Install the NVMe driver on your custom image before deploying workloads on ECS instances that use the image. This enables enhanced storage performance with the Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) protocol.
The NVMe interface standard for non-volatile memory is a high-speed protocol designed for solid-state storage, such as flash-based SSDs. Compared with traditional protocols like SCSI and virtio-blk, NVMe delivers higher speed and greater bandwidth.
Scenarios
Perform the steps in this topic if you encounter one of the following situations:
You import a locally built custom image to Alibaba Cloud and the Image Check reports that the NVMe driver is missing.
You cannot select a custom image when purchasing an ECS instance type that supports the NVMe protocol. This occurs when the image’s NVMe attribute does not match the instance type’s requirement.
NoteFor a list of instance families that support NVMe, see Instance family overview. You can also confirm NVMe support by checking the
NvmeSupportparameter in the DescribeInstanceTypes API operation.To check whether a custom image supports NVMe, verify the
NvmeSupportparameter in the DescribeImages API operation.For more information about why some images do not appear when you create ECS instances, see Why am I unable to find specific images when I create ECS instances?.
Procedure
Launch an ECS instance from your existing custom image. This instance serves as an intermediate environment to update the image. Then connect to the instance.
ImportantYou are charged for the intermediate instance. Release the instance after you create the new custom image to avoid ongoing charges.
Select a configuration method based on your instance’s operating system. Then verify and install the NVMe driver.
Console configuration
In the ECS console - Instances, locate the target instance and go to its details page. In the upper-right corner, click More actions and then select Set NVMe driver status.
Click One-click install to install the NVMe driver. The system automatically sets the NVMe driver status to Installed.
Automatic configuration using Cloud Assistant
Cloud Assistant provides the
ecs_nvme_configplug-in to help you quickly configure the NVMe driver. However, it supports only specific operating systems.Run the following command to check whether the Cloud Assistant Agent is installed and whether the
ecs_nvme_configplug-in is available:acs-plugin-manager --list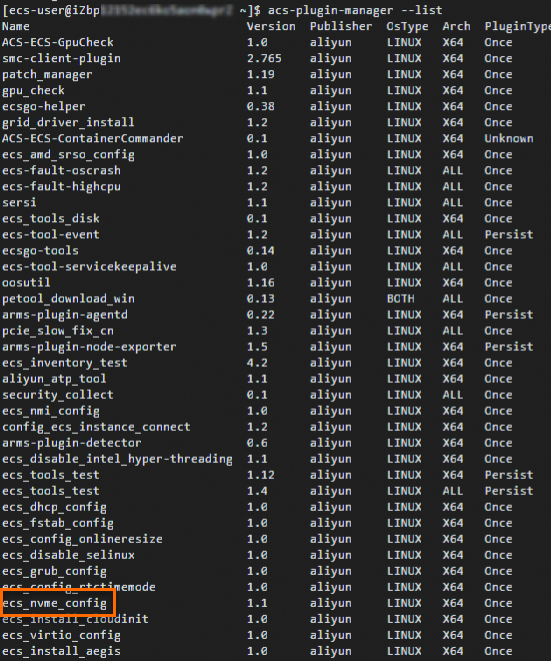
If no Cloud Assistant-related output appears, first install the Cloud Assistant Agent.
If the plug-in list appears and includes
ecs_nvme_config, proceed to the next step.
Use the
ecs_nvme_configplug-in to complete NVMe configuration.Run the following command to use the
ecs_nvme_configplug-in to check whether the NVMe module exists and whether it can be configured:sudo acs-plugin-manager --exec --plugin ecs_nvme_config --params --checkIf the output contains the following message, the NVMe driver is already installed. Skip further configuration and proceed directly to creating a custom image.
[SUCCESS] Summary: Your image can Runnig on nvme instanceIf the returned result contains a message similar to the following
[ERROR]message, you must proceed to the next step.[ERROR] 1.initrd/initramfs not has nvme module, Please run acs-plugin-manager --exec --plugin ecs_nvme_config --params -f/--fix to enable nvme;
Configure the NVMe driver and related parameters based on the check result:
sudo acs-plugin-manager --exec --plugin ecs_nvme_config --params --fixAfter completing the configuration, run the following command to restart the instance.
sudo rebootAfter the instance restarts, run the check command again to verify successful configuration:
sudo acs-plugin-manager --exec --plugin ecs_nvme_config --params --checkSample success output:
[OK] 1.initrd/initramfs already contain nvme module; [OK] 2.fstab file looks fine and does not contain any device names; [OK] 3.The nvme parameters already included. [SUCCESS] Summary: Your image can Runnig on nvme instanceCreate a new custom image from the instance where you installed the driver. Then modify the attributes of the new custom image and set the NVMe driver attribute to Supported.
ImportantIf you do not set the NVMe driver attribute to Supported, the system will not recognize the image as NVMe-compatible. As a result, you will still be unable to select NVMe-capable instance types when creating instances from this image.
Manual configuration (CentOS/Alibaba Cloud Linux)
Run the following command to check whether the kernel has loaded the NVMe driver:
cat /boot/config-`uname -r` | grep -i nvme | grep -v "^#"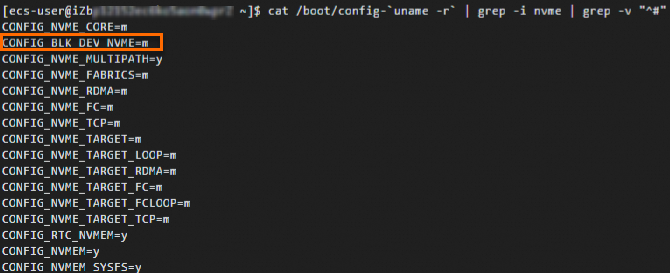
If the output contains
CONFIG_BLK_DEV_NVME=y, the operating system can boot directly on NVMe-enabled instance families. Proceed directly to Console configuration.If the output contains
CONFIG_BLK_DEV_NVME=m, perform the following steps.
Run the following command to check whether the initramfs contains the NVMe driver:
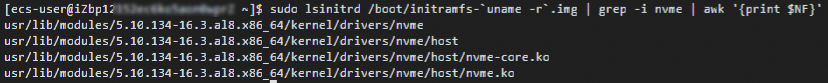
sudo lsinitrd /boot/initramfs-`uname -r`.img | grep -i nvme | awk '{print $NF}'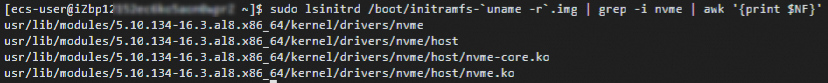
If the returned result matches the figure, the operating system can boot on instance families that support the NVMe protocol, and you can proceed to step d.
If the command returns no output, perform the following steps (Step c).
Run the following commands to make the initramfs include the NVMe driver:
mkdir -p /etc/dracut.conf.d echo 'add_drivers+=" nvme nvme-core "' | sudo tee /etc/dracut.conf.d/nvme.conf > /dev/null sudo dracut -v -fNoteIf the dracut tool is not installed, run sudo yum -y install dracut to install it.
Add the
io_timeoutparameter for NVMe in GRUB.NoteAdd the
io_timeoutparameter for NVMe in GRUB to prevent I/O failures caused by NVMe device timeouts. Setting this value to the maximum supported limit ensures the system continues processing I/O requests without premature failure.In most Linux distributions, the
io_timeoutparameter has a default value of 30 seconds. Before you add a value for theio_timeoutparameter, you must run theecho 4294967295 > /sys/module/nvme_core/parameters/io_timeoutorecho 4294967295 > /sys/module/nvme/parameters/io_timeoutcommand to verify whether theio_timeoutparameter can be set to its maximum value of 4,294,967,295 seconds. If the command returns-bash: echo: write error: Invalid argument, the current Linux version supports only setting it to 255 seconds.Method 1: Add parameters using grubby
Check whether the
grubbycommand is available:which grubbyIf the output includes the path to
grubby(for example,/usr/sbin/grubby), the system supportsgrubby. You can perform the steps in What to do next.If no output appears, your system does not support
grubby. See Method 2 to add the parameters.
Run the following command to add kernel parameters using
grubby:sudo grubby --update-kernel=ALL --args="nvme_core.io_timeout=4294967295 nvme_core.admin_timeout=4294967295"
Method 2: Add parameters by editing the GRUB configuration file
Run the following command to open the grub file:
sudo vi /etc/default/grubPress i to enter insert mode. Locate the
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=line and add thenvme_core.io_timeout=4294967295 nvme_core.admin_timeout=4294967295parameters.The following figure shows the file content after adding the parameters.
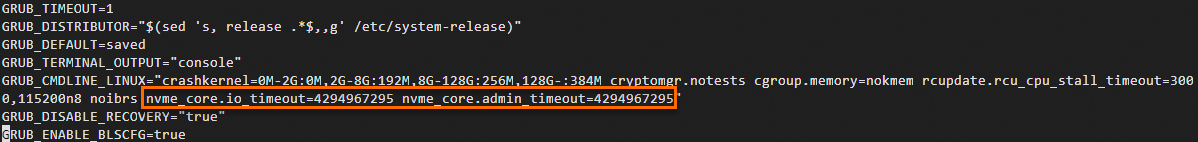 Note
NoteIf these parameters already exist in the configuration file, do not add them again.
Press Esc to exit insert mode. Enter
:wqand press Enter to save and close the file.Execute the following command to apply the GRUB configuration.
Select the command that corresponds to the instance startup mode of your ECS instance:
Legacy BIOS boot mode
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfgUEFI boot mode
View the GRUB configuration file:
# For CentOS, run: cat /boot/efi/EFI/centos/grub.cfg # For Alibaba Cloud Linux, run: cat /boot/efi/EFI/alinux/grub.cfgRun the appropriate command based on the output:
If the configuration file points to another config file (for example,
/boot/grub/grub.cfg), run the following command:
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfgOtherwise, run the following command (choose the line that matches your system):
# For CentOS sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/efi/EFI/centos/grub.cfg # For Alibaba Cloud Linux sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/efi/EFI/alinux/grub.cfg
Create a new custom image from the instance where you installed the driver. Then modify the attributes of the new custom image and set the NVMe driver attribute to Supported.
ImportantIf you do not set the NVMe driver attribute to Supported, the system will not recognize the image as NVMe-compatible. As a result, you will still be unable to select NVMe-capable instance types when creating instances from this image.
Run the following command again to check for NVMe-related output.
sudo lsinitrd /boot/initramfs-`uname -r`.img | grep -i nvme | awk '{print $NF}'If the command returns driver filenames (for example, nvme.ko), the configuration is complete. The operating system is now ready to boot on NVMe-enabled ECS instance types.
Manual configuration (Ubuntu/Debian)
(Optional) Run the following command to check whether the initrd contains the NVMe driver:
lsinitramfs /boot/initrd.img-`uname -r` | grep -i nvmeThe following output indicates that the Ubuntu operating system loads the NVMe driver in the initrd by default.
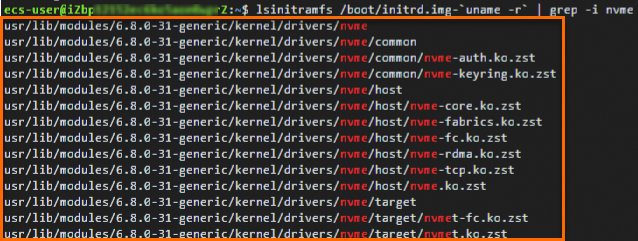
Add the
io_timeoutparameter for NVMe in GRUB.NoteAdd the
io_timeoutparameter for NVMe in GRUB to prevent I/O failures caused by NVMe device timeouts. Setting this value to the maximum supported limit ensures the system continues processing I/O requests without premature failure.In most Linux distributions, the
io_timeoutparameter is configured with a default value of 30 seconds. Before you add a value for theio_timeoutparameter, you must run theecho 4294967295 > /sys/module/nvme_core/parameters/io_timeoutcommand or theecho 4294967295 > /sys/module/nvme/parameters/io_timeoutcommand to verify whether theio_timeoutparameter can be set to its maximum value of 4,294,967,295 seconds. If the command returns the error-bash: echo: write error: Invalid argument, the current Linux distribution supports only a value of 255 seconds.Run the following command to open the /etc/default/grub file:
sudo vi /etc/default/grubPress the i key to enter edit mode, and add the following parameters to the
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=line:nvme_core.multipath=n nvme_core.io_timeout=4294967295 nvme_core.admin_timeout=4294967295.After you add the parameter, the file content is as follows:
 Note
NoteIf these parameters already exist in the configuration file, do not add them again.
Press Esc to exit insert mode. Enter
:wqand press Enter to save and close the file.
Run the following command to apply the configured GRUB settings.
Depending on the ECS instance's instance startup mode, select one of the following commands that applies to you:
This command works for Ubuntu and Debian systems regardless of boot mode:
sudo update-grub2Legacy BIOS boot mode
sudo grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfgUEFI boot mode
sudo grub-mkconfig -o /boot/efi/EFI/debian/grub.cfg
Create a new custom image from the instance where you installed the driver. Then modify the attributes of the new custom image and set the NVMe driver attribute to Supported.
ImportantIf you do not set the NVMe driver attribute to Supported, the system will not recognize the image as NVMe-compatible. As a result, you will still be unable to select NVMe-capable instance types when creating instances from this image.
(Optional) Redeploy your workload using the new custom image that supports NVMe. For example, create an instance from a custom image or shared image. During creation, select an instance type that supports the NVMe protocol.
After verifying the deployment, delete the original custom image to avoid charges for idle resources.
References
ECS instance types based on the NVMe protocol support only Enterprise SSD (ESSD) disks and ESSD AutoPL disks. These disks support Multi-attach, allowing them to attach to multiple ECS instances simultaneously for data sharing. For more information, see Attach a cloud disk to multiple ECS instances (multi-attach).
If improper configuration of the
io_timeoutparameter causes an NVMe disk to become unavailable on an ECS instance running Linux, see What do I do if an NVMe disk on a Linux ECS instance is unavailable due to an invalid I/O timeout parameter? for troubleshooting steps.