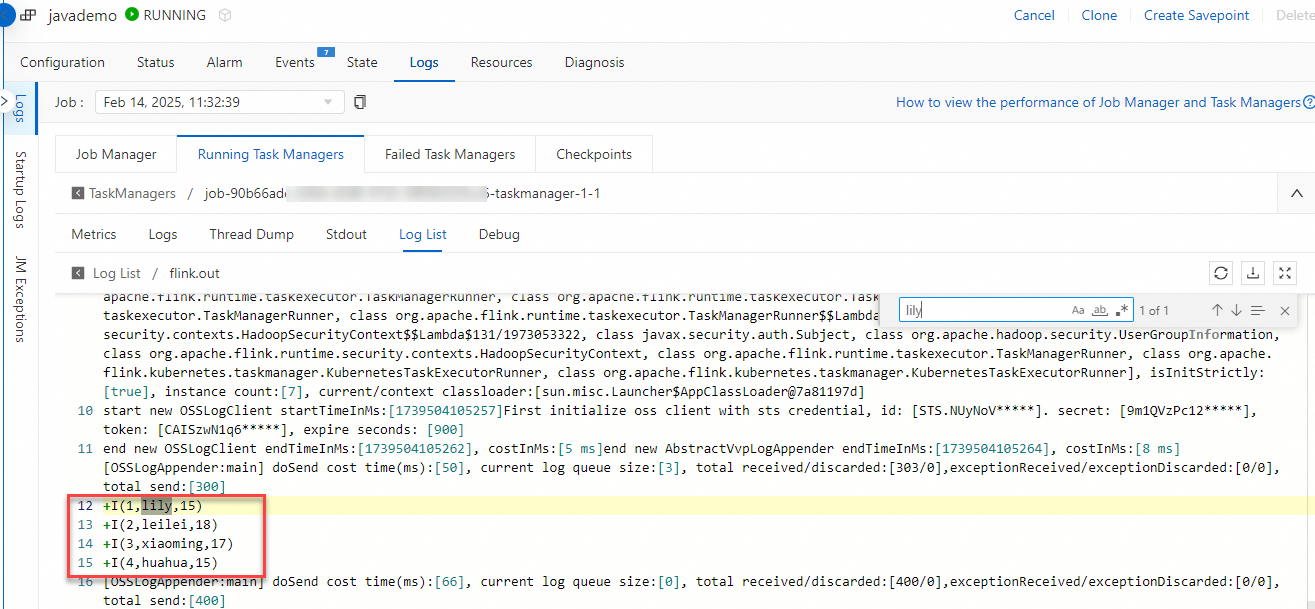
Step 5: View the results in the TaskManager logs
After the deployment's state becomes RUNNING, go to the deployment details page. Select the Logs tab and the Running Task Managers subtab. Click an item in the Path, ID column, switch to the Log List subtab, and click the log with the .out suffix. Search for lily and check the data processing results.