Dataphin lets you create Python computing tasks for various application scenarios. This topic describes how to create a Python computing task in Dataphin.
Background information
Python 3.7 is better suited for diverse big data processing scenarios. For example, Python 3.7 supports the list.clear() method, which is not available in Python 2.7. For more information, see Python.
Limits
Python 3.7 is not backward compatible with Python 2.7. You cannot directly upgrade existing Python 2.7 tasks.
Starting from version 2.9.3, Dataphin uses Python 3.7 by default for developing computing tasks. You can only modify the version of Python tasks that are in a draft state. The supported versions are Python 2.7, Python 3.7, and Python 3.11.
Task execution
When you run a Python task in Dataphin, the scheduling cluster executes it by cloning a built-in template image. This image contains common Python packages that you can use to develop your tasks. For more information, see Appendix: Python built-in resource packages.
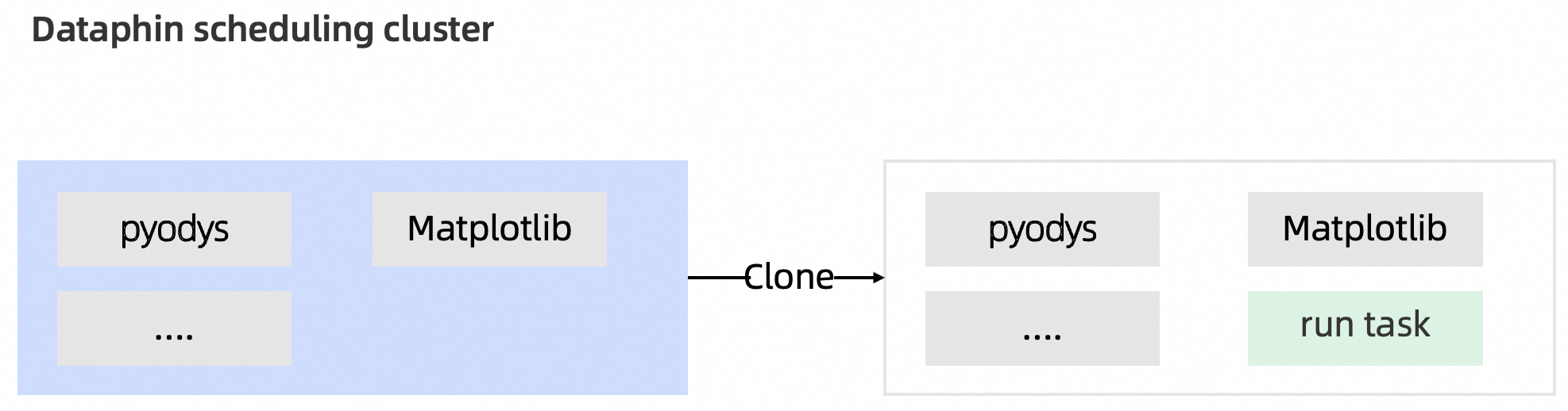
If the built-in resource packages do not meet your needs, you can install additional packages using the Python third-party package management feature in the Management Center. At runtime, the system automatically adds any referenced resource packages to the runtime environment for task execution. Because Dataphin runs by cloning a built-in template image for each task, if you use the
pip installcommand to install a resource package, thepip installcommand is re-executed every time the task runs. For this reason, we recommend that you use the third-party Python package management feature. For more information, see Developing Python computing tasks using third-party libraries.
Procedure
On the Dataphin home page, choose Development > Data Development from the top menu bar.
On the Development page, select a project from the top menu bar. If you are using Dev-Prod mode, you also need to select an environment.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Data Processing > Script Task. In the Script Task list, click the
 icon and select Python.
icon and select Python.In the New Python Task dialog box, configure the following parameters.
Parameter
Description
Task Name
Enter a name for the code task.
The name can be up to 256 characters long and cannot contain the following characters: vertical bar (|), forward slash (/), backslash (\), colon (:), question mark (?), angle brackets (<>), asterisk (*), or double quotation mark (").
Schedule Type
Select a schedule type for the task. The Schedule Type can be one of the following:
Recurring Task: The task is automatically included in the periodic scheduling of the system.
One-Time Task: The task must be run manually.
Select Directory
Select a folder to store the task.
If you have not created a folder, follow these steps to create a new folder:
Above the task list, click the
 icon to open the Create Folder dialog box.
icon to open the Create Folder dialog box.In the Create Folder dialog box, enter a Name for the folder and select a location for Select Directory as needed.
Click Confirm.
Use Template
Reference a code template for efficient development. The code in a template task is read-only. You only need to configure the template parameters to complete code development.
Python third-party package
To use third-party Python packages, select a Python Version, then select the Python third-party packages to import. The Python version defaults to the one set in Development Platform Settings > Default Python Version. Supported versions include Python 2.7, Python 3.7, and Python 3.11. If you select multiple packages, adjust their upload order in the list below.
For more information about Python third-party packages, see Install and manage Python third-party packages.
NoteAfter you add a third-party module to the Python third-party packages, you must declare a reference to the module in the task before you can import it in your code. You can edit the referenced module in the Python third-party packages configuration item of the computing task properties.
Description
Enter a brief description of the task. The description can be up to 1,000 characters in length.
Click Confirm.
On the Python task tab, write the code for the computing task in the code editor. After you write the code, click Run above the code editor.
NoteWhen you develop a PYTHON computing task, you may need to use specific resource packages for your business scenario. Dataphin comes with common resource packages pre-installed. To use them, add an
import {package_name}statement at the beginning of your code, such asimport configparser. For more information, see Appendix: Python built-in resource packages.When you develop a PYTHON computing task, explicitly declare the file encoding in a comment within the first two lines of the Python file. This prevents potential errors caused by the system's default encoding during code execution.
To import uploaded resource files in Python, see Upload and reference resources.
Click Property in the right-side sidebar. On the Property panel, configure parameters such as Basic Information, Runtime Resource, Python Third-party Package, Runtime Parameter, Schedule Property (for recurring tasks), Schedule Dependency (for recurring tasks), Runtime Configuration, and Resource Configuration.
Basic Information
Configure the basic information for the task, such as the task name, owner, and description. For more information, see Configure basic task information.
Runtime Resource
Specify the CPU and memory resources to allocate for running the task. The default value is 0.1 cores and 256 MB. For more information, see Configure offline task running resources.
Python Third-party Package
Select the Python third-party packages that you want to import. For more information, see Install Python Module.
Runtime Parameter
If your task uses parameter variables, you can assign values to them here. The parameter variables are automatically replaced with the assigned values when the node is scheduled. For more information, see Configure and use node parameters.
Schedule Property (for recurring tasks)
If the schedule type for the offline computing task is Recurring Task, you must configure its scheduling properties in addition to the Basic Information. For more information, see Configure scheduling properties.
Schedule Dependency (for recurring tasks)
If the schedule type for an offline computing task is Recurring Task, you must configure its scheduling dependencies in addition to the Basic Information. For more information, see Configure scheduling dependencies.
Runtime Configuration
You can configure a task-level runtime timeout period and a retry policy for failed tasks. If you do not configure these settings, the default tenant-level settings are used. For more information, see Configure computing task runtime.
Resource Configuration
Assign the task to a resource group. The resources of the specified resource group are used for task scheduling at runtime. For more information, see Configure computing task resources.
On the current Python task tab, save and submit the task.
Click the
 icon above the code editor to save the code.
icon above the code editor to save the code.Click the
 icon above the code editor to submit the code.
icon above the code editor to submit the code.
On the Submitting Log page, review the Submission Content, check the Pre-check results, and enter any remarks. For more information, see Offline computing task submission instructions.
After you confirm the information, click Confirm And Submit.
NoteTo ensure data security, if your Python task code contains
from dataphin import hivecorimport dataphin, submitting the task triggers a code review. A code review ticket is automatically created, and the task can be submitted only after the code is approved.The code must be reviewed by a project administrator for the current project. If there are multiple project administrators, approval from any one of them is sufficient.
What to do next
If you use the Dev-Prod mode, you must publish the task to the production environment from the release list after you submit the task. For more information, see Manage release tasks.
If you use the Basic mode, the Python task can be scheduled in the production environment after it is submitted. You can view the published task in the Operation Center. For more information, see View and manage script tasks, and View and manage one-time tasks.