When you use Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances, you may encounter image-related issues, such as slow instance startup, high system load, and or have questions, such as how to compile the kernel. This topic provides answers to some frequently asked questions (FAQ) about images that you may have when you use ECS instances.
FAQ about Windows images
How do I update the virtio driver on a Windows instance?
How do I manage Windows Server Semi-Annual Channel images and instances?
What do I do if I cannot change the screen resolution of a Windows instance that runs a UEFI image after I connect to the instance by using VNC?
What do I do if I am prompted that the Windows Server operating system of my instance is not genuine?
You must activate the operating system. For more information, see How to use the KMS domain name to activate a Windows instance in a VPC?
What do I do if a system time error occurs due to frequent timeBeginPeriod calls in Windows?
In Windows Server 2008, frequent timeBeginPeriod calls may cause the system time to become inaccurate. You can perform the following operations to resolve the issue.
NoteFor information about system functions that may affect system time accuracy, see Wait Functions.
Connect to the instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Windows instance by using a password or key.
Download CheckTimeBeginPeriod.zip.
Decompress CheckTimeBeginPeriod.zip.
Decompress bin.zip, go to the bin folder, and then double-click an .exe file.
For a 64-bit operating system, double-click InjectDllx64.exe.
For a 32-bit operating system, double-click InjectDllx86.exe.
The processes that call the timeBeginPeriod function are displayed.
Stop or update the processes that call the timeBeginPeriod function based on your business requirements.
If the issue persists, submit a ticket to contact Alibaba Cloud technical support.
What do I do if the "Content from the website listed below is being blocked by the Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration" error message appears?
When you attempt to open a website in Internet Explorer on a Windows ECS instance or Windows simple application server, the following error message appears: Content from the website listed below is being blocked by the Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration. For information about how to resolve the issue, see What do I do if I am prompted with the error message "Content from the website listed below is being blocked by the Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration"?
When I replace the system disk of a Windows ECS instance or re-initialize the system disk, why is user data not automatically executed?
Cause
After a Windows ECS instance is started, a cache file is created in the
C:\ProgramData\aliyun\vminit\INSTANCE_<Instance ID>\METASERVERdirectory. The cache file is used to mark whether the instance is initialized. If you create a custom image from the instance and use the custom image to re-initialize or replace the system disk of the instance, a cache file whose ID is the same as the ID of the instance is stored in theC:\ProgramData\aliyun\vminit\INSTANCE_<Instance ID>\METASERVERdirectory. The Vminit component determines whether this is the first time an ECS instance is started based on the existence of a cache file. If a cache file whose ID is the same as the ID of the instance exists, the Vminit component determines that this is not the first time the ECS instance is started, and the script in the user data is not automatically executed.NoteThe Vminit component is automatically installed when you create a Windows instance. Similar to the Linux cloud-init service, the Vminit component initializes the configurations of Windows instances during the boot phase. For more information about the Vminit component, see Vminit component.
Solution
Before you create a custom image from the ECS instance, we recommend that you check for and delete the cache file in the
C:\ProgramData\aliyun\vminit\INSTANCE_<Instance ID>\METASERVERdirectory.
FAQ about CentOS and Red Hat images
How do I resolve a CentOS DNS resolution timeout issue?
Cause
The DNS resolution mechanism of CentOS 6 and CentOS 7 has changed. A DNS resolution timeout error may occur in CentOS 6 or CentOS 7 instances that were created before February 22, 2017 or that use custom images created before February 22, 2017.
Solution
To resolve the issue, perform the following steps:
Download the fix_dns.sh script.
Place the downloaded script in the /tmp directory of the CentOS operating system.
Run the bash /tmp/fix_dns.sh command to execute the script.
Take note of the following matters concerning the script:
After I use a CentOS 7 or Windows instance for an extended period of time without restarting the instance, the instance is disconnected from the network, the network is unavailable, or the public or private IP address of the instance cannot be pinged. What do I do?
For information about the cause of and solution to this issue, see Check and fix the problem of missing IP addresses of CentOS 7 instances and Windows instances.
What do I do if a CentOS 7.9 for Arm operating system fails to generate dump files?
Problem description
When the CentOS 7.9 for Arm operating system is down and you run the
ls /var/crashcommand to query dump files, novmcorefile is generated.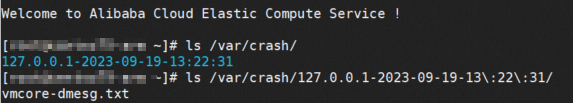
Cause
The CentOS 7.9 for Arm operating system has a kernel in which the
CONFIG_ARM64_USER_VA_BITS_52option is set to y to enable 52-bit virtual addressing for userspace. The version of the makedumpfile software that comes with the operating system does not match the kernel version. As a result, dump files cannot be generated.Solution
ImportantThis solution applies only to operating systems that have the kdump service enabled. If the kdump service is disabled and you resolve the preceding issue as described in this topic, configure the
crashkernelparameter in theproc/cmdlinefile.Run the following command to download the kexec-tools package:
wget http://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos-vault/7.9.2009/os/Source/SPackages/kexec-tools-2.0.15-51.el7.src.rpmRun the following command to install the RPM Package Manager (RPM) package:
rpm -ivh kexec-tools-2.0.15-51.el7.src.rpmRun the following commands to download a patch file:
cd /root/rpmbuild/SOURCES wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/patch/rhelonly-kexec-tools-2.0.20-makedumpfile-arm64-Add-support-for-ARMv8.2-LVA-52-bi.patchModify the kexec-tools.spec file.
Run the following commands to open the kexec-tools.spec file:
cd /root/rpmbuild/SPECS/ vi kexec-tools.specPress the
Ikey to enter Insert mode and add the following lines to the corresponding position in the file:Patch999: rhelonly-kexec-tools-2.0.20-makedumpfile-arm64-Add-support-for-ARMv8.2-LVA-52-bi.patch %patch999 -p1Add the lines as shown in the following figure.
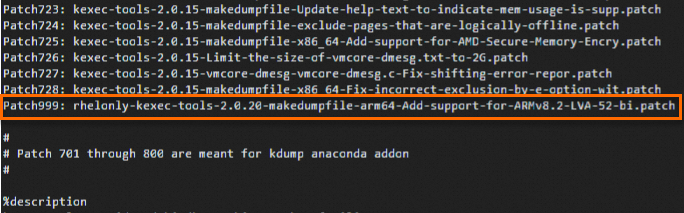
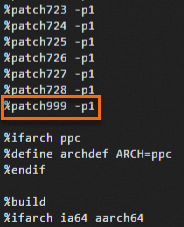
Press the
Esckey to exit Insert mode and enter:wqto save and close the file.
Run the following command to check installation dependencies:
yum-builddep kexec-tools.specRun the following commands to build an RPM package:
yum -y install rpm-build rpmbuild -ba kexec-tools.specRun the following commands to install the modified RPM package:
cd /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/aarch64 rpm -ivh kexec-tools-2.0.15-51.el7.aarch64.rpm
If downtime occurs again, you can query dump files by running the
ls -lh /var/crashcommand. If you find that avmcorefile is generated, this indicates that the issue is resolved.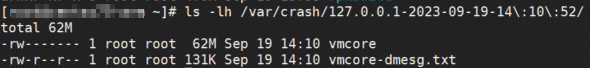
How do I convert CentOS 7 to RHEL 7?
CentOS 7 will reach end of life (EOL) on June 30, 2024. Alibaba Cloud will no longer provide support for the operating system from that date. To prevent the impacts of CentOS 7 EOL, you can convert CentOS 7 to RHEL 7. The following section describes how to convert CentOS 7 to RHEL 7 on Alibaba Cloud. For more information, see Converting from an RPM-based Linux distribution to RHEL.
ImportantTo prevent data loss or exceptions that are caused by accidental operations, we recommend that you stop important applications, database services, and data storage services and create disk snapshots to back up important data before the conversion.
(Conditionally required) If you use ECS instances and installed Server Guard on the instances, uninstall Server Guard first.
For more information, see Uninstall the Security Center agent.
NoteServer Guard is the default security enhancement tool for CentOS. RHEL 7 uses the security enhancement tools provided by Red Hat. Server Guard may be incompatible and conflict with tools in RHEL 7. Uninstall Server Guard during the conversion process to ensure system stability and compatibility.
Run the following commands to upgrade the system software packages to the latest versions:
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repoRun the following commands to update the system software package and restart the system:
sudo yum -y update sudo rebootRun the following commands to download the convert2rhel tool from the Red Hat official website and install the tool:
sudo curl -o /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release https://www.redhat.com/security/data/fd431d51.txt sudo curl --create-dirs -o /etc/rhsm/ca/redhat-uep.pem https://ftp.redhat.com/redhat/convert2rhel/redhat-uep.pem sudo curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/convert2rhel.repo https://ftp.redhat.com/redhat/convert2rhel/7/convert2rhel.repo sudo yum -y install convert2rhelPurchase an RHEL subscription on Alibaba Cloud and obtain the address of the RHEL 7 RPM repository.
For more information, submit a ticket.
Run the following commands to install the RHEL 7 RPM repository:
sudo rpm -ivh --replacefiles <RPM repository address> sudo sed -i 's/enabled=1/enabled=0/g' /etc/yum.repos.d/rh-cloud.repoReplace
<RPM repository address>with the actual RPM repository address of RHEL 7. You can obtain the address when you purchase the RHEL subscription.Run the following command to convert CentOS 7 to RHEL 7:
sudo convert2rhel -y --no-rhsm --enablerepo rhui-rhel-7-server-rhui-rpms --enablerepo rhui-rhel-7-server-rhui-extras-rpms --enablerepo rhui-rhel-7-server-rhui-optional-rpmsThe conversion process takes some time. The following command output indicates that the conversion is complete.
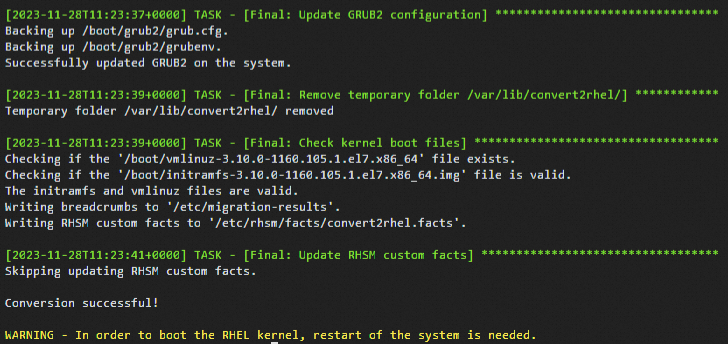
Run the following command to restart the system:
After the conversion is complete, a message is displayed to prompt you to restart the system. Restart the system to boot the new RHEL kernel. Then, check whether the operating system conversion was successful.
sudo rebootNoteAfter you convert CentOS 7 to RHEL 7, if you want to upgrade RHEL 7 to RHEL 8, see How do I upgrade Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7 to RHEL 8?
Red Hat 8.1 and Red Hat 8.2 images start slowly on ECS bare metal instances. What do I do?
When a Red Hat 8.1 or Red Hat 8.2 image is used on an ECS bare metal instance, the image takes up to 2 minutes longer to start than a Red Hat 7 image. To resolve this issue, you can change the kernel startup parameter settings from console=ttyS0 console=ttyS0,115200n8 to
console=tty0 console=ttyS0,115200n8in the/boot/grub2/grubenvfile of the Red Hat 8.1 or Red Hat 8.2 image, and restart the instance for the change to take effect.
FAQ about Ubuntu images
After the Server Guard (AliYunDun) process is started on ECS instances that run Ubuntu operating systems of specific versions, the average load of the instances increases. Why?
After the Server Guard process is started on ECS instances that run Ubuntu operating systems of specific versions, such as Ubuntu 18.04, the average load of the instances increases. After the Server Guard process is terminated, the average load drops to a normal level.
FAQ about FreeBSD images
How do I install patches and compile the kernel on FreeBSD?
Kernels in Alibaba Cloud FreeBSD public images are already patched to meet the startup requirements for series-V or later instance families. You can call the DescribeInstanceTypeFamilies operation with the
Generationparameter specified to query the instance families.In the following scenarios, you can use the FreeBSD kernel source code to install patches and compile the kernel to resolve and prevent the issue that the instance is unable to start:
If you use a FreeBSD image that is not provided by Alibaba Cloud or a custom image that is derived from a FreeBSD image that is not provided by Alibaba Cloud to create an instance of a series-V or later instance family, the instance may be unable to start.
If you use a FreeBSD public image to create an instance of a series-V or later instance family and use freebsd-update to update the kernel with new patches, the instance may be unable to start.
You do not need to install patches for FreeBSD 13 or later. In this example, FreeBSD 12.3 is used to describe how to use FreeBSD kernel source code to install kernel patches and compile the kernel.
Download and decompress the FreeBSD kernel source code package.
wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/freebsd/releases/amd64/12.3-RELEASE/src.txz -O /src.txz cd / tar -zxvf /src.txzDownload patches.
In this example, the patch
0001-virtio.patchis downloaded.cd /usr/src/sys/dev/virtio/ wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/0001-virtio.patch patch -p4 < 0001-virtio.patchCopy the kernel files, and compile and install the kernel.
N in the
make -j<N>command indicates the number of jobs that run in parallel. Set N based on your compiling environment. For example, for a single-vCPU environment, we recommend that you set -j<N> to-j2. This indicates that the ratio of the number of vCPUs to the N value is1:2.cd /usr/src/ cp ./sys/amd64/conf/GENERIC . make -j2 buildworld KERNCONF=GENERIC make -j2 buildkernel KERNCONF=GENERIC make -j2 installkernel KERNCONF=GENERICAfter the kernel is compiled, delete the source code.
rm -rf /usr/src/* rm -rf /usr/src/.*
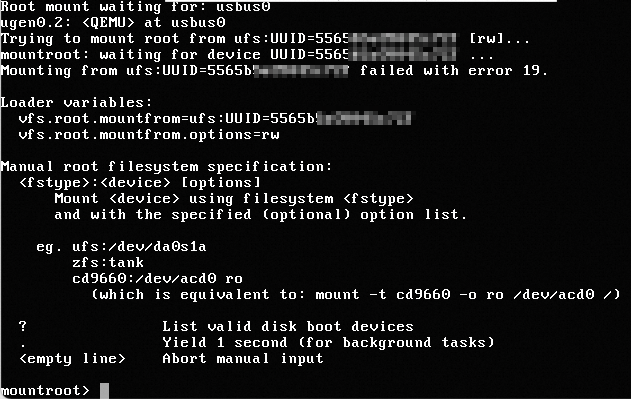
The system disk of an ECS instance that runs a FreeBSD operating system cannot be found in the KVM environment. What do I do?
Problem description
When you logged on to an ECS instance that runs a FreeBSD operating system in the Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) environment by using Virtual Network Computing (VNC), the system disk of the instance cannot be found and the logon failed, as shown in the following figure.
Solution
Enter a question mark (?) in the VNC interface to view the ufsid of the root file system.
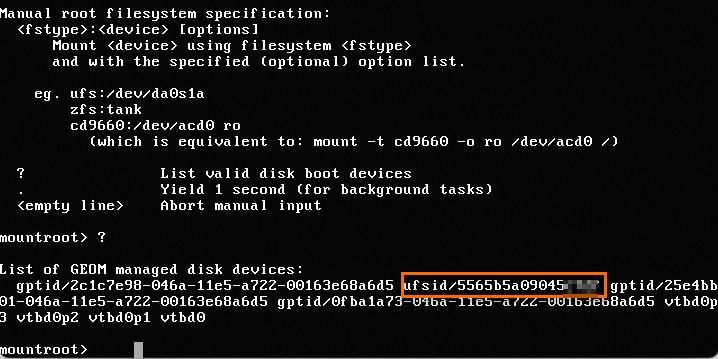
Enter
ufs:/dev/ufsid/5565b5a09045****and press the Enter key to access the operating system.Enter a username and password to log on to the system.
Run the following command to check the configurations in the
/etc/fstabfile:cat /etc/fstabThe command output shown in the following figure indicates that the root file system is configured to be mounted based on a UUID in the
/etc/fstabfile. However, FreeBSD operating systems do not support mounting devices based on UUIDs. You must configure the root file system to be mounted based on the ufsid.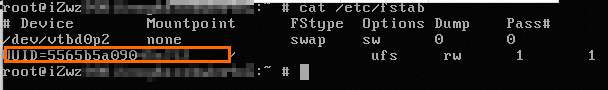
Configure the root file system to be mounted based on the ufsid.
Run the following command to open the
/etc/fstabfile:vi /etc/fstabPress the I key to enter Insert mode.
Change
UUID=5565b5a09045****to/dev/ufsid/5565b5a09045****.Press the Esc key, enter
:wq, and then press the Enter key to save the change and exit.
Run the following command to restart the system for the change to take effect:
reboot
FAQ about Fedora images
Why am I unable to use an SSH key pair that uses the ssh-rsa signature algorithm to connect to an ECS instance that runs Fedora 33 64-bit?
When you use an SSH key pair that uses the ssh-rsa signature algorithm to connect to an ECS instance that runs Fedora 33 64-bit, you may be unable to connect to the instance. You can use one of the following methods to resolve the issue:
Replace the SSH key pair that uses the ssh-rsa signature algorithm with an SSH key pair that uses a different signature algorithm, such as the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA).
Run the update-crypto-policies --set LEGACY command in the system to change
POLICYtoLEGACY. Then, you can continue to use the SSH key pair that uses the ssh-rsa signature algorithm.
After I used a Fedora CoreOS image to create an instance of a specific instance family, I found that the number of CPUs in the lscpu command output is only half the number of vCPUs of the selected instance type. Why?
After you used a Fedora CoreOS image to create an instance of a specific instance family, such as g5, you ran the lscpu command on the instance to view CPU information. In the command output, the total number of vCPUs that is indicated by the
On-line CPU(s) listvalue is only half the number of vCPUs of the selected instance type. For example, if an instance type that has two vCPUs is used to create an instance, theOn-line CPU(s) listvalue indicates only one vCPU, as shown in the following figure.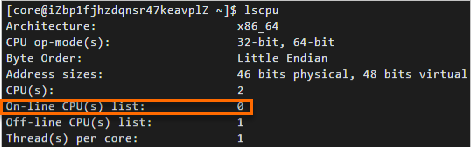 Note
NoteThe
On-line CPU(s) listvalue indicates vCPU serial numbers. In the preceding figure, only a single vCPU whose serial number is 0 is available.This is because, in the Fedora CoreOS kernel, the mitigations boot parameter is set to
auto,nosmtby default to disable simultaneous multithreading (SMT) for vulnerable systems. To view the mitigations parameter that is set toauto,nosmt, you can run the cat /proc/cmdline command.For more information about SMT, see Automatically disable SMT when needed to address vulnerabilities and Policy for disabling SMT.
Others
FAQ about Linux time and time zones
How do I adapt Linux custom images to NVMe-based system disks?
How do I resolve downtime issues that occur on migrated instances?
How do I install GRand Unified Bootloader (GRUB) on a Linux server?
How do I collect kdump information after the operating system of an instance fails?
What do I do if I cannot connect to an instance by using an RSA key?
What do I do if the kdump service cannot generate crash dump files on an ECS bare metal instance?
For information about the cause of and solution to this issue, see What do I do if crash dump files fail to be generated on some ECS instances?
A softlockup error occurs during the writeback process of the Linux operating system kernel. What do I do?
A softlockup error occurs when some earlier versions of the Linux kernel write data back to file caches. For information about how to resolve this issue, see Solution to the issue that a softlockup occurs during the writeback process of the Linux operating system kernel.
A softlockup error occurs when I delete cgroups from an ECS instance. What do I do?
For information about how to resolve this issue, see A softlockup error occurs when I delete cgroups in an ECS instance. What do I do?
An ECS instance goes down. What do I do?
Does the FTP service come with public images?
No, the FTP service does not come with public images. You must configure the FTP service on your own. For more information, see Manually build an FTP site on a Windows instance and Manually build an FTP site on a CentOS 7 instance.
Why does ECS disable virtual memory and leave swap partitions unconfigured by default?
When physical memory is insufficient, the memory manager saves memory data that has been inactive for an extended period of time to a swap partition or virtual memory file. This mechanism helps increase the amount of available memory.
However, if memory usage is already high and I/O performance is poor, this mechanism decreases the amount of available memory instead. Alibaba Cloud ECS cloud disks use distributed file systems for storage and provide multiple strongly consistent replicas for each piece of data. This mechanism ensures the security of user data but deteriorates the storage and I/O performance of local disks by tripling the number of I/O operations.
Therefore, virtual memory is disabled for Windows and swap partitions are not configured for Linux by default to prevent I/O performance from being further decreased when system resources are insufficient.
How do I enable the kdump service in a public image?
By default, the kdump service is disabled in public images. If you want an instance to generate a core file when the instance is down so that you can use the file to analyze the cause of the fault, you can perform the following steps to enable the kdump service. In the following example, the CentOS 7.2 public image is used. Operations may vary based on the version of your operating system.
Configure the directory in which to generate the core file.
Run the vim /etc/kdump.conf command to open the kdump configuration file.
Run the path command to configure the directory in which to generate the core file. In this example, the directory is /var/crash, and the following path command is used:
path /var/crashSave and close the /etc/kdump.conf file.
Enable the kdump service.
Use one of the following methods based on the operating system to enable the kdump service:
Method 1: Run the following commands to enable the kdump service:
systemctl enable kdump.servicesystemctlstartkdump.serviceMethod 2: Run the following commands to enable the kdump service:
chkconfig kdump onservice kdump startMethod 3: If Cloud Assistant is installed on your instance, enable the kdump service based on the instructions in How do I resolve downtime issues with migrated instances? Enable the kdump service.
After an IPv6 address is assigned to a Linux instance on which the NTP service is installed, the time of the instance cannot be synchronized with the UTC time. What do I do?
Problem description
After you run the
ntpq -pcommand on the Linux instance to synchronize time, a timeout error occurs, as shown in the following figure.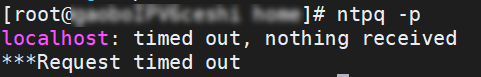
Solution
NoteThis solution is applicable to instances that run the following operating systems: CentOS 7 and earlier, Ubuntu 20.04 and earlier, Anolis OS RHCK, Anolis OS ANCK, Alibaba Cloud Linux, and Debian.
Connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance by using a password or key.
Run the following command to modify the /etc/ntp.conf configuration file:
vi /etc/ntp.confPress the I key to enter Insert mode.
Add
restrict -6 ::1to the file, as shown in the following figure.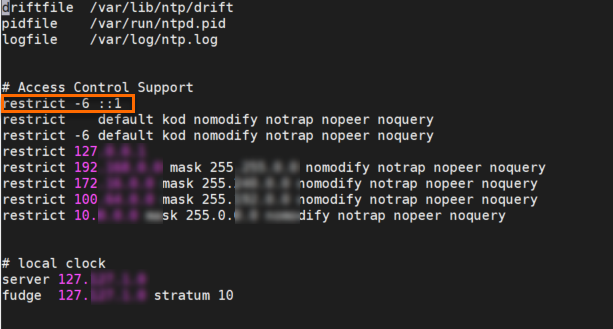
Press the Esc key. Then, enter
:wqand press the Enter key to save the modification and exit.Run the following command to restart the NTP service:
systemctl restart ntp
I cannot hot-swap disks or ENIs for a running instance that uses a custom image. Why?
Problem description
Hot swapping of disks or elastic network interfaces (ENIs) involves the actions of attaching disks to, detaching disks from, binding ENIs to, and unbinding ENIs from an instance that is in the Running state. You cannot hot-swap disks or ENIs for a Running instance that uses a custom image.
You can hot-swap disks and ENIs for instances on Alibaba Cloud. However, a hot swapping operation may fail if the operating system kernel of the instance does not support the operation. If the operating system kernel of the instance does not support the operation, the following issues may occur:
After you attach a disk to or bind an ENI to an instance, the disk or ENI cannot be found in the operating system.
You cannot detach a disk or unbind an ENI from an instance.
Solution
The operating system kernels of ECS instances and ECS bare metal instances support different features to allow hot swapping. We recommend that you enable the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) hot swapping and the Advanced Configuration and Power Management Interface (ACPI) hot swapping features in the operating system kernels of all your instances. By default, PCI hot swapping and ACPI hot swapping are enabled in all operating systems, except for early versions, such as CentOS 5. Perform the following steps to check whether PCI hot swapping or ACPI hot swapping is enabled in the kernel:
Connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance by using a password or key.
Run the following command to view the kernel version of the instance:
uname -rThe command output that is shown in the following figure indicates that the kernel version is
3.10.0-1127.19.1.el7.x86_64.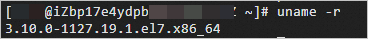
Run the following command to check the files in the
/bootdirectory:ll /bootThe
config-3.10.0-1127.19.1.el7.x86_64information that is displayed in the command output indicates that the config-3.10.0-1127.19.1.el7.x86_64 file is the configuration file for the system kernel.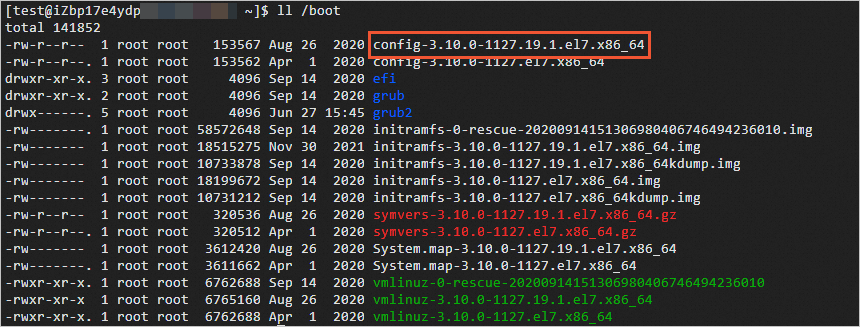
Run the following command to check the system kernel configuration:
cat /boot/config-3.10.0-1127.19.1.el7.x86_64If the following configuration items are set to
y, the operating system supports the hot swapping features:CONFIG_HOTPLUG_PCI_PCIE=y CONFIG_HOTPLUG_PCI=y CONFIG_HOTPLUG_PCI_ACPI=yIf one of the following configuration items is set to
is not set, the corresponding hot swapping feature is not supported by the kernel and you must modify the kernel configuration.If one of the following configuration items is set to
m, the configuration item is compiled into a module. For example, theCONFIG_HOTPLUG_PCI_ACPIconfiguration item is set to m, as shown in the following figure. This indicates that CONFIG_HOTPLUG_PCI_ACPI is compiled into a module. You must load the module to use the corresponding feature.CONFIG_HOTPLUG_PCI_PCIE=y CONFIG_HOTPLUG_PCI=y CONFIG_HOTPLUG_PCI_ACPI=mFor example, if you use a CentOS 5.x operating system with kernel version 2.6, the module that corresponds to the
CONFIG_HOTPLUG_PCI_ACPIconfiguration item is acpiphp.ko. To load the module, you must run themodprobe acpiphpcommand. If the module fails to be loaded, upgrade to a later kernel version or stop the instance, and then perform hot swapping operations.ImportantWe recommend that you do not arbitrarily upgrade the kernel versions or operating system versions of instances. For information about how to upgrade the kernel version, see How to avoid boot failures during kernel upgrade of a Linux instance.
What do I do if an instance is shut down after an operating system kernel error occurs?
Problem description
When an unexpected kernel error (kernel panic) occurs within the operating system of an instance, a second kernel (capture kernel) is loaded to perform a memory dump and generate a Kdump log file. Due to compatibility issues with the ECS Bare Metal Instance type, the disk identification fails during the startup of the second kernel. As a result, the Kdump log collection fails and the second kernel fails to start. The instance is in the Stopped state. You must restart the instance in the ECS console.
For more information about ECS Bare Metal Instance types, see Overview of instance families.
Cause
ECS bare metal instances may fail to generate dump files by using the Kdump service that comes with operating systems.
This issue occurs when you use the following images for 6th-generation ECS bare metal instances.
CentOS 8.3 or earlier
Ubuntu 16 or 18
Debian 10
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 with kernel versions earlier than
4.19.91-24.al7(This issue is fixed in Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 starting with kernel version4.19.91-24.al7.)
This issue occurs when you select a Debian 10 image for 7th-generation ECS bare metal instances.
Solution
CentOS images
We recommend that you replace the operating system with a later version. For more information, see Replace the operating system (system disk) of an instance.
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 images
We recommend that you perform the following steps to upgrade the kernel version to
4.19.91-24.al7or later:Connect to the instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance by using a password or key.
Run the following command to query the kernel version:
uname -rRun the following command to upgrade the kernel version:
sudo yum update kernelRun the following command to restart the ECS instance for the new kernel version to take effect:
sudo reboot
