This feature natively integrates the processing capabilities of large AI models into the DataWorks Data Integration pipeline. It upgrades traditional data synchronization from simple data transport to intelligent processing. You can call AI models in real time to analyze, process, and enhance data as it is transferred from the source to the destination. This process unlocks the hidden value of unstructured data.
Function introduction
Applicable customers: This feature is designed for enterprise users who need to perform advanced analysis and processing on data during data synchronization. It is especially useful for companies that want to use AI to improve data quality and extract value from data.
Seamless integration into the sync pipeline: AI processing is a built-in step in Data Integration that connects seamlessly with the processes of reading data from the source and writing data to the destination.
Support for various NLP tasks: You can perform multiple natural language processing (NLP) tasks on text data during synchronization, such as sentiment analysis, summary generation, keyword extraction, and text translation.
Scenarios
Industry | Typical application |
Customer service / E-commerce | Analyze the sentiment of user comments and customer service tickets in real time. Automatically extract core issues and key feedback points. |
Compliance / Legal / Scientific research | During synchronization, automatically generate summaries and extract key information from policy documents, legal contracts, and research papers. |
Manufacturing / Supply chain / Healthcare | Intelligently analyze device logs, supply chain feedback, or doctor-patient communication records to enable threat alerts and service quality optimization. |
Cross-language collaboration | Automatically translate social media comments, news articles, or business documents into a single language during synchronization to allow for centralized analysis. |
Preparations
Create a workspace that uses Data Studio (new version).
Prepare the large model service required for AI-assisted processing. The preparation process varies based on the selected large model service provider:
Alibaba Cloud DataWorks model service: Deploy a model and start the model service in Model Service Management.
Alibaba Cloud Model Studio: Activate Alibaba Cloud Model Studio and obtain an API key.
Alibaba Cloud PAI-Marketplace: Activate Platform for AI (PAI) and obtain a token for the model service.
You can manually configure data source information or use existing data sources for offline sync tasks.
Ensure that the workspace is attached to a resource group and that the resource group can connect to the data source.
Billing
In addition to DataWorks subscription fees and resource group fees, this feature also incurs model inference (call) fees.
Example
This example uses Hologres to demonstrate how to use the AI-assisted processing feature during an offline sync task from one Hologres table to another. The goal is to translate the data in the feedback_info column of the source table into English and synchronize it with the destination table.
1. Create an offline sync task
Go to the Workspaces page in the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select a desired region. Find the desired workspace and choose in the Actions column.
In the navigation pane on the left, click
 to go to the Data Studio page. To the right of Workspace Directories, click
to go to the Data Studio page. To the right of Workspace Directories, click  and choose . The New Node dialog box is displayed.
and choose . The New Node dialog box is displayed.Set the Path, Data Source and Destination, and Name for the node, then click OK to create an offline sync node.
This topic uses a Hologres-to-Hologres sync task as an example to describe the AI-assisted processing feature.
2. Configure the sync task
After you create the offline sync node, the task configuration page is displayed. On this page, configure the following settings:
1. Data source
Configure the source and destination for the data synchronization task.
Type: The source and destination data source types selected in the Create an offline sync task step. This setting cannot be modified. To change the data source types, you must create a new offline sync task.
Data Source:Select an existing data source from the drop-down list, or click Add Data Source to create a new one.
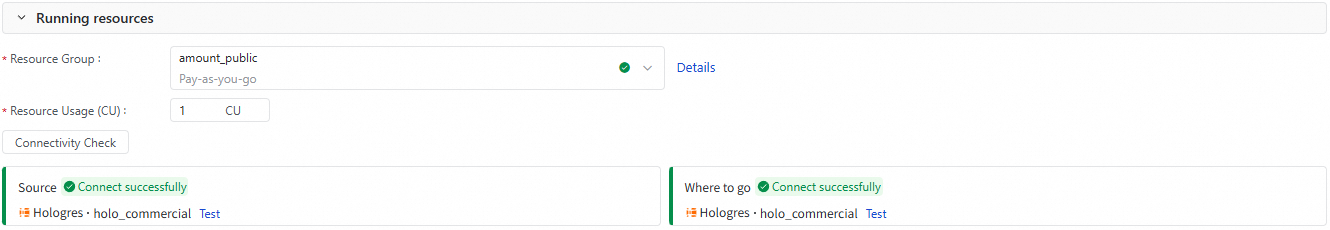
2. Runtime resource
Select the Resource Group for the sync task. If you use a serverless resource group, you can also specify the number of CUs to allocate for the task in the Resource Usage(CU) field.
After you select a Resource Group, Data Integration automatically checks the connectivity between the resource group and the source and destination data sources. You can also click Connectivity Check to perform the check manually.
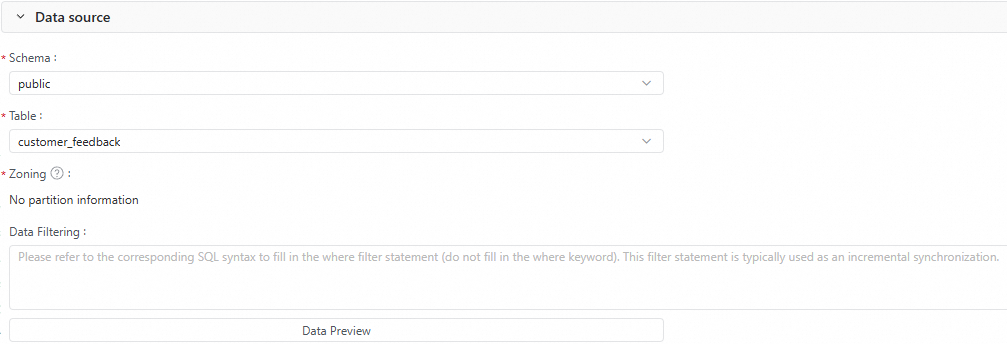
3. Source
Configure the information for the source table, such as the Schema, Table, Partition, and Data Filtering conditions. You can click Data Preview to preview the data that will be synchronized.
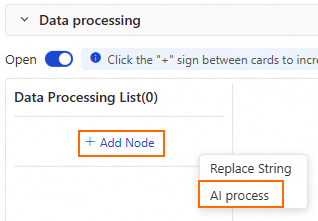
4. Data processing
In the data processing section, you can Enable the data processing feature. This feature requires additional computing resources and increases the resource overhead of the task.
Click Add Node, select AI Process.
Configure the settings for AI-assisted processing.
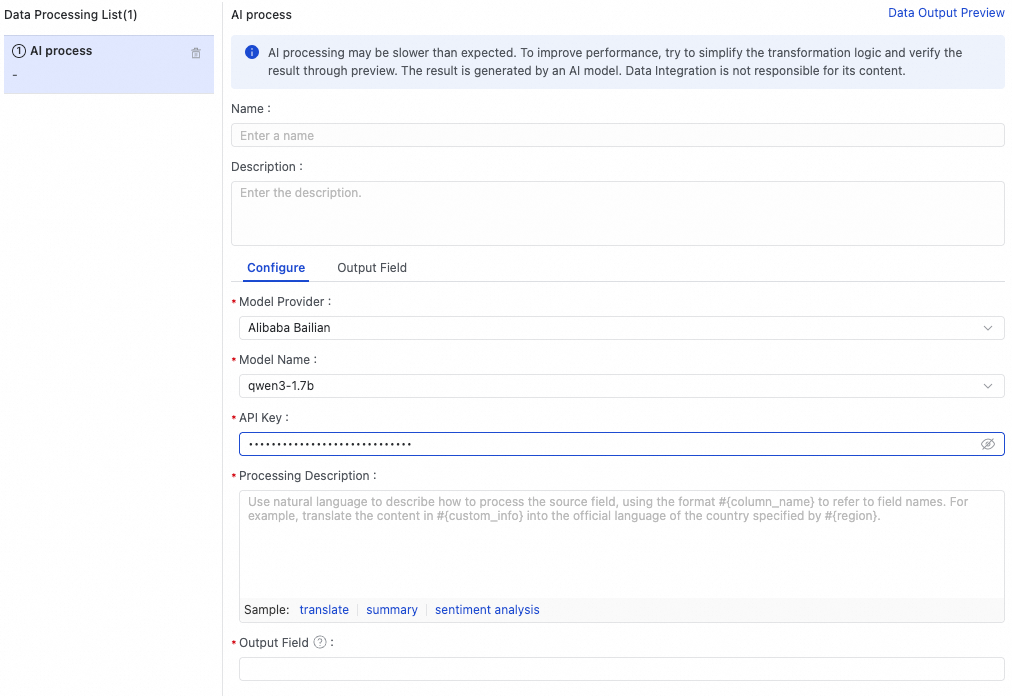
The following table describes the key parameters.
Parameter
Description
Model Provider
Supported providers are DataWorks Model Service, Aliyun Bailian, and PAI Model Gallery.
Model Endpoint
Select PAI Model Gallery and enter the model invocation Endpoint. To obtain the Endpoint, see Test service invocation.
Model Name
The model responsible for intelligent data processing. Select one as needed.
API Key
The API key to access the model. Obtain it from the model provider.
Alibaba Cloud Model Studio: Obtain a Model Studio API key.
Alibaba Cloud PAI-Marketplace: Go to the deployed EAS task, start online debugging, and obtain the token. Enter the token as the API key.
Processing Description
Use natural language to describe the processing for the source field. Write the field name in the
#{column_name}format. For example, in this case, enterTranslate '#{feedback_info}' into English.Output Field
Enter the name of the field where the result will be stored. If the field does not exist, a new field is automatically created.
NoteIn this example, the
feedback_infofield from the source table is translated into English and stored in thefeedback_processedfield.You can click Data Output Preview in the upper-right corner of the AI-assisted processing section to preview the final output data.
(Optional) You can configure multiple data processing flows that execute sequentially.
5. Destination
Configure the information for the destination table of the data synchronization, such as the Schema, Table, and Partition.
You can click Generate Target Table Schema to quickly generate the schema for the destination table.
If a destination table already exists, you can select it.
Configure the Write Mode and the Write Conflict Strategy.
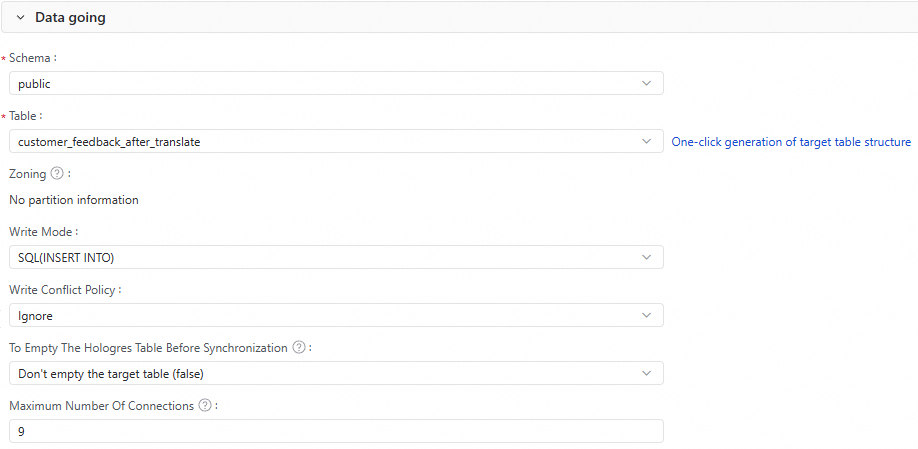
Configure whether to delete existing data in the Hologres table before synchronization.
(Optional) Configure the Maximum Connections.
The Maximum Connections setting takes effect only when the write mode is
SQL(INSERT INTO). When you start the task, ensure that the Hologres instance has a sufficient number of idle connections. A single task can use up to nine connections.
6. Destination field mapping
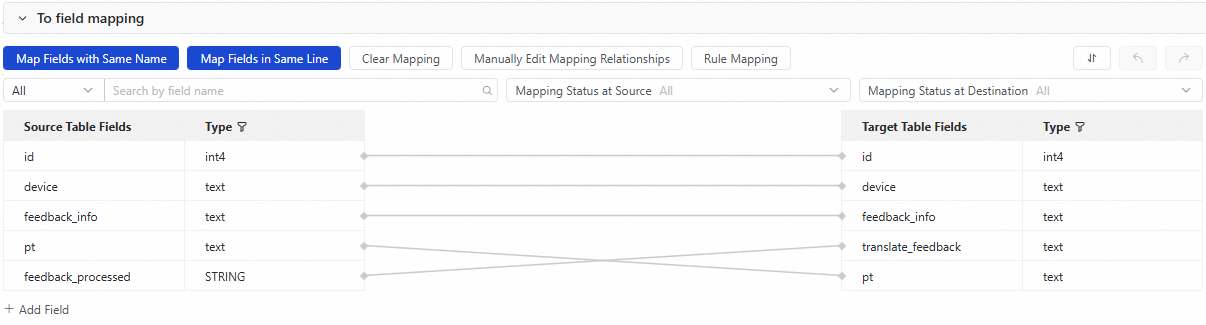
After you configure the source, data processing, and destination, the field mapping between the source and destination tables is displayed. By default, fields are mapped by name and position. You can modify the mapping as needed.
In this example, in addition to mapping the existing source table fields (id, device, feedback_info, and pt) by name, you must also manually map the feedback_processed field, which stores the translated result from the source table, to the translate_feedback field in the destination table.
3. Test the task
In the right-side panel of the offline sync task configuration page, click Debugging Configurations. Configure the Resource Group and any related Script Parameters to use for testing this node.
In the toolbar at the top of the node configuration page, click Save and then click Run. After the task finishes running, verify that the result is successful. You can then check the destination database to confirm that the table data is correct.
4. Configure scheduling
To run an offline sync node periodically, you must set the Scheduling Policies in the Scheduling section on the right side of the page and configure the relevant node scheduling properties.
5. Publish the node
Click the Publish icon in the node toolbar to start the publishing flow. This flow publishes the task to the production environment. Periodic scheduling takes effect only after the task is published.
What to do next: Task O&M
After the node is published, you can click Backfill Data or Perform O&M in the publishing flow.
Backfill Data: You can use this option to backfill data for the current node only. For more complex data backfill features, go to Operation Center. For more information, see Run a data backfill task and view the data backfill instance (New).
Perform O&M: After a task is published, it is automatically managed by Operation Center. In Operation Center, you can view the running status of the task or manually trigger its execution. For more information, see Operation Center.