SQL mode lets you create an API based on Dataphin logical tables by writing SQL statements. This topic describes how to create an API in SQL mode.
Prerequisites
To create an API based on logical tables, you must first create the logical tables. These tables include logical dimension tables, logical fact tables, and logical aggregate tables. For more information, see Dimensional modeling.
After you create the logical tables, configure a sync task in Integration as follows:
The destination data source of the sync task must be a data source supported by DataService Studio. You must also have read-through permissions for the data source.
Go to O&M > Recurring Tasks. Select the node that corresponds to the logical table. Choose Data Backfill > Backfill Current and Downstream Nodes. In the node list, select Layer 6 and then select all nodes in the list. Verify that the data backfill instance ran successfully. For more information, see Appendix: Backfill data for auto triggered tasks.
In Ad Hoc Query, verify that the data meets your expectations and that the logical table contains data. For more information, see Query and download data.
Configure a sync task in Integration. Select Logical Table Input Configuration (LogicalTable) for the input component and MySQL Output Component for the output component. For more information, see Configure the LogicalTable input component and Configure the MySQL output component.
After you configure and publish the sync task, you can create, submit, and publish a logical table API in DataService Studio.
Limits
APIs created from logical tables are subject to the limitations of the compute engine. For more information about supported compute engines, see Compute engines supported by DataService Studio.
Permissions
Project administrators and developers can create APIs.
Notes
The request and response parameters of an API must be obtained from the same Dataphin logical table. Otherwise, the API call will fail.
Step 1: Select a method to create an API
In the top menu bar of the Dataphin home page, choose Service > API Development.
In the upper-left corner, select a project. In the navigation pane on the left, click API Service. On the API page, click +Create API.
In the Create API dialog box, select Logical Table API-SQL Mode (Dataphin table).
Step 2: Configure API parameters
On the Create API page, configure the basic information and parameters for the API.
API basic information
Parameter
Description
API Name
Enter a name for the API. The name must meet the following requirements:
It can contain only Chinese characters, letters, digits, and underscores (_).
It must be 4 to 100 characters in length.
It must start with a letter.
It must be globally unique.
Request Method
Request methods include GET and LIST.
GET: Requests the server to obtain a specified resource.
LIST: Requests the server to obtain a portion of resources.
Data Update Frequency
Define the update frequency of the data returned by the API to help callers understand the timeliness of the data. Supported update frequencies are Daily, Hourly, Every Minute, and Custom. If you select Custom, you can enter up to 128 characters.
API Group
Select an API group configured in the current project. To create an API group, see Create a service group.
Description
Enter a brief description of the API. The description cannot exceed 128 characters.
Protocol
The API supports the HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
HTTP: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the most widely used network protocol.
HTTPS: If the gateway is configured as an Alibaba Cloud API Gateway dedicated or shared instance, you can select the HTTPS protocol. Make sure that the SSL Certificate for the independent domain is valid to prevent call failures. To configure an SSL Certificate, choose Platform Management Network Configuration and go to the Network Configuration page.
Timeout
The timeout period is used to monitor the duration of API calls. The default value is 3 seconds. You can set a positive integer from 3 to 60 seconds.
If an API call exceeds the specified Timeout period, an error is returned. This helps you promptly detect and handle exceptions during API calls. For information about how to view exceptions, see View and manage Service Monitoring APIs.
Cache Settings
You can Enable or Disable caching. If you enable caching, you must configure the Cache Timeout. The default value is 300 seconds. You can set a positive integer from 60 to 1,000,000 seconds (approximately 277.78 hours).
Version Number
Enter a version number for the API. Each configuration has its own version number for comparison with the previous version. The version number must be unique for the API. The version number must meet the following requirements:
It cannot exceed 64 characters.
It can contain uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, underscores (_), periods (.), and hyphens (-).
Return Type
The default value is JSON.
API request and response parameters
When you configure API Request Parameters and Response Parameters, you must first identify the Dataphin Logical Table as the source for the input and output parameters. Then, you need to write an API SQL statement to parse the Request Parameters and Response Parameters. Finally, you can configure the basic information for the Request Parameters and Response Parameters.
On the Parameter Checking page, after you select a Mode and a Dataphin Logical Table, all fields in the selected logical table are displayed below. You can refer to these fields when you write the API SQL statement.
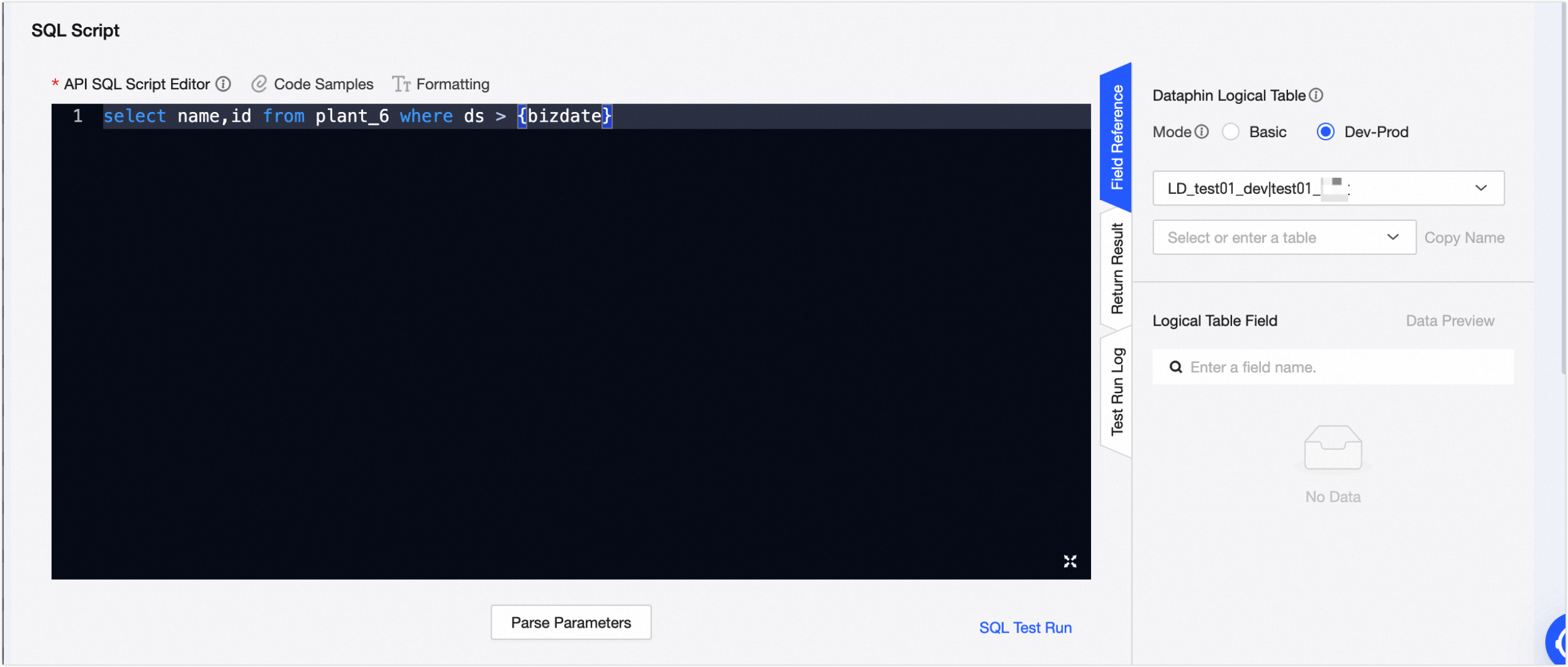
Parameter
Description
Mode
Select the business category where the logical table is located and the logical table in the selected category. Two modes are supported: Basic and Dev_Prod.
In Basic mode, the production database is read during development, submission, and online publishing.
In Dev-Prod mode, the development database is read during development and submission, and the production database is read during online publishing.
Logical table fields
You can copy all table fields or a single field.
You can write an API SQL script based on the reference examples. Keep the following points in mind when you write the script:
When you create an API based on a service unit, the SQL script must follow MySQL syntax.
The following are not supported:
Multiple SQL statements are not supported.
Non-SELECT syntax, such as INSERT, UPDATE, CREATE, or DELETE.
Multi-table join queries or nested queries are not supported.
You cannot assign aliases to query tables.
If you use aggregate functions, such as Min, Max, Sum, and Count, you must specify an alias, which is used as the response parameter name. Example:
sum(num) as total_num.
The following are SQL script templates that Dataphin can parse to obtain Response Parameters and Request Parameters:
Template 1: Query and return all fields from the data table.
Command format
select <response_parameter> from <table_name> where <request_parameter>=${request_parameter_value}Example
-- Query id_card and name from TableA when c=id_card. select TableA.id_card,TableA.name from BusinessUnitA.TableA where TableA.c=${id_card}
Template 2: Query and return specified fields from the data table.
Command format
select <response_parameter> from <logical_table_name> where <request_parameter> in (${request_parameter_value})Example
-- Query id_card and name from TableA when c is in id_card. select TableA.id_card,TableA.name from BusinessUnitA.TableA where TableA.c in (${id_card})
Template 3: Use aggregate functions, such as max, sum, min, and count, on fields. You can also use `like` for fuzzy matching.
Command format
select max(<response_parameter_1>) as <alias_c>,sum(<response_parameter_1>) as <alias_b> ,min(<response_parameter_1>) as <alias_d>,count(*) as <alias_e> from <logical_table_name> where <request_parameter_name_1> like ${request_parameter_value_1}Example
-- In TableA, when field c is like id_card, return the maximum value of field a as parameter c, the minimum value of a as parameter d, and the sum of a as parameter b. select max(TableA.a) as c,sum(TableA.a) as b ,min(TableA.a) as d,count(*) as e from BusinessUnitA.TableA where TableA.c like ${id_card}
Template 4: Perform calculations on fields. Supported operations include addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (×), division (/), modulo (%), integer division (//), and power (**). The logical operators `and` and `or` are also supported.
Command format
select (<response_parameter_1>+<response_parameter_2>) as <alias>,(<response_parameter_2>+<response_parameter_3>) as <alias> from <logical_table_name> where <field_c>=${request_parameter_name_1} and <field_b>>=${request_parameter_name_2} or <field_c><=${request_parameter_name_3}Example
-- In TableA, when field c=id_card, or field b>=num, and field c<=num1, return the parameter values of a+b and b+c as parameters acd and bcf, respectively. select (TableA.a + TableA.b) as acd, (TableA.b + TableA.c) as bcf from BusinessUnitA.TableA where TableA.c=${id_card} and/or TableA.b>=${num} and/or TableA.c<=${num1}
ImportantIn the four templates, the request and response parameters of the API must be obtained from the same logical table. Otherwise, the API call will fail.
Click Parse Parameters. Dataphin automatically parses the input and output parameters from the API SQL statement and adds them to the Request Parameters and Response Parameters sections.
The basic information for request and response parameters is similar. The following table describes the basic information for request and response parameters and the information that you need to configure.
Parameter
Description
Parameter Name
Displays the name of the parameter that is exposed externally.
Parameter Type
Parameter types include DOUBLE, FLOAT, STRING, DATE(yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss), BOOLEAN, INT, LONG, SHORT, BYTE, BIGDECIMAL, and BINARY. Select the parameter type that corresponds to the bound field of the parameter name.
If the field type of the logical table is not in the list of available parameter types, select String.
Parameter Value Type
Select the type of the parameter value. Single Value and Multiple Values are supported.
Single Value: The parameter is passed based on the parameter type. The input parameter is parsed as a single value. The applicable operators are
=, like, >=, <=, >, <, !=, and between.Multiple Values: The input parameter is parsed as multiple values separated by commas (,). The applicable operator is
in.
Parameter Processing
Configure this parameter when the operator is LIKE. If you do not select a parameter processing method, you must manually enter wildcard characters for matching when you enter parameters. You can select Fuzzy Match (%keyword%), Right Match (%keyword), or Left Match (keyword%).
Example
Enter examples of request and response parameter values to help developers understand them. You can enter up to 1,000 characters.
Description
Enter a brief description of the request and response parameters. You can enter up to 1,000 characters.
Required
Specify whether the request parameter is required when calling the API.
Select No: The SQL statement for calling the API can be executed without this parameter.
Select Yes: The SQL statement for calling the API cannot be executed without this parameter.
For example, if the request parameter is `id`, the parameter is required, and the response parameter is `name`, the following statements return different results:
select name from tableA where id=5;: The `name` field and data results are returned.select name from tableA;: The SQL statement execution fails.
Operation
The following operations are supported for request and response parameters:
Request parameters: You can perform batch modifications on the parameter type, parameter value type, parameter processing (supported only when the operator is LIKE), and whether the parameter is required.
Response parameters: You can perform batch modifications on the parameter type of response parameters.
Click SQL Test Run. In the Request Parameter Input dialog box, set Parameter Type, Parameter Value Type, Parameter Processing, and Test Run Input Value, and then click OK.
Run Log: View the actual SQL statement that is executed during the SQL test run.
Test Run Input Value: Specify the value for the bound field. You can view the value of the bound field in the Data Preview panel.
Batch Operations: Modify the parameter type, parameter value type, and parameter processing of request parameters in batches. Parameter processing is supported only when the operator is LIKE.
Click Fill Parameter Example Values. The system populates the request and response parameters with example values from the most recent successful test run. If a parameter already has an example value, it is not overwritten. You can modify the values.
Click Submit to create the API.
What to do next
After you create an API, test it and publish it to the DataService Studio marketplace to make it available for applications to call. For more information, see Test and publish an API.
To delete an API, manage API versions, or transfer ownership, see View and manage APIs.