You can reduce fine-tuning costs by enabling a scaling group to automatically schedule spot instances. If spot instances are interrupted or reclaimed, new ones are launched in the scaling group and training is resumed from the most recent checkpoint, which ensures continuous progress.
Solution overview
This solution enables low-cost fine-tuning of large models based on scaling groups. It prioritizes spot instances and leverages Object Storage Service (OSS) for persistent checkpoint storage. It maintains training continuity with the following key features:
Spot instance first: Spot instances are prioritized for training tasks in the scaling group, with checkpoints automatically saved to OSS buckets for resilience.
Auto-scale with failover continuity: When spot instances are interrupted or reclaimed, Auto Scaling first tries to provision replacement spot instances in other zones. If spot instance types are unavailable, it automatically falls back to pay-as-you-go instances. In both cases, training seamlessly resumes from the most recent checkpoint.
Auto-fallback to spot instances: Once spot instance types are available again, Auto Scaling automatically switches back from pay-as-you-go to spot instances, and training resumes from the most recent checkpoint.

To maximize cost savings, configure your scaling group to use spot instances for the entire training process, though this may delay training completion time. If spot instance types become unavailable, pause training and resume later when spot inventory is restored. For more information about how to optimize costs by combining scaling groups with spot Instances, see Use spot instances to reduce costs.
Cost comparison
The cost comparison in the table below is for reference only, as actual savings depend on real-world usage.
Assuming a 12-hour training period, the unit price for a spot instance is 3.5 RMB per hour, while a pay-as-you-go instance costs 10 RMB per hour. The following table provides the cost comparison between the two options.
Mode | All spot | Hybrid (spot + pay-as-you-go) | All pay-as-you-go |
Description | When a spot instance is interrupted and reclaimed, training is paused. Once the inventory of spot instance types is restored, a new spot instance is automatically created to resume training. | A spot instance runs for 1 hour before being interrupted and reclaimed. After interruption, a pay-as-you-go instance is used for 0.5 hours while waiting for spot capacity. Training then switches back to a new spot instance once the inventory of spot instance types becomes available. | Training is conducted exclusively on pay-as-you-go instances. |
Cost | 12h x 3.5 RMB/h = 42 | 8h x 3.5 RMB/h + 4h x 10 RMB/h = 68 | 12h x 10 RMB/h = 120 |
Cost savings compared to using only pay-as-you-go instances | 65% | 43.33% | 0% |
Procedure
Create a base image containing the essential training environment.
This image serves as the startup template for instances in the scaling group. The built-in auto-start script ensures new instances can quickly resume training and run automatically.
Create and configure a scaling group.
A scaling group ensures the training task continues by automatically launching new spot or pay-as-you-go instances when existing ones are interrupted or reclaimed.
Start training.
Once a scaling group is configured, a scale-out event is automatically triggered. This creates new instances, which immediately begin running the training task based on the predefined automation rules.
Test: Simulate interruption and reclamation
Manually trigger instance interruption and reclamation to confirm that the system automatically launches a new instance and resumes the interrupted training task correctly. This validation is critical for ensuring stability and reliability during resource reclamation scenarios.
1. Create a base image containing the essential training environment
This topic demonstrates the steps for self-cognitive fine-tuning of the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B model by using the Swift training framework in a single-machine, single-GPU setup.
To improve task instance startup efficiency, first create an instance with the required training environment and dependencies, then generate a custom image from it to serve as the scaling group’s launch template. This image should include pre-installed automated training scripts and a startup service to ensure the entire process runs without manual intervention. The architecture of the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance used to create the image is shown in the following figure.
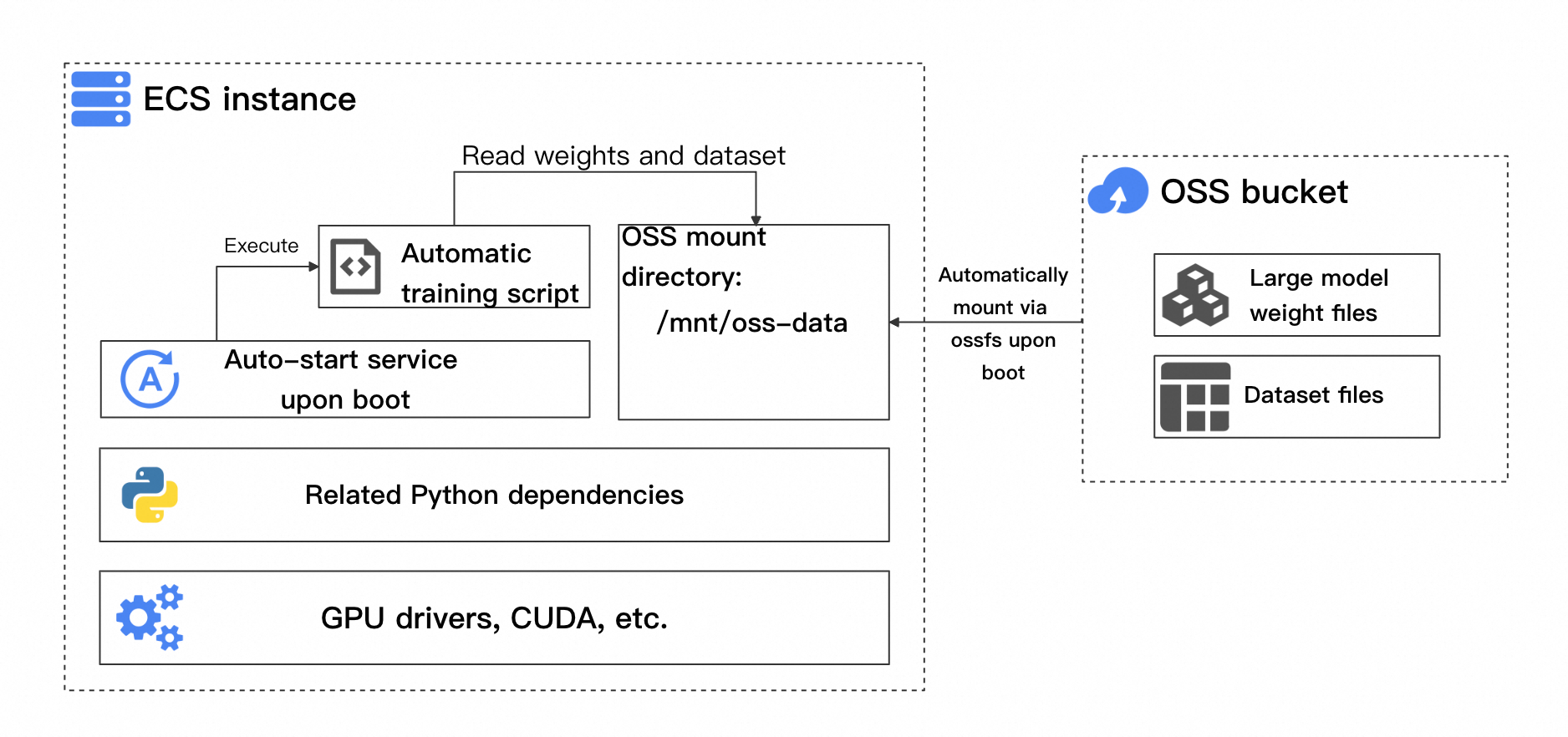
The essential points are summarized here:
Basic training environment dependencies: The required dependencies include a GPU driver, CUDA, and Python packages. The specific dependencies depend on the chosen training framework.
Automatic training script: This script should automatically detect whether to resume training from the most recent checkpoint and determine if training has already been completed.
Automatically mount the bucket at startup: When the training script begins, it reads the model weight file, dataset, and training-generated checkpoints directly from the OSS bucket.
Automatically start training on instance launch: After an instance starts, the training script runs automatically, reading files from the OSS bucket to begin or resume training.
Once you've understood the essential points, follow these steps to build the image:
1.1 Create an instance and build a basic environment
This instance serves as a template for creating an image. Later, Auto Scaling will automatically launch new instances from this image in the scaling group.
Go to the ECS console to create a GPU-accelerated instance.
First, you need to create a pay-as-you-go GPU-accelerated instance to set up the basic environment. This example uses the
ecs.gn7i-c8g1.2xlargeinstance type, deployed in Zone J of the China (Hangzhou) region. The configuration steps are illustrated in the following figure.① Billing Method: Set the value to Pay-as-you-go.
② Region: Select China (Hangzhou).
③④ Network and Zone: Select the VPC and vSwitches. If no VPCs or vSwitches exist, follow the on-screen instructions to create them.

⑤⑥ Instance > All Instance Types: Select
ecs.gn7i-c8g1.2xlarge.
⑦⑧⑨ Image > Public Images: Select Ubuntu 22.04 64 bit.
⑩ Auto-Install GPU Driver: Specify CUDA Version 12.4.1, Driver Version 550.127.08, and CUDNN Version 9.2.0.82.

⑪ System Disk > Size: Enter 60 GiB.

⑫ Public IP Address: Select Assign Public IPv4 Address to enable Internet access and file download.
⑬ Bandwidth Billing Method: Select Pay-by-traffic.
⑭ Maximum Bandwidth: Select 100 Mbps.
⑮ Security Group: Click the New Security Group tab.
⑯ Security Group Type: Set the value to Basic Security Group.
⑰ Open IPv4 Ports/Protocols: Select SSH (TCP:22) and ICMP (IPv4) to facilitate subsequent remote connection.

⑱⑲⑳ Log Credential: Select Key Pair. This key pair is required for logging on to the ECS instance. You can also set the value to Custom Password. Complete the settings as prompted.
㉑ Instance Name: Enter a name for the ECS instance. Use a clear and memorable instance name to make searching easier. In this example,
ess-lora-deepseek7b-templateis used.
Click Confirm Order. Wait until the ECS instance is created.
Once the ECS instance is ready, connect to it and wait for the GPU driver installation to complete.
Go to ECS console - Instance.
Locate the ECS instance you created in the previous step, and click Connect in the Actions column. Use Workbench to establish a connection, and log on to the ECS instance as prompted.
If the ECS instance isn't found, check whether your current region matches the instance's region. You can switch regions by using the dropdown list in the upper-left corner.
If the ECS instance is stopped, refresh the page and wait for it to start.

Once you've connected to the ECS instance, wait until the GPU driver installation is complete. After installation, the system will prompt you to reconnect to the ECS instance.
If the interface becomes unresponsive, try refreshing the page and reconnecting to the ECS instance.

Install Python dependencies.
To install the Python dependencies needed for training, run the following commands:
This example uses the Ubuntu 22.04 64-bit image, which includes Python 3.10. As a result, you won't need to install Python dependencies separately.
# The Ubuntu 22.04 64-bit image includes Python 3.10 by default, so no extra installation is needed. python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip # Switch to Alibaba Cloud internal image repository. pip config set global.index-url http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/pypi/simple/ pip install modelscope==1.22.3 pip install openai==1.61.0 pip install tqdm==4.67.1 pip install "vllm>=0.5.1" -U pip install "lmdeploy>=0.5,<0.6.5" -U --no-deps pip install autoawq -U --no-deps pip install auto_gptq optimum bitsandbytes -U pip install ms-swift[all] pip install timm -U pip install deepspeed==0.14.* -U pip install qwen_vl_utils decord librosa pyav icecream -U
While waiting for the dependencies to install, you can click theicon to enable the multi-terminal feature and proceed with the steps in Step 1.2.
1.2 Create and attach an OSS bucket
To store the model weight file, dataset, and checkpoints generated during training, you must first create an OSS bucket. Once the bucket is created, attach it to your ECS instance as an additional data disk.
Go to the OSS console to create a bucket.
The following figures show the key parameter settings for this example. Retain the default values for any parameters not listed.
② Bucket Name: Enter a name for the bucket. The bucket name is required when mounting the bucket.
③ Region: Select a region. The selected region must match the region of the ECS instance. In this example, the region must be China (Hangzhou).
You can use an ECS instance to access OSS buckets within the same region over an internal network, and there are no charges for traffic on this network. For more information, see Access to OSS resources from an ECS instance by using an internal endpoint of OSS.

Create and bind a RAM role.
A Resource Access Management (RAM) role is used to grant an ECS instance permissions to access OSS buckets. To create and bind a RAM role, perform the following steps:
In the RAM console, create a RAM role. The following figures show the key parameter settings for this example.

② Principal Type: Select Cloud Service.
③ Principal Name: Select Elastic Compute Service, which specifies that the RAM role will be assigned to the ECS instance.
④ Click OK and specify a name for the RAM role as prompted.

In the RAM console, create a custom policy as shown in the following figure.


③ This policy grants all the necessary permissions to access an OSS bucket. The policy script is as follows:
ImportantWhen configuring the custom policy, replace
<bucket_name>with the name of the bucket you actually created.{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "oss:*", "Resource": [ "acs:oss:*:*:<bucket_name>", "acs:oss:*:*:<bucket_name>/*" ] } ] }Click OK and configure the policy name as prompted.
In the RAM console, grant permissions to the RAM role.
⑥ Principal: Select the RAM role that you created.
⑦ Policy: Select the custom policy that you created.

Click Grant permissions.
Log on to the ECS console and assign the RAM role to the ECS instance.
If the ECS instance isn't found, check whether your current region matches the instance's region. You can switch regions by using the dropdown list in the upper-left corner.

Mount the OSS bucket to the ECS instance.
Connect to the ECS instance created in Step 1.1, and run the following commands to install ossfs:
wget https://gosspublic.alicdn.com/ossfs/ossfs_1.91.5_ubuntu22.04_amd64.deb apt-get update DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install gdebi-core DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive gdebi -n ossfs_1.91.5_ubuntu22.04_amd64.debRun the following commands to mount the OSS bucket: Update the parameter settings in the commands with the following values:
<bucket_name>: Replace this with the name of the bucket you created.<ecs_ram_role>: Replace this with the name of the RAM role you created.<internal_endpoint>: Replace this withoss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com.ImportantIn this example, the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region. As a result, the VPC endpoint used is
oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com.
# Replace the bucket name, VPC endpoint, and RAM role with their respective actual values. BUCKET_NAME="<bucket_name>" ECS_RAM_ROLE="<ecs_ram_role>" INTERNAL_ENDPOINT="<internal_endpoint>" # The mount directory of the bucket. BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH="/mnt/oss-data" #1. Back up the fstab file before mounting. cp /etc/fstab /etc/fstab.bak #2. Create the mount directory. mkdir $BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH #3. Mount the bucket to the instance. ossfs $BUCKET_NAME $BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH -ourl=$INTERNAL_ENDPOINT -oram_role=http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/ram/security-credentials/$ECS_RAM_ROLE #4. Enable automatic mounting upon instance startup. echo "ossfs#$BUCKET_NAME $BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH fuse _netdev,url=http://$INTERNAL_ENDPOINT,ram_role=http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/ram/security-credentials/$ECS_RAM_ROLE,allow_other 0 0" | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab
Check if the storage space is available.
Upload any file to the OSS bucket.

Run the following command in the instance to check if the file is visible in the mount directory:
ls /mnt/oss-data/If it appears, this means the mount was successful.

1.3 Prepare a model and dataset
The model weight file and dataset referenced in this topic can be downloaded from the ModelScope community. After connecting to the ECS instance, download the model and dataset to the mount directory of the OSS bucket and wait for all files to finish downloading.
Download a dataset
# The mount directory of the bucket. BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH="/mnt/oss-data" # Download the fine-tuning dataset from the ModelScope community. # Use the modelscope tool installed in Step 1.1. modelscope download --dataset swift/self-cognition --local_dir $BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH/self-cognition modelscope download --dataset AI-ModelScope/alpaca-gpt4-data-zh --local_dir $BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH/alpaca-gpt4-data-zh modelscope download --dataset AI-ModelScope/alpaca-gpt4-data-en --local_dir $BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH/alpaca-gpt4-data-enIf the progress is stuck, try pressing Enter multiple times.
Download the model weight file
ImportantIf the model weight file is too large and the download fails or a
please try againmessage appears, simply retry the commands to resume the download.# The mount directory of the bucket. BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH="/mnt/oss-data" # Download the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B model from the ModelScope community. modelscope download --model deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B --local_dir $BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7BIf the progress is stuck, try pressing Enter multiple times.
Verify if the model weight file is valid
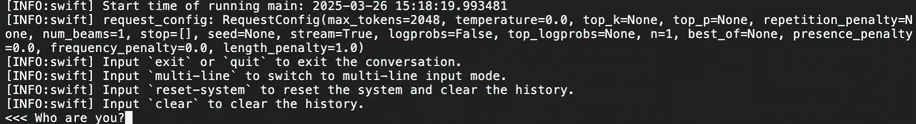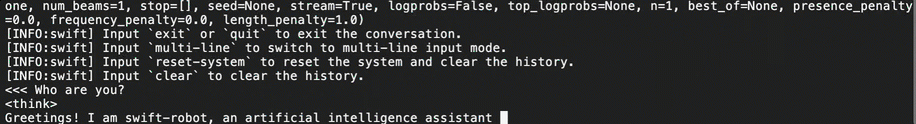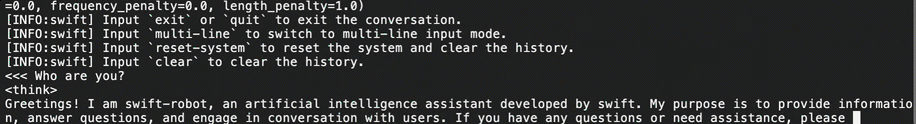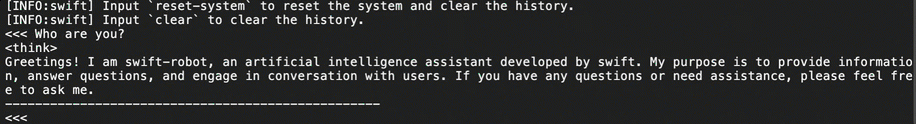
Once the download is complete, run the following command in the terminal to test the model's functionality and verify if the model weight file is complete.
# The mount directory of the bucket. BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH="/mnt/oss-data" CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 swift infer \ --model $BUCKET_MOUNT_PATH/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B \ --stream true \ --infer_backend pt \ --max_new_tokens 2048Once the model weight file is loaded, as shown in the following figure, you can begin conversing with the large model. If the model weight file fails to load, try downloading it again.
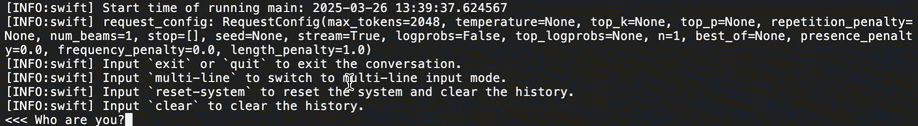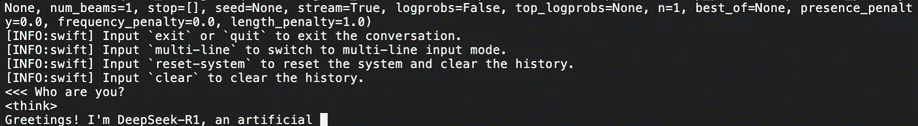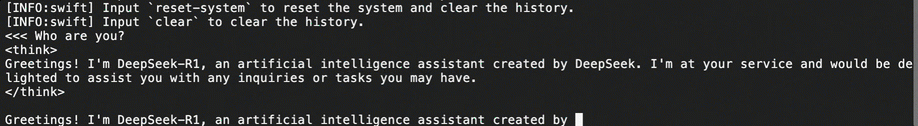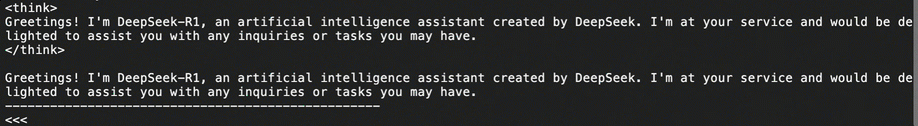
Enter
exitonce the test is complete.
1.4 Write an automatic training script
Write an automatic training script.
Run the following commands to create an automatic training script and grant it executable permissions. This script will automatically resume training from the most recent checkpoint and monitor the training progress until completion.
# Create an automatic training script. cat <<EOF > /root/train.sh #!/bin/bash # The mount directory of the bucket. BUCKET_MONTH_PATH="/mnt/oss-data" # The storage directory of the model weight file and dataset. MODEL_PATH="\$BUCKET_MONTH_PATH/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B" DATASET_PATH="\$BUCKET_MONTH_PATH/alpaca-gpt4-data-zh#500 \$BUCKET_MONTH_PATH/alpaca-gpt4-data-en#500 \$BUCKET_MONTH_PATH/self-cognition#500" # Set the output directory. OUTPUT_DIR="\$BUCKET_MONTH_PATH/output" mkdir -p "\$OUTPUT_DIR" # Confirm that the training has been completed without requiring any operation. if [ -f "\$OUTPUT_DIR/logging.jsonl" ]; then last_line=\$(tail -n 1 "\$OUTPUT_DIR/logging.jsonl") if echo "\$last_line" | grep -q "last_model_checkpoint" && echo "\$last_line" | grep -q "best_model_checkpoint"; then echo "Training already completed. Exiting." exit 0 fi fi # Initialize the recovery parameters. RESUME_ARG="" # Find the most recent checkpoint LATEST_CHECKPOINT=\$(ls -dt \$OUTPUT_DIR/checkpoint-* 2>/dev/null | head -1) if [ -n "\$LATEST_CHECKPOINT" ]; then RESUME_ARG="--resume_from_checkpoint \$LATEST_CHECKPOINT" echo "Resume training from: \$LATEST_CHECKPOINT" else echo "No checkpoint found. Starting new training." fi # Start the training command. CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 swift sft \\ --model \$MODEL_PATH \\ --train_type lora \\ --dataset \$DATASET_PATH \\ --torch_dtype bfloat16 \\ --num_train_epochs 1 \\ --per_device_train_batch_size 1 \\ --per_device_eval_batch_size 1 \\ --learning_rate 1e-4 \\ --lora_rank 8 \\ --lora_alpha 32 \\ --target_modules all-linear \\ --gradient_accumulation_steps 16 \\ --eval_steps 50 \\ --save_steps 10 \\ --save_total_limit 5 \\ --logging_steps 5 \\ --max_length 2048 \\ --output_dir "\$OUTPUT_DIR" \\ --add_version False \\ --overwrite_output_dir True \\ --system 'You are a helpful assistant.' \\ --warmup_ratio 0.05 \\ --dataloader_num_workers 4 \\ --model_author swift \\ --model_name swift-robot \\ \$RESUME_ARG EOF # Grant the executable permissions. chmod +x /root/train.shSet up a Linux service and enable auto-start on system boot.
Run the following commands to create a Linux service and enable the training script to start automatically on system startup:
# Create a log storage directory. mkdir -p /root/train-service-log # Write a service configuration file. cat <<EOF > /etc/systemd/system/train.service [Unit] Description=Train AI Model Script After=network.target local-fs.target remote-fs.target Requires=local-fs.target remote-fs.target [Service] ExecStart=/root/train.sh WorkingDirectory=/root/ User=root Environment="PATH=/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin" Environment="CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0" StandardOutput=append:/root/train-service-log/train.log StandardError=append:/root/train-service-log/train_error.log [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF # Reload the systemd configurations. systemctl daemon-reload # Enable the training.service to start automatically on system startup. systemctl enable train.serviceExecuting the commands produces the following result:

1.5 Build an image
Once you've completed all the previous steps, build a custom image from your configured instance. This image will serve as the startup template for scaled-out instances, eliminating the need to reinstall dependencies each time.
Go to the ECS console.
Create an image following the steps shown in the figure below.

Wait for the image to be created, which typically takes about 5 minutes. You can monitor the progress in the ECS console.

Once the image is ready, you can release the instance created in Step 1.1.
2. Create a scaling group
You can configure a scaling group to automate instance management. The scaling group ensures that new spot or pay-as-you-go instances are automatically created to resume training if existing instances are suspended or reclaimed. When available, spot instances will automatically replace pay-as-you-go instances to reduce costs.
2.1 Create a scaling group
To create a scaling group, perform the following steps:
Go to the Auto Scaling console.
ImportantThe scaling group must be in the same region as the ECS instance created in Step 1.1.

Configure the scaling group following the steps shown in the figure below. For more information about how to configure a scaling group, see Parameters.
 Important
ImportantWhen configuring your VPC (⑤) and vSwitch (⑥), we recommend selecting vSwitches across multiple zones. This enables Auto Scaling to distribute instances efficiently and increases the chances of utilizing spot instances.

 Important
ImportantTo reduce costs by using only spot instances, you must disable these options: Use Pay-as-you-go Instances to Supplement Spot Capacity (⑮) and Replace Pay-as-you-go Instances with Spot Instances (⑯).
Click Create. Then, follow the on-screen instructions to create a scaling configuration.

2.2 Create a scaling configuration
A scaling configuration defines the specifications and image of the instances in a scaling group. After you create a scaling configuration, Auto Scaling uses it to automatically launch new instances in the scaling group based on the defined instance settings. To create a scaling configuration, perform the following steps:
① Scaling Configuration Name: Enter ② Billing Method: Select Spot Instance.
|
③④ Select Image > Custom Image: Click the Custom Image tab and select the custom image created in Step 1.5. ⑤ Instance Configuration Mode: Select Specify Instance Type. ⑥ Instance Usage Duration: Select 1-Hour Usage Duration. With this option, after spot instances run for 1 hour, Auto Scaling will assess whether to suspend and reclaim them. If you select No Specified Usage Duration, pay-as-you-go instances may be used at a lower cost. However, due to their higher likelihood of termination and reclamation, valid checkpoints might not be created before the instances are reclaimed, which could result in slower training progress. For more information about the differences between the two options, see Use spot instances to reduce costs. ⑦ Highest Price per Instance: Select Use Automatic Bid. With this option, Auto Scaling will automatically adjust the bid price according to the current market price. ⑧ Select Instance Type: Choose the instance type you selected in Step 1.1, which is
|
⑨ Security Group: Choose the security group you selected in Step 1.1. This example illustrates an offline training solution, where assigning a public IP address is not required.
|
⑩ Logon Credentials: Select Image Preset Password.
|
⑪⑫⑬ Select the RAM role created in Step 1.2. When instances are automatically created in the scaling group, the RAM role is automatically assigned to the new instances.
|
Click Create. If a message appears stating that the scaling strength is insufficient, simply click Continue.
Enable the scaling group and scaling configuration as prompted.
|
|
|
3. Start training
Once the scaling group is configured, adjust the expected number of instances to 1. The process is illustrated in the figure below.
|
|
Afterward, Auto Scaling automatically provisions a new instance in the scaling group to start training.
Auto Scaling periodically checks if the number of instances in the scaling group matches the expected count. If there are no instances in the scaling group (i.e., the count is 0), a scale-out operation is automatically triggered to create new instances.
After you adjust the expected number of instances, the creation of instances may be delayed. You can monitor the progress of scaling activities on the Scaling Activities tab of the scaling group.
After an instance is created and started, you can locate the
outputdirectory in the OSS bucket, which stores the checkpoints generated during training.
4. Test: Simulate interruption and reclamation
Once an instance begins running the training task, check the output directory of the OSS bucket to see if a folder, such as checkpoint-10, has been created. After a checkpoint is generated, you can manually release the instance to simulate an interruption and reclamation. To release the instance manually, follow these steps:
Manually release an instance.
Go to the Instances tab of the scaling group. Click the instance ID to go to the instance details page.

On the Instance Details tab, choose in the upper-right corner. Then, release the instance as prompted.

Verify if the training can be resumed from the most recent checkpoint.
Wait for a new instance to be created in the scaling group. Once the instance is ready, connect to it and view the training logs.
Go to the Instances tab of the scaling group. Click the instance ID to go to the instance details page.
Click Connect in the upper-right corner and connect to the instance as prompted.
To view the model training logs, run the following command. The log path is the one you specified in Step 1.4.
cat /root/train-service-log/train.logThe command output shows that the training task resumes from the most recent checkpoint.

What to do next
Use the fine-tuned model for inference
Release resources used in this topic
Suggestions for applying this solution to a production environment
Before applying this solution to a production environment, make sure to review the following suggestions and adjust the solution to fit your specific business needs.
Integrate CloudMonitor to detect interruptions and reclamations
For production environments, we recommend that you integrate CloudMonitor into your training code to detect and handle spot instance interruptions and reclamations. By saving checkpoints 5 minutes before interruptions or reclamations, you can minimize progress loss when resuming training. The updated solution architecture is as follows:

Create a comprehensive task recovery mechanism
In the example in this topic, resuming training will automatically start from the most recent checkpoint. However, the validity of the checkpoint is not automatically verified. In practical applications, it's recommended to implement an anomaly detection mechanism to filter out invalid checkpoints and ensure training resumes from the most recent valid one.
Enhance the conclusion of the training task
You can integrate the logic for determining the end of training into the training code. Once training is complete, use the CLI or SDK to call an API operation and set the expected number of instances to 0. Auto Scaling will then automatically release any excess instances in the scaling group, preventing unnecessary costs from resource waste.
You can also report custom events to CloudMonitor once the training is complete. CloudMonitor will then notify you of the training result via email, text message, or DingTalk chatbot.
Switch to a more efficient storage model
When training a model with a large number of parameters, OSS can lead to system bottlenecks. To enhance overall system efficiency, we recommend using a high-throughput, low-latency file system, such as CPFS, for mounting.
Configure multi-zone vSwitches
If you configure a vSwitch in only one zone, Auto Scaling will be able to create instances in just that zone for the scaling group. This may lead to a scale-out failure if there are not enough resources available in that zone. We recommend configuring vSwitches across multiple zones. When a spot instance is reclaimed, Auto Scaling automatically launches a new spot instance in a different zone. This increases the likelihood of using spot instances.