DSC provides and enables built-in audit alert rules for data assets by default. These built-in rules include database policies, OSS policies, and MaxCompute policies. You can also create custom policies. Audit alert rules help identify potential risks and threats during database operation, ensuring database security and compliance with classified protection requirements. This topic describes the supported built-in audit alert rules for data audit and how to create custom audit alert rules.
Prerequisites
The data audit mode is enabled for data assets whose audit logs you want to view and are allowed to view. For more information, see Set and enable the data audit mode.
Background information
After you enable the data audit mode, DSC collects audit logs from databases based on the enabled data audit mode. DSC then uses enabled audit alert rules to identify risks in data assets, such as abnormal operations, data leaks, vulnerability exploits, and SQL injections. If risks are identified, DSC sends alert notifications.
Usage notes
Built-in audit alert rules: You can use built-in audit alert rules to detect risks in OSS, MaxCompute, RDS, and PolarDB. These rules are enabled by default and take effect for supported asset types.
Custom audit alert rules: You can create custom audit alert rules from multiple dimensions: sensitive data type, data sensitivity, database, table, field, source, and database instance. This enables fine-grained monitoring. You can create custom rules for different scenarios and application types to manage database access accurately.
View built-in audit alert rules
The built-in audit alert rules include database policies, OSS policies, and MaxCompute policies. You can follow these steps to view built-in audit alert rules and their details.
Log on to the Data Security Center console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Policy Management tab, click the Database Policy, OSS Policy, or MaxCompute Policy tab. In the Rule classification list, view the types of built-in audit alert rules.
Select the check box before a rule to view all rules of this type.

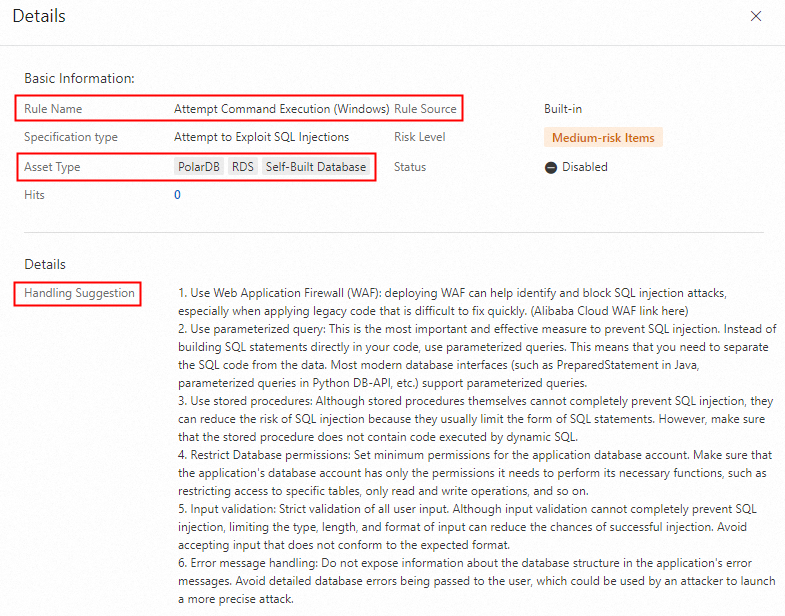
In the rule list on the right, view the values in the Rule Name, Rule Type, Risk Level, Status, Hits, and other columns.
Find a rule that you want to manage and click Details in the Actions column to view the supported Asset Type and Details.
Create a custom audit alert rule
If built-in audit alert rules cannot meet your audit requirements, you can create custom audit alert rules. After creation, custom rules are enabled by default.
On the tab, click Add Rule.
In the Add Rule panel, configure the parameters and click Submit.
Parameter
Description
Basic Information
Rule Name: The name of the audit alert rule. We recommend that you specify a name that can help you identify the rule.
Rule Type: The type of the audit alert rule. Select a type from the drop-down list.
Valid values: Attempt to Exploit SQL Injections, Bypass Attempt by Using SQL Injections, Stored Procedure Abuse, Buffer Overflow, Error-based SQL Injection, Boolean-based SQL Injection, Time-based SQL Injection, Denial-of-service Vulnerability, Database Detection, Data Breach Attack, Covert Channel Attack, Risky Operation by Application Account, Risk Operation by O&M Engineer, Abnormal Statement, High Traffic Volume, Configuration Operation, Sensitive Data Audit, Union-based SQL Injection, and Other.
Risk Level: The risk level of the audit alert rule. Select a risk level from the drop-down list. Valid values: High, Medium, and Low.
Asset Type: The type of the assets to which the audit alert rule is applied. Select a type from the drop-down list.
ImportantYou must select the Asset Type that is supported by the selected Rule Type based on the types of built-in audit rules. Otherwise, the custom audit alert rule does not take effect.
Rule Description: The description of the audit alert rule.
Sensitive Data Model
When you set the Asset Type parameter to RDS, PolarDB, or Self-Managed Database, you can configure the sensitive data identification template and model.
Asset
The assets to which the audit alert rule is applied based on the specified asset type.
Client
The client conditions under which the audit alert rule takes effect based on the specified asset type.
Behavior
The operation types and status code for the audit alert rule to take effect.
Result
The conditions under which the audit alert rule takes effect based on the specified asset type.
When you set the Asset Type parameter to Redis, this parameter is not supported.
Enable or disable an audit alert rule
If you no longer need a built-in audit alert rule or an enabled custom audit alert rule, you can turn off Status for the rule. To re-use an audit alert rule, you can turn on Status for the rule.
On the Policy Management tab, click the Database Policy, OSS Policy, MaxCompute Policy, or Custom Policy tab.
In the rule list, find the rule that you want to manage and turn on or turn off the switch in the Status column.

Configure notification settings
To receive audit-related alert notifications promptly, you need to choose from the left-side navigation pane, and then configure alert notifications on the Alert Notification tab. For more information, see Configure email, phone call, and text message alert notifications.
What to do next
After you enable an audit alert rule, DSC generates alerts for operations that trigger the rule. You can view these alerts on the Audit Alerts page of DSC. You can handle risks based on the alerts and audit logs. For more information, see View and handle audit alerts.
References
DSC provides a whitelist feature. You can add trusted data asset-related accounts and IP addresses to the whitelist. DSC does not generate audit alerts for risky operations from accounts or IP addresses in the whitelist. This helps reduce false alerts. For more information, see Manage the whitelist.