In a Kubernetes cluster, a pod is typically assigned a private IP address. However, some scenarios require a pod to have an independent public IP address. This allows the pod to communicate with external networks without being affected by the traffic of other pods. The Terway and ack-extend-network-controller components of Alibaba Cloud both support associating an Elastic IP Address (EIP) with a specific pod. This provides the pod with an independent public egress.
Prerequisites
You must create an ACK managed cluster or an ACK dedicated cluster that uses the Terway network plugin. For more information, see Create an ACK managed cluster and Create an ACK dedicated cluster (no longer available for creation). For more information about Terway network modes, see Use the Terway network plugin.
Starting from November 2023, Terway no longer provides updates for the EIP feature. The feature is officially removed in v1.7.0. We recommend that you use the ack-extend-network-controller component to attach independent public EIPs to pods. For more information, see Migrate the EIP feature from Terway to ack-extend-network-controller.
Limits
Before you use an EIP, you must understand its limits. For more information, see Limits.
This feature is supported only for ECS nodes.
Billing
Enabling the Terway and ack-extend-network-controller plugins does not incur additional fees. However, you may be charged for the cloud resources that you use. For more information about the billing of ACK cloud resources, see Cloud resource fees.
Background information
In a Terway network, traffic from a pod to the Internet is typically routed using host Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) or external SNAT through an EIP. Inbound Internet traffic to a pod usually flows through a LoadBalancer service. However, some scenarios require a pod to have an independent public IP address. For example:
The port mapped for the pod is random. This is common for User Datagram Protocol (UDP) game servers or conference calls. For example, the Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) uses different ports for different clients.
Pods compete for Internet traffic, and a specific pod requires an independent public egress.
Step 1: Configure RAM permissions for attaching EIPs
ack-extend-network-controller (recommended)
Grant RAM permissions to an ACK managed cluster or an ACK dedicated cluster
Create a custom policy with the following content. For more information, see Step 1: Create a custom policy.
{ "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "vpc:DescribeVSwitches", "vpc:AllocateEipAddress", "vpc:AllocateEipAddressPro", "vpc:DescribeEipAddresses", "vpc:AssociateEipAddress", "vpc:UnassociateEipAddress", "vpc:ReleaseEipAddress", "vpc:AddCommonBandwidthPackageIp", "vpc:RemoveCommonBandwidthPackageIp", "vpc:TagResources", "ecs:DescribeNetworkInterfaces" ], "Resource": [ "*" ], "Condition": {} }Grant permissions to the Worker RAM role of the cluster. For more information, see Step 2: Grant permissions to the Worker RAM role of the cluster.
Terway
Terway requires EIP-related permissions to request and configure EIPs for pods. You must configure additional permissions.
Grant RAM permissions to an ACK managed cluster or an ACK managed cluster of Basic Edition created in or after June 2020
Create a custom policy with the following content. For more information, see Step 1: Create a custom policy.
{ "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "vpc:DescribeVSwitches", "vpc:AllocateEipAddress", "vpc:DescribeEipAddresses", "vpc:AssociateEipAddress", "vpc:UnassociateEipAddress", "vpc:ReleaseEipAddress", "vpc:AddCommonBandwidthPackageIp", "vpc:RemoveCommonBandwidthPackageIp" ], "Resource": [ "*" ], "Condition": {} }Grant permissions to the Worker RAM role of the cluster. For more information, see Step 2: Grant permissions to the Worker RAM role of the cluster.
Grant RAM permissions to an ACK dedicated cluster or an ACK managed cluster created before June 2020
Create a custom policy with the following content. For more information, see Step 1: Create a custom policy.
{ "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "vpc:DescribeVSwitches", "vpc:AllocateEipAddress", "vpc:DescribeEipAddresses", "vpc:AssociateEipAddress", "vpc:UnassociateEipAddress", "vpc:ReleaseEipAddress", "vpc:AddCommonBandwidthPackageIp", "vpc:RemoveCommonBandwidthPackageIp" ], "Resource": [ "*" ], "Condition": {} }On the AliyunCSManagedNetworkRole RAM role page, go to the Permissions tab and click Add Permissions. Then, click Custom Policy, select the custom policy that you created in the previous step, and click OK.
Step 2: Install or upgrade the plugin for the cluster
Do not enable the EIP configuration capabilities of both ack-extend-network-controller and Terway at the same time. This may cause EIP resources to be repeatedly allocated and lead to EIP binding failures. We recommend that you use the ack-extend-network-controller plugin.
Plugin comparison
Item | ack-extend-network-controller | Terway |
Supported cluster types |
|
|
Fixed EIP | Supported | Not supported |
Configuration phase | After a pod IP address is allocated, the controller allocates and attaches an EIP to the pod. | The EIP is allocated and attached during the CNI execution process. |
Supported versions | v0.2.0 or later | Later than or equal to v1.0.10.280-gdc2cb6c-aliyun, and earlier than v1.7.0 |
Install or upgrade the plugin
If you use the ack-extend-network-controller plugin, install it from the ACK App Marketplace and enable the EIP controller. If you use the Terway network plugin, upgrade Terway to version v1.0.10.280-gdc2cb6c-aliyun or later.
Install ack-extend-network-controller (recommended)
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the App Marketplace page, enter
ack-extend-network-controllerin the search box and click the application.On the application details page, click Deploy in the upper-right corner.
In the Create panel, select the cluster and namespace, and then click Next.
On the parameter configuration page, select a version number, set the parameters, and then click OK.
The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Type
Required
Description
clusterID
string
Yes
The cluster ID.
regionID
string
Yes
The ID of the zone where the cluster is deployed.
enableControllers
[]string
Yes
Set this parameter to
eipto enable the EIP feature.networkController.vpcid
string
Yes
The VPC ID of the cluster.
networkController.eipController.maxConcurrentReconciles
int
No
The number of concurrent EIP controllers.
networkController.eipController.garbageCollectionPeriodInMinutes
int
No
The period at which the EIP controller cleans up fixed EIPs.
customStatefulWorkloadKinds
[]string
No
The Kind of the custom stateful controller.
enableVirtualNode
bool
No
Specifies whether to support ECI virtual nodes.
ImportantIf you enable this parameter, the controller allocates EIPs to pods of ECI instances. The pod annotation that you configure cannot be the same as the EIP feature supported by ECI. Use this parameter with caution.
enableRRSA
bool
No
Authenticates requests using RRSA.
NoteSupported by ack-extend-network-controller v0.10.0 and later.
Only the ack-pod-identity-webhook injection method is supported for configuring RRSA. Configure the corresponding label for the kube-system namespace. For more information about the configuration, see Isolate pod permissions based on RRSA.
rrsaRoleName
string
No
The role name.
NoteSupported by ack-extend-network-controller v0.10.0 and later.
credential.accessKey
string
No
The AccessKey ID of the account that has the permissions to attach EIPs.
If you have completed Step 1: Configure RAM permissions for attaching EIPs, you do not need to configure this parameter.
ImportantThis configuration stores sensitive information in a Kubernetes Secret. This method is not recommended.
credential.accessSecret
string
No
The AccessKey secret of the account that has the permissions to attach EIPs.
If you have completed Step 1: Configure RAM permissions for attaching EIPs, you do not need to configure this parameter.
ImportantThis configuration stores sensitive information in a Kubernetes Secret. This method is not recommended.
kubeClientQPS
float32
No
The queries per second (QPS) limit for the component to access the cluster's API server.
NoteSupported by ack-extend-network-controller v0.12.2 and later.
kubeClientBurst
int
No
The maximum number of burst requests for the component to access the cluster's API server.
NoteSupported by ack-extend-network-controller v0.12.2 and later.
The following code provides a sample configuration:
clusterID: "c11ba338192xxxxxxx" regionID: "cn-hangzhou" vpcID: "vpc-bp1rkq0zxxxxxx" enableControllers: - eip networkController: eipController: maxConcurrentReconciles: 1 garbageCollectionPeriodInMinutes: 1 customStatefulWorkloadKinds: - foo credential: accessKey: "" accessSecret: ""
To update the version and parameters of the ack-extend-network-controller plugin, see Modify a Helm chart.
Upgrade Terway
Make sure that the cluster uses the Terway plugin, and then upgrade the Terway plugin (terway-eni or terway-eniip) to a version that supports the EIP feature. For more information about how to upgrade the Terway plugin, see Manage components.
The Terway plugin version must be v1.0.10.280-gdc2cb6c-aliyun or later, and earlier than v1.7.0. For more information about Terway plugin versions, see Terway.
Step 3: Enable the EIP feature
Introduction to annotations for enabling EIPs
ACK lets you use annotations to enable the EIP feature. You can choose to automatically allocate EIPs or assign fixed EIPs to pods based on your requirements.
Automatically allocate an EIP
When you use the automatic EIP allocation feature, EIP resources may be repeatedly requested and released if a pod is rebuilt or Container Network Interface (CNI) execution fails. To prevent this issue, you can specify an EIP instance.
Pod Annotations | Value |
network.alibabacloud.com/pod-with-eip k8s.aliyun.com/pod-with-eip | Specifies whether to automatically create and attach an EIP. Valid values:
|
k8s.aliyun.com/eci-with-eip (compatible) | |
network.alibabacloud.com/eip-bandwidth k8s.aliyun.com/eip-bandwidth | Supported only when you create an EIP. The peak bandwidth of the EIP. Unit: Mbit/s. For more information, see Request an EIP. |
network.alibabacloud.com/eip-internet-charge-type k8s.aliyun.com/eip-internet-charge-type | Supported only when you create an EIP. The metering method of the EIP. Valid values:
For more information, see Request an EIP. |
k8s.aliyun.com/eip-charge-type (compatible) | |
network.alibabacloud.com/eip-instance-charge-type k8s.aliyun.com/eip-instance-charge-type | Supported only when you create an EIP. The billing method of the EIP. Valid values:
For more information, see Request an EIP. Note Supported only in ack-extend-network-controller. The PrePaid subscription configuration is not supported. |
network.alibabacloud.com/eip-common-bandwidth-package-id k8s.aliyun.com/eip-common-bandwidth-package-id | Attaches an existing Internet Shared Bandwidth instance. Note The Terway plugin must be v1.2.3 or later. No version limit applies to the ack-extend-network-controller plugin. |
network.alibabacloud.com/eip-isp k8s.aliyun.com/eip-isp | Supported only when you create an EIP. The line type of the EIP. Valid values:
For more information, see Request an EIP. Note The Terway plugin must be v1.2.3 or later. No version limit applies to the ack-extend-network-controller plugin. |
network.alibabacloud.com/eip-public-ip-address-pool-id k8s.aliyun.com/eip-public-ip-address-pool-id | Supported only when you create an EIP. The EIP address pool. For more information about the limits and steps for using EIP address pools, see Create and manage IP address pools. Note Supported only in ack-extend-network-controller. |
network.alibabacloud.com/eip-resource-group-id k8s.aliyun.com/eip-resource-group-id | Supported only when you create an EIP. The EIP resource group. For more information, see Request an EIP. Note Supported only by ack-extend-network-controller v0.4.0 and later. |
network.alibabacloud.com/eip-name k8s.aliyun.com/eip-name | Supported only when you create an EIP. The EIP name. For more information, see Request an EIP. Note Supported only by ack-extend-network-controller v0.6.0 and later. |
network.alibabacloud.com/eip-description k8s.aliyun.com/eip-description | Supported only when you create an EIP. The EIP description. For more information, see Request an EIP. Note Supported only by ack-extend-network-controller v0.6.0 and later. |
network.alibabacloud.com/eip-security-protection-types k8s.aliyun.com/eip-security-protection-types | Supported only when you create an EIP. The security protection level of the EIP. Anti-DDoS Proxy-enabled EIPs are supported. If you configure multiple levels, separate them with commas ( Note Supported only by ack-extend-network-controller v0.9.0 and later. |
network.alibabacloud.com/eip-tags k8s.aliyun.com/eip-tags | Supported only when you create an EIP. The EIP tag configuration. The value must be in a valid JSON format. For more information, see Manage tags. Example: Note Supported only by ack-extend-network-controller v0.11.0 and later. |
Specify an EIP instance
You can attach an existing EIP by specifying its instance ID. The pod annotation does not modify the EIP instance configuration. The annotation only attaches the EIP to the specified pod.
This feature is not applicable to multi-replica controllers. Make sure that only one pod references the EIP instance. We recommend that you use this feature only with a stateful application StatefulSet.
Pod Annotations | Value |
network.alibabacloud.com/pod-eip-instanceid k8s.aliyun.com/pod-eip-instanceid | Uses the specified EIP. Enter the EIP instance ID. For example, eip-bp14qxxxxxxx. Important Avoid allocating the same EIP instance to pods with different names. The EIP controller detaches the EIP after the pod exits. During this period, you cannot use the same EIP instance in a new container. You can check whether a Pod EIP resource with the same name as the pod exists to determine if the pod and EIP have been detached. |
k8s.aliyun.com/eci-eip-instanceid (compatible) |
Introduction to annotations for setting the EIP release policy
A fixed EIP ensures that a pod continues to use the same EIP address after the pod is rebuilt. This policy can be combined with the automatic EIP allocation feature for fixed EIPs in stateful applications.
This feature is supported only by ack-extend-network-controller and only for stateful replica controllers. It cannot be used for stateless controllers.
If you specify an EIP instance ID, the EIP instance is not released.
Pod Annotation | Value |
network.alibabacloud.com/pod-eip-release-strategy k8s.aliyun.com/pod-eip-release-strategy | The release policy for the Pod EIP. Valid values:
You can directly configure an expiration time. Go-type time expressions are supported. For example, |
Enable EIP in an ack-extend-network-controller or Terway cluster
Enable in ack-extend-network-controller
ack-extend-network-controller needs to access Alibaba Cloud OpenAPI to create resources. You must configure the required permissions in RAM. Then, you can install ack-extend-network-controller from the App Marketplace and use an annotation to create and associate an EIP with a specified pod.
Create and associate an EIP with a specified pod using an annotation
You can create or associate an EIP with a pod by specifying an annotation in the pod. For more information about annotations, see the FAQ section in this topic.
Create an application, and create and associate an EIP with a specified pod.
Deployment
Use the following example to create a deployment. An EIP instance with a bandwidth of 5 Mbit/s is automatically allocated to each pod.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: example labels: app: example spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: example template: metadata: labels: app: example annotations: k8s.aliyun.com/pod-with-eip: "true" k8s.aliyun.com/eip-bandwidth: "5" spec: readinessGates: - conditionType: "k8s.aliyun.com/eip" containers: - name: example image: nginxAfter the pod is created, you can query the
podeips.alibabacloud.comresource that has the same name as the pod to track information about the allocated EIP.kubectl get podeip -n <namespace> <podname> -o yamlExpected output:
apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1beta1 kind: PodEIP metadata: creationTimestamp: "2023-12-15T04:25:37Z" finalizers: - podeip-controller.alibabacloud.com/finalizer generation: 1 name: example-xxx namespace: default resourceVersion: "222800" uid: 43xxx-f1xx-4xxx-b3xx-969faxxx spec: allocationID: eip-2ze2qe8zsxxx allocationType: releaseStrategy: Follow type: Auto status: eipAddress: 39.102.XX.XX internetChargeType: PayByTraffic isp: BGP networkInterfaceID: eni-2zeagv8f3xxxx podLastSeen: "2023-12-15T05:18:47Z" privateIPAddress: 192.168.XX.XX resourceGroupID: rg-acfmwxxxxxsq status: InUseStatefulset
Use the following example to create a StatefulSet resource. Two pods are created, and an EIP instance is automatically allocated to each pod. The release policy is set to delete the PodEIP 10 minutes after the pod is deleted.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: example labels: app: example spec: serviceName: "example" replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: example template: metadata: labels: app: example annotations: k8s.aliyun.com/pod-with-eip: "true" k8s.aliyun.com/pod-eip-release-strategy: "10m" spec: containers: - name: example image: nginxAfter the pod is created, you can retrieve the allocated EIP information from the
podeips.alibabacloud.comresource that has the same name as the pod.kubectl get podeip -n <namespace> -o yamlExpected output:
apiVersion: v1 items: - apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1beta1 kind: PodEIP metadata: creationTimestamp: "2023-12-15T03:28:01Z" finalizers - podeip-controller.alibabacloud.com/finalizer generation: 1 name: example-0 namespace: default resourceVersion: "227221" uid: 79954xx-17xx-4dxx-b7xx-15b84xxx spec: allocationID: eip-2ze08metxxx allocationType: releaseAfter: 10m releaseStrategy: TTL type: Auto status: eipAddress: 39.105.XX.XX internetChargeType: PayByTraffic isp: BGP networkInterfaceID: eni-2ze4tkg4xxx podLastSeen: "2023-12-15T05:31:34Z" privateIPAddress: 192.168.XX.XX resourceGroupID: rg-acfmwxxx status: InUse - apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1beta1 kind: PodEIP metadata: creationTimestamp: "2023-12-15T03:28:03Z" finalizers: - podeip-controller.alibabacloud.com/finalizer generation: 1 name: example-1 namespace: default resourceVersion: "227222" uid: 1339xxxe7-97xx-46xx-9bxx-537690xxx spec: allocationID: eip-2zetwhffqxxx allocationType: releaseAfter: 10m releaseStrategy: TTL type: Auto status: eipAddress: 39.105.XX.XX internetChargeType: PayByTraffic isp: BGP networkInterfaceID: eni-2zeagv8f3wxxx podLastSeen: "2023-12-15T05:31:34Z" privateIPAddress: 192.168.XX.XX resourceGroupID: rg-acfmwqnwxxx status: InUse - apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1beta1 kind: PodEIP metadata: creationTimestamp: "2023-12-15T04:25:37Z" finalizers: - podeip-controller.alibabacloud.com/finalizer generation: 1 name: example-5bxxx-9xx namespace: default resourceVersion: "227220" uid: 43cdfxxx-f1xx-42xx-b3xx-969fxxx spec: allocationID: eip-2ze2qe8zsmnxxx allocationType: releaseStrategy: Follow type: Auto status: eipAddress: 39.102.XX.XX internetChargeType: PayByTraffic isp: BGP networkInterfaceID: eni-2zeagv8f3wxxx podLastSeen: "2023-12-15T05:31:34Z" privateIPAddress: 192.168.XX.XX publicIpAddressPoolID: pippool-2ze498cxxx resourceGroupID: rg-acfmwqnxxx status: InUse kind: List metadata: resourceVersion: ""After a pod from a stateful application is deleted, its corresponding PodEIP custom resource (CR) is retained for 10 minutes before being deleted. If a pod with the same name is created during this time, it will reuse the EIP.
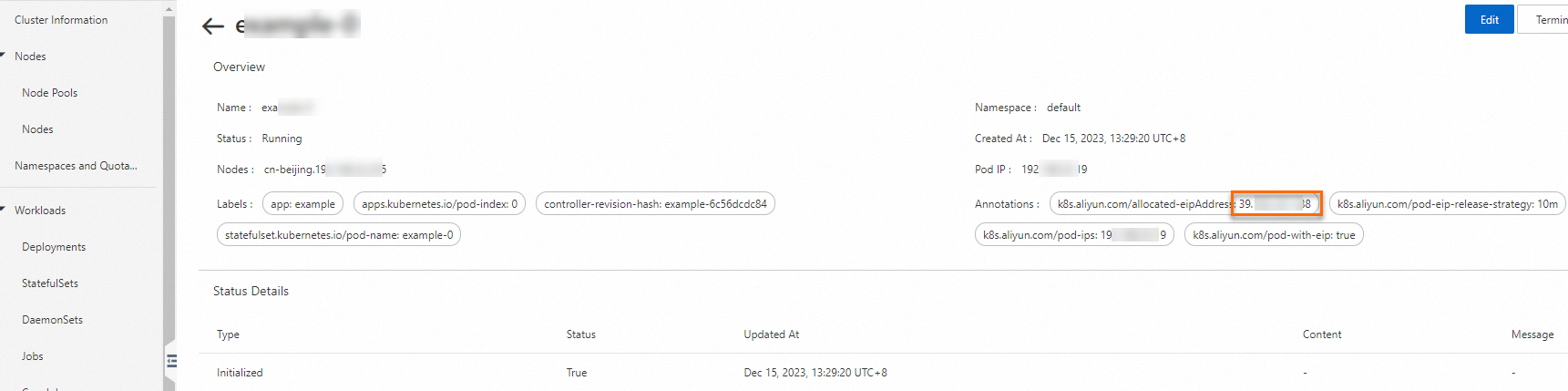
Verify the configuration.
After the pod enters the Running state, you can check the value of the k8s.aliyun.com/allocated-eipAddress annotation in the pod to view its associated EIP address. You can then access the pod using this EIP.
Enable in Terway
Configure Terway to support the EIP feature.
Modify the Terway ConfigMap.
kubectl edit cm eni-config -n kube-systemAdd the following content to eni_conf.
"enable_eip_pool": "true"NoteIf you want to forcibly detach a previous instance when you specify an EIP, you must also add the "allow_eip_rob": "true" parameter to eni_conf.
After you modify the file, press the Esc key, enter :wq!, and then press the Enter key to save the modified configuration file and exit edit mode.
Recreate the Terway instance.
kubectl delete pod -n kube-system -l app=terway-eniip # If you installed the terway-eni component, replace terway-eniip with terway-eni.
Use an annotation to create and associate an EIP with a pod.
You can create or associate an EIP with a pod by specifying an annotation in the pod. For more information about EIP limits, see Limits.
Configure annotations for different scenarios as follows:
Automatic EIP allocation scenario
Add the following annotations to automatically allocate an EIP to a pod and specify the bandwidth of the EIP.
k8s.aliyun.com/pod-with-eip: "true": Allocates an independent public EIP to the target pod.k8s.aliyun.com/eip-bandwidth: "5": Specifies the bandwidth of the EIP. The default bandwidth is 5 Mbit/s, which is the same as the default value for EIPs.
The following code provides a sample YAML file.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nginx-deployment-basic labels: app: nginx spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: annotations: network.alibabacloud.com/pod-with-eip: "true" # Automatically allocate a public EIP address to the Nginx container. network.alibabacloud.com/eip-bandwidth: "5" # Specify the bandwidth of the EIP. The default bandwidth is 5 Mbit/s, which is consistent with the default value for EIPs. labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginxSpecify EIP scenario
ImportantA single EIP cannot be associated with multiple pods. Therefore, this scenario is not applicable to deployments and StatefulSets.
By default, if the EIP is already attached to an instance, the EIP cannot be attached to the pod. If you want to detach the EIP from the previous instance before you attach it to the new one, you must configure "allow_eip_rob": "true" in the ConfigMap as described in the preceding step.
You can specify an EIP instance ID only for single-replica instances. For example, a deployment cannot have more than one replica.
Add the following annotation to specify an EIP instance ID for a pod:
k8s.aliyun.com/pod-eip-instanceid: "<youreipInstanceId>"Verify the configuration.
After the pod enters the Running state, you can check the value of the network.alibabacloud.com/allocated-eipAddress annotation in the pod to view its associated EIP address. You can then access the pod using this EIP.
FAQ
Why does a pod become Ready?
The controller configures the EIP address for the pod after the pod IP address is allocated. The pod may enter the Ready state before the EIP is successfully attached. You can use the following methods to control when the pod enters the Ready state.
Configure readiness gates for the pod
Configuring readiness gates for a pod is supported only by ack-extend-network-controller.
After you configure readinessGates in the pod, the controller sets the pod conditions after the EIP is successfully attached. The pod does not enter the Ready state until the EIP is attached.
kind: Pod
...
spec:
readinessGates:
- conditionType: "k8s.aliyun.com/eip"
status:
conditions:
- lastProbeTime: "2022-12-12T03:45:48Z"
lastTransitionTime: "2022-12-12T03:45:48Z"
reason: Associate eip succeed
status: "True"
type: k8s.aliyun.com/eip
...Configure an init container for the pod
You can configure an init container for the pod. In the init container, you can check whether the EIP has been successfully allocated. For more information, see the following example.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: example
annotations:
network.alibabacloud.com/pod-with-eip: "true"
spec:
containers:
- name: example
image: busybox:1.28
command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo The app is running! && sleep 3600']
initContainers:
- name: init
image: busybox:1.28
command: ['timeout', '-t' ,'60', 'sh','-c', "until grep -E '^k8s.aliyun.com\\/allocated-eipAddress=\\S?[0-9]+\\S?' /etc/podinfo/annotations; do echo waiting for annotations; sleep 2; done"]
volumeMounts:
- name: podinfo
mountPath: /etc/podinfo
volumes:
- name: podinfo
downwardAPI:
items:
- path: "labels"
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.labels
- path: "annotations"
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.annotationsWhy can't I access the pod using the EIP?
This issue is usually caused by access control list (ACL) rules. Check the following access control policies:
Cloud Firewall: EIPs are subject to the access control rules of Cloud Firewall. You must allow inbound and outbound traffic for the EIP and the business port that is used by the pod in Cloud Firewall. For more information, see Configure an access control policy for the Internet border.
Node security group: After an EIP is attached to a pod, traffic that passes through the EIP is still subject to the security group policy of the node on which the pod is located. Make sure that the IP address of the client is allowed for inbound and outbound traffic in the security group of the node, and that the business port of the pod is open. For more information, see Configure cluster security groups.