Cloud Backup offers two primary vault types: backup vaults for operational recovery and archive vaults for long-term retention. Together, they support all data storage scenarios, from hot to cold.
Background information
Cloud Backup delivers backup, disaster recovery, and policy-based archiving for a wide range of resources, including cloud-native services like ECS, CPFS, NAS, OSS, and Tablestore, as well as on-premises files, databases, and virtual machines.
Backup vaults
Backup vaults store backup data and use a tiered storage architecture with a Standard tier and an Archive tier to balance access performance and storage cost.
Tiered storage
Backup vaults use a tiered storage architecture that includes a Standard tier and an Archive tier.
Standard tier: By default, backup data is stored in the Standard tier after a backup is complete. This tier supports fast access and restoration, making it suitable for backup data that requires quick restoration or frequent verification to ensure business continuity.
Archive tier: When automatic archiving is enabled in a backup policy, data is automatically moved from the Standard tier to the Archive tier. This tier provides long-term, low-cost storage and is suitable for backup data that is rarely accessed but requires long-term retention.
Backup vault types
Backup vaults are classified into the following types based on the data source:
Backup vault type | Description |
General backup vault | Stores backup data from various sources, including ECS file backups, OSS backups, on-premises and Alibaba Cloud NAS backups, CPFS backups, Tablestore backups, local file backups, SAP HANA backups, and VMware backups. |
Replication target vault (formerly mirror vault) | Serves as the destination for backup replication. It stores backup data replicated from other regions or other accounts. |
Database backup vault | Stores backup data for databases such as MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server. |
OSS backup vault (30-day free trial) | These vaults store backup data for Alibaba Cloud OSS, NAS, and Tablestore during a 30-day free trial. After you convert to a paid plan, the vault type changes to a general backup vault.
|
NAS backup vault (30-day free trial) | |
Tablestore backup vault (30-day free trial) | |
Container backup vault | Stores backup data for Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) clusters. |
Archive vaults
Archive vaults are designed for policy-based archiving, storing data moved from on-premises locations to the cloud. Based on the storage class, archive vaults are classified into archive storage vaults and cold archive vaults.
Archive vaults can be used only to archive data from on-premises NAS (such as Isilon), Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), and S3-compatible storage.
Archive storage vault
Archive storage vaults provide a highly durable data storage service at an extremely low cost. Data must be restored before it can be accessed, a process that takes about 5 minutes. Retrieving data from an archive vault incurs data restoration fees. This service is suitable for data that needs to be stored for a long period, such as archival data, medical images, scientific materials, and video footage. For pricing details, see Cloud Backup Pricing.
The system automatically selects the redundancy type based on what the region supports. In regions that support zone-redundant storage (ZRS), a ZRS-enabled archive vault is created by default. In other regions, a locally redundant storage (LRS)-based archive vault is created. You do not need to select the type manually.
Currently, the regions that support ZRS are China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Zhangjiakou), China (Ulanqab), China (Shenzhen), Hong Kong (China), Japan (Tokyo), Singapore, Indonesia (Jakarta), Germany (Frankfurt), and Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur).
Cold archive vault
Cold archive vaults provide highly durable data storage with the lowest storage fees among all storage classes. Data must be restored before it can be accessed, and retrieving data incurs data restoration fees. This service is suitable for scenarios that require the long-term storage of extremely cold data, such as data retained for compliance, raw data from big data and artificial intelligence (AI) domains, media assets from the film and television industry, and archived videos from the online education industry. For pricing details, see Cloud Backup Pricing.
Because cold archive storage supports only LRS, a LRS-enabled cold archive vault is created by default.
Redundancy types
For backup vaults (including the Standard and Archive tiers) and archive vaults, Cloud Backup uses two data redundancy methods: ZRS and LRS.
ZRS: Data is distributed and stored across multiple zones within the same region. If a zone becomes unavailable, data access is not affected.
LRS: Data is stored on multiple devices within a single zone to ensure data durability and availability in the event of hardware failure.
The system automatically selects the redundancy type based on what the region supports. In regions that support ZRS, a ZRS-enabled backup or archive vault is created by default. In other regions, a LRS-based backup or archive vault is created. You do not need to select the type manually.
Currently, the regions that support ZRS are China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Zhangjiakou), China (Ulanqab), China (Shenzhen), Hong Kong (China), Japan (Tokyo), Singapore, Indonesia (Jakarta), Germany (Frankfurt), and Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur).
Cold Archive vaults support only LRS. Data with LRS redundancy is stored within a specific zone. If that zone becomes unavailable, the data becomes inaccessible. If your business requires higher availability, use storage classes that support ZRS (backup vaults and archive storage vaults) to store and use your data.
Archive tier vs. archive vaults
Item | Archive tier (in a backup vault) | Archive storage vault | Cold archive vault |
Applicable feature | Automatic archiving. Data is automatically moved from a backup vault's Standard tier to its Archive tier based on a backup policy. | On-premises data archiving. Data from on-premises sources is archived directly into a standalone archive vault based on an archive policy. | On-premises data archiving. Data from on-premises sources is archived directly into a standalone cold archive vault based on an archive policy. |
Type | An Infrequent Access storage tier within a backup vault. | A standalone vault type. | A standalone vault type. |
Purpose | For backup data that requires long-term retention but is rarely accessed. The automatic archiving feature moves backup data from the Standard tier to the Archive tier to reduce data protection costs. | For long-term, low-cost storage of cold data from on-premises data centers that is rarely accessed but must be retained. | For long-term, low-cost storage of extremely cold data from on-premises data centers that is almost never accessed but must be retained. |
Billing | The billing logic is the same across all archive storage types (archive tier, archive storage vault, and cold archive vault):
For pricing details, see Cloud Backup Pricing Details. | ||
Billing information
Fees are incurred for using vaults. For more information, see Billing methods and billable items.
Resource plans are available to provide discounts and reduce costs. For more information, see Resource plan purchase guide.
View vaults
Method 1: View vaults on the Vault Management page
Go to the Cloud Backup console - Storage Vaults page. In the upper-left corner of the top menu bar, select the region where your resources are located.
On the Storage Vaults page, view the list of vaults and perform operations as needed.
The Storage Vaults page displays all backup vaults and archive vaults in Cloud Backup. View details for each vault, including its name, ID, type, number of backup plans, source data volume, vault data volume, and status.
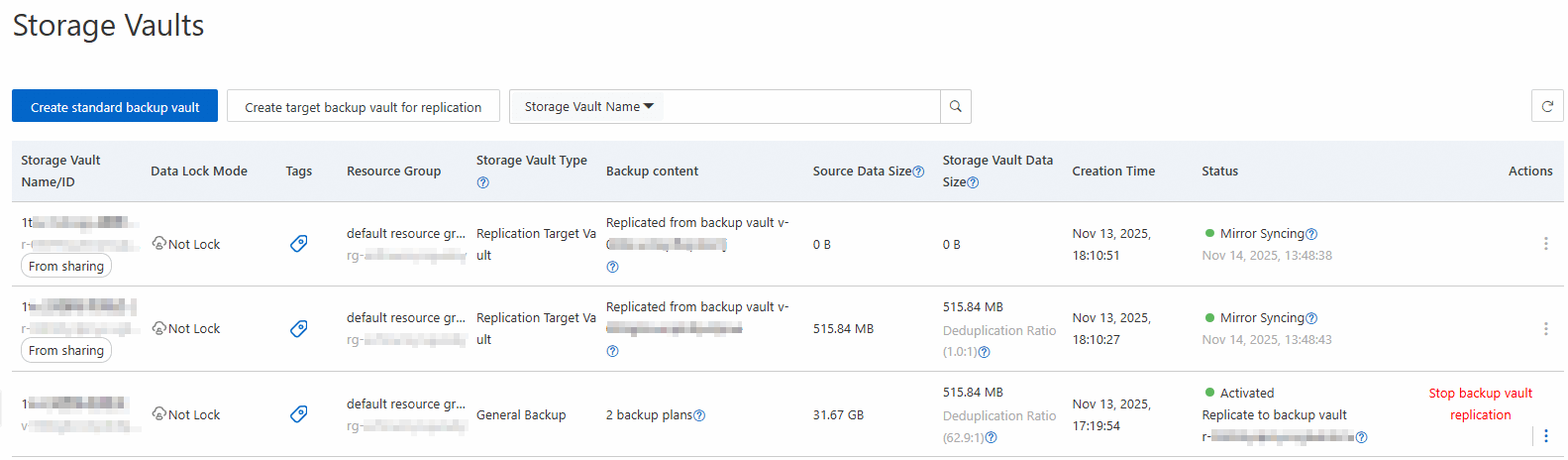
Method 2: View vaults on the Overview page of the Cloud Backup console.