This topic describes how to use the reindex feature to migrate data from a self-managed Elasticsearch (ES) cluster on an ECS instance to an Alibaba Cloud ES instance. The process includes creating an index and migrating the data.
Background
Data migration using reindex is supported only for single-zone instances. If you use a multi-zone instance, use one of the following solutions to migrate data from your self-managed ES cluster to Alibaba Cloud:
If the source data volume is large, use the OSS snapshot method. For more information, see Advanced: Migrate a self-managed ES cluster to Alibaba Cloud ES using OSS.
To filter the source data, use the Logstash migration solution. For more information, see Migrate data from a self-managed Elasticsearch cluster to Alibaba Cloud using Logstash.
Prerequisites
You have performed the following operations:
Create a single-zone Alibaba Cloud ES instance.
For more information, see Create an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch instance.
Prepare a self-managed ES cluster and the data to be migrated.
If you do not have a self-managed ES cluster, you can use an Alibaba Cloud ECS instance to build one. For more information, see Install and run Elasticsearch. The self-managed ES cluster must meet the following conditions:
The network type of the ECS instance where the cluster is located must be a virtual private cloud (VPC). ECS instances connected using ClassicLink are not supported. The ECS instance must be in the same VPC as the Alibaba Cloud ES instance.
The security group of the ECS instance must not restrict access from the IP addresses of the nodes in the Alibaba Cloud ES instance. You can view the node IP addresses in the Kibana console. Port 9200 must also be open.
The self-managed cluster must be able to connect to the Alibaba Cloud ES instance. On the machine from which you run the script, run the
curl -XGET http://<host>:9200command to verify the connection.NoteYou can run the scripts in this topic on any machine that can access port 9200 of both the self-managed ES cluster and the Alibaba Cloud ES cluster.
Limitations
Alibaba Cloud ES provides two deployment modes: basic control (v2) architecture and cloud-native new control (v3) architecture. You can check the deployment mode in the Basic Information section of the instance.
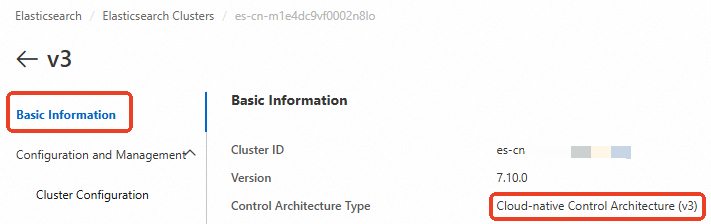
For clusters that use the cloud-native new control (v3) architecture, you must use PrivateLink to establish a private connection to the Alibaba Cloud ES cluster for cross-cluster reindex operations. Select a solution from the following table based on your business scenario.
Scenario | ES cluster network architecture | Solution |
Data migration between Alibaba Cloud ES clusters | Both ES clusters use the basic control (v2) architecture. | reindex method: Cross-cluster reindex between Alibaba Cloud ES clusters. |
One of the ES clusters uses the cloud-native new control (v3) architecture. Note The other ES cluster can use either the cloud-native new control (v3) architecture or the basic control (v2) architecture. | ||
Migrate data from a self-managed ES cluster on an ECS instance to an Alibaba Cloud ES cluster | The Alibaba Cloud ES cluster uses the basic control (v2) architecture. | reindex method: Migrate data from a self-managed Elasticsearch cluster to Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch using reindex. |
The Alibaba Cloud ES cluster uses the cloud-native new control (v3) architecture. | reindex method: Migrate data from a self-managed Elasticsearch cluster to Alibaba Cloud by establishing a private connection to the instance. |
Usage notes
In October 2020, Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch adjusted its network architecture. The architecture used before this adjustment is referred to as the old network architecture, and the one used after is the new network architecture.Instances that use the new network architecture do not support interoperability operations, such as cross-cluster reindex, cross-cluster search, or cross-cluster replication, with instances that use the old network architecture. To enable interoperability, make sure that the instances use the same network architecture.For the China (Zhangjiakou) region and regions outside China, the time of the network architecture adjustment is not fixed. Contact Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch technical support to verify network interoperability.
Alibaba Cloud ES instances that use the cloud-native new control (v3) architecture are deployed in a VPC that belongs to an Alibaba Cloud service account and cannot access resources in other network environments. In contrast, instances that use the basic control (v2) architecture are deployed in your VPC, and their network access is not affected.
To ensure data consistency, we recommend that you stop writing and updating data in the self-managed ES cluster before the migration. This ensures that read operations are not affected. After the migration is complete, you can switch your read and write operations to the Alibaba Cloud ES cluster. If you cannot stop write operations, we recommend that you use a script to set up a loop task to reduce write service downtime. For more information, see the Migrate a large volume of data (without deletions and with an update time field) section in Step 4: Migrate data.
When you use a domain name to access a self-managed ES or an Alibaba Cloud ES cluster, you cannot use a URL that includes a path, such as
http://host:port/path.
Procedure
Step 1: Obtain an endpoint domain name (optional)
If your Alibaba Cloud ES instance uses the cloud-native new control (v3) architecture, you must use PrivateLink to connect the VPC of the self-managed ES cluster on the ECS instance to the VPC of the Alibaba Cloud service account. Then, you must obtain the endpoint domain name to use in subsequent configurations. For more information, see Configure a private connection for an Elasticsearch cluster.
Step 2: Create a destination index
Before you start, create an index in the Alibaba Cloud ES cluster. The new index must use the same configuration as the index that you want to migrate from the self-managed ES cluster. Alternatively, you can enable the automatic index creation feature for the Alibaba Cloud ES cluster, but this method is not recommended.
The following example shows a Python 2 script that you can use to create indexes in batches in the Alibaba Cloud ES cluster. These indexes must have the same configurations as the indexes that you want to migrate from the self-managed ES cluster. By default, the number of replicas for the new indexes is set to 0.
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# File name: indiceCreate.py
import sys
import base64
import time
import httplib
import json
## The host of the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster.
oldClusterHost = "old-cluster.com"
## The username for the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster. This can be empty.
oldClusterUserName = "old-username"
## The password for the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster. This can be empty.
oldClusterPassword = "old-password"
## The host of the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster. You can obtain it from the Basic Information page of the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch instance.
newClusterHost = "new-cluster.com"
## The username for the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster.
newClusterUser = "elastic"
## The password for the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster.
newClusterPassword = "new-password"
DEFAULT_REPLICAS = 0
def httpRequest(method, host, endpoint, params="", username="", password=""):
conn = httplib.HTTPConnection(host)
headers = {}
if (username != "") :
'Hello {name}, your age is {age} !'.format(name = 'Tom', age = '20')
base64string = base64.encodestring('{username}:{password}'.format(username = username, password = password)).replace('\n', '')
headers["Authorization"] = "Basic %s" % base64string;
if "GET" == method:
headers["Content-Type"] = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
conn.request(method=method, url=endpoint, headers=headers)
else :
headers["Content-Type"] = "application/json"
conn.request(method=method, url=endpoint, body=params, headers=headers)
response = conn.getresponse()
res = response.read()
return res
def httpGet(host, endpoint, username="", password=""):
return httpRequest("GET", host, endpoint, "", username, password)
def httpPost(host, endpoint, params, username="", password=""):
return httpRequest("POST", host, endpoint, params, username, password)
def httpPut(host, endpoint, params, username="", password=""):
return httpRequest("PUT", host, endpoint, params, username, password)
def getIndices(host, username="", password=""):
endpoint = "/_cat/indices"
indicesResult = httpGet(oldClusterHost, endpoint, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword)
indicesList = indicesResult.split("\n")
indexList = []
for indices in indicesList:
if (indices.find("open") > 0):
indexList.append(indices.split()[2])
return indexList
def getSettings(index, host, username="", password=""):
endpoint = "/" + index + "/_settings"
indexSettings = httpGet(host, endpoint, username, password)
print index + " The original settings are as follows:\n" + indexSettings
settingsDict = json.loads(indexSettings)
## By default, the number of shards is the same as that of the index in the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster.
number_of_shards = settingsDict[index]["settings"]["index"]["number_of_shards"]
## By default, the number of replicas is 0.
number_of_replicas = DEFAULT_REPLICAS
newSetting = "\"settings\": {\"number_of_shards\": %s, \"number_of_replicas\": %s}" % (number_of_shards, number_of_replicas)
return newSetting
def getMapping(index, host, username="", password=""):
endpoint = "/" + index + "/_mapping"
indexMapping = httpGet(host, endpoint, username, password)
print index + " The original mapping is as follows:\n" + indexMapping
mappingDict = json.loads(indexMapping)
mappings = json.dumps(mappingDict[index]["mappings"])
newMapping = "\"mappings\" : " + mappings
return newMapping
def createIndexStatement(oldIndexName):
settingStr = getSettings(oldIndexName, oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword)
mappingStr = getMapping(oldIndexName, oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword)
createstatement = "{\n" + str(settingStr) + ",\n" + str(mappingStr) + "\n}"
return createstatement
def createIndex(oldIndexName, newIndexName=""):
if (newIndexName == "") :
newIndexName = oldIndexName
createstatement = createIndexStatement(oldIndexName)
print "The settings and mapping for the new index " + newIndexName + " are as follows:\n" + createstatement
endpoint = "/" + newIndexName
createResult = httpPut(newClusterHost, endpoint, createstatement, newClusterUser, newClusterPassword)
print "Result of creating the new index " + newIndexName + ": " + createResult
## main
indexList = getIndices(oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword)
systemIndex = []
for index in indexList:
if (index.startswith(".")):
systemIndex.append(index)
else :
createIndex(index, index)
if (len(systemIndex) > 0) :
for index in systemIndex:
print index + " might be a system index and will not be re-created. Handle it separately if needed."Step 3: Configure the reindex whitelist
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Elasticsearch Clusters.
Navigate to the desired cluster.
In the top navigation bar, select the resource group to which the cluster belongs and the region where the cluster resides.
On the Elasticsearch Clusters page, find the cluster and click its ID.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
In the YML File Configuration section, click Modify Configuration on the right.
In the YML File Configuration panel, modify Other Configurations to set the reindex whitelist.
The following example shows a sample configuration.
reindex.remote.whitelist: ["10.0.xx.xx:9200","10.0.xx.xx:9200","10.0.xx.xx:9200","10.15.xx.xx:9200","10.15.xx.xx:9200","10.15.xx.xx:9200"]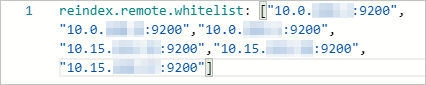
To configure the reindex whitelist, use the reindex.remote.whitelist parameter to specify the endpoint of the self-managed ES cluster. This adds the endpoint to the remote access whitelist of the Alibaba Cloud ES cluster. The configuration rules vary based on the network architecture of the Alibaba Cloud ES cluster:
For the basic control (v2) architecture, specify a combination of a host and a port. Use commas to separate multiple host configurations. For example: otherhost:9200,another:9200,127.0.10.**:9200,localhost:**. The protocol information is not recognized.
For the cloud-native new control (v3) architecture, specify a combination of the endpoint domain name and port that correspond to the instance. For example: ep-bp1hfkx7coy8lvu4****-cn-hangzhou-i.epsrv-bp1zczi0fgoc5qtv****.cn-hangzhou.privatelink.aliyuncs.com:9200.
NoteFor more information about the parameters, see Configure YML parameters.
Select the This operation will restart the cluster. Continue? option and click the OK button.
After you click OK, the Elasticsearch instance restarts. During the restart, you can monitor the progress in the Task List. The configuration is complete after the instance restarts.
Step 4: Migrate data
This section uses an instance with the basic control (v2) architecture as an example and provides three data migration methods. Select a method based on your data volume and business requirements.
Small data volume
You can use the following script.
#!/bin/bash
# file:reindex.sh
indexName="Your index name"
newClusterUser="Username for the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster"
newClusterPass="Password for the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster"
newClusterHost="Host of the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster"
oldClusterUser="Username for the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster"
oldClusterPass="Password for the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster"
# The host of the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster must be in the format of [scheme]://[host]:[port], for example, http://10.37.*.*:9200.
oldClusterHost="Host of the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster"
curl -u ${newClusterUser}:${newClusterPass} -XPOST "http://${newClusterHost}/_reindex?pretty" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d'{
"source": {
"remote": {
"host": "'${oldClusterHost}'",
"username": "'${oldClusterUser}'",
"password": "'${oldClusterPass}'"
},
"index": "'${indexName}'",
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
},
"dest": {
"index": "'${indexName}'"
}
}'Large data volume, no delete operations, and with update time
If the data volume is large and no delete operations are performed, you can use scroll migration to reduce the downtime of write services. Scroll migration requires a field, such as an update time field, to track new data. After the initial data migration is complete, stop all write operations. Then, run the reindex operation one last time to migrate the latest updates. Finally, switch your read and write operations to the Alibaba Cloud ES cluster.
#!/bin/bash
# file: circleReindex.sh
# CONTROLLING STARTUP:
# This is a script for remote reindexing. Requirements:
# 1. The index has been created in the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster, or the cluster supports automatic creation and dynamic mapping.
# 2. An IP address whitelist must be configured in the YML file of the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster, for example, reindex.remote.whitelist: 172.16.**.**:9200.
# 3. The host must be in the format of [scheme]://[host]:[port].
USAGE="Usage: sh circleReindex.sh <count>
count: The number of executions. A negative number indicates a loop for incremental execution. A positive number indicates a one-time or multiple executions.
Example:
sh circleReindex.sh 1
sh circleReindex.sh 5
sh circleReindex.sh -1"
indexName="Your index name"
newClusterUser="Username for the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster"
newClusterPass="Password for the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster"
oldClusterUser="Username for the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster"
oldClusterPass="Password for the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster"
## http://myescluster.com
newClusterHost="Host of the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster"
# The host of the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster must be in the format of [scheme]://[host]:[port], for example, http://10.37.*.*:9200.
oldClusterHost="Host of the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster"
timeField="Update time field"
reindexTimes=0
lastTimestamp=0
curTimestamp=`date +%s`
hasError=false
function reIndexOP() {
reindexTimes=$[${reindexTimes} + 1]
curTimestamp=`date +%s`
ret=`curl -u ${newClusterUser}:${newClusterPass} -XPOST "${newClusterHost}/_reindex?pretty" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"source": {
"remote": {
"host": "'${oldClusterHost}'",
"username": "'${oldClusterUser}'",
"password": "'${oldClusterPass}'"
},
"index": "'${indexName}'",
"query": {
"range" : {
"'${timeField}'" : {
"gte" : '${lastTimestamp}',
"lt" : '${curTimestamp}'
}
}
}
},
"dest": {
"index": "'${indexName}'"
}
}'`
lastTimestamp=${curTimestamp}
echo "The ${reindexTimes}th reindex. The update deadline for this execution is ${lastTimestamp}. Result: ${ret}"
if [[ ${ret} == *error* ]]; then
hasError=true
echo "An exception occurred during this execution. Subsequent operations are interrupted. Please check."
fi
}
function start() {
## If the number is negative, the loop runs continuously.
if [[ $1 -lt 0 ]]; then
while :
do
reIndexOP
done
elif [[ $1 -gt 0 ]]; then
k=0
while [[ k -lt $1 ]] && [[ ${hasError} == false ]]; do
reIndexOP
let ++k
done
fi
}
## main
if [ $# -lt 1 ]; then
echo "$USAGE"
exit 1
fi
echo "Start the reindex operation for the index ${indexName}."
start $1
echo "A total of ${reindexTimes} reindex operations were performed."Large data volume, no delete operations, and without update time
If the data volume is large and the index mapping does not contain an update time field, you must modify the upstream service code to add this field. After you add the field, first migrate the historical data. Then, use the scroll migration method described in the previous section.
#!/bin/bash
# file:miss.sh
indexName="Your index name"
newClusterUser="Username for the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster"
newClusterPass="Password for the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster"
newClusterHost="Host of the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster"
oldClusterUser="Username for the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster"
oldClusterPass="Password for the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster"
# The host of the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster must be in the format of [scheme]://[host]:[port], for example, http://10.37.*.*:9200
oldClusterHost="Host of the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster"
timeField="updatetime"
curl -u ${newClusterUser}:${newClusterPass} -XPOST "http://${newClusterHost}/_reindex?pretty" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"source": {
"remote": {
"host": "'${oldClusterHost}'",
"username": "'${oldClusterUser}'",
"password": "'${oldClusterPass}'"
},
"index": "'${indexName}'",
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": {
"exists": {
"field": "'${timeField}'"
}
}
}
}
},
"dest": {
"index": "'${indexName}'"
}
}'FAQ
Problem: When I run the curl command, the error message
{"error":"Content-Type header [application/x-www-form-urlencoded] is not supported","status":406}is returned.Solution: Add
-H "Content-Type: application/json"to the curl command and try again.// Get information about all indexes in the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster. If you do not have permissions, you can remove the "-u user:pass" parameter. oldClusterHost is the host of the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster. Replace it with your actual host. curl -u user:pass -XGET http://oldClusterHost/_cat/indices | awk '{print $3}' // Based on the returned index list, obtain the settings and mapping of the user index to be migrated. Replace indexName with the name of the user index you want to query. curl -u user:pass -XGET http://oldClusterHost/indexName/_settings,_mapping?pretty=true // Based on the obtained _settings and _mapping information of the corresponding index, create the corresponding index in the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster. You can set the number of replicas to 0 to speed up data synchronization. After the data migration is complete, reset the number of replicas to 1. // newClusterHost is the host of the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster, testindex is the name of the created index, and testtype is the type of the corresponding index. curl -u user:pass -XPUT http://<newClusterHost>/<testindex> -d '{ "testindex" : { "settings" : { "number_of_shards" : "5", // Assume that the number of shards for the corresponding index in the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster is 5. "number_of_replicas" : "0" // Set the number of replicas for the index to 0. } }, "mappings" : { // Assume that the mappings for the corresponding index in the self-managed Elasticsearch cluster are configured as follows. "testtype" : { "properties" : { "uid" : { "type" : "long" }, "name" : { "type" : "text" }, "create_time" : { "type" : "long" } } } } } }'Problem: The data volume of a single index is large, and the data synchronization speed is slow. What can I do?
Solution:
The reindex feature is implemented based on the scroll method. You can increase the scroll size or configure scroll slices to improve efficiency. For more information, see the reindex API documentation.
If the source data volume is large, use the OSS snapshot method. For more information, see Advanced: Migrate a self-managed ES cluster to Alibaba Cloud ES using OSS.
If the data volume of a single index is large, you can set the number of replicas of the destination index to 0 and set the refresh interval to -1 before migration to accelerate data synchronization. After the data migration is complete, revert these settings to their original values.
// Before migrating index data, you can set the number of replicas to 0 and disable refresh to speed up data migration. curl -u user:password -XPUT 'http://<host:port>/indexName/_settings' -d' { "number_of_replicas" : 0, "refresh_interval" : "-1" }' // After the index data is migrated, you can reset the number of replicas to 1 and the refresh interval to 1s (1s is the default value). curl -u user:password -XPUT 'http://<host:port>/indexName/_settings' -d' { "number_of_replicas" : 1, "refresh_interval" : "1s" }'