
We believe that Context Length Scaling and Total Parameter Scaling are two major trends in the future of large models. To further improve training and inference efficiency under long-context and large-parameter settings, we design a brand-new model architecture called Qwen3-Next.Compared to the MoE structure of Qwen3, Qwen3-Next introduces several key improvements: a hybrid attention mechanism, a highly sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) structure, training-stability-friendly optimizations, and a multi-token prediction mechanism for faster inference.
Based on this new architecture, we train the Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Base model — an 80-billion-parameter model that activates only 3 billion parameters during inference. This base model achieves performance comparable to (or even slightly better than) the dense Qwen3-32B model, while using less than 10% of its training cost (GPU hours). In inference, especially with context lengths over 32K tokens, it delivers more than 10x higher throughput — achieving extreme efficiency in both training and inference.
We develop and release two post-trained versions based on Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Base: Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct and Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Thinking. We solve the long-standing stability and efficiency issues in reinforcement learning (RL) training caused by the hybrid attention + high-sparsity MoE architecture. This led to improvements in both RL training speed and final performance.
The Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct performs comparably to our flagship model Qwen3-235B-A22B-Instruct-2507, and shows clear advantages in tasks requiring ultra-long context (up to 256K tokens). The Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Thinking excels at complex reasoning tasks — outperforming higher-cost models like Qwen3-30B-A3B-Thinking-2507 and Qwen3-32B-Thinking, outpeforming the closed-source Gemini-2.5-Flash-Thinking on multiple benchmarks, and approaching the performance of our top-tier model Qwen3-235B-A22B-Thinking-2507.
We have already released Qwen3-Next on Hugging Face and ModelScope. Additionally, everyone can use the Qwen3-Next service via Alibaba Cloud Model Studio and NVIDIA API Catalog.
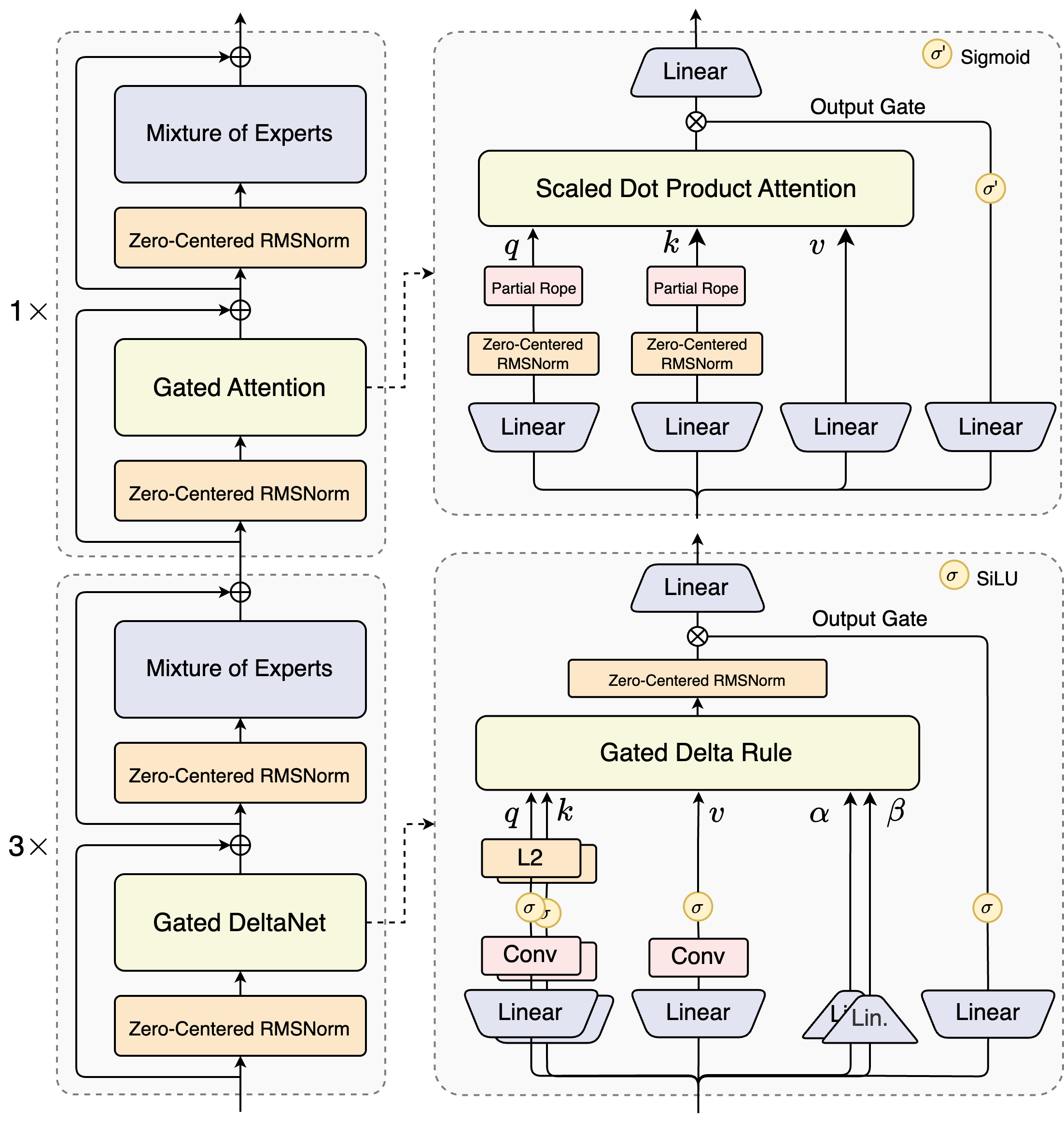
Linear attention breaks the quadratic complexity of standard attention and is more efficient for long contexts. However, we find that using only linear attention or only standard attention has limitations: linear attention is fast but weak at recall; standard attention is expensive and slow during inference.
Through systematic experiments, we find that Gated DeltaNet [1] offers stronger in-context learning ability than commonly used methods like Sliding Window Attention or Mamba2. When we mix Gated DeltaNet with standard attention at a 3:1 ratio (75% layers use Gated DeltaNet, 25% keep standard attention), the model consistently outperforms any monolithic architecture — achieving both better performance and higher efficiency.
In the standard attention layers, we add several enhancements:
Qwen3-Next uses a highly sparse MoE design: 80B total parameters, but only ~3B activated per inference step. Experiments show that, with global load balancing [4], increasing total expert parameters while keeping activated experts fixed steadily reduces training loss.
Compared to Qwen3’s MoE (128 total experts, 8 routed), Qwen3-Next expands to 512 total experts, combining 10 routed experts + 1 shared expert — maximizing resource usage without hurting performance.
We found that the attention output gating mechanism helps eliminate issues like Attention Sink [5] and Massive Activation [6] , ensuring numerical stability across the model.
In Qwen3, we use QK-Norm, but notice some layer norm weights become abnormally large. To fix this and further improve stability, Qwen3-Next adopts Zero-Centered RMSNorm [7], and applies weight decay to norm weights to prevent unbounded growth.
We also normalize MoE router parameters during initialization [8] , ensuring each expert is unbiasedly selected early in training — reducing noise from random initialization.
These stability-focused designs make small-scale experiments more reliable and help large-scale training run smoothly.
Qwen3-Next introduces a native Multi-Token Prediction (MTP) 3[10] mechanism, which not only yields an MTP module with a high acceptance rate for Speculative Decoding but also enhances the overall performance.Additionally, Qwen3-Next specifically optimizes the multi-step inference performance of MTP, further improving the acceptance rate of Speculative Decoding in real scenarios through multi-step training that maintains consistency between training and inference.
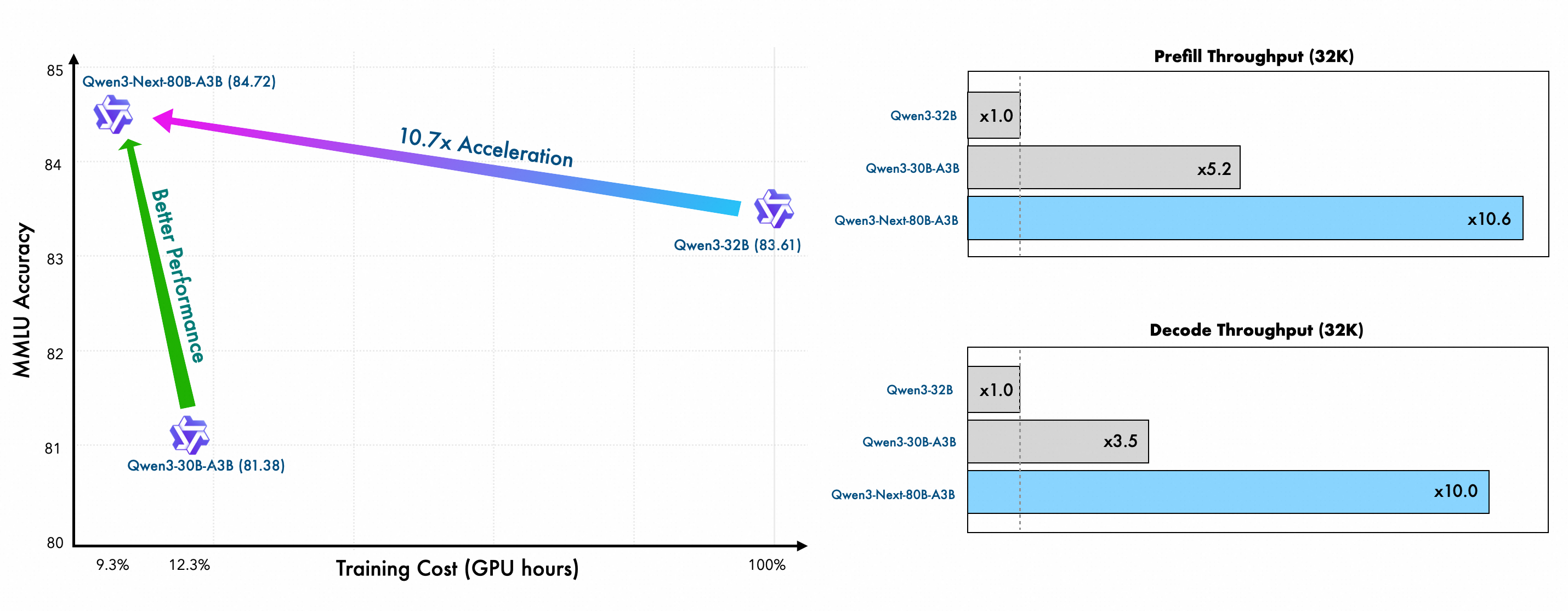
Qwen3-Next is trained on a uniformly sampled subset (15T tokens) of Qwen3’s 36T-token pretraining corpus. It uses less than 80% of the GPU hours needed by Qwen3-30A-3B, and only 9.3% of the compute cost of Qwen3-32B — while achieving better performance. This shows outstanding training efficiency and value.
Thanks to its hybrid architecture, Qwen3-Next also shines in inference:
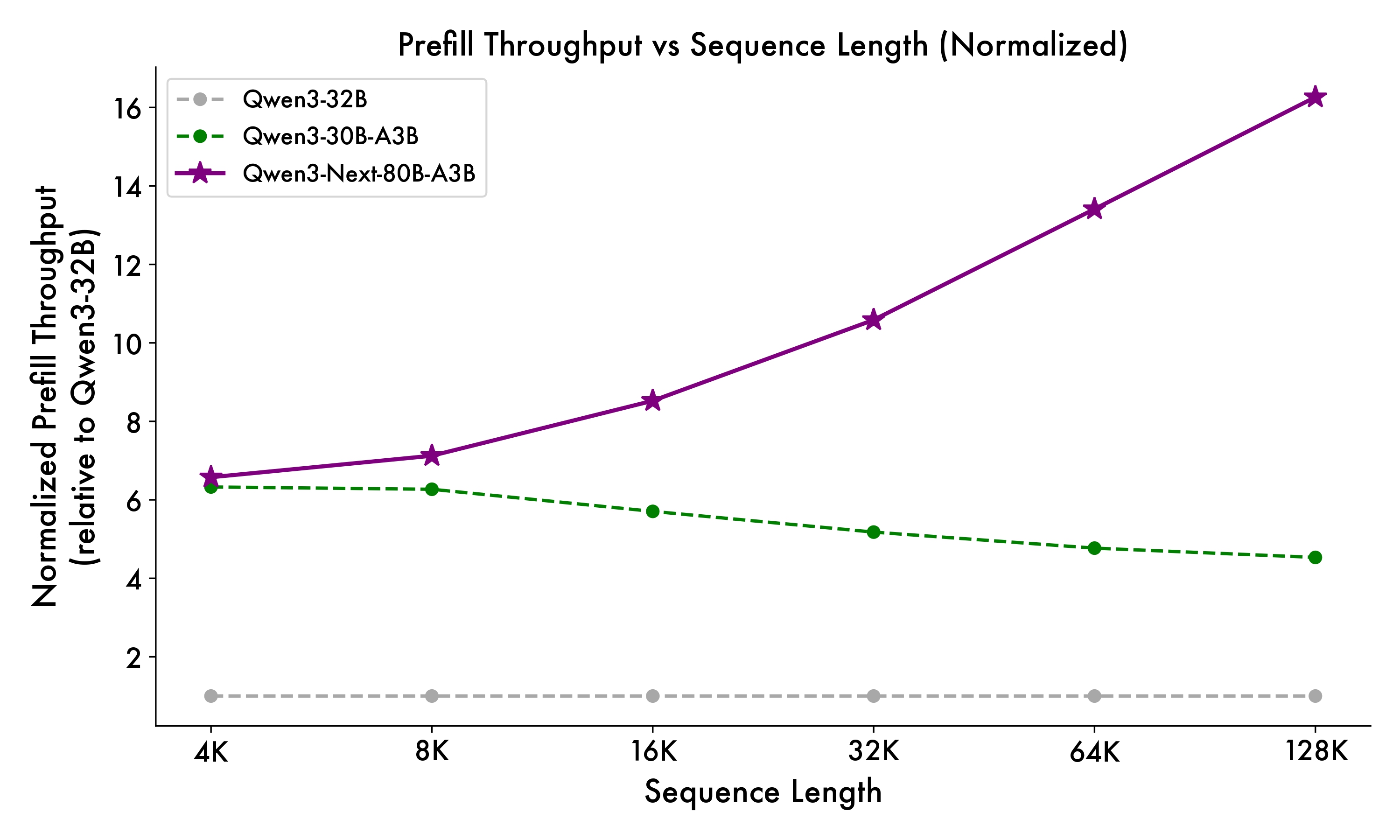
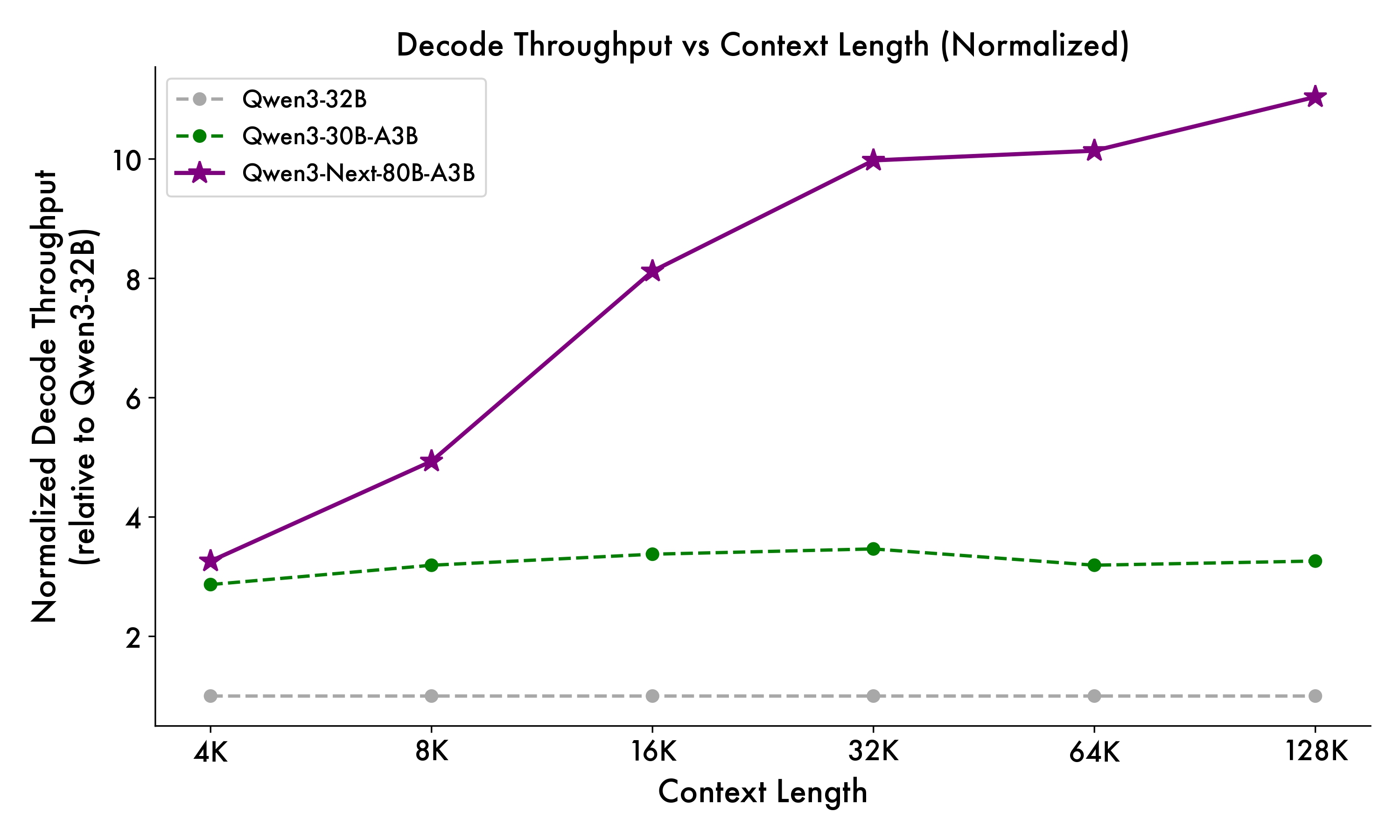
Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Base activates only 1/10th of the non-embedding parameters used by Qwen3-32B-Base — yet outperforms it on most benchmarks, and significantly beats Qwen3-30B-A3B. This demonstrates exceptional efficiency and strong performance.
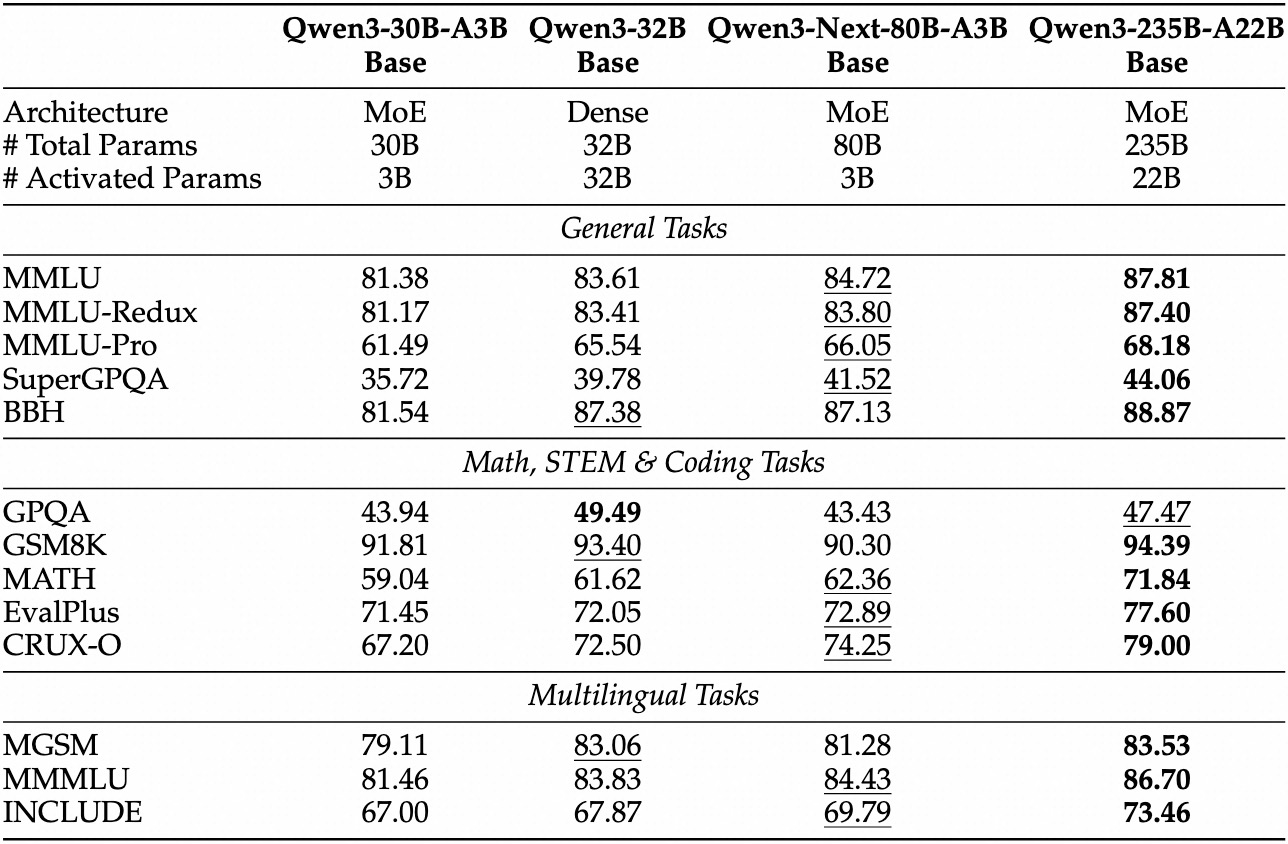
Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct significantly outperforms Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507 and Qwen3-32B-Non-thinking, and achieves results nearly matching our flagship Qwen3-235B-A22B-Instruct-2507.
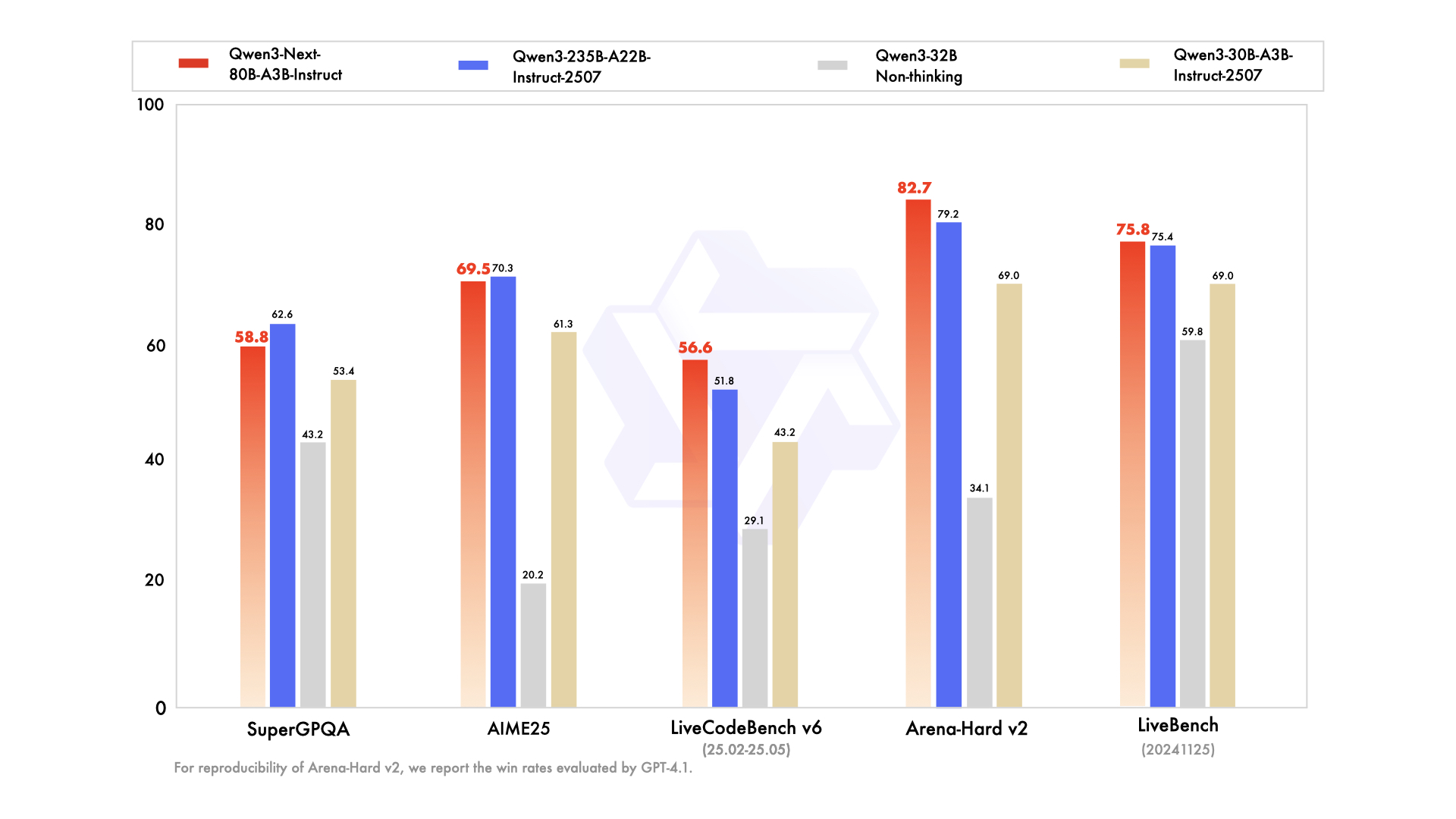
On RULER, Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct outperforms Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507 (which has more attention layers) across all lengths — and even beats Qwen3-235B-A22B-Instruct-2507 (which has more layers overall) within 256K context. This proves the strength of the Gated DeltaNet + Gated Attention hybrid design for long-context tasks.
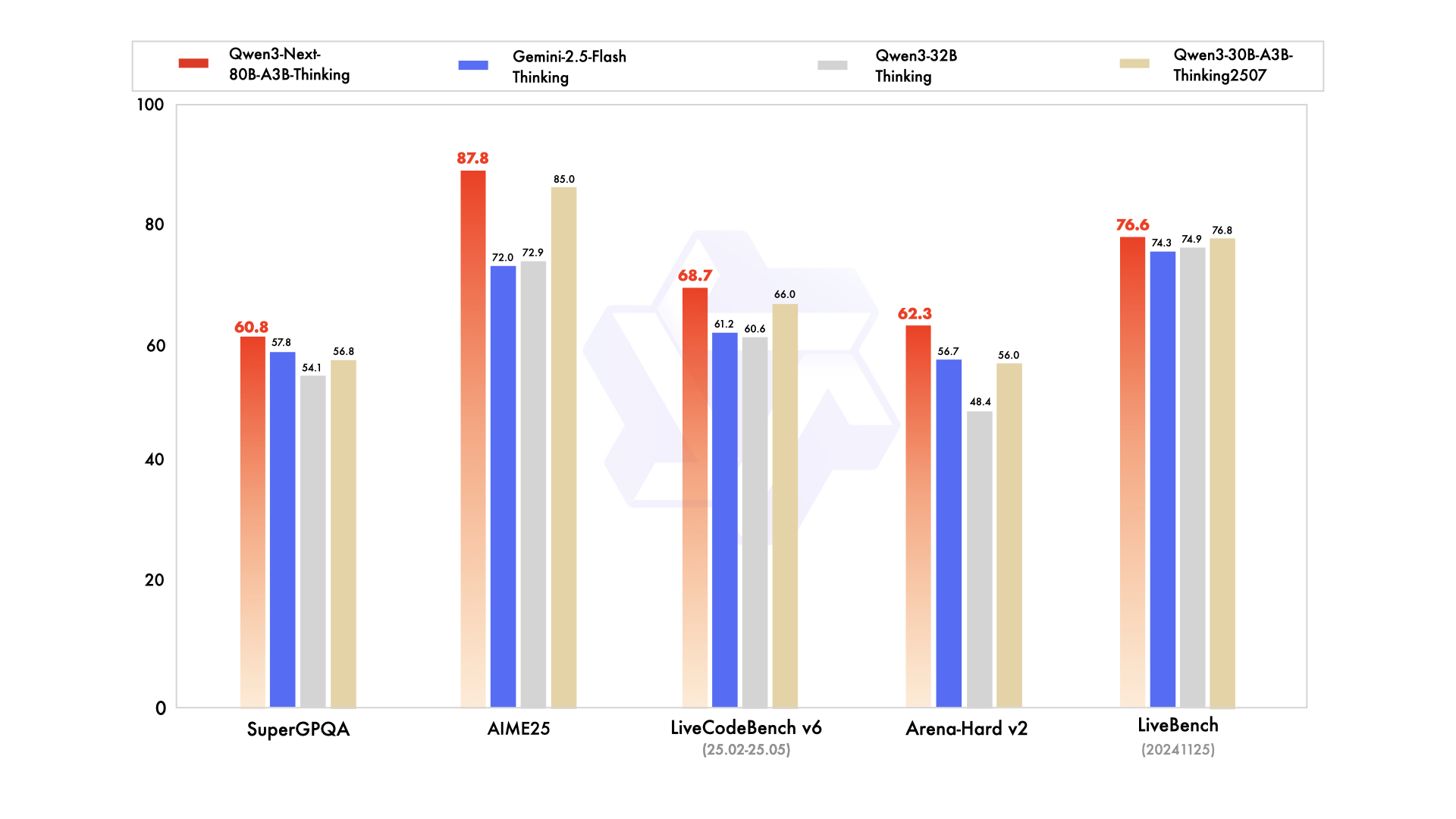
Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Thinking outperforms higher-cost models like Qwen3-30B-A3B-Thinking-2507 and Qwen3-32B-Thinking. It beats the closed-source Gemini-2.5-Flash-Thinking on multiple benchmarks, and comes close to our latest flagship model Qwen3-235B-A22B-Thinking-2507 on key metrics.
All examples below are based on the Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct version. For the Thinking model, please refer to https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Thinking
The code for Qwen3-Next has been merged into the main branch of Hugging Face transformers.
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@mainWith earlier versions, you will encounter the following error:
KeyError: 'qwen3_next'The following contains a code snippet illustrating how to use the model generate content based on given inputs.
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct"
# load the tokenizer and the model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
dtype="auto",
device_map="auto",
)
# prepare the model input
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=16384,
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print("content:", content)Note:
Note:
Tip
For deployment, you can use the latest sglang or vllm to create an OpenAI-compatible API endpoint.
SGLang is a fast serving framework for large language models and vision language models. SGLang could be used to launch a server with OpenAI-compatible API service.
SGLang has supported Qwen3-Next in its main branch, which can be installed from source:
pip install 'sglang[all] @ git+https://github.com/sgl-project/sglang.git@main#subdirectory=python'The following command can be used to create an API endpoint at http://localhost:30000/v1 with maximum context length 256K tokens using tensor parallel on 4 GPUs.
SGLANG_ALLOW_OVERWRITE_LONGER_CONTEXT_LEN=1 python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct --port 30000 --tp-size 4 --context-length 262144 --mem-fraction-static 0.8The following command is recommended for MTP with the rest settings the same as above:
SGLANG_ALLOW_OVERWRITE_LONGER_CONTEXT_LEN=1 python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct --port 30000 --tp-size 4 --context-length 262144 --mem-fraction-static 0.8 --speculative-algo NEXTN --speculative-num-steps 3 --speculative-eagle-topk 1 --speculative-num-draft-tokens 4Note
Note
vLLM is a high-throughput and memory-efficient inference and serving engine for LLMs. vLLM could be used to launch a server with OpenAI-compatible API service.
vLLM has supported Qwen3-Next in its main branch, which can be installed from source:
pip install vllm --pre --extra-index-url https://wheels.vllm.ai/nightlyThe following command can be used to create an API endpoint at http://localhost:8000/v1 with maximum context length 256K tokens using tensor parallel on 4 GPUs.
VLLM_ALLOW_LONG_MAX_MODEL_LEN=1 vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct --port 8000 --tensor-parallel-size 4 --max-model-len 262144The following command is recommended for MTP with the rest settings the same as above:
VLLM_ALLOW_LONG_MAX_MODEL_LEN=1 vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct --port 8000 --tensor-parallel-size 4 --max-model-len 262144 --speculative-config '{"method":"qwen3_next_mtp","num_speculative_tokens":2}'Note
Note
Qwen3 excels in tool calling capabilities. We recommend using Qwen-Agent to make the best use of agentic ability of Qwen3. Qwen-Agent encapsulates tool-calling templates and tool-calling parsers internally, greatly reducing coding complexity.
To define the available tools, you can use the MCP configuration file, use the integrated tool of Qwen-Agent, or integrate other tools by yourself.
from qwen_agent.agents import Assistant
# Define LLM
llm_cfg = {
'model': 'Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct',
# Use a custom endpoint compatible with OpenAI API:
'model_server': 'http://localhost:8000/v1', # api_base
'api_key': 'EMPTY',
}
# Define Tools
tools = [
{'mcpServers': { # You can specify the MCP configuration file
'time': {
'command': 'uvx',
'args': ['mcp-server-time', '--local-timezone=Asia/Shanghai']
},
"fetch": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["mcp-server-fetch"]
}
}
},
'code_interpreter', # Built-in tools
]
# Define Agent
bot = Assistant(llm=llm_cfg, function_list=tools)
# Streaming generation
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': 'https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/ Introduce the latest developments of Qwen'}]
for responses in bot.run(messages=messages):
pass
print(responses)Qwen3-Next natively supports context lengths of up to 262,144 tokens. For conversations where the total length (including both input and output) significantly exceeds this limit, we recommend using RoPE scaling techniques to handle long texts effectively. We have validated the model's performance on context lengths of up to 1 million tokens using the YaRN method.
YaRN is currently supported by several inference frameworks, e.g., transformers, vllm and sglang. In general, there are two approaches to enabling YaRN for supported frameworks:
In the config.json file, add the rope_scaling fields:
{
...,
"rope_scaling": {
"rope_type": "yarn",
"factor": 4.0,
"original_max_position_embeddings": 262144
}
}VLLM_ALLOW_LONG_MAX_MODEL_LEN=1 vllm serve ... --rope-scaling '{"rope_type":"yarn","factor":4.0,"original_max_position_embeddings":262144}' --max-model-len 1010000For sglang, you can use
SGLANG_ALLOW_OVERWRITE_LONGER_CONTEXT_LEN=1 python -m sglang.launch_server ... --json-model-override-args '{"rope_scaling":{"rope_type":"yarn","factor":4.0,"original_max_position_embeddings":262144}}' --context-length 1010000NOTE:
Qwen3-Next represents a major leap forward in model architecture, introducing innovations in attention mechanisms, including linear attention and attention gate, as well as increased sparsity in its MoE design. Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B delivers performance on par with the larger Qwen3-235B-A22B-2507 across both thinking and non-thinking modes, while offering significantly faster inference, especially in long-context scenarios. With this release, we aim to empower the open-source community to evolve alongside cutting-edge architectural advances. Looking ahead, we will further refine this architecture to develop Qwen3.5, targeting unprecedented levels of intelligence and productivity.
Original source: https://qwen.ai/blog?id=3425e8f58e31e252f5c53dd56ec47363045a3f6b&from=research.research-list
NBA China and Alibaba Cloud Announce Multiyear Collaboration to Reimagine Fan Engagement

1,354 posts | 481 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - September 12, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - September 16, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - February 17, 2026
ApsaraDB - February 4, 2026
Alibaba Cloud Community - February 5, 2026
Alibaba Cloud Community - February 5, 2026

1,354 posts | 481 followers
Follow Container Compute Service (ACS)
Container Compute Service (ACS)
A cloud computing service that provides container compute resources that comply with the container specifications of Kubernetes
Learn More Container Service for Kubernetes
Container Service for Kubernetes
Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes is a fully managed cloud container management service that supports native Kubernetes and integrates with other Alibaba Cloud products.
Learn More Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Top-performance foundation models from Alibaba Cloud
Learn More Alibaba Cloud for Generative AI
Alibaba Cloud for Generative AI
Accelerate innovation with generative AI to create new business success
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Community