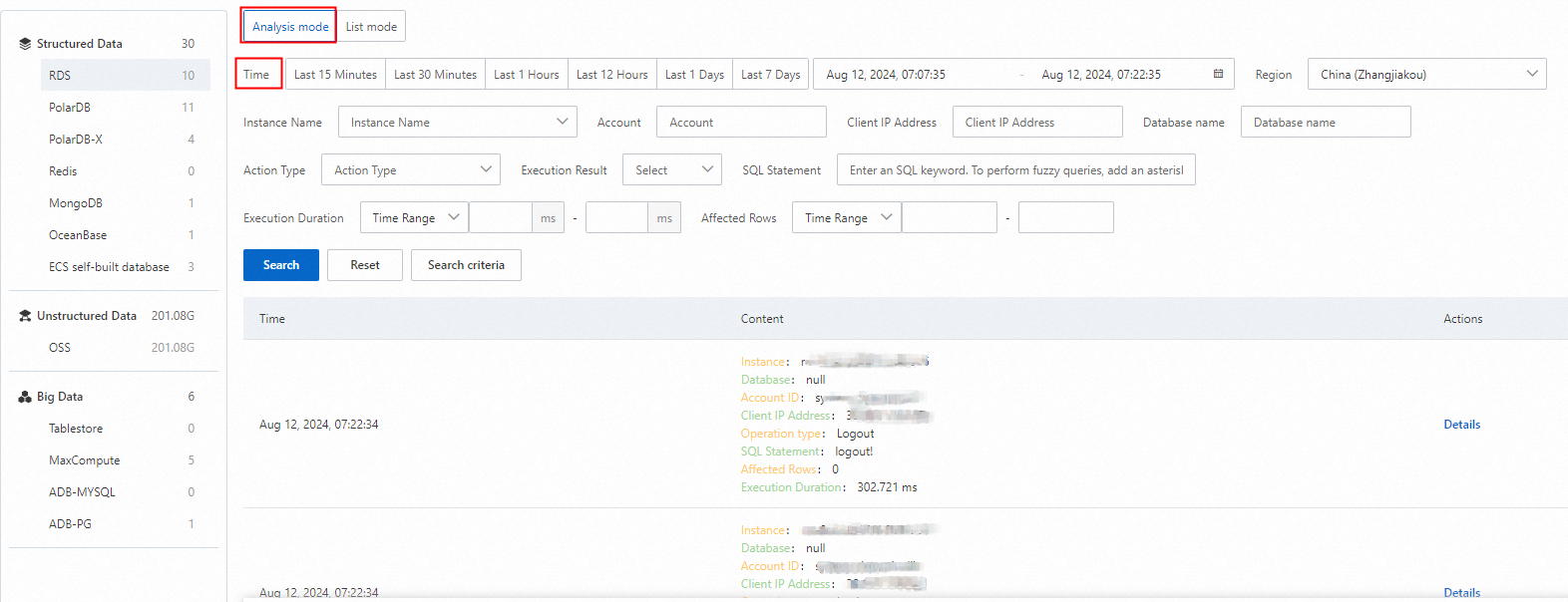
Audit logs record detailed information about database activities. By viewing audit logs, you can track potential malicious activities or unauthorized access to a database, investigate the causes of security events, and meet compliance requirements. This topic describes how to view audit logs.
Prerequisites
The log audit feature is enabled for the data assets that you want to audit. For more information, see Configure and enable an audit mode.
Log details
Log storage location
After you enable the data audit mode, Data Security Center (DSC) collects and stores logs in Logstores of Simple Log Service (SLS):
Project
The format is
sddp-${uid}-${regionId}. In this format,${uid}is the ID of your Alibaba Cloud account and${regionId}is the ID of the region where the database is located.Logstore
Category
Database type
Logstore
Relational database
RDS
rds_log
PolarDB
dsc_polardb_log
PolarDB-X
dsc_drds_log
OceanBase
dsc_oceanbase_log
Non-relational database
Redis
dsc_redis_log
MongoDB
dsc_mongodb_log
Unstructured database
OSS
dsc_oss_log
Big data
TableStore
dsc_ots_log
MaxCompute
dsc_odps_tunnel_log
ADB-MYSQL
dsc_ads_log
ADB-PG
dsc_gpdb_log
Self-managed database
MySQL
dsc_self_built_db_log
SQLServer
PostgreSQL
Oracle
Common field descriptions
Field | Description |
client_ip | The IP address of the client. |
clusterId | The cluster ID. |
collector_type | The log collection type. |
db | The database name. |
db_type | The database engine type. |
effect_row | The number of affected rows. |
execute_time | The execution time. |
fail | The execution result. |
hash | The hash value. |
instance_id | The instance ID. |
latency | The execution duration, in microseconds. |
node_name | The node name. |
operate_type | The operation type. |
origin_time | The original execution time of the SQL statement. |
region_id | The region ID. |
return_rows | The number of rows returned in the result set. |
sql | The SQL text. |
thread_id | The thread ID. |
uid | The user ID. |
update_rows | The number of updated rows. |
user | The logon username. |
View data audit logs (New version)
Log on to the Data Security Center console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Log Analysis.
In the upper-right corner of the Log Analysis page, click New Version.
If Old Version appears in the upper-right corner, skip this step.
In the product type navigation bar on the left side of the Log Analysis page, click a product type to view its log storage location.
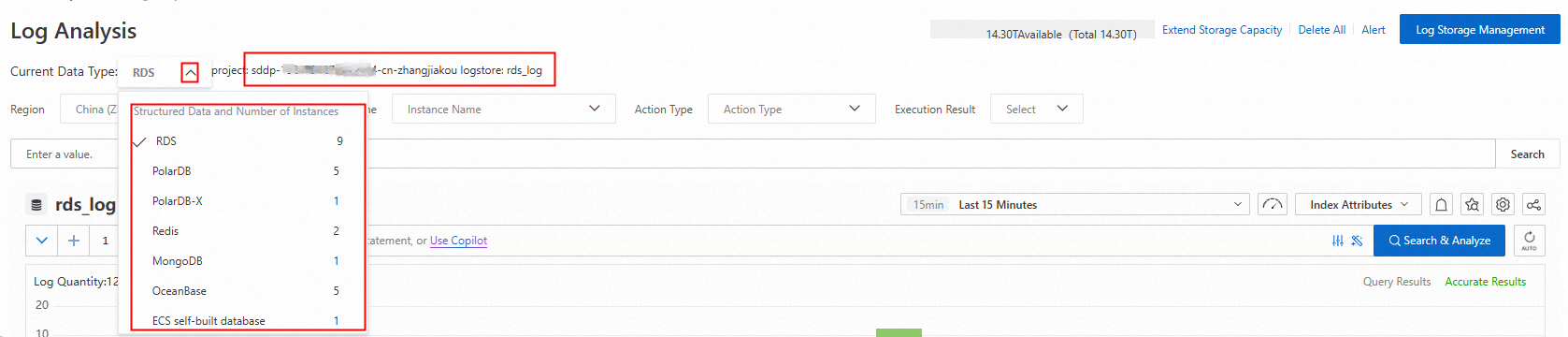
In the log area on the right, you can search for and view the operation logs of the target database or bucket using parameters such as region, instance, account, and operation type.
You can also enter a query and analysis statement to analyze the logs of the target data asset based on the query syntax and analysis syntax. For more information, see Quick guide to query and analysis.
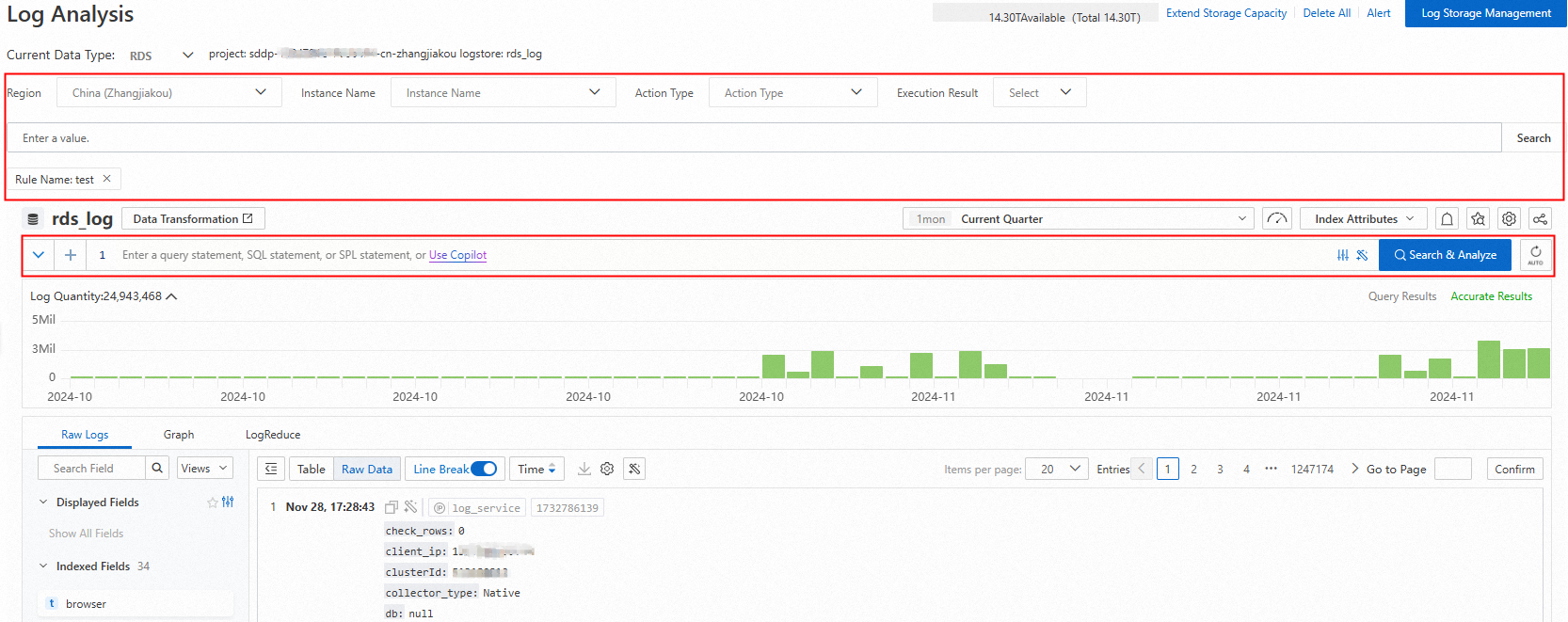
Query and analysis examples
View the access details of a table in a database of an RDS instance. The details include the access user, operation type, and operation result.
* and instance_id: rm-bp1******5u5w and db: s****p and table_name : sys_d*****it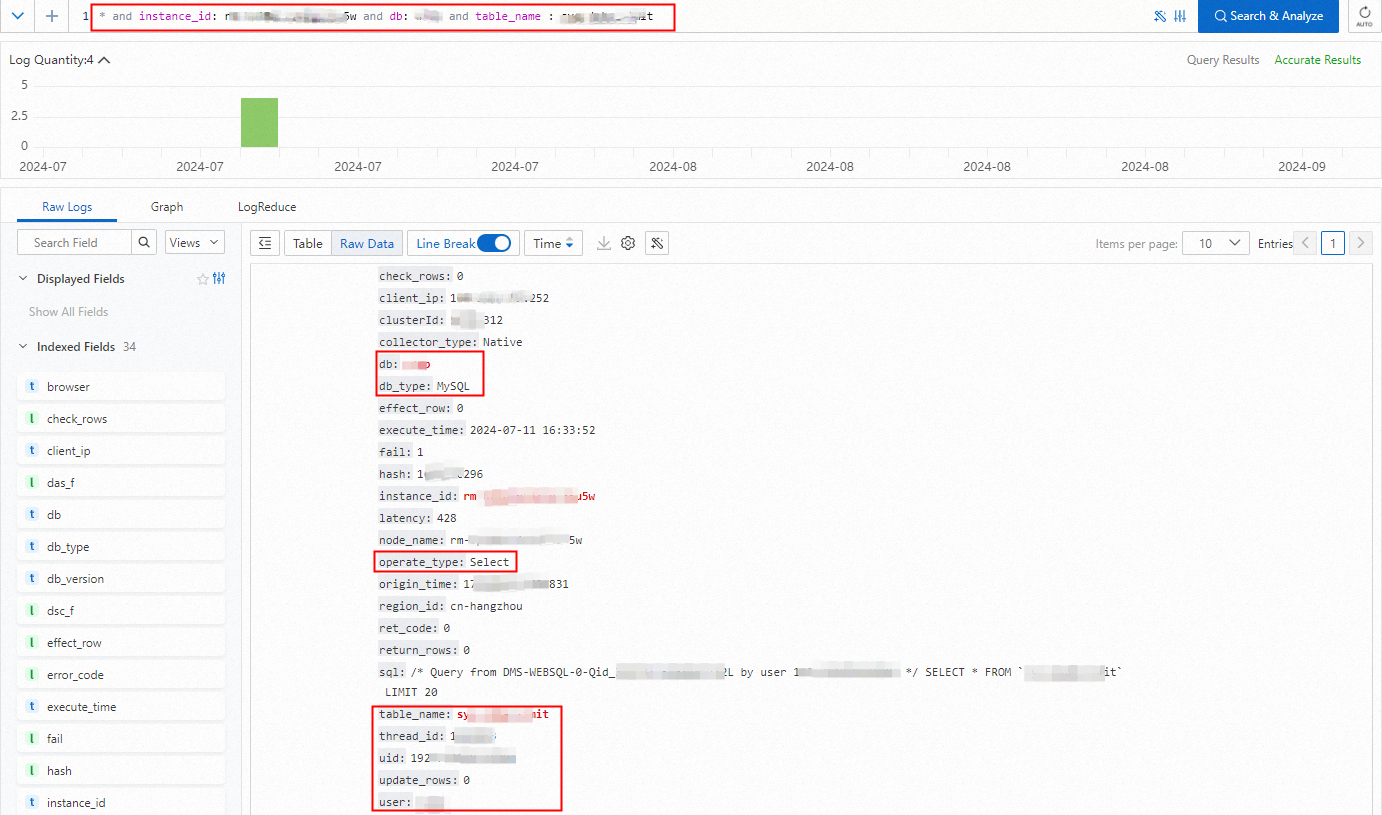
View the distribution of IP addresses that are used to access a data table in an RDS instance.
* and instance_id: rm-bp1*****5u5w and db: s****p and table_name : sys_d*****it | select user,client_ip,count(*) group by user,client_ip
Calculate statistics on the outbound traffic over the internet for all files in a directory of a specified bucket.
* and __topic__ : oss_access_log and bucket: examplebucket and host : "examplebucket.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com" not sync_request : cdn | select SUM(content_length_out) AS total_traffic_out_byte WHERE url_decode(object) LIKE 'exampledir/%'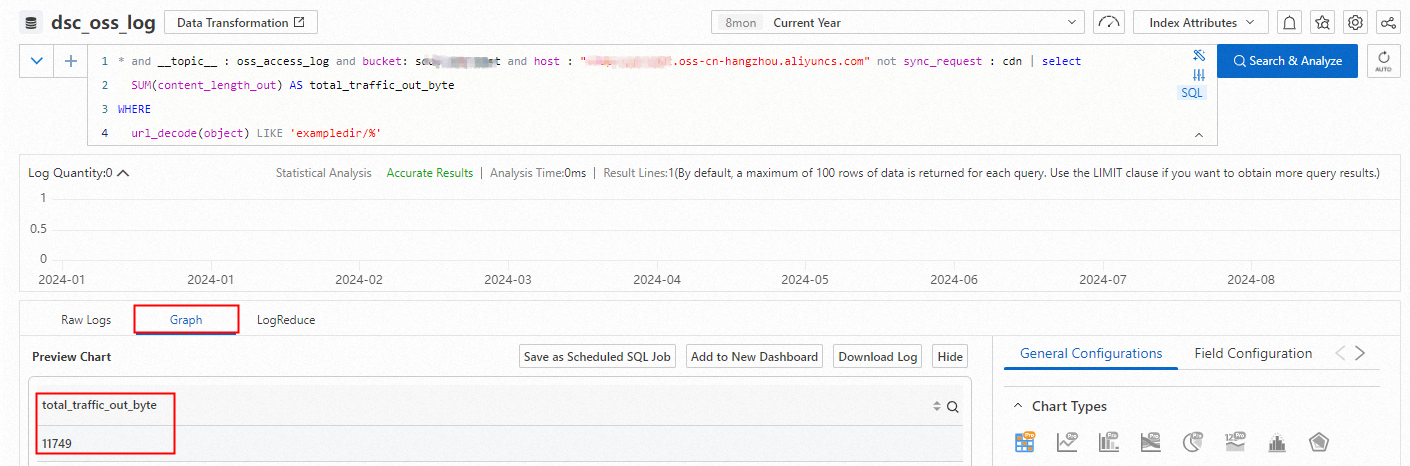
Download logs
DSC collects and stores logs in SLS. The DSC console integrates the log download feature from the SLS console, which lets you download logs or query and analysis results to your computer. The download procedure in the DSC console is similar to the one in the SLS console. For more information, see Download logs from the SLS console.
View data audit logs (Old version)
References
Audit logs that you can query online are stored in the storage space provided by DSC. You can view the current storage usage and manage the storage rules for online and archived logs. For more information, see Manage log storage.
By default, DSC provides built-in audit rules for data assets. These include database audit rules, OSS audit rules, and MaxCompute audit rules. You can also create custom audit rules. After you enable audit alert rules, you can use audit logs to detect risks in data assets, such as abnormal operations, data leaks, vulnerabilities, and SQL injection attacks. For more information, see Configure and enable audit alert rules.
After you enable audit alert rules, DSC generates an audit alert in DSC for each behavior that hits the rule conditions. You can analyze and handle the related risks based on the alert information and audit logs. For more information, see View and handle audit alerts.