Alibaba Cloud DataHub is a platform for processing streaming data. It lets you publish, subscribe to, and distribute streaming data, which helps you easily build analytics and applications based on streaming data. You can use Data Transmission Service (DTS) to synchronize data from an RDS for MySQL instance to DataHub. This lets you quickly perform real-time data analysis using big data products, such as stream computing.
Prerequisites
A source RDS for MySQL instance is created.
NoteFor more information about how to create a source RDS for MySQL instance, see Create an RDS for MySQL instance.
For more information about the supported versions, see Overview of data synchronization scenarios.
The DataHub service is activated, and a project has been created to receive the synchronized data. For more information, see Quick Start and Manage projects.
Notes
DTS does not synchronize foreign keys from the source database to the destination database. Therefore, the cascade and delete operations on the source database are not synchronized to the destination database.
Category | Description |
Limits on the source database |
|
Other limits |
|
Special cases |
|
Supported synchronization topologies
One-way one-to-one synchronization.
One-way one-to-many synchronization.
One-way many-to-one synchronization.
For more information about the supported synchronization topologies, see Data synchronization topologies.
Supported SQL operations
Operation type | SQL operation |
DML | INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE |
DDL | ADD COLUMN |
Procedure
Use one of the following methods to go to the Data Synchronization page and select the region in which the data synchronization instance resides.
DTS console
Log on to the DTS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Synchronization.
In the upper-left corner of the page, select the region in which the data synchronization task resides.
DMS console
NoteThe actual operations may vary based on the mode and layout of the DMS console. For more information, see Simple mode and Customize the layout and style of the DMS console.
Log on to the DMS console.
In the top navigation bar, move the pointer over Data + AI and choose .
From the drop-down list to the right of Data Synchronization Tasks, select the region in which the data synchronization instance resides.
Click Create Task to go to the task configuration page.
Configure the source and destination databases. The following table describes the parameters.
WarningAfter you configure the source and destination databases, we recommend that you read the Limits that are displayed on the page. Otherwise, the task may fail or data inconsistency may occur.
Category
Configuration
Description
N/A
Task Name
The name of the DTS task. DTS automatically generates a task name. We recommend that you specify a descriptive name that makes it easy to identify the task. You do not need to specify a unique task name.
Source Database
Select a DMS database instance
The database that you want to use. You can choose whether to use an existing database based on your business requirements.
If you select an existing database, DTS automatically populates the parameters for the database.
If you do not select an existing database, you must configure the following database information.
Database Type
Select MySQL.
Access Method
Select Cloud Instance.
Instance Region
Select the region where the source RDS for MySQL instance resides.
Replicate Data Across Alibaba Cloud Accounts
This example shows how to migrate data within the same Alibaba Cloud account. Select No.
RDS Instance ID
Select the ID of the source RDS for MySQL instance.
Database Account
Enter the database account of the source RDS for MySQL instance. The account must have the read permissions on the objects to be synchronized.
Database Password
The password that is used to access the database.
Encryption
Specifies whether to encrypt the connection to the database. You can select Non-encrypted or SSL-encrypted based on your business requirements. If you want to set this parameter to SSL-encrypted, you must enable SSL encryption for the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance before you configure the DTS task. For more information, see Use a cloud certificate to enable SSL encryption.
Destination Database
Select a DMS database instance
The database that you want to use. You can choose whether to use an existing database based on your business requirements.
If you select an existing database, DTS automatically populates the parameters for the database.
If you do not select an existing database, you must configure the following database information.
Database Type
Select DataHub.
Access Method
Select Cloud Instance.
Instance Region
Select the region where the DataHub instance resides.
Project
Select the Project of the destination DataHub.
Click Test Connectivity and Proceed in the lower part of the page.
NoteMake sure that the CIDR blocks of DTS servers can be automatically or manually added to the security settings of the source and destination databases to allow access from DTS servers. For more information, see Add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers.
If the source or destination database is a self-managed database and its Access Method is not set to Alibaba Cloud Instance, click Test Connectivity in the CIDR Blocks of DTS Servers dialog box.
Configure the objects to be synchronized.
In the Configure Objects step, configure the objects that you want to synchronize.
Configuration
Description
Synchronization Types
The synchronization types. By default, Incremental Data Synchronization is selected. You must also select Schema Synchronization and Full Data Synchronization. After the precheck is complete, DTS synchronizes the historical data of the selected objects from the source database to the destination cluster. The historical data is the basis for subsequent incremental synchronization.
Naming Rules For Additional Columns
When DTS synchronizes data to DataHub, it adds some additional columns to the destination table. If the names of the additional columns conflict with the names of existing columns in the destination table, the data synchronization task fails. Select New Rule or Old Rule as required.
WarningBefore you select a naming rule, check whether the names of the additional columns conflict with the names of existing columns in the destination table. Otherwise, data loss or task failure may occur. For more information about the rules and definitions of additional columns, see Names and definitions of additional columns.
Processing Mode of Conflicting Tables
Precheck and Report Errors: checks whether the destination database contains tables that have the same names as tables in the source database. If the source and destination databases do not contain tables that have identical table names, the precheck is passed. Otherwise, an error is returned during the precheck, and the data synchronization task cannot be started.
NoteIf the source and destination databases contain tables with identical names and the tables in the destination database cannot be deleted or renamed, you can use the object name mapping feature to rename the tables that are synchronized to the destination database. For more information, see Map object names.
Ignore Errors and Proceed: skips the precheck for identical table names in the source and destination databases.
WarningIf you select Ignore Errors and Proceed, data inconsistency may occur and your business may be exposed to potential risks.
If the source and destination databases have the same schema and a data record in the destination database has the same primary key value or unique key value as a data record in the source database:
During full data synchronization, DTS does not synchronize the data record to the destination database. The existing data record in the destination database is retained.
During incremental data synchronization, DTS synchronizes the data record to the destination database. The existing data record in the destination database is overwritten.
If the source and destination databases have different schemas, data may fail to be initialized. In this case, only some columns are synchronized, or the data synchronization instance fails. Proceed with caution.
Capitalization of Object Names in Destination Instance
The capitalization of database names, table names, and column names in the destination instance. By default, DTS default policy is selected. You can select other options to ensure that the capitalization of object names is consistent with that in the source or destination database. For more information, see Specify the capitalization of object names in the destination instance.
Source Objects
Select one or more objects from the Source Objects section and click the
 icon to add the objects to the Selected Objects section. Note
icon to add the objects to the Selected Objects section. NoteYou can select tables as the objects to be synchronized.
Selected Objects
To rename an object that you want to synchronize to the destination instance, right-click the object in the Selected Objects section. For more information, see the "Map the name of a single object" section of the Map object names topic.
To rename multiple objects at a time, click Batch Edit in the upper-right corner of the Selected Objects section. For more information, see the "Map multiple object names at a time" section of the Map object names topic.
NoteTo specify WHERE conditions to filter data, right-click a table in the Selected Objects box and set the filter conditions in the dialog box that appears. For more information, see Set filter conditions.
Right-click a table in the Selected Objects box. In the dialog box that appears, clear Synchronize All Tables. Then, you can set the Shardkey, which is the key used for partitioning.
Click Next: Advanced Settings to configure advanced settings.
Configuration
Description
Dedicated Cluster for Task Scheduling
By default, DTS schedules the task to the shared cluster if you do not specify a dedicated cluster. If you want to improve the stability of data synchronization instances, purchase a dedicated cluster. For more information, see What is a DTS dedicated cluster.
Set Alerts
Specifies whether to configure alerting for the data synchronization instance. If the task fails or the synchronization latency exceeds the specified threshold, alert contacts will receive notifications. Valid values:
No: does not enable alerting.
Yes: configures alerting. In this case, you must also configure the alert threshold and alert notification settings. For more information, see the "Configure monitoring and alerting when you create a DTS task" section of the Configure monitoring and alerting topic.
Retry Time for Failed Connections
The retry time range for failed connections. If the source or destination database fails to be connected after the data synchronization task is started, DTS immediately retries a connection within the time range. Valid values: 10 to 1440. Unit: minutes. Default value: 720. We recommend that you set this parameter to a value greater than 30. If DTS reconnects to the source and destination databases within the specified time range, DTS resumes the data synchronization task. Otherwise, the data synchronization task fails.
NoteIf you specify different retry time ranges for multiple data synchronization tasks that have the same source or destination database, the shortest retry time range takes precedence.
When DTS retries a connection, you are charged for the DTS instance. We recommend that you specify the retry time range based on your business requirements. You can also release the DTS instance at your earliest opportunity after the source and destination instances are released.
Retry Time for Other Issues
The retry time range for other issues. For example, if the DDL or DML operations fail to be performed after the data synchronization task is started, DTS immediately retries the operations within the time range. Valid values: 1 to 1440. Unit: minutes. Default value: 10. We recommend that you set this parameter to a value greater than 10. If the failed operations are successfully performed within the specified time range, DTS resumes the data synchronization task. Otherwise, the data synchronization task fails.
ImportantThe value of the Retry Time for Other Issues parameter must be smaller than the value of the Retry Time for Failed Connections parameter.
Enable Throttling for Full Data Synchronization
During full data synchronization, DTS uses the read and write resources of the source and destination databases. This may increase the load on the database servers. You can configure the Queries per second (QPS) to the source database, RPS of Full Data Migration, and Data migration speed for full migration (MB/s) parameters for full data synchronization tasks to reduce the load on the destination database server.
NoteYou can configure this parameter only if Full Data Synchronization is selected for the Synchronization Types parameter.
Enable Throttling for Incremental Data Synchronization
Specifies whether to enable throttling for incremental data synchronization. You can enable throttling for incremental data synchronization based on your business requirements. To configure throttling, you must configure the RPS of Incremental Data Synchronization and Data synchronization speed for incremental synchronization (MB/s) parameters. This reduces the load on the destination database server.
Environment Tag
You can select an environment tag to identify the instance based on your requirements. In this example, you do not need to select a tag.
Whether to delete SQL operations on heartbeat tables of forward and reverse tasks
Specifies whether to write SQL operations on heartbeat tables to the source database while the DTS instance is running. Valid values:
Yes: does not write SQL operations on heartbeat tables. In this case, a latency of the DTS instance may be displayed.
No: writes SQL operations on heartbeat tables. In this case, features such as physical backup and cloning of the source database may be affected.
Configure ETL
Specifies whether to enable the extract, transform, and load (ETL) feature. For more information, see What is ETL? Valid values:
Yes: configures the ETL feature. You can enter data processing statements in the code editor. For more information, see Configure ETL in a data migration or data synchronization task.
No: does not configure the ETL feature.
Monitoring and Alerting
Specifies whether to configure alerting for the data synchronization instance. If the task fails or the synchronization latency exceeds the specified threshold, alert contacts will receive notifications. Valid values:
No: does not enable alerting.
Yes: configures alerting. In this case, you must also configure the alert threshold and alert notification settings. For more information, see the "Configure monitoring and alerting when you create a DTS task" section of the Configure monitoring and alerting topic.
Save the task settings and run a precheck.
To view the parameters to be specified when you call the relevant API operation to configure the DTS task, move the pointer over Next: Save Task Settings and Precheck and click Preview OpenAPI parameters.
If you do not need to view or have viewed the parameters, click Next: Save Task Settings and Precheck in the lower part of the page.
NoteBefore you can start the data synchronization task, DTS performs a precheck. You can start the data synchronization task only after the task passes the precheck.
If the data synchronization task fails the precheck, click View Details next to each failed item. After you analyze the causes based on the check results, troubleshoot the issues. Then, rerun the precheck.
If an alert is triggered for an item during the precheck:
If an alert item cannot be ignored, click View Details next to the failed item and troubleshoot the issue. Then, run a precheck again.
If an alert item can be ignored, click Confirm Alert Details. In the View Details dialog box, click Ignore. In the message that appears, click OK. Then, click Precheck Again to run a precheck again. If you ignore the alert item, data inconsistency may occur, and your business may be exposed to potential risks.
Purchase the instance.
Wait until the Success Rate becomes 100%. Then, click Next: Purchase Instance.
On the buy page, configure the Billing Method and Instance Class parameters for the data synchronization task. The following table describes the parameters.
Section
Parameter
Description
New Instance Class
Billing Method
Subscription: You pay for a subscription when you create a data synchronization instance. The subscription billing method is more cost-effective than the pay-as-you-go billing method for long-term use.
Pay-as-you-go: A pay-as-you-go instance is billed on an hourly basis. The pay-as-you-go billing method is suitable for short-term use. If you no longer require a pay-as-you-go data synchronization instance, you can release the instance to reduce costs.
Resource Group Settings
The resource group to which the data synchronization instance belongs. Default value: default resource group. For more information, see What is Resource Management?
Instance Class
DTS provides instance classes that vary in synchronization speed. You can select an instance class based on your business requirements. For more information, see Instance classes of data synchronization instances.
Subscription Duration
If you select the subscription billing method, specify the subscription duration and the number of data synchronization instances that you want to create. The subscription duration can be one to nine months, one year, two years, three years, or five years.
NoteThis parameter is available only if you select the Subscription billing method.
Read and select Data Transmission Service (Pay-as-you-go) Service Terms.
Click Buy and Start. In the dialog box that appears, click OK.
You can view the progress of the task in the task list.
Topic schema definition
When DTS synchronizes data changes to a DataHub topic, it adds additional columns to the topic to store metadata in addition to the changed data. The following is an example.
In this example, the business fields are id, name, and address. Because the old version of the naming rules for additional columns is used, DTS adds the dts_ prefix to the business fields.
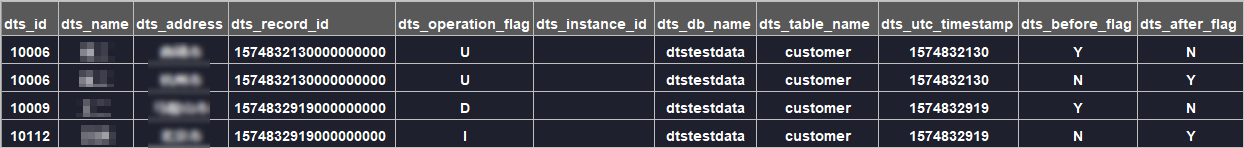
Schema definition:
Old additional column name | New additional column name | Data type | Description |
|
| String | The unique ID of the incremental log record. Note
|
|
| String | The operation type. Valid values:
|
|
| String | The server ID of the database. |
|
| String | The database name. |
|
| String | The table name. |
|
| String | The operation timestamp, which is the timestamp of the binary log (UTC time). |
|
| String | Indicates whether all column values are the values before the update. Valid values: Y and N. |
|
| String | Indicates whether all column values are the values after the update. Valid values: Y and N. |
Additional information about dts_before_flag and dts_after_flag
The values of dts_before_flag and dts_after_flag in an incremental log record vary based on the operation type:
INSERT
For an INSERT operation, all column values are the newly inserted values, which are the values after the operation. Therefore, the value of
dts_before_flagis N and the value ofdts_after_flagis Y. The following is an example.
UPDATE
For an UPDATE operation, DTS splits the operation into two incremental log records. These two log records have the same values for
dts_record_id,dts_operation_flag, anddts_utc_timestamp.The first incremental log record contains the values before the update. Therefore, the value of
dts_before_flagis Y and the value ofdts_after_flagis N. The second incremental log record contains the values after the update. Therefore, the value ofdts_before_flagis N and the value ofdts_after_flagis Y. The following is an example.
DELETE
For a DELETE operation, the incremental log contains the values of the deleted record. Therefore, the value of
dts_before_flagis Y and the value ofdts_after_flagis N. The following is an example.