DataWorks allows you to create and manage Data Integration tasks directly within the Data Studio module. This provides a unified environment for the entire ETL/ELT pipeline, eliminating the need to switch between modules.
Overview
DataWorks allows you to define and manage Data Integration tasks in the Data Studio module, similar to standard task nodes. This approach unifies the entire data pipeline into a single view, so you do not need to switch between functional modules.

Single-table batch synchronization tasks can be added to a workflow with dependencies, while other integration task types run as standalone nodes.
Core mechanism:
Configuration consistency: Whether you create a task in Data Studio or the Data Integration module, the configuration interface, parameter settings, and underlying functionality are identical.
Bidirectional synchronization: Tasks created in the Data Integration module are automatically synchronized and displayed in the
data_integration_jobsdirectory within Data Studio. These tasks are categorized by thesource-type-destination-typechannel for unified management.
Prerequisites
Data source preparation
You have created the source and destination data sources. For details about data source configuration, see: Data Source Management.
Ensure your data sources support real-time synchronization. See: Supported data sources and synchronization solutions.
Some data sources, such as Hologres and Oracle, require logging to be enabled. The method for enabling logs varies by data source. For details, see the data source configuration documentation: Data source list.
Resource group: You have purchased and configured a serverless resource group.
Network connectivity: You have established network connectivity between the resource group and your data sources. Network connectivity configuration.
Create an integration task in Data Studio
This section explains how to create a Data Integration task in Data Studio, using a single-table batch synchronization from MySQL to MaxCompute as an example.
Create a node
Go to the Workspaces page in the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select a desired region. Find the desired workspace and choose in the Actions column.
Click the + icon at the top, or in the toolbar at the top of the workflow, select .
Configure basic information
First, determine whether to use batch or real-time synchronization based on your requirements for latency, data volume, and complexity. Then, select a compatible synchronization mode (such as single table batch synchronization, full database real-time Synchronization, or full-incremental synchronization for entire databases) based on your source and destination database types, network environment, and supported features.
In the Create Node dialog box, configure the following settings:
Path: Select the location in the Data Studio directory tree where you want to store the task node.
Data Source Type: Select your source data source, such as
MySQL.Destination Type: Select your destination data source, such as
MaxCompute (ODPS).Specific Type: Select a synchronization mode.
Name: Enter a name for your task node, such as
mysql_to_mc_user_table.
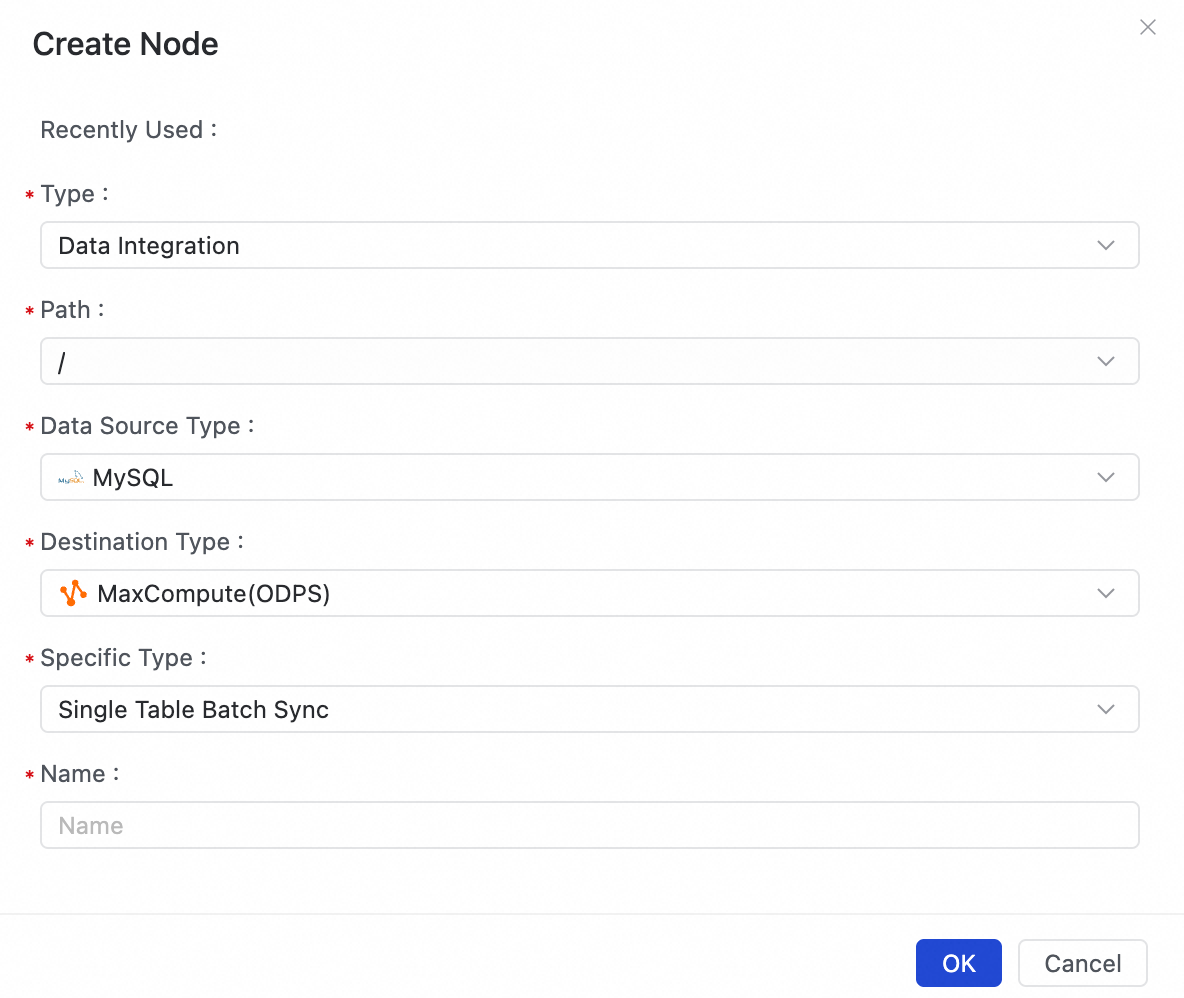
Click OK. The task is created, and you are redirected to its visual configuration page.
Configure task details
Except for the creation process, task configuration is identical to the process in the Data Integration module and is not detailed again here.
Configure scheduling (single-table batch synchronization only)
Configure properties for the node, such as schedule time, scheduling policies, and scheduling dependencies, so that the scheduling system can run it automatically at regular intervals. You can also set scheduling parameters to pass dynamic variables to node instances at runtime.
Publish and operate
After you configure the task, click the Publish button on the task toolbar to submit the integration task to the production environment. The task is then managed by the unified scheduling and monitoring system in the Operation Center.
After the task is published, you can view its running status, logs, alerts, and dependencies in the Operations Center. For information about operations such as instance management, rerunning failed tasks, performance tuning, and handling dirty data, see Task O&M and tuning.
Choosing a task type
Understanding the use cases for each synchronization mode and its behavior with scheduling and dependencies is key to building efficient, reliable workflows.
Single-table batch synchronization
For configuration details, see: Configure a task in the codeless UI and Configure a task in the code editor.
Description: Synchronizes data periodically in batches from a single source table to a single destination table. The task runs based on a defined scheduling cycle (for example, daily or hourly).
Use cases:
Synchronizing business data daily (T+1) to build the ODS or DWD layers of a data warehouse.
Archiving business tables periodically from a production database to a data lake or data warehouse.
Migrating data periodically for reports across different data sources.
Single-table real-time synchronization
For configuration details, see: Single-table real-time task configuration.
Description: This process typically uses change data capture (CDC) from logs or consumes data from a message queue.
Use cases:
Synchronizing real-time changes from a business database to a data warehouse, such as MaxCompute or Hologres, to build a real-time data warehouse.
Providing a data source for real-time monitoring dashboards or recommendation systems.
Implementing real-time data replication for a single table between different database instances.
Full-database batch synchronization
For configuration details, see: Full-database batch synchronization task.
Description: Performs one-time or periodic batch data synchronization for all or multiple tables in a source database.
Use cases:
Performing an initial, full migration of an entire business database to a cloud data warehouse.
Performing regular full or incremental backups of an entire database.
Importing all historical data in a one-time operation to initialize a new data analytics environment.
Full-database real-time synchronization
For configuration details, see: Full-database real-time synchronization task.
Description: Captures schema changes and data changes in real time from all or specified tables in a source database and synchronizes them to the destination.
Use cases:
Replicating an entire production Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) database to an analytical database in real time to enable read/write splitting and real-time analytics.
Building a real-time disaster recovery solution for a database.
Maintaining real-time data consistency between a data lake or data platform and multiple upstream business systems.
Full-incremental synchronization for entire databases
For configuration details, see: Full and incremental synchronization task for an entire database.
Description: The CDC data captured during real-time synchronization includes three types of operations:
Insert,Update, andDelete. For append-only storage systems, such as non-Delta MaxCompute tables, physicalUpdateorDeleteoperations are not natively supported. Writing the CDC stream directly to these systems can lead to data inconsistencies (for example, delete operations are not reflected). This mode resolves the issue by creating aBasetable for full snapshots and aLogtable for incremental logs at the destination.Use cases:
The destination table is a non-Delta MaxCompute table, and the source tables do not have an auto-increment column, which prevents the use of batch incremental synchronization. In this scenario, you can use a full-incremental task for entire databases to write incremental data within minutes. The final merged state becomes visible on a T+1 basis.
Feature comparison
Task type | Creation location | Workflow orchestration | Scheduling configuration | Data Studio debugging | Data source isolation |
Single-table batch synchronization | Data Studio only | ||||
Real-time single-table synchronization | Data Studio / Data Integration |
(standalone node only) | (Requires publishing to the Operation Center to run) | ||
Full-database batch synchronization | Data Studio / Data Integration | (standalone node only) | (scheduling can be set for sub-tasks) | (Requires publishing to the Operation Center to run) | |
Full-database real-time synchronization | Data Studio / Data Integration | (standalone node only) | (Requires publishing to the Operation Center to run) | ||
Full-incremental synchronization for entire databases | Data Studio / Data Integration | (standalone node only) | (scheduling can be set for sub-tasks) | (Requires publishing to the Operation Center to run) |
FAQ
For frequently asked questions about Data Integration, see the Data Integration FAQ.