This topic describes how to connect to an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance from a database client over SSL connections. After you configure SSL encryption for an RDS instance, you can connect to the RDS instance from a database client by using pgAdmin, PostgreSQL CLI, or Java Database Connectivity (JDBC).
Prerequisites
The SSL encryption feature is enabled for the RDS instance. If the SSL encryption feature is disabled, enable the feature based on the instructions provided in Configure a cloud certificate to enable SSL encryption feature or Configure a custom certificate to enable SSL encryption feature.
The following files are obtained:
The client.crt file that contains the client certificate and the client.key file that contains the private key of the client certificate: If you have configured a client certificate authority (CA) certificate in the ApsaraDB RDS console, you must obtain these files. Otherwise, these files are optional. For more information, see Configure a client CA certificate on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
The file that contains the server CA certificate: For more information about how to obtain this file, see Configure SSL encryption for an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance or Configure a custom certificate on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Procedure
Use pgAdmin to connect to the RDS instance over SSL connections
pgAdmin is a recommended PostgreSQL client that you can use to connect to an RDS instance. When you download the PostgreSQL software package from the PostgreSQL official website and install PostgreSQL, pgAdmin 4 is automatically downloaded and installed. The following section provides an example on how to use pgAdmin 4 V6.2.0 to connect to an RDS instance.
If you do not want to install PostgreSQL, you can download only pgAdmin for remote connections.
Start pgAdmin 4.
NoteIf this is the first time you log on to pgAdmin of a later version, you must specify a master password that is used to protect saved passwords and other credentials.
Right-click Servers and choose .
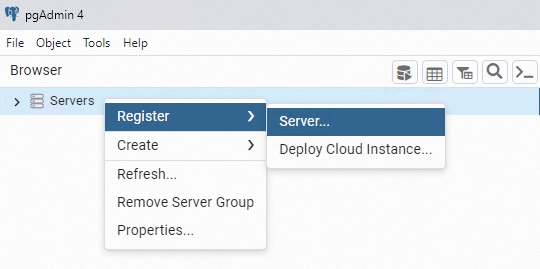
On the General tab of the Register - Server dialog box, enter the name of the server on which pgAdmin is installed.
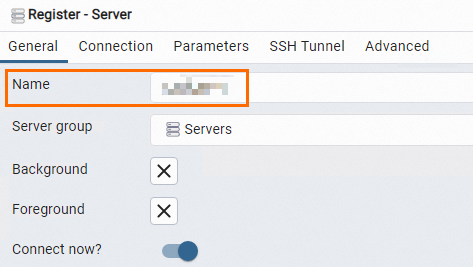
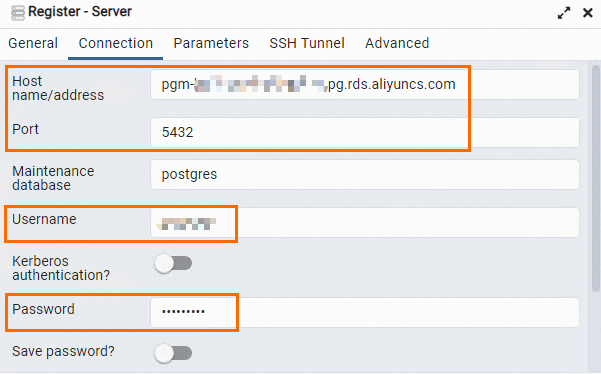
Click the Connection tab and enter the information that is used to connect to the RDS instance.
Parameter
Description
Host name/address
The endpoint and port that are used to connect to the RDS instance.
If you want to connect to the RDS instance over an internal network, enter the internal endpoint and internal port of the RDS instance.
If you want to connect to the RDS instance over the Internet, enter the public endpoint and public port of the RDS instance.
You can view the preceding information on the Database Connection page of the RDS instance.
For more information, see View and change the endpoints and port numbers of an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Port
Username
The username and password that are used to log on to the RDS instance.
For more information about how to create an account on an RDS instance, see Create a database and an account.
Password
On the Parameters tab, configure the required parameters related to the SSL authentication mode and the certificate.
Parameter
Description
SSL mode
If SSL encryption is enabled for the RDS instance, the RDS instance allows SSL connections from the database client. You must set the SSL mode parameter based on the following scenarios:
No access control lists (ACLs) are configured for the RDS instance. For more information, see Configure a client CA certificate on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
If you want to connect to the RDS instance from the database client over SSL, set the SSL mode parameter to Require, Verify-CA, or Verify-Full.
If you do not want to connect to the RDS instance from the database client over SSL, set the SSL mode parameter to Disable.
ACLs are configured for the RDS instance. In this case, you can connect to the RDS instance from the database client only over SSL. Set the SSL mode parameter to Require, Verify-CA, or Verify-Full. For more information, see Configure a client CA certificate on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
The following list describes the values of the SSL mode parameter:
Require: The database client encrypts the SSL connections that are used to transmit data. However, the database client does not validate the RDS instance.
Verify-CA: The database client encrypts the SSL connections that are used to transmit data and validates the RDS instance.
Verify-Full: The database client encrypts the SSL connections that are used to transmit data, validates the RDS instance, and verifies that the CN or Domain Name System (DNS) specified in the server certificate is consistent with the endpoint that is configured at connection establishments.
Client certificate
You must set this parameter if you have configured a client certificate. This parameter specifies the save path of the client.crt file that contains the client certificate. For more information, see Configure a client CA certificate on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Client certificate key
You must set this parameter if you have configured a client certificate. This parameter specifies the save path of the client.key file that contains the private key of the client certificate. For more information, see Configure a client CA certificate on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Root certificate
You must set this parameter if you set the SSL mode parameter to Verify-CA or Verify-Full. This parameter specifies the save path of the file that contains the server CA certificate.
NoteWhen you run the sample command, you must use the actual path to the client.crt, client.key, and server-ca.crt files.
You can run the sample command to configure a custom certificate. You can also configure a cloud certificate. For example, you can replace
server-ca.crtwithApsaraDB-CA-Chain.pemto configure a cloud certificate.
Click Save.
If the information that you enter is correct, the page that is shown in the following figure appears, which indicates that the connection to the RDS instance is successful.
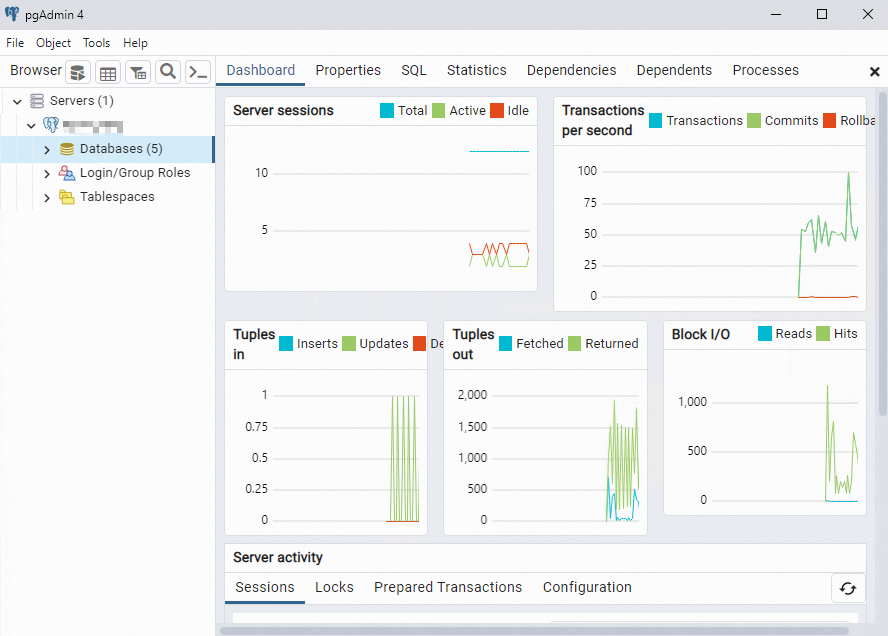 Important
ImportantThe postgres database is the default system database. Do not perform operations on the postgres database.
Use psql to connect to the RDS instance over SSL
This method uses psql to connect to an RDS instance over SSL. Make sure that the PostgreSQL client is installed on your computer. For more information, see PostgreSQL documentation.
In the /var/lib/pgsql directory, create a folder named .postgresql.
mkdir /var/lib/pgsql/.postgresqlCopy the following files to the .postgresql folder:
client.crt and client.key: If you have configured a client CA certificate in the ApsaraDB RDS console, you must obtain these files. Otherwise, these files are optional. For more information, see Configure a client CA certificate on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
server-ca.crt: For more information about how to obtain this file, see Configure SSL encryption for an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance or Configure a custom certificate on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
cp client.crt client.key server-ca.crt /var/lib/pgsql/.postgresql/NoteWhen you run the sample command, you must use the actual path to the client.crt, client.key, and server-ca.crt files.
You can run the sample command to configure a custom certificate. You can also configure a cloud certificate. For example, you can replace
server-ca.crtwithApsaraDB-CA-Chain.pemto configure a cloud certificate.
Modify the permissions on the .postgresql folder.
chown postgres:postgres /var/lib/pgsql/.postgresql/* chmod 600 /var/lib/pgsql/.postgresql/*Run the following command to modify the file that contains the environment variables:
vim /var/lib/pgsql/.bash_profileEnter
ito enable the edit mode. Then, add the following content to the file:export PGSSLCERT="/var/lib/pgsql/.postgresql/client.crt" export PGSSLKEY="/var/lib/pgsql/.postgresql/client.key" export PGSSLROOTCERT="/var/lib/pgsql/.postgresql/ca1.crt"Press
Escto exit the edit mode. Then, enter:wqto save the file and exit.Reload the environment variables.
source .bash_profileSpecify the method that is used by the database client to validate the RDS instance.
export PGSSLMODE="verify-full"If SSL encryption is enabled for the RDS instance, the RDS instance allows SSL connections from the database client. You must configure the PGSSLMODE parameter based on your business requirements.
ACL configured
SSL connection required
PGSSLMODE value
No
Yes
require, verify-ca, or verify-full
No
disable
Yes
The database client can connect to the RDS instance only over SSL.
require, verify-ca, or verify-full
NoteThe following list describes the values of the PGSSLMODE parameter:
require: The database client encrypts the SSL connections that are used to transmit data. However, the database client does not validate the RDS instance.
verify-ca: The database client encrypts the SSL connections that are used to transmit data and validates the RDS instance.
verify-full: The database client encrypts the SSL connections that are used to transmit data, validates the RDS instance, and verifies that the CN or DNS specified in the server certificate is consistent with the endpoint that is configured during connection establishment.
Connect to the RDS instance.
psql -h <Endpoint> -U <Username> -p <Port number> -d <Database name>The following table provides details about how to obtain the values of the preceding parameters from the ApsaraDB RDS console.
Parameter
Method to obtain
Endpoint
The endpoint that is protected by SSL encryption for the RDS instance. This endpoint is specified by the Protected Host parameter on the SSL Encryption tab of the Data Security page.
Username
The username of the account that is used to log on to the RDS instance. You can obtain the username from the Accounts page.
Port number
The port number that is used to connect to the RDS instance. The default port number is 5432. If you have changed the default port number, you can obtain the new port number from the Database Connection page.
Database name
The name of the database that you want to connect on the RDS instance. You can obtain the name of the database from the Database Connection page. The postgres database is the default system database. Do not perform operations on the postgres database.
Use JDBC to connect to the RDS instance over SSL connections
Download the following files to your computer:
client.crt and client.key: If you have configured a client CA certificate in the ApsaraDB RDS console, you must obtain these files. Otherwise, these files are optional. For more information, see Configure a client CA certificate on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
server-ca.crt: For more information about how to obtain this file, see Configure SSL encryption for an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance or Configure a custom certificate on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Convert the client.key file to the PK8 format.
openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -inform PEM -in client.key -outform der -out client.pk8 -v1 PBE-MD5-DES # Enter the password that is used to connect to the RDS instance. Enter Encryption Password: Verifying - Enter Encryption Password:WarningYou must run the openssl command on the host on which your application resides to convert the client.key file to the PK8 format. If you do not run the command on the host on which your application resides, the following error messages may be displayed:
org.postgresql.util.PSQLException: Could not decrypt SSL key file C:/Users/XXX/XXX/client.pk8org.postgresql.util.PSQLException: SSL error: Received fatal alert: unexpected_message
In this example, the database client runs Maven. In this case, import the Maven dependencies of PostgreSQL into the pom.xml file.
<dependency> <groupId>org.postgresql</groupId> <artifactId>postgresql</artifactId> <version>42.2.10</version> </dependency>Compile a code snippet that is used to establish a JDBC-based SSL connection to the RDS instance.
NoteYou can run the sample command to configure a custom certificate. You can also configure a cloud certificate. For example, you can replace
server-ca.crtwithApsaraDB-CA-Chain.pemto configure a cloud certificate.public class PgSslDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // Specify the endpoint that is used to connect to the RDS instance. String hostname = "pgm-bp1gclw58u36s6****.pg.rds.aliyuncs.com"; // Specify the port number that is used to connect to the RDS instance. String port = "5432"; // Specify the name of the database to which you want to connect on the RDS instance. String dbname = "postgres"; String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:postgresql://" + hostname + ":" + port + "/" + dbname + "?binaryTransfer=true"; Properties properties = new Properties(); // Specify the username that is used to connect to the specified database on the RDS instance. properties.setProperty("user", "test_user"); // Specify the password that is used to connect to the specified database on the RDS instance. properties.setProperty("password", "test_pwd"); // Specify the save path of the file that contains the certificate. String path = "D:\\ssl\\"; // Configure SSL encryption. properties.setProperty("ssl", "true"); // Specify the public key of the CA. properties.setProperty("sslrootcert", path + "/" + "server-ca.crt"); // Specify the private key of the client certificate. properties.setProperty("sslkey", path + "/" + "client.pk8"); // Specify the client certificate. properties.setProperty("sslcert", path + "/" + "client.crt"); // Enter the password that you specified when you converted the client.key file to the PK8 format. properties.setProperty("sslpassword", "test_ssl_pwd"); // Specify the SSL mode. Valid values: require, verify-ca, and verify-full. properties.setProperty("sslmode", "verify-ca"); try { Class.forName("org.postgresql.Driver"); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, properties); // In this example, the postgres database contains a table named example from which data is queried. PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("select * from " + "students01"); ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); while (resultSet.next()) { ResultSetMetaData rsmd = resultSet.getMetaData(); int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); Map map = new HashMap(); for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) { map.put(rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1).toLowerCase(), resultSet.getObject(i + 1)); } System.out.println(map); } } catch (Exception exception) { exception.printStackTrace(); } } }