Alibaba Cloud Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a globally distributed network of Points of Presence (POPs). It caches content from your origin server on POPs worldwide. When end users request your content, they can retrieve it from the nearest POP instead of the origin server. This approach improves resource access speed and reduces the load on your origin server.
Alibaba Cloud operates more than 3,200 POPs worldwide. In the Chinese mainland, it has over 2,300 POPs that cover all 31 provincial-level regions. Outside the Chinese mainland, it has more than 900 POPs in over 70 countries and regions. The total network bandwidth capacity of CDN is 180 Tbps. For more information about Alibaba Cloud's POPs, see POP distribution.
Onboarding with CDN is fast and simple. You do not need to adjust your business architecture or perform any complex configurations. Simply add your domain name in the CDN console and complete a few steps to enable global acceleration. To get started, see our Beginners' guide.
Why choose Alibaba Cloud CDN
Alibaba Cloud CDN helps you accelerate the delivery of static resources and improve resource access speeds:
Extensive POP resources: Provides users with nearby access from the same ISP, which resolves latency and speed issues caused by long-distance or cross-ISP access.
Elastic scalability: Built on a global network of over 3,200 POPs, CDN allows for elastic resource scaling to ensure high availability for your business.
Intelligent Scheduling System: Monitors the health of POPs in real time and assigns the optimal access POP based on the user's location and ISP for optimal performance.
Smart routing: Uses techniques such as protocol and connection optimization to reduce overall latency and increase transfer speeds, especially in weak network conditions.
Efficient caching strategies: Achieves a higher cache hit ratio by serving content from nearby POPs, improving access speed.
Reduced IT costs: Offloads your business's computing, bandwidth, and connection requirements to the edge, which lowers your IT costs.
High bandwidth capacity: The total network bandwidth capacity is 180 Tbps.
Standard APIs: Provides industry-standard APIs for improved usability and compatibility.
For more reasons to choose Alibaba Cloud CDN, see Competitive advantages of Alibaba Cloud CDN.
How it works
CDN accelerates content delivery by handling your domain's DNS resolution. It intelligently routes user requests to the nearest POP. If the requested resource is already cached at this POP, the POP delivers it directly to the user without a request to the origin server.
Assume your accelerated domain name is www.aliyundoc.com. After you enable the CDN service, the process is as follows when an end user in Singapore sends an HTTP request.

User initiates a request: The end user requests a resource from
www.aliyundoc.com. This request first goes to the local DNS for the domain's IP address.DNS forwards the request: The local DNS checks its cache for an IP address record for
www.aliyundoc.com. If a record exists, the local DNS returns it to the user. If not, the local DNS queries the authoritative DNS for the domain's resolution record.CNAME record takes effect: After the authoritative DNS resolves
www.aliyundoc.com, it returns the CNAME recordwww.aliyundoc.com.example.com.Smart scheduling: The local DNS sends a resolution request for
www.aliyundoc.com.example.comto the CDN routing system, which then assigns the optimal POP IP address.POP IP is returned: The local DNS receives the optimal POP IP address from CDN.
User accesses the POP: The Local DNS returns the optimal POP IP address to the user. The user then sends a request for the resource to this POP IP address.
POP responds:
Cache Hit: If the POP has the requested resource cached, it returns the resource directly to the user, completing the request.
Cache Miss: If the POP does not have the resource cached, or if the cached resource has expired, the POP requests the resource from the origin server. After the POP retrieves the resource, it caches it based on your configured caching rules and returns it to the user, completing the request. For information about how to configure caching policies, see Configure a time-to-live (TTL) for a cached file.
Service architecture
The following diagram shows the architecture of Alibaba Cloud CDN, which consists of four major systems: route quality, routing, cache, and support.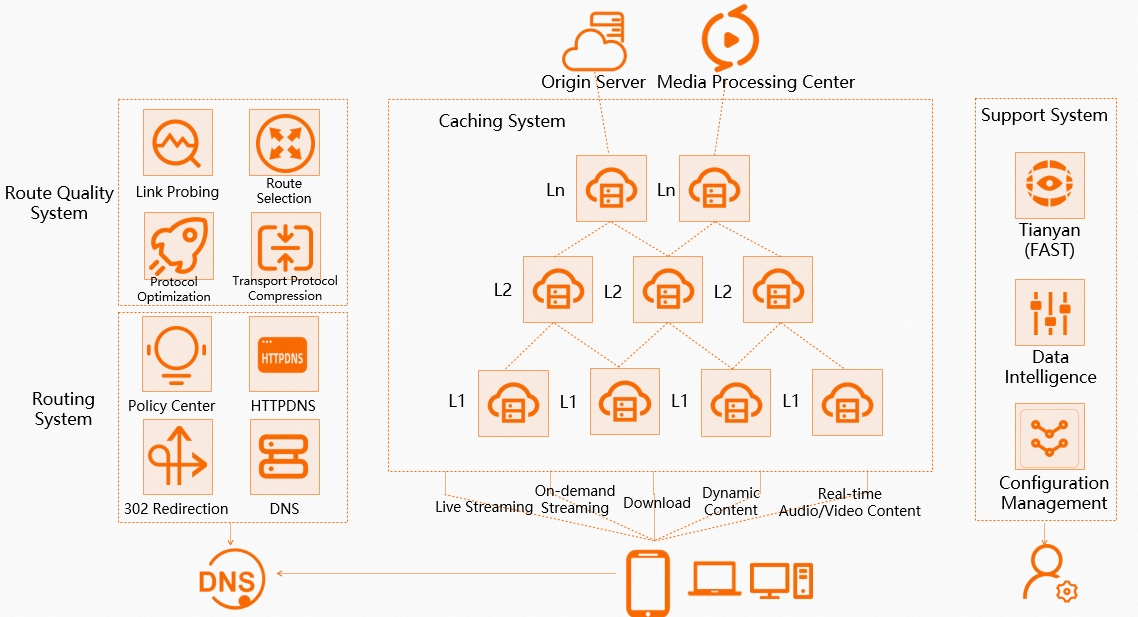
Route quality system
The route quality system monitors the real-time load and health of all POPs and routes in the cache system. It sends this information to the routing system. The routing system obtains the user's ISP and region from the user's IP address and combines this information with the route quality data to assign an optimal POP to the user requests.
Routing system
This system supports multiple routing modes, including policy-based, DNS, DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH), and 302 redirect. When an end user initiates a request, it first undergoes DNS resolution, and then is processed by the CDN routing system.
Cache system
The user accesses the cache POP that is assigned as the optimal access POP. If the POP has the requested resource cached, the resource is returned. If neither the L1 (edge) POP nor the L2 (regional) POP has the resource cached, an origin request is sent to retrieve the resource. The resource is then cached in the system for subsequent user requests, avoiding repeated origin traffic. This multi-tiered caching architecture improves content delivery efficiency, reduces origin bandwidth, and enhances user experience.
Support system
The support system includes Tianyan, data intelligence, and a configuration management system. They provide resource monitoring, data analytics, and configuration management capabilities.
Resource monitoring: Tianyan can monitor the running status of user services on the caching system. For example, it monitors common metrics for CDN-accelerated domain names, such as queries per second (QPS), bandwidth, and HTTP status codes.
Data analytics: You can analyze data for CDN-accelerated domain names, such as top URLs, page views (PVs), and unique visitors (UVs).
Configuration management: The configuration management system lets you configure cache rules, such as cache file types and ignoring query parameters during caching, to improve the operational efficiency of the caching system.
Billing
CDN billing includes basic and value-added services:
Billing of basic services: This includes two billing methods: pay-by-traffic and pay-by-peak-bandwidth. The default method is pay-by-traffic. For more details, see Billing of basic services.
Billing of value-added services: Billable items for value-added services include the number of static HTTPS requests, static QUIC requests, and real-time log deliveries. For more details, see Billing of value-added services.
For more information about CDN billing, see CDN Pricing.
Once you've familiarized yourself with the billing methods for CDN, you can activate CDN.
Differences between CDN, DCDN, and ESA
Item | CDN | Dynamic Content Delivery Network (DCDN) | ESA |
Common use cases | Mobile app updates, game package updates, video on demand (VOD) (long-form and short-form videos), and image- and text-based websites. | Online shopping malls, online payments, interactive chat, online education, global multiplayer games, and financial services. | Includes but is not limited to the gaming, e-commerce, finance, and retail industries. |
Coverage |
|
|
|
Acceleration | Primarily accelerates static content, suitable for high-bandwidth and high-traffic scenarios. Dynamic requests are sent directly to the origin server.
| Supports pure dynamic acceleration and hybrid dynamic-static acceleration.
| Supports cache acceleration for dynamic and static resources. In addition, various upgrades provide users with a faster access experience.
|
Protocol support |
|
|
|
Scheduling |
|
|
|
Edge computing |
|
|
|
Security policy |
|
|
|
Log analysis |
|
|
|
Static content refers to files where the data remains the same across different requests. Examples include images, videos, website files (HTML, CSS, JS), software installation packages, APK files, and compressed archives.
Dynamic content refers to content where the data differs across different requests. Examples include website files (ASP, JSP, PHP, Perl, CGI), API endpoints, and database interaction requests.
For more information about dynamic and static resources, see What are static content and dynamic content?
Management tools
After creating and logging on to an Alibaba Cloud account, you can manage CDN from anywhere using these tools:
Manage in the CDN console
The management console is a web-based service page with interactive, easy-to-use UI. For information about console operations, see User Guide.
Manage by using APIs
CDN supports RPC API operations that support GET and POST requests. For API documentations, see API Reference.
Related services
Learn about services related to CDN to better understand its role and use cases within the Alibaba Cloud ecosystem ecosystem.
Related product | Purpose |
DCDN can distinguish between dynamic and static resources to accelerate each type separately, balancing performance and security. | |
Using OSS with CDN can improve website access speed and effectively reduce OSS Internet egress costs. | |
Applying CDN to video live streaming provides an integrated solution for media storage, slicing and transcoding, access control, and content delivery acceleration. | |
Using CDN for video on demand reduces buffering and provides a smooth playback experience. | |
Leverage the powerful and stable resolution and scheduling that Alibaba Cloud DNS provides to ensure a smooth access experience. | |
Use ECS as an origin server to improve website availability, protect origin server information, and reduce bandwidth costs. | |
You can set the IP address of a SLB instance as the origin address to reduce the load on your origin server. |
Best practices
To learn about specific use cases for CDN, see the following topics: