Resource Management is utilized for storing and managing files essential for code development, such as JAR, JSON, Python, and other resource files. This topic outlines the process for creating resources and references.
Create resources
On the Dataphin home page, click Development from the top menu bar.
To enter the New Resource dialog box, follow the steps below:
Select Project (Dev-Prod mode requires selecting the environment) -> click Resource -> click the new
 icon.
icon.In the New Resource dialog box, configure the following parameters:
Parameter
Description
Type
Select the Type of file to upload. The system supports various file types by default, including file (.xls, .xlsx, .doc, .docx, .txt, .csv), archive (.zip, .tgz, .tar.gz, .tar, .jar), jar, Python, cplus, and others.
file: Text files, typically used for data information required by tasks.
archive: Compressed packages, generally used for dependencies of tasks.
Python: Python files, often used for Python task dependencies.
cplus: C++ source code files, commonly used for registering UDFs in Impala tasks.
Name
Enter the Name of the resource, adhering to the following naming convention:
The resource name must be unique within the project and cannot begin with a number.
The name may include numbers, letters, underscores (_), hyphens (-), or periods (.).
The name must be between 3 and 200 characters in length.
Description
Provide a brief description of the resource, not exceeding 1000 characters.
Upload File
Choose the Upload File corresponding to the selected Type.
Compute Type
Select the compute type for the resource.
Compute engine: Selecting a compute engine uploads the resource to the engine associated with the project, such as MaxCompute. This is typically for creating UDFs within the engine. For JAR files, the system will execute the engine's
add jar xxx.jarcommand.No affiliated engine: Selecting this option uploads the resource solely to Dataphin, suitable for text files and other types that are to be used, such as file and archive.
Select Directory
Choose the directory for storing the resource. If the desired directory does not exist, create it by entering the directory name and selecting its location as shown below.
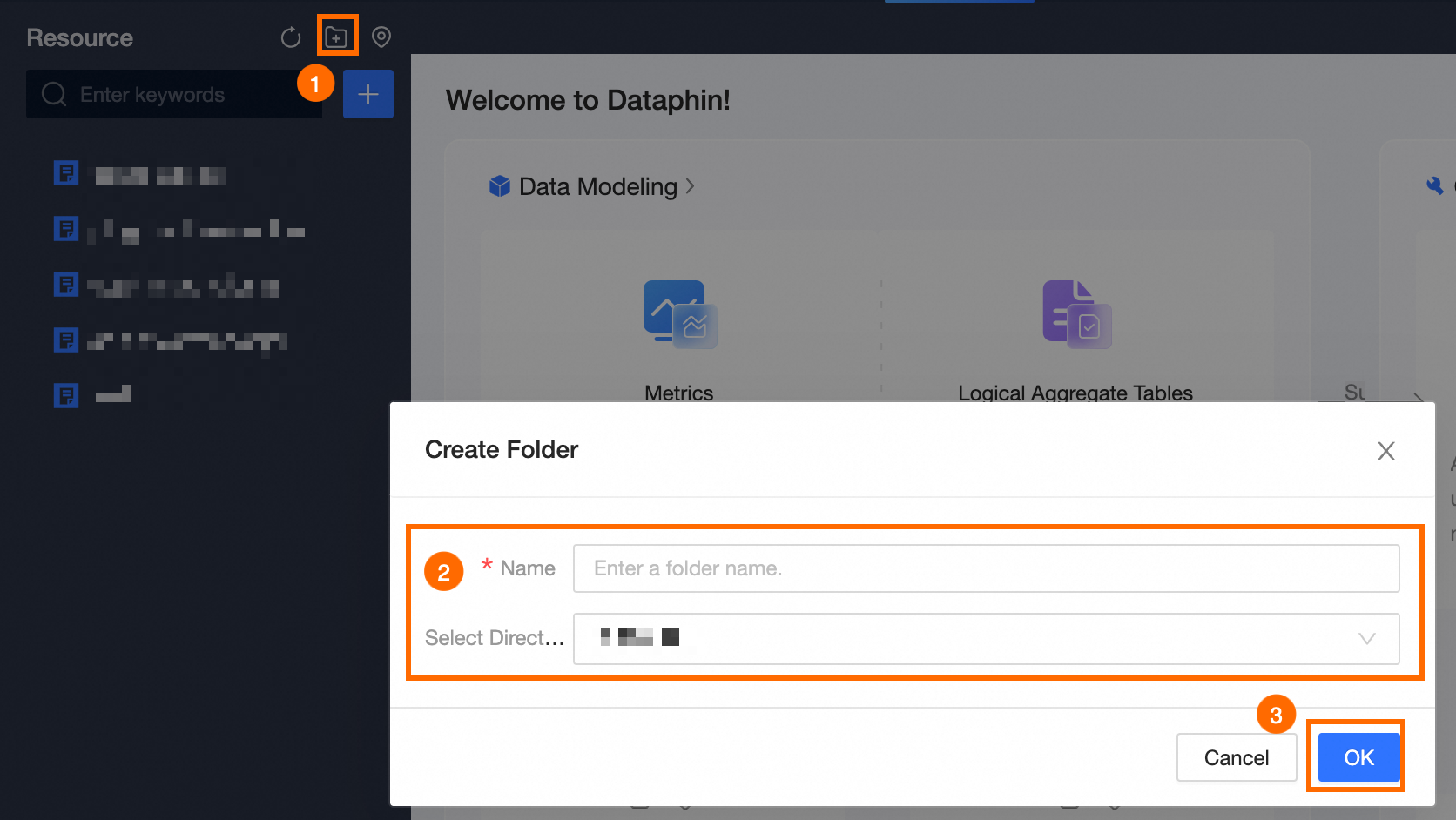
Click Submit.
In the Submit Remarks dialog box, provide remarks for the resource, limited to 128 characters.
Click Confirm And Submit to finalize the resource creation.
NoteIn a Dev-Prod project mode, you must publish resources to the production environment. For detailed instructions, see Manage publishing tasks.
Reference resources
Supported reference methods
Once the resource upload is complete, you can quickly copy the resource's reference statement to aid in the development of compute tasks by following the steps below:
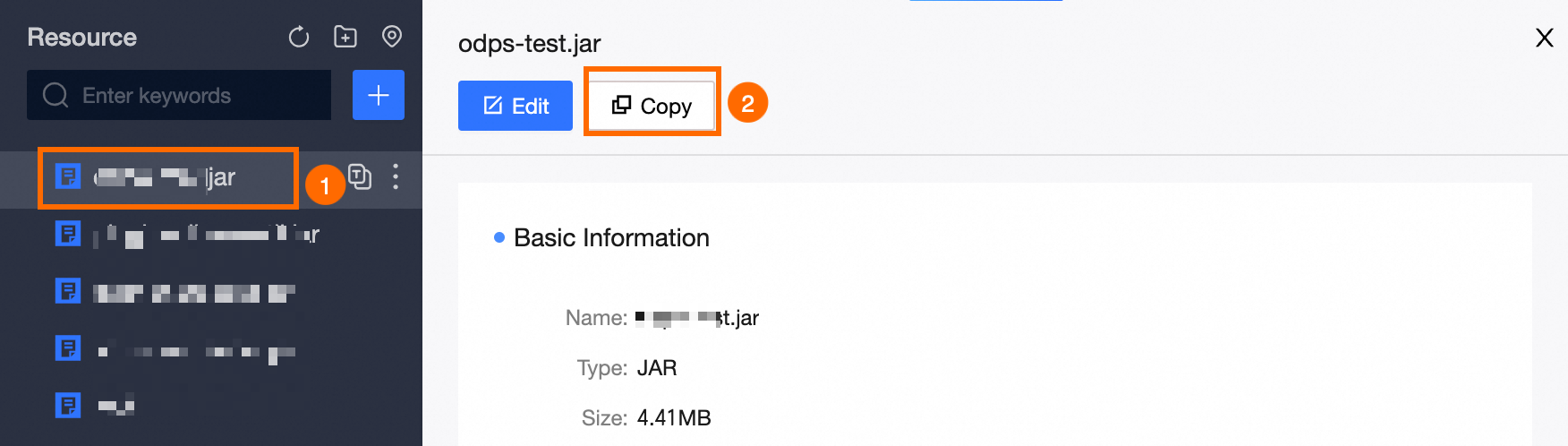
Alternatively, directly use the
@resource_reference{"resource name"}statement in compute tasks for referencing.
Reference statement description
The @resource_reference{"resource name"} statement effectively defines the file path of the resource as a variable. For instance, in the Python code example below:
@resource_reference{"dataphin.xls"} # Reference dataphin.xls resource
# Import the xlrd module.
import xlrd
wb = xlrd.open_workbook('dataphince.xls') # Open excel
sh = wb.sheet_by_name('Sheet1') # Locate the worksheet by workbook
# Traverse excel and print all data
for i in range(sh.nrows):
print(sh.row_values(i))The @resource_reference{"dataphin.xls"} statement is equivalent to dataphin.xls = "/path/to/dataphin.xls". In subsequent code, the variable name dataphin.xls can be used to access the resource.