PyTorch is an open source deep learning framework that is widely used in training jobs of various deep learning models. This topic describes how to use Arena to submit standalone PyTorch training jobs that use a single GPU or multiple GPUs and how to use TensorBoard to visualize training jobs.
Prerequisites
A Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster that contains GPU-accelerated nodes is created. For more information, see Create an ACK cluster that contains GPU-accelerated nodes.
Internet access is enabled for nodes in the cluster. For more information, see Enable an existing ACK cluster to access the Internet.
The Arena component is installed. For more information, see Configure the Arena client.
A persistent volume claim (PVC) instance named
training-datais created, and the MNIST dataset is stored in the/pytorch_datapath. For more information, see Configure a shared NAS volume.
Background information
You must download training code from a remote Git repository and read the training data from the shared storage system, which includes persistent volumes (PVs) and persistent volume claims (PVCs) based on File Storage NAS (NAS). torchrun is a command-line tool provided by PyTorch to simplify and manage distributed training jobs. In this example, torchrun is used to run standalone PyTorch training jobs that use a single GPU or multiple GPUs. For more information about the training code, see main.py.
Procedure
Step 1: View GPU resources
Run the following command to query the GPU resources available in the cluster:
arena top nodeExpected output:
NAME IPADDRESS ROLE STATUS GPU(Total) GPU(Allocated)
cn-beijing.192.168.xxx.xxx 192.168.xxx.xxx <none> Ready 0 0
cn-beijing.192.168.xxx.xxx 192.168.xxx.xxx <none> Ready 0 0
cn-beijing.192.168.xxx.xxx 192.168.xxx.xxx <none> Ready 2 0
cn-beijing.192.168.xxx.xxx 192.168.xxx.xxx <none> Ready 2 0
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Allocated/Total GPUs In Cluster:
0/4 (0.0%)The output shows that the cluster contains two GPU-accelerated nodes. Each GPU-accelerated node contains two idle GPUs that can be used to run training jobs.
Step 2: Submit a PyTorch training job
Run the following command to submit a standalone PyTorch training job that uses a single GPU:
arena submit pytorch \
--name=pytorch-mnist \
--namespace=default \
--workers=1 \
--gpus=1 \
--working-dir=/root \
--image=kube-ai-registry.cn-shanghai.cr.aliyuncs.com/kube-ai/pytorch-with-tensorboard:2.5.1-cuda12.4-cudnn9-runtime \
--sync-mode=git \
--sync-source=https://github.com/kubeflow/arena.git \
--env=GIT_SYNC_BRANCH=v0.13.1 \
--data=training-data:/mnt \
--tensorboard \
--logdir=/mnt/pytorch_data/logs \
"torchrun /root/code/arena/examples/pytorch/mnist/main.py --epochs 10 --backend nccl --data /mnt/pytorch_data --dir /mnt/pytorch_data/logs"Expected output:
service/pytorch-mnist-tensorboard created
deployment.apps/pytorch-mnist-tensorboard created
pytorchjob.kubeflow.org/pytorch-mnist created
INFO[0002] The Job pytorch-mnist has been submitted successfully
INFO[0002] You can run `arena get pytorch-mnist --type pytorchjob -n default` to check the job statusIf you want to run a standalone PyTorch training job that uses multiple GPUs, such as two GPUs, you can assign two GPUs and start two training processes by specifying --gpus=2 and --nproc-per-node=2:
arena submit pytorch \
--name=pytorch-mnist \
--namespace=default \
--workers=1 \
--gpus=2 \
--nproc-per-node=2 \
--working-dir=/root \
--image=kube-ai-registry.cn-shanghai.cr.aliyuncs.com/kube-ai/pytorch-with-tensorboard:2.5.1-cuda12.4-cudnn9-runtime \
--sync-mode=git \
--sync-source=https://github.com/kubeflow/arena.git \
--env=GIT_SYNC_BRANCH=v0.13.1 \
--data=training-data:/mnt \
--tensorboard \
--logdir=/mnt/pytorch_data/logs \
"torchrun /root/code/arena/examples/pytorch/mnist/main.py --epochs 10 --backend nccl --data /mnt/pytorch_data --dir /mnt/pytorch_data/logs"If you are using a non-public Git repository, you can specify the Git username and password by configuring the GIT_SYNC_USERNAME and GIT_SYNC_PASSWORD environment variables.
arena submit pytorch \
...
--sync-mode=git \
--sync-source=https://github.com/kubeflow/arena.git \
--env=GIT_SYNC_BRANCH=v0.13.1 \
--env=GIT_SYNC_USERNAME=<username> \
--env=GIT_SYNC_PASSWORD=<password> \
"torchrun /root/code/arena/examples/pytorch/mnist/main.py --epochs 10 --backend nccl --data /mnt/pytorch_data --dir /mnt/pytorch_data/logs"The arena command uses git-sync to synchronize the source code. This allows you to use the environment variables defined in the git-sync project.
In this example, the source code is pulled from a GitHub repository. If the code cannot be pulled due to network-related reasons, you can manually download the code to the shared storage system. After you download the code to the /code/github.com/kubeflow/arena path in NAS, you can submit a training job by using the following code:
arena submit pytorch \
--name=pytorch-mnist \
--namespace=default \
--workers=1 \
--gpus=1 \
--working-dir=/root \
--image=kube-ai-registry.cn-shanghai.cr.aliyuncs.com/kube-ai/pytorch-with-tensorboard:2.5.1-cuda12.4-cudnn9-runtime \
--data=training-data:/mnt \
--tensorboard \
--logdir=/mnt/pytorch_data/logs \
"torchrun /mnt/code/github.com/kubeflow/arena/examples/pytorch/mnist/main.py --epochs 10 --backend nccl --data /mnt/pytorch_data --dir /mnt/pytorch_data/logs"The following table describes the parameters in the preceding sample code block.
Parameter | Required | Description | Default value |
| Yes | The name of the job, which is globally unique. | N/A |
| No | The namespace to which the pod belongs. |
|
| No | Specifies the number of worker nodes. The master node is included. For example, a value of 3 indicates that the training job runs on one master node and two worker nodes. |
|
| No | Specifies the number of GPUs that are used by the worker nodes on which the training job runs. |
|
| No | Specifies the directory in which the command is executed. |
|
| Yes | Specifies the address of the image that is used to deploy the runtime. | N/A |
| No | Specifies the synchronization mode. Valid values: git and rsync. In this example, the git mode is used. | N/A |
| No | Specifies the address of the repository from which the source code is synchronized. This parameter is used together with the --sync-mode parameter. In this example, the git mode is used. You must specify an address that supports Git, such as a GitHub project or an Alibaba Cloud Code project. The project code is downloaded to the | N/A |
| No | Mounts a shared PV to the runtime in which the training job runs. The value of this parameter consists of two parts that are separated by a colon ( Note Run the If no PVC is available, you can create a PVC. For more information, see Configure a shared NAS volume. | N/A |
| No | Specifies that TensorBoard is used to visualize training results. You can configure the --logdir parameter to specify the path from which TensorBoard reads event files. If you do not configure this parameter, TensorBoard is not used. | N/A |
| No | The path from which TensorBoard reads event files. You must specify this parameter and the --tensorboard parameter. |
|
Step 3: View the PyTorch training job
Run the following command to view the training job that is submitted by using Arena:
arena list -n defaultExpected output:
NAME STATUS TRAINER DURATION GPU(Requested) GPU(Allocated) NODE pytorch-mnist RUNNING PYTORCHJOB 11s 1 1 192.168.xxx.xxxRun the following command to query the GPU resources used by the training job:
arena top job -n defaultExpected output:
NAME STATUS TRAINER AGE GPU(Requested) GPU(Allocated) NODE pytorch-mnist RUNNING PYTORCHJOB 18s 1 1 192.168.xxx.xxx Total Allocated/Requested GPUs of Training Jobs: 1/1Run the following command to query the GPU resource usage of the cluster:
arena top nodeExpected output:
NAME IPADDRESS ROLE STATUS GPU(Total) GPU(Allocated) cn-beijing.192.168.xxx.xxx 192.168.xxx.xxx <none> Ready 0 0 cn-beijing.192.168.xxx.xxx 192.168.xxx.xxx <none> Ready 0 0 cn-beijing.192.168.xxx.xxx 192.168.xxx.xxx <none> Ready 2 1 cn-beijing.192.168.xxx.xxx 192.168.xxx.xxx <none> Ready 2 0 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Allocated/Total GPUs In Cluster: 1/4 (25.0%)The output shows that the cluster has four GPUs. One GPU is allocated.
Run the following command to view the training job details:
arena get pytorch-mnist -n defaultExpected output:
Name: pytorch-mnist Status: RUNNING Namespace: default Priority: N/A Trainer: PYTORCHJOB Duration: 45s CreateTime: 2025-02-12 11:20:10 EndTime: Instances: NAME STATUS AGE IS_CHIEF GPU(Requested) NODE ---- ------ --- -------- -------------- ---- pytorch-mnist-master-0 Running 45s true 1 cn-beijing.192.168.xxx.xxx Tensorboard: Your tensorboard will be available on: http://192.168.xxx.xxx:31949NoteIf TensorBoard is used in a training job, the URL of the TensorBoard instance is displayed in the job details. Otherwise, the URL is not displayed.
Step 4: View the TensorBoard instance
Run the following command on your on-premises machine to map port 6006 of TensorBoard in the cluster to the on-premises port 9090:
ImportantPort forwarding set up by using kubectl port-forward is not reliable, secure, or extensible in production environments. It is only for development and debugging. Do not use this command to set up port forwarding in production environments. For more information about networking solutions used for production in ACK clusters, see Ingress management.
kubectl port-forward -n default svc/pytorch-mnist-tensorboard 9090:6006Enter http://127.0.0.1:9090 into the address bar of the web browser to access TensorBoard.
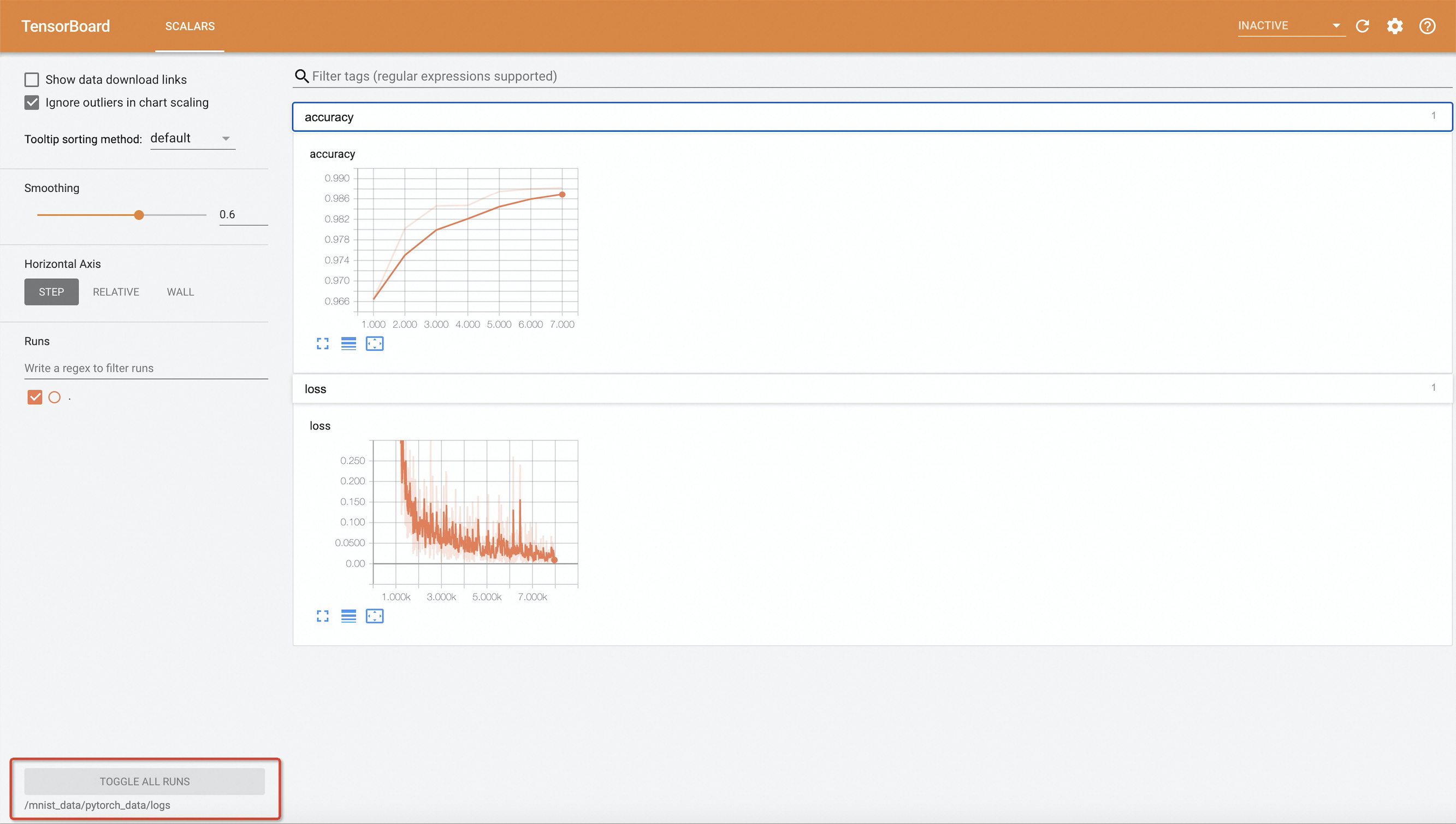 Note
NoteIn the example, the source code that is used to submit the standalone PyTorch job indicates that training results are written to events after every 10 epochs. If you want to modify the value of --epochs, set the value to a multiple of 10. Otherwise, the training results cannot be visualized in TensorBoard.
Step 5: View training job logs
Run the following commands to view the training job logs:
arena logs pytorch-mnist -n defaultExpected output:
Train Epoch: 10 [55680/60000 (93%)] Loss: 0.025778
Train Epoch: 10 [56320/60000 (94%)] Loss: 0.086488
Train Epoch: 10 [56960/60000 (95%)] Loss: 0.003240
Train Epoch: 10 [57600/60000 (96%)] Loss: 0.046731
Train Epoch: 10 [58240/60000 (97%)] Loss: 0.010752
Train Epoch: 10 [58880/60000 (98%)] Loss: 0.010934
Train Epoch: 10 [59520/60000 (99%)] Loss: 0.065813
Accuracy: 9921/10000 (99.21%)If you want to view job logs in real time, add the
-fparameter.If you want to view only the last lines of the log, add the
-t Nor--tail Nparameter.For more information, see
arena logs --help.
(Optional) Step 6: Clear the environment
If you no longer require the training job, run the following command to delete the training job:
arena delete pytorch-mnist -n defaultExpected output:
INFO[0001] The training job pytorch-mnist has been deleted successfully