This topic describes how to quickly build retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) applications using the OpenAPI of AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, with Python as the development environment.
Architecture
The RAG architecture uses information retrieval systems to enhance the capabilities of large language models (LLMs). It provides relevant contextual information, such as industry-specific or proprietary data documents. The following figure shows the RAG architecture. 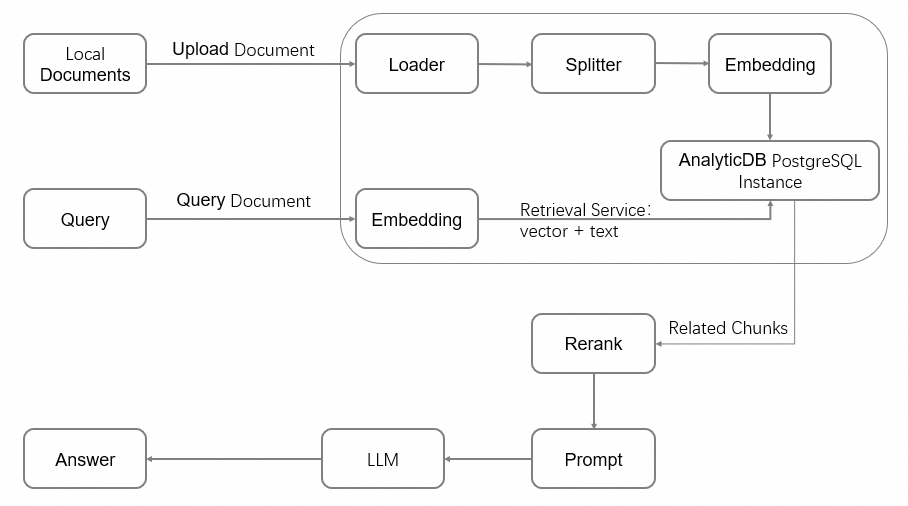
This Quick Start uses the self-developed FastANN vector engine of AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL. It provides document processing capabilities through OpenAPI.
OpenAPI encapsulates the following AI service capabilities:
Multi-tenant management.
Document processing: loading, splitting, embedding, and multimode processing.
Search capabilities: vector search, full-text index, and reranking.
Preparations
An Alibaba Cloud account is required. If you do not have an account, you can register one on the Alibaba Cloud official website.
Authorize a service-linked role. The first time you use AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, you must authorize the creation of a service-linked role in the console. To do this, perform the following steps:
- Log on to the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL console.
In the upper-right corner of the page, click Create Instance.
In the Create Service Linked Role dialog box that appears, click OK.
An Alibaba Cloud account or RAM user must have permissions to manage AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL (permissions) (AliyunGPDBFullAccess).
You have created an AccessKey.
Billing
When you create an instance, you are charged for its compute and storage resources. For more information, see Pricing.
Free trial
Alibaba Cloud offers a free trial for Storage-elastic Mode instances. If you are a new user of AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, you can visit Alibaba Cloud Free Trial to apply for a free trial. If you are not eligible for a free trial, follow the steps in this topic to create an instance in the console.
Procedure
Create an instance
- Log on to the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL console.
In the upper-right corner of the page, click Create Instance to open the buy page.
On the instance purchase page, configure the core parameters to quickly select an instance type. You can keep the default values for other parameters. For more information about the parameters, see Create an instance.
Configuration Item
Description
Example for This Tutorial
Product Type
Subscription: This is a subscription billing method. You pay upfront when you create the instance. This method is suitable for long-term use and is more cost-effective than pay-as-you-go. The longer the subscription duration, the higher the discount.
Pay-as-you-go: This is a post-paid billing method. You are billed hourly. This method is suitable for short-term use. You can release the instance immediately after use to save costs.
Pay-as-you-go
Region and Zone
The geographic location of the instance.
You cannot change the region and zone after the instance is created. Create the instance in the same region as the ECS instances that you want to connect to. This enables service interconnection over the internal network.
China (Hangzhou): Zone J
Instance Resource Type
Elastic Storage Mode: Supports independent disk scale-out and smooth online scale-out.
Serverless Pro: Specify only the required computing resources. You do not need to reserve storage resources.
Elastic Storage Mode
Database Engine Version
Select 7.0 Standard Edition for a richer feature experience. 6.0 Standard Edition is also supported.
7.0 Standard Edition
Instance Edition
High-performance (Basic Edition): Suitable for most business analysis scenarios.
High-availability Edition: Recommended for core business services.
High-performance (Basic Edition)
Vector Engine Optimization
Select Enable.
Enable
Virtual Private Cloud
Select the ID of the VPC.
To interconnect with an ECS instance in the same region over the internal network, select the same VPC as the ECS instance. You can select an existing VPC or create a VPC and vSwitch as prompted on the page.
vpc-xxxx
vSwitch
Select a vSwitch in the VPC. If no vSwitches are available, no vSwitch resources are available in the zone. You can switch to another zone or create a vSwitch in the current zone as prompted on the page.
vsw-xxxx
Click Buy Now, confirm the order information, and click Activate Now.
After you complete the payment, click Management Console to go to the instance list and view the new instance.
NoteThe initialization of an AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance takes some time. Wait for the instance status to change to Running before you proceed with the next steps.
Create an initial account
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL provides two types of users:
Privileged user: The initial account is a privileged user with the RDS_SUPERUSER role. This role grants all operational permissions on the database.
Regular user: By default, a regular user has no permissions. A privileged user, or another user with the GRANT permission, must explicitly grant permissions on database objects to the regular user. For more information about how to create a regular user, see Create and manage users.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Account Management.
Click Create Account. In the Create Account window, enter an account name, set a password, and then click OK.
Parameter
Description
Account
The name of the initial account.
Contain lowercase letters, digits, and underscores (_).
Must start with a lowercase letter and end with a lowercase letter or a digit.
Cannot start with gp.
Must be 2 to 16 characters in length.
New Password and Confirm Password
The password of the initial account.
Must contain at least three of the following character types: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special characters.
Special characters include
! @ # $ % ^ & * ( ) _ + - =.Must be 8 to 32 characters in length.
ImportantFor security, change your password regularly and avoid reusing old ones.
Prepare the Development Environment
Check the Python environment.
This tutorial uses Python 3 SDK. Run the following commands to check if Python 3.9 or later and pip are installed.
If Python is not installed or the version does not meet the requirements, you can install Python.
python -V pip --versionInstall the SDK.
Install the
alibabacloud_gpdb20160503andalibabacloud_tea_openapiSDKs for identity authentication and client building. The SDK versions used in this tutorial are as follows.pip install --upgrade alibabacloud_gpdb20160503 alibabacloud_tea_openapiConfigure environment variables.
Configure sensitive information, such as identity authentication information and instance ID, as environment variables to prevent information leakage caused by hard coding.
Linux and macOS
Run the
vim ~/.bashrccommand to open the~/.bashrcfile.For macOS, run
vim ~/.bash_profile.Add the following content to the configuration file.
On the RAM User List page, click a username to obtain the AccessKey ID and AccessKey Secret of the RAM user.
View the instance ID and region ID in the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL console.
# Replace access_key_id with the AccessKey ID of the RAM user. export ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID="access_key_id" # Replace access_key_secret with the AccessKey Secret of the RAM user. export ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET="access_key_secret" # Replace instance_id with the instance ID of AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, such as gp-bp166cyrtr4p***** export ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID="instance_id" # Replace instance_region with the region ID where the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance resides, such as cn-hangzhou export ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION="instance_region"In the Vim editor, press Esc, enter
:wq, and then save and exit the editor.Run the
source ~/.bashrccommand to make the configuration file take effect.For macOS, run
source ~/.bash_profile.
Windows
To temporarily set environment variables in the current session, run the following commands in CMD.
# Replace access_key_id with the AccessKey ID of the RAM user. set ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID=access_key_id # Replace access_key_secret with the AccessKey Secret of the RAM user. set ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET=access_key_secret # Replace instance_id with the instance ID of AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, such as gp-bp166cyrtr4p***** set ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID=instance_id # Replace instance_region with the region ID where the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance resides, such as cn-hangzhou set ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION=instance_region
Prepare the Database Environment
Procedure
Build a client to perform operations such as creating a vector database.
Initialize the vector database.
All vector data is stored in the fixed `knowledgebase` database. Therefore, initialize each instance once. Initializing the vector database performs the following actions:
Create the `knowledgebase` database and grant read and write permissions to it.
Create a Chinese tokenizer and full-text index related features. This feature is database-level.
Create a namespace to create document libraries.
Create a document library (DocumentCollection) to store chunked text and vector data.
Sample Code
Before running, replace account and account_password with your actual database account and password. You can modify other configuration information as needed.
from alibabacloud_tea_openapi import models as open_api_models
from alibabacloud_gpdb20160503.client import Client
from alibabacloud_gpdb20160503 import models as gpdb_20160503_models
import os
# --- Get authentication and instance information from environment variables ---
ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID = os.environ['ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID']
ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET = os.environ['ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET']
ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID = os.environ['ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID']
ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION = os.environ['ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION']
# Build and return an AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL API client
def get_client():
config = open_api_models.Config(
access_key_id=ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID,
access_key_secret=ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET
)
config.region_id = ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION
# https://api.aliyun.com/product/gpdb
if ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION in ("cn-beijing", "cn-hangzhou", "cn-shanghai", "cn-shenzhen", "cn-hongkong",
"ap-southeast-1"):
config.endpoint = "gpdb.aliyuncs.com"
else:
config.endpoint = f'gpdb.{ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION}.aliyuncs.com'
return Client(config)
# Initialize the vector database
def init_vector_database(account, account_password):
request = gpdb_20160503_models.InitVectorDatabaseRequest(
region_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION,
dbinstance_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID,
manager_account=account,
manager_account_password=account_password
)
response = get_client().init_vector_database(request)
print(f"init_vector_database response code: {response.status_code}, body:{response.body}")
# Create a namespace
def create_namespace(account, account_password, namespace, namespace_password):
request = gpdb_20160503_models.CreateNamespaceRequest(
region_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION,
dbinstance_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID,
manager_account=account,
manager_account_password=account_password,
namespace=namespace,
namespace_password=namespace_password
)
response = get_client().create_namespace(request)
print(f"create_namespace response code: {response.status_code}, body:{response.body}")
# Create a document collection
def create_document_collection(account,
account_password,
namespace,
collection,
metadata: str = None,
full_text_retrieval_fields: str = None,
parser: str = None,
embedding_model: str = None,
metrics: str = None,
hnsw_m: int = None,
pq_enable: int = None,
external_storage: int = None,):
request = gpdb_20160503_models.CreateDocumentCollectionRequest(
region_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION,
dbinstance_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID,
manager_account=account,
manager_account_password=account_password,
namespace=namespace,
collection=collection,
metadata=metadata,
full_text_retrieval_fields=full_text_retrieval_fields,
parser=parser,
embedding_model=embedding_model,
metrics=metrics,
hnsw_m=hnsw_m,
pq_enable=pq_enable,
external_storage=external_storage
)
response = get_client().create_document_collection(request)
print(f"create_document_collection response code: {response.status_code}, body:{response.body}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# The initial database account of the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance.
account = "testacc"
# The password for the initial account.
account_password = "Test1234"
# The name of the namespace to create.
namespace = "ns1"
# The password for the namespace. This password is used for subsequent data read and write operations.
namespace_password = "ns1password"
# The name of the document library to create.
collection = "dc1"
metadata = '{"title":"text", "page":"int"}'
full_text_retrieval_fields = "title"
embedding_model = "m3e-small"
init_vector_database(account, account_password)
create_namespace(account, account_password, namespace, namespace_password)
create_document_collection(account,account_password, namespace, collection,
metadata=metadata, full_text_retrieval_fields=full_text_retrieval_fields,
embedding_model=embedding_model)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
account | The initial database account of the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance. |
account_password | The password for the initial account. |
namespace | The name of the namespace to create. |
namespace_password | The password for the namespace. This password is used for subsequent data read and write operations. |
collection | The name of the document library to create. |
metadata | Custom map-structured metadata. The key is the field name, and the value is the field type. |
full_text_retrieval_fields | Custom comma-separated full-text index fields. The fields must be keys in the metadata. |
parser | Full-text index parameter that specifies the tokenizer. The default value is zh_cn. |
embedding_model | |
metrics | Vector index parameter, indexing algorithm. |
hnsw_m | vector index parameter: the maximum number of neighbors in the HNSW algorithm, ranging from 1 to 1000. |
pq_enable | The vector index parameter, which specifies whether the index enables PQ (Product quantization) algorithm acceleration. |
external_storage | Vector Index parameter that specifies whether to use mmap cache. Important The external_storage parameter is supported only in version 6.0. It is not supported in version 7.0. |
View Table Schema
After the preceding code runs successfully, you can log on to the database to view the table schema as follows:
Log on to the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL console.
You can click Log On to Database in the upper-right corner of the target instance's product page.
On the Log on to Instance page, enter the database account and database password, then click Log on.
After a successful logon, you will see a new database named "knowledgebase" in the target instance. A schema named "ns1" is created in the "knowledgebase" database, and a table named "dc1" is created under this schema. The table schema is as follows.
Field | Type | Field Source | Description |
id | text | Fixed field | Primary key, representing the UUID of a single chunk of text. |
vector | real[] | Fixed field | Vector data ARRAY. Its length corresponds to the dimensions of the specified embedding model. |
doc_name | text | Fixed field | Document name. |
content | text | Fixed field | A single chunk of text, obtained after the document is processed by the Loader and Splitter. |
loader_metadata | json | Fixed field | Metadata corresponding to the document when parsed by the Loader. |
to_tsvector | TSVECTOR | Fixed field | Stores full-text index fields. The data source is the field data specified by full_text_retrieval_fields. "content" is a default field. In this call scenario, full-text search is performed from both "content" and "title" data sources. |
title | text | Metadata definition | User-defined. |
page | int | Metadata definition | User-defined. |
Document Management
Upload documents.
This topic uses asynchronous upload of local documents as an example. The sample code is as follows:
import time import io from typing import Dict, List, Any from alibabacloud_tea_util import models as util_models from alibabacloud_gpdb20160503 import models as gpdb_20160503_models def upload_document_async( namespace, namespace_password, collection, file_name, file_path, metadata: Dict[str, Any] = None, chunk_overlap: int = None, chunk_size: int = None, document_loader_name: str = None, text_splitter_name: str = None, dry_run: bool = None, zh_title_enhance: bool = None, separators: List[str] = None): with open(file_path, 'rb') as f: file_content_bytes = f.read() request = gpdb_20160503_models.UploadDocumentAsyncAdvanceRequest( region_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION, dbinstance_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID, namespace=namespace, namespace_password=namespace_password, collection=collection, file_name=file_name, metadata=metadata, chunk_overlap=chunk_overlap, chunk_size=chunk_size, document_loader_name=document_loader_name, file_url_object=io.BytesIO(file_content_bytes), text_splitter_name=text_splitter_name, dry_run=dry_run, zh_title_enhance=zh_title_enhance, separators=separators, ) response = get_client().upload_document_async_advance(request, util_models.RuntimeOptions()) print(f"upload_document_async response code: {response.status_code}, body:{response.body}") return response.body.job_id def wait_upload_document_job(namespace, namespace_password, collection, job_id): def job_ready(): request = gpdb_20160503_models.GetUploadDocumentJobRequest( region_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION, dbinstance_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID, namespace=namespace, namespace_password=namespace_password, collection=collection, job_id=job_id, ) response = get_client().get_upload_document_job(request) print(f"get_upload_document_job response code: {response.status_code}, body:{response.body}") return response.body.job.completed while True: if job_ready(): print("successfully load document") break time.sleep(2) if __name__ == '__main__': job_id = upload_document_async("ns1", "Ns1password", "dc1", "test.pdf", "/root/test.pdf") wait_upload_document_job("ns1", "Ns1password", "dc1", job_id)Parameters
Parameter
Description
namespace
The name of the namespace where the document library resides.
namespace_password
The password for the namespace.
collection
The name of the document library to store the documents.
file_name
The document name, including the file name extension.
file_path
The local document path. The maximum file size is 200 MB.
metadata
The document metadata. It must be consistent with the metadata specified when creating the document library.
chunk_overlap
The chunking strategy for large data. The amount of overlapping data between consecutive chunks during chunking. The maximum value cannot exceed chunk_size.
chunk_size
The chunking strategy for large data. The size of each chunk when data is split into smaller parts. The maximum value is 2048.
document_loader_name
If unspecified, a loader is automatically selected based on the file name extension. For details, see Document Understanding.
text_splitter_name
The name of the chunker. For more information about document chunking, see Document chunking.
dry_run
Specifies whether to only perform document understanding and chunking, without vectorization and storage. Valid values:
true: Only perform document understanding and chunking.
false (default): First perform document understanding and chunking, then perform vectorization and storage.
zh_title_enhance
Specifies whether to enable Chinese title enhancement. Valid values:
true: Enable Chinese title enhancement.
false: Disable Chinese title enhancement.
separators
The separator for the large data chunking strategy. Generally, you do not need to specify this parameter.
(Optional) Other document management operations.
View Document List
def list_documents(namespace, namespace_password, collection): request = gpdb_20160503_models.ListDocumentsRequest( region_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION, dbinstance_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID, namespace=namespace, namespace_password=namespace_password, collection=collection, ) response = get_client().list_documents(request) print(f"list_documents response code: {response.status_code}, body:{response.body}") if __name__ == '__main__': list_documents("ns1", "Ns1password", "dc1")Parameters
Parameter
Description
namespace
The name of the namespace where the document library resides.
namespace_password
The password for the namespace.
collection
The document library name.
View Document Details
def describe_document(namespace, namespace_password, collection, file_name): request = gpdb_20160503_models.DescribeDocumentRequest( region_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION, dbinstance_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID, namespace=namespace, namespace_password=namespace_password, collection=collection, file_name=file_name ) response = get_client().describe_document(request) print(f"describe_document response code: {response.status_code}, body:{response.body}") if __name__ == '__main__': describe_document("ns1", "Ns1password", "dc1", "test.pdf")Parameters
Parameter
Description
namespace
The name of the namespace where the document library resides.
namespace_password
The password for the namespace.
collection
The document library name.
file_name
The document name.
Response Parameters
Parameter
Description
DocsCount
The number of chunks the document is split into.
TextSplitter
The document splitter name.
DocumentLoader
The document loader name.
FileExt
The file name extension of the document.
FileMd5
The MD5 hash value of the document.
FileMtime
The latest upload time of the document.
FileSize
The file size in bytes.
FileVersion
The document version, an INT type, indicating how many times the document has been uploaded and updated.
Delete Documents
def delete_document(namespace, namespace_password, collection, file_name): request = gpdb_20160503_models.DeleteDocumentRequest( region_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION, dbinstance_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID, namespace=namespace, namespace_password=namespace_password, collection=collection, file_name=file_name ) response = get_client().delete_document(request) print(f"delete_document response code: {response.status_code}, body:{response.body}") if __name__ == '__main__': delete_document("ns1", "Ns1password", "dc1", "test.pdf")Parameters
Parameter
Description
namespace
The name of the namespace where the document library resides.
namespace_password
The password for the namespace.
collection
The document library name.
file_name
The document name.
Document Retrieval
This section uses plain text retrieval as an example. The sample code is as follows:
def query_content(namespace, namespace_password, collection, top_k,
content,
filter_str: str = None,
metrics: str = None,
use_full_text_retrieval: bool = None):
request = gpdb_20160503_models.QueryContentRequest(
region_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION,
dbinstance_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID,
namespace=namespace,
namespace_password=namespace_password,
collection=collection,
content=content,
filter=filter_str,
top_k=top_k,
metrics=metrics,
use_full_text_retrieval=use_full_text_retrieval,
)
response = get_client().query_content(request)
print(f"query_content response code: {response.status_code}, body:{response.body}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
query_content('ns1', 'Ns1password', 'dc1', 10, 'What is ADBPG?')Parameters
Parameter | Description |
namespace | The name of the namespace where the document library resides. |
namespace_password | The password for the namespace. |
collection | The document library name. |
top_k | The number of top-k retrieval results to return. |
content | The text content to retrieve. |
filter_str | The filter statement before retrieval. |
metrics | The vector distance algorithm. We recommend that you do not set this parameter. The algorithm used when creating the index is used for calculation. |
use_full_text_retrieval | Specifies whether to use full-text index. Valid values:
|
Response Parameters
Parameter | Description |
Id | The UUID of the chunk after splitting. |
FileName | The document name. |
Content | The retrieved content, which is a chunk after splitting. |
LoaderMetadata | The metadata generated during document upload. |
Metadata | User-defined metadata. |
RetrievalSource | The retrieval source. Valid values:
|
Score | The similarity score obtained based on the specified similarity algorithm. |
Integrate LangChain
LangChain is an open-source framework for building applications based on large language models (LLMs). It connects models with external data through a set of interfaces and tools. This section shows how to integrate the retrieval capabilities of AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL into LangChain to implement a Q&A system.
Install modules.
pip install --upgrade langchain openai tiktokenBuild AdbpgRetriever.
from langchain_core.retrievers import BaseRetriever from langchain_core.callbacks import CallbackManagerForRetrieverRun from langchain_core.documents import Document class AdbpgRetriever(BaseRetriever): namespace: str = None namespace_password: str = None collection: str = None top_k: int = None use_full_text_retrieval: bool = None def query_content(self, content) -> List[gpdb_20160503_models.QueryContentResponseBodyMatchesMatchList]: request = gpdb_20160503_models.QueryContentRequest( region_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_REGION, dbinstance_id=ADBPG_INSTANCE_ID, namespace=self.namespace, namespace_password=self.namespace_password, collection=self.collection, content=content, top_k=self.top_k, use_full_text_retrieval=self.use_full_text_retrieval, ) response = get_client().query_content(request) return response.body.matches.match_list def _get_relevant_documents( self, query: str, *, run_manager: CallbackManagerForRetrieverRun ) -> List[Document]: match_list = self.query_content(query) return [Document(page_content=i.content) for i in match_list]Create a Chain.
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate from langchain.schema import StrOutputParser from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough OPENAI_API_KEY = "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY" os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = OPENAI_API_KEY template = """Answer the question based only on the following context: {context} Question: {question} """ prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template) model = ChatOpenAI() def format_docs(docs): return "\n\n".join([d.page_content for d in docs]) retriever = AdbpgRetriever(namespace='ns1', namespace_password='Ns1password', collection='dc1', top_k=10, use_full_text_retrieval=True) chain = ( {"context": retriever | format_docs, "question": RunnablePassthrough()} | prompt | model | StrOutputParser() )Q&A.
chain.invoke("What is AnalyticDB PostgreSQL?") # Response: # AnalyticDB PostgreSQL is a cloud-native Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) service provided by Alibaba Cloud. Based on the open-source PostgreSQL database extension, it delivers a high-performance, high-capacity data warehouse solution. # It combines PostgreSQL's flexibility and compatibility with high concurrency and high-speed query capabilities for data analytics and reporting. # # AnalyticDB PostgreSQL is particularly well-suited for processing large-scale datasets, supporting real-time analytics and decision support. It serves as a powerful tool for enterprises to perform data mining, business intelligence (BI), reporting, and data visualization. # As a managed service, it simplifies data warehouse management and operations and maintenance (O&M), enabling users to focus on data analytics rather than underlying infrastructure. # Key features include the following: # # High-performance analytics - Uses columnar storage and Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) architecture to quickly query and analyze large volumes of data. # Easy scalability - Resources can be easily scaled horizontally and vertically based on data volume and query performance requirements. # PostgreSQL compatibility - Supports PostgreSQL SQL language and most tools in the PostgreSQL ecosystem, making it easy for existing PostgreSQL users to migrate and adapt. # Security and reliability - Provides features such as data backup, recovery, and encryption to ensure data security and reliability. # Cloud-native integration - Tightly integrated with other Alibaba Cloud services such as data integration and data visualization tools. # In summary, AnalyticDB PostgreSQL is a high-performance, scalable cloud data warehouse service that enables enterprises to perform complex data analytics and reporting in cloud environments.
Appendix
Full-Text Index
To improve retrieval accuracy, AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL supports full-text index in addition to vector similarity. It can also be used simultaneously with vector similarity retrieval for dual-path retrieval.
Define full-text index fields.
Before using full-text index, specify which fields serve as data sources for full-text index. The document library interface uses the `content` field by default. You can also specify other custom metadata fields.
Tokenization
When creating a document library, you can specify the `Parser` field as the tokenizer. In most cases, use the default Chinese `zh_cn`. If you have special tokenization character requirements, you can contact Alibaba Cloud technical support.
When inserting data, the tokenizer splits the data from the specified full-text index fields according to the delimiters and saves it to `to_tsvector` for subsequent full-text index use.
Embedding Models
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL supports the following embedding models:
embedding_model | Dimensions | Description |
m3e-small | 512 | From moka-ai/m3e-small. Supports Chinese only, not English. |
m3e-base | 768 | From moka-ai/m3e-base. Supports Chinese and English. |
text2vec | 1024 | From GanymedeNil/text2vec-large-chinese. Supports Chinese and English. |
text-embedding-v1 | 1536 | From Alibaba Cloud Model Studio's general text embedding. Supports Chinese and English. |
text-embedding-v2 | 1536 | An upgraded version of text-embedding-v1. |
clip-vit-b-32 (multimodal) | 512 | An open-source multimodal model that supports images. |
Custom embedding models are not supported yet.
Supports more models. For more information, see Create a Document Library.
Vector Index
Vector index supports the following parameters:
Parameter | Description |
metrics | The similarity distance metric algorithm. Valid values:
|
hnsw_m | The maximum number of neighbors in the HNSW algorithm. OpenAPI automatically sets different values based on vector dimensions. |
pq_enable | Specifies whether to enable the PQ vector dimensionality reduction feature. Valid values:
PQ vector dimensionality reduction relies on existing vector sample data for training. If the data volume is less than 500,000, we recommend that you do not set this parameter. |
external_storage | Specifies whether to use mmap to build the HNSW index. Valid values:
Important The external_storage parameter is supported only in version 6.0. It is not supported in version 7.0. |
Document Understanding
Select an appropriate loader based on the document type:
UnstructuredHTMLLoader:
.htmlUnstructuredMarkdownLoader:
.mdPyMuPDFLoader:
.pdfPyPDFLoader:
.pdfRapidOCRPDFLoader:
.pdfJSONLoader:
.jsonCSVLoader:
.csvRapidOCRLoader:
.png,.jpg,.jpeg, or.bmpUnstructuredFileLoader:
.eml,.msg,.rst,.txt,.xml,.docx,.epub,.odt,.pptx, or.tsv
If `document_loader_name` is not specified, the loader is automatically determined based on the document's file name extension. If a document type has multiple loaders, such as PDF, you can specify any of them.
Document Chunking
The effect of document chunking is determined by `chunk_overlap`, `chunk_size`, `text_splitter_name`, and . The valid values for `text_splitter_name` are as follows:
ChineseRecursiveTextSplitter: Inherits from RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter. It uses
["\n\n","\n", "。|!|?","\.\s|\!\s|\?\s", ";|;\s", ",|,\s"]as delimiters by default and uses regular expressions for matching. It performs better for Chinese text than RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.SpacyTextSplitter uses
["\n\n", "\n", " ", ""]as the default separator. It supports chunking for multiple programming languages such asc++,go,java,js,php,proto,python,rst,ruby,rust,scala,swift,markdown,latex,html,sol, andcsharp.RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter: The default delimiter is
\n\n. It uses the en_core_web_sm model from the Spacy library for splitting and works well for English documents.MarkdownHeaderTextSplitter: For Markdown types, it uses
[ ("#", "head1"), ("##", "head2"), ("###", "head3"), ("####", "head4") ]for splitting.