Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) is a high-performance service for managing and running containerized applications in the cloud. This document explains how to quickly deploy and expose a sample containerized application—a Rubik's cube game—in an ACK cluster. You can deploy the application using either the ACK console or the kubectl command-line tool.
Overview
 The sample application used in this tutorial, ACK-Cube, is an online Rubik's cube game. The game is deployed from a container image to a managed ACK Pro cluster. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a running Rubik's cube game. The process includes the following steps:
The sample application used in this tutorial, ACK-Cube, is an online Rubik's cube game. The game is deployed from a container image to a managed ACK Pro cluster. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a running Rubik's cube game. The process includes the following steps:
Activate services and create an ACK cluster: Quickly activate the required services, grant permissions, and create an ACK cluster.
Deploy the Rubik's cube game application: Choose one of two methods to deploy the game: through the console UI or by using kubectl.
Access the application from the internet: To access the game, get the external IP address of the
ack-cubeservice after the application is configured.
1. Create a cluster
When you use ACK for the first time, you must activate the service, grant required permissions, and enable related cloud products before creating a cluster. Otherwise, not all features will be available.
We recommend following the official documentation to complete setup and authorization for full functionality. For details, see Quickly create an ACK managed cluster.
For billing information on ACK clusters and associated resources, see Billing .
When you create an ACK managed cluster, you can choose to enable the intelligent managed mode. After this mode is enabled, you only need to configure simple planning parameters to create an ACK cluster that complies with best practices with one click. The cluster will create an intelligent managed node pool by default, and the lifecycle of nodes in this pool will be managed and maintained by ACK. For more information, see Create an ACK managed cluster (intelligent managed mode).
If you need to customize detailed configurations for your cluster, you can refer to the complete process in Create an ACK managed cluster to complete cluster creation.
Log on to the ACK console. On the Clusters page, click Create Kubernetes Cluster.
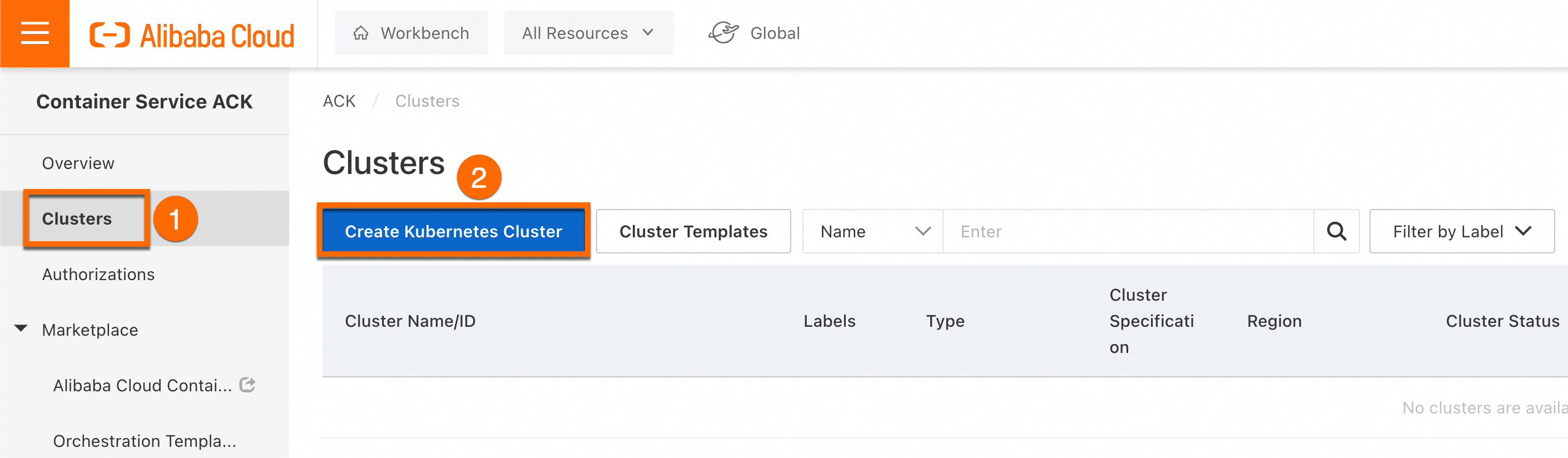
In the upper part of the page that appears, click the ACK Managed Cluster tab, enable Intelligent Managed. If you need to access the cluster over the Internet, select Expose API Server With EIP. Then, click Confirm Configurations, review your selected configurations, and click Create Cluster.

2. Deploy the application
ou can deploy the Rubik's cube game using the console or the kubectl tool.
Console deployment: Deploy, expose, and access the application through the console UI.
kubectl deployment: Connect to the cluster by using a tool like CloudShell, a kubectl client, or Workbench, and then deploy, expose, and access the application.
A public image is used in this topic. To pull public images to a cluster or node, the cluster or node must have Internet access:
Enable an existing ACK cluster to access the Internet: We recommend that you read this topic to create an Internet NAT gateway in the virtual private cloud (VPC) where the cluster is deployed. This way, all resources in the cluster can access the Internet.
Assign a static public IP address to the node to allow the node to pull the image over the Internet. You need to assign a static public IP address to each node in the cluster.
Console deployment
2.1 Deploy and expose the application
This section shows you how to deploy a stateless workload (a Deployment) for the Rubik's cube game in your new ACK cluster and expose it to the internet. For details on Deployment creation parameters, see Create a stateless application by using a Deployment.
On the Clusters page, click the name of your target cluster (for example,
ACK-Demo).In the left-side navigation pane of the details page, choose .
In the upper-right corner of the Deployments page, click Create from Image.
On the Basic Information tab, set the application name to
ack-cube.Click Next. On the Container tab, configure the container parameters.
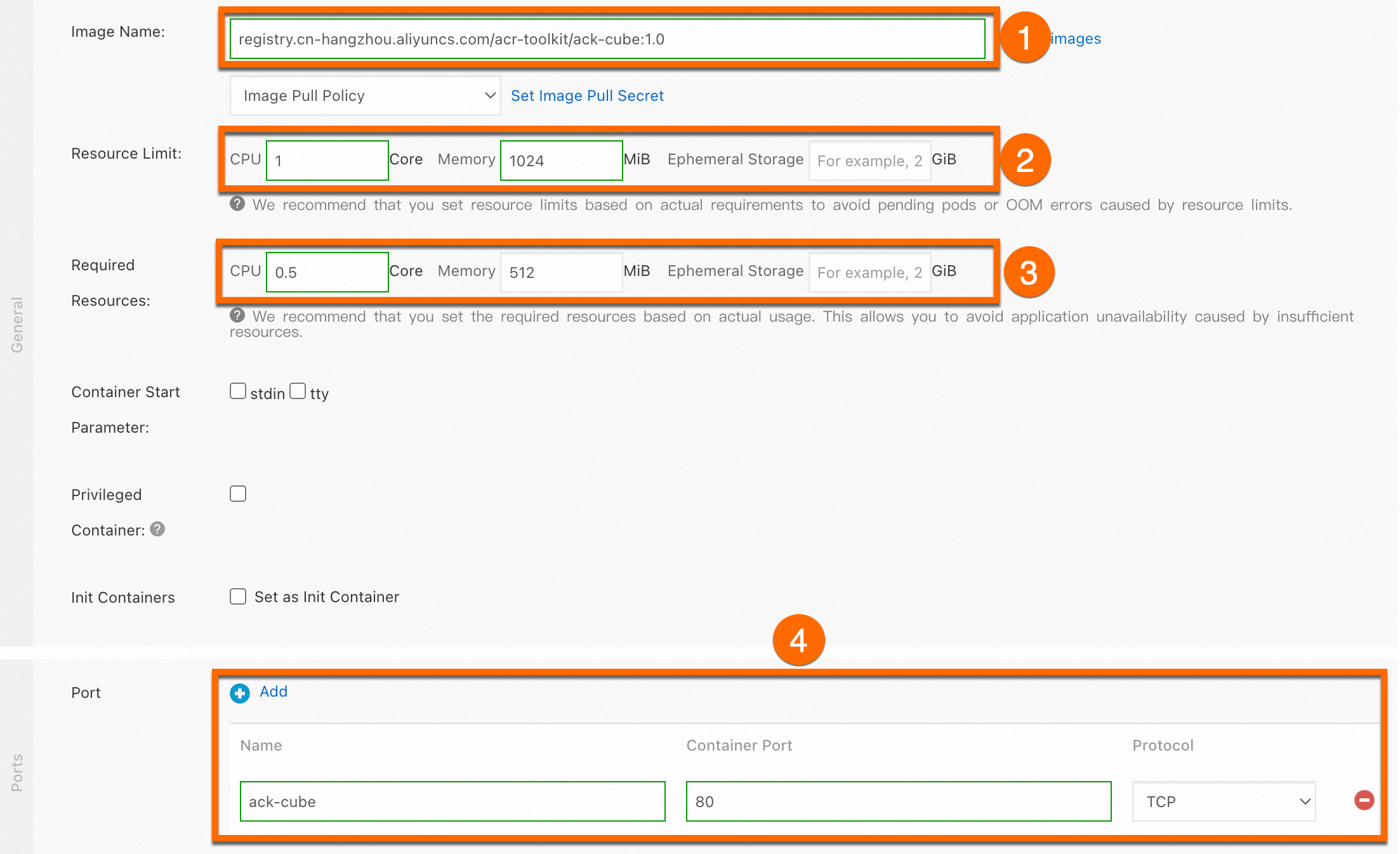
Parameter
Description
Example value
Image Name
The name of the container image.
Enter
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acr-toolkit/ack-cube:1.0.Resource Limit
The maximum resources the application can use. This prevents it from consuming excessive resources.
CPU: 1 Core, Memory: 1024 MiB. Leave Ephemeral Storage empty.
Required Resources
The amount of resources to reserve for the application to ensure it has enough resources to run.
CPU: 0.5 Core, Memory: 512 MiB. Leave Ephemeral Storage empty.
Port
The port settings for the container.
Name:
ack-cubeContainer Port:
80Protocol: TCP
Click Next. On the Advanced tab, click Create in the Services section. In the Create Service dialog box, configure the parameters to expose the
ack-cubeapplication, and then click OK.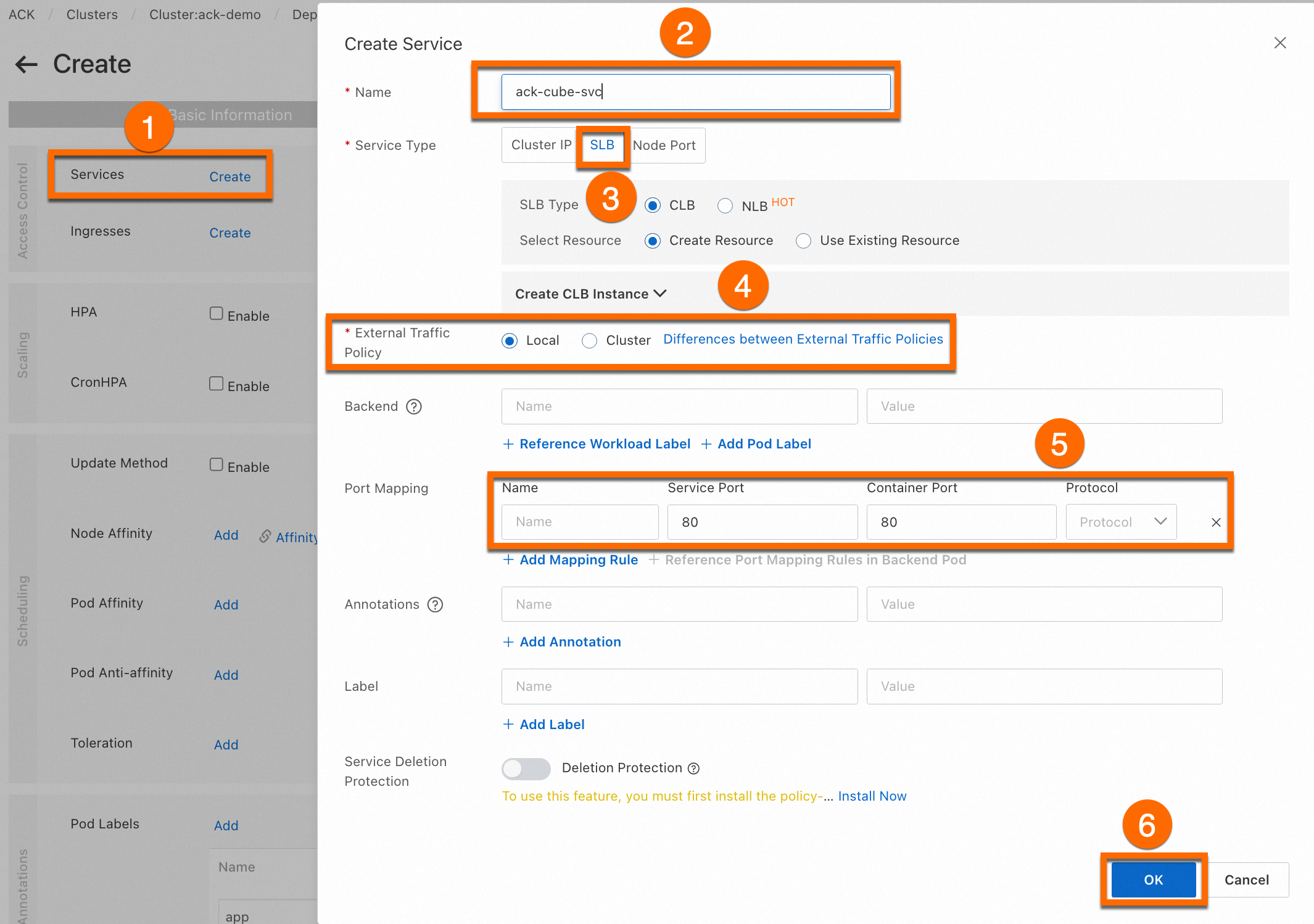
Parameter
Description
Example value
Name
The name of the Service.
ack-cube-svcType
The Service type, which defines how the Service is accessed. Choose Server Load Balancer > Classic Load Balancer (CLB) > Create Resource. You can keep the default CLB settings for a test environment.
Use the default settings.
Port
The Service Port and Container Port. The Container Port must match the port exposed by the backend pod.
Service Port:
80Container Port:
80Protocol: TCP
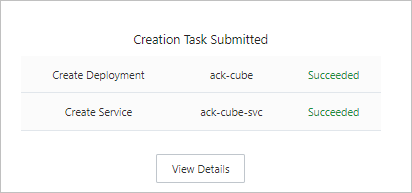
After you configure the workload parameters, click Create. A success page appears, listing the application's objects. Click View Details to review them.
2.2 Access the application
This section explains how to access the application through its Service.
Log on to the ACK console. On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster. In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Find the application named ack-cube in the default namespace. Click the Access Method tab, find the newly created Service (named ack-cube-svc), and click the link in the External Endpoint column to access the Rubik's cube game.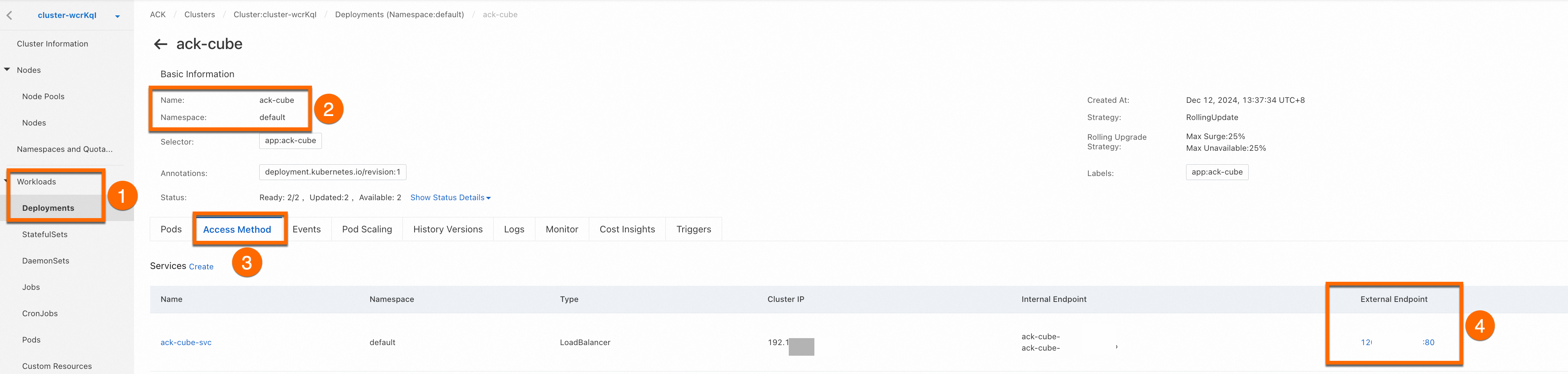
Kubectl deployment
2.1 Connect to the cluster
You can connect to the cluster by using kubectl, Workbench, or CloudShell.
CloudShell
When CloudShell starts, it provisions a Linux virtual machine for you at no cost. This VM includes pre-installed common environments and tools. You can use it with the CloudShell Web IDE to manage your cloud resources. This section shows you how to quickly connect to an ACK cluster by using CloudShell. For more information, see Use kubectl on Workbench or Cloud Shell to connect to ACK clusters.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click your target cluster. On the Cluster Information page, choose .
After a few seconds, the CloudShell interface starts, and you can use kubectl commands to manage your cluster and applications.
Workbench
You can use Workbench, a browser-based remote connection tool provided by Alibaba Cloud, to access your ACK cluster directly from your browser without installing any additional software. For detailed instructions, see Connect to an instance by using Workbench.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click your target cluster. On the Cluster Information page, choose .
After a few seconds, the Workbench interface starts. Follow the on-screen instructions to manage your cluster and applications by using kubectl commands.
Kubectl client
If you need to access the cluster from your local machine over the internet, you can install and configure the kubectl client. This section shows you how to quickly connect to an ACK cluster by using a kubectl client. For more information, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
Install and set up kubectl. For more information, see Install and set up kubectl.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click your target cluster. On the Clusters page, click the name of your target cluster (for example,
ACK-Demo). On the Cluster Information page, click the Connection Information tab. Copy the content from the Public Access tab, which contains the public access credentials for the cluster. Paste the copied credentials into theconfigfile in the$HOME/.kubedirectory, then save the file.NoteIf the
.kubedirectory andconfigfile do not exist in the$HOME/directory on your client machine, create them.Run a kubectl command to verify the connection to the cluster.
For example, run the following command to query namespaces:
kubectl get namespaceExpected output:
NAME STATUS AGE arms-prom Active 4h39m default Active 4h39m kube-node-lease Active 4h39m kube-public Active 4h39m kube-system Active 4h39m
2.2 Deploy and expose the application
This section explains how to use kubectl to deploy a stateless workload (a Deployment) in your ACK cluster and expose it by using a Service of the LoadBalancer type. For more information about exposing applications, see Use an automatically created SLB instance to expose an application.
Create a file named
ack-cube.yamlwith the following content.apiVersion: apps/v1 # for versions before 1.8.0 use apps/v1beta1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: ack-cube # The name of the application. labels: app: ack-cube spec: replicas: 2 # The number of replicated pods. selector: matchLabels: app: ack-cube # You must specify the same value for the selector of the Service that is used to expose the application. template: metadata: labels: app: ack-cube spec: containers: - name: ack-cube image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acr-toolkit/ack-cube:1.0 # Replace with the address of the image that you want to use in the <image_name:tags> format. ports: - containerPort: 80 # The container port that you want to expose. resources: limits: # The resource limits. cpu: '1' memory: 1Gi requests: # The resource requests. cpu: 500m memory: 512MiRun the following command to deploy the
ack-cubesample application.kubectl apply -f ack-cube.yamlRun the following command to check the status of the sample application.
kubectl get deployment ack-cubeExpected output:
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE ack-cube 2/2 2 2 96sCreate a file named
ack-cube-svc.yamlwith the following content. Change theselectorvalue to match thematchLabelsvalue in theack-cube.yamlfile (in this example,app: ack-cube) to associate the Service with the backend application.apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: labels: app: ack-cube name: ack-cube-svc namespace: default spec: ports: - port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 80 selector: app: ack-cube # You must specify the value of the matchLabels parameter in the YAML file that is used to create the Deployment. type: LoadBalancerRun the following command to create the
ack-cube-svcService and expose the application.Creating a Service of type
LoadBalancerautomatically provisions a public-facing Server Load Balancer (SLB) instance and binds it to this Service.kubectl apply -f ack-cube-svc.yamlRun the following command to confirm that the
LoadBalancerService was created successfully.The sample application is exposed to the internet at the IP address listed in the
EXTERNAL-IPcolumn.kubectl get svc ack-cube-svcExpected output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE ack-cube-svc LoadBalancer 172.16.72.161 47.94.xx.xx 80:31547/TCP 32sEnter the
EXTERNAL-IPaddress (for example,47.94.xx.xx) into your web browser's address bar to access the Rubik's cube game application.
3. (Optional) Clean up resources
The cost of a managed ACK Pro cluster has two components: cluster management fees (charged by ACK) and fees for other Alibaba Cloud resources used (charged by each respective cloud product).
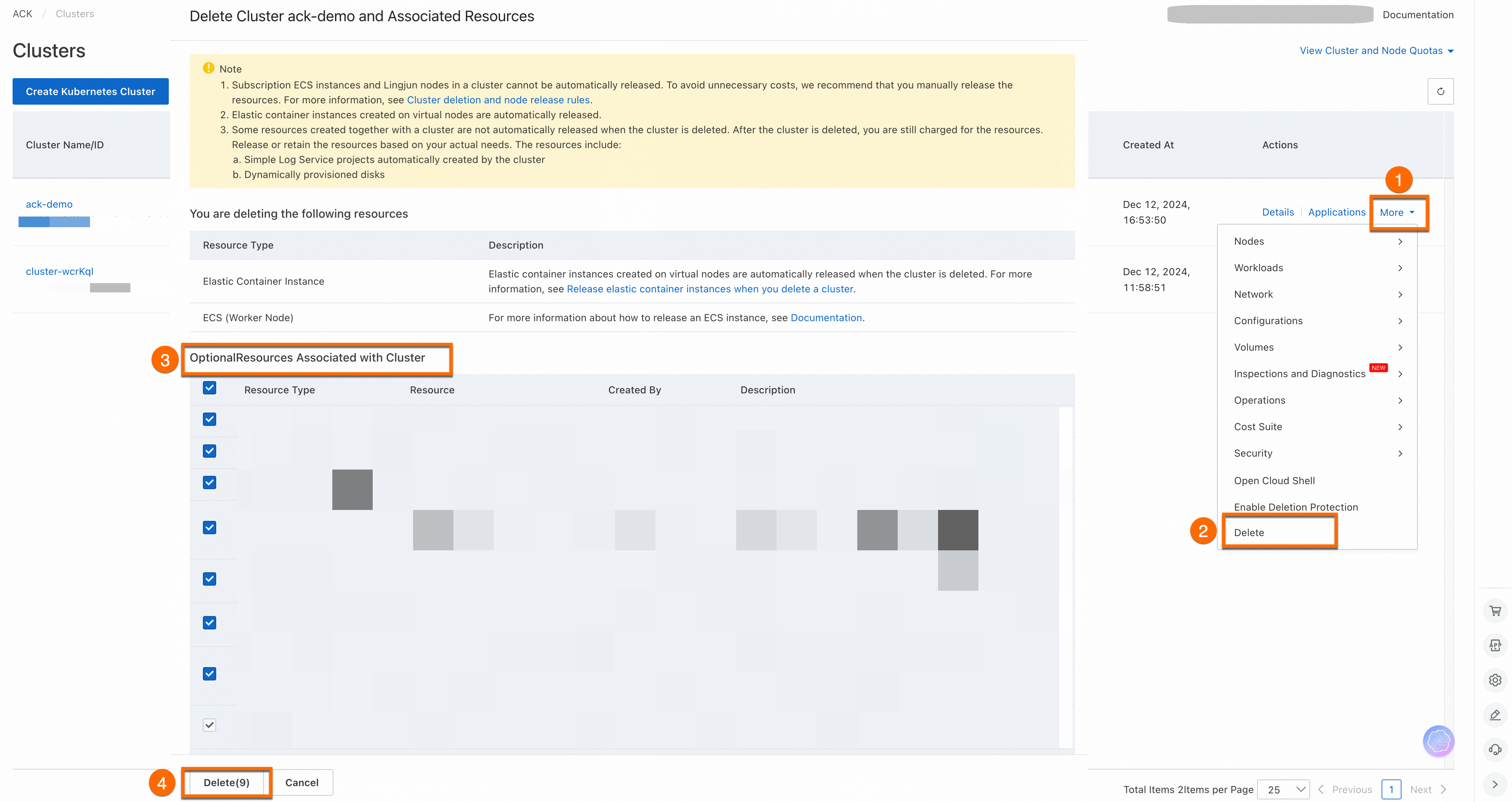
If you no longer need the cluster, log in to the ACK console. On the Clusters page, find the target cluster, click More in the Actions column, and then click Delete. On the Delete Cluster And Associated Resources page, select the resources to delete, and then click Delete. For more information about deleting ACK clusters, see Delete a cluster.
Intelligent Managed clusters have Deletion Protection enabled by default. Before you delete the cluster, you must first disable this feature.
Related documents
If your business's resource requirements are difficult to predict or change periodically, such as for web applications, game services, or online education, we recommend that you configure auto-scaling for your cluster. This includes both workload scaling and resource scaling. For more information, see Auto scaling overview.
In addition to exposing applications with a Service, you can use an Ingress to manage Layer 7 network routing for your applications. For more information, see Ingress management.
In addition to container performance, you can also monitor your cluster infrastructure, application performance, and business metrics. Monitoring and logging allow you to check the system's operational status and diagnose issues. For more information, see Observability system overview.