By Jiang Jiangwei (Xiaoxie), VP of Alibaba Group and Head of Smart Infrastructure Product Division.
It is now a common practice for enterprises to digitize and migrate their businesses to the cloud. 5G, industrial internet, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing are the primary constituents of the digital economy and will become the major components of China's new infrastructure. The cloud will bring revolutionary changes in research and development (R&D) and operations and maintenance (O&M) across IT departments. This article is based on the video of Jiang Jiangwei's speech, where he introduces Alibaba's internet-oriented and cloud-oriented R&D model.
E-commerce and cloud architectures have evolved along the same lines in order to achieve two goals. First, from the R&D perspective, the goal is to make system R&D methods like server R&D. For example, when adding a server for customer access, transaction, commodity, and user systems, we want to simply configure the IP address to launch the server and obtain its computing capabilities. Second, from the O&M perspective, we want to manage hundreds of thousands of servers just as a single server. Therefore, from both perspectives, we hope to use and manage several servers as a single server through the continuous evolution of R&D.
Now with cloud migration as an inevitable trend, developers have three basic concerns.
Resource budgets were often inaccurately evaluated. Especially when businesses were growing at a high speed, some may suddenly exceed estimated budgets, for example, due to advertising business growth. In this case, middleware resources are needed. If resource budgets are accurate, the O&M personnel or resource supply staff may provide resources according to the budget. However, resource budget cycles were measured in weeks, which was not a refined granularity. More resources are required when the resource budget is insufficient. The additional resource needs had to be evaluated, approved at each level of the company, and the purpose of the resource use needed to be explained. This created a great deal of difficulty for engineers.
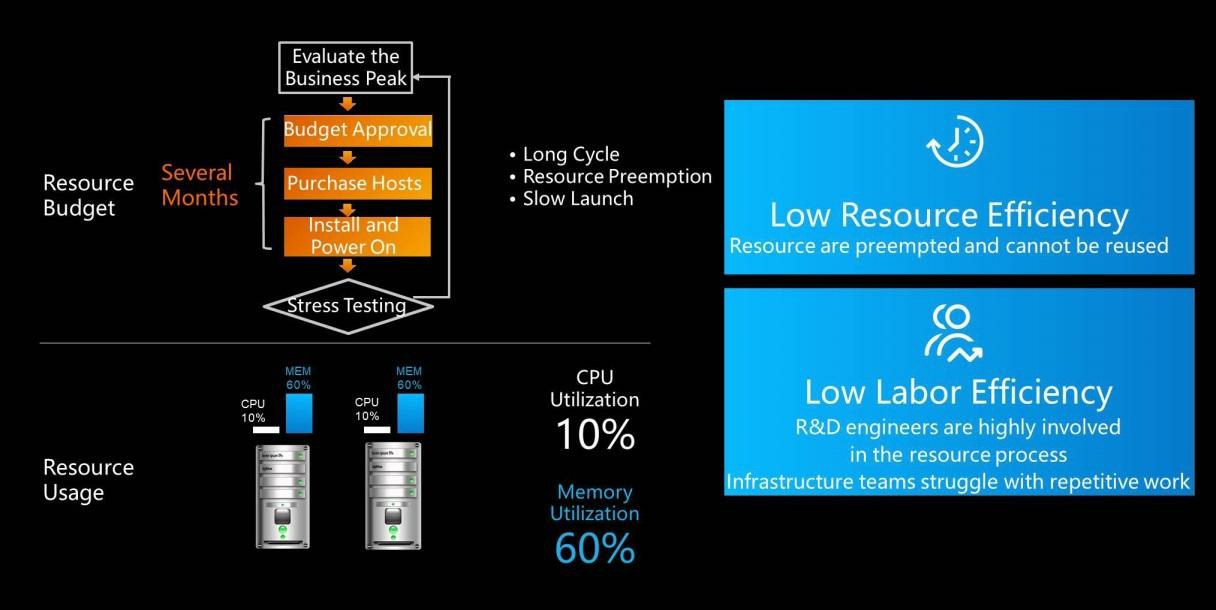
Inaccurate resource forecasts were the norm. Improper resource forecasting used to create problems that engineers must pay attention to while purchasing and using resources. In fact, resource utilization measured across different departments or applications was very low. For example, message-oriented middleware would lack resources due to the sudden increase in message usage by a service. However, the other systems might have a lot of resources at such times, so the overall system load would be very low, and it was difficult to allow resources to be used across systems. With no centralized resource scheduling capabilities, business departments could only manage and use their own resources. As a result, the overall online system resource utilization was low. However, due to the difficulty of recycling and borrowing resources, departments were unwilling to release resources to each other.
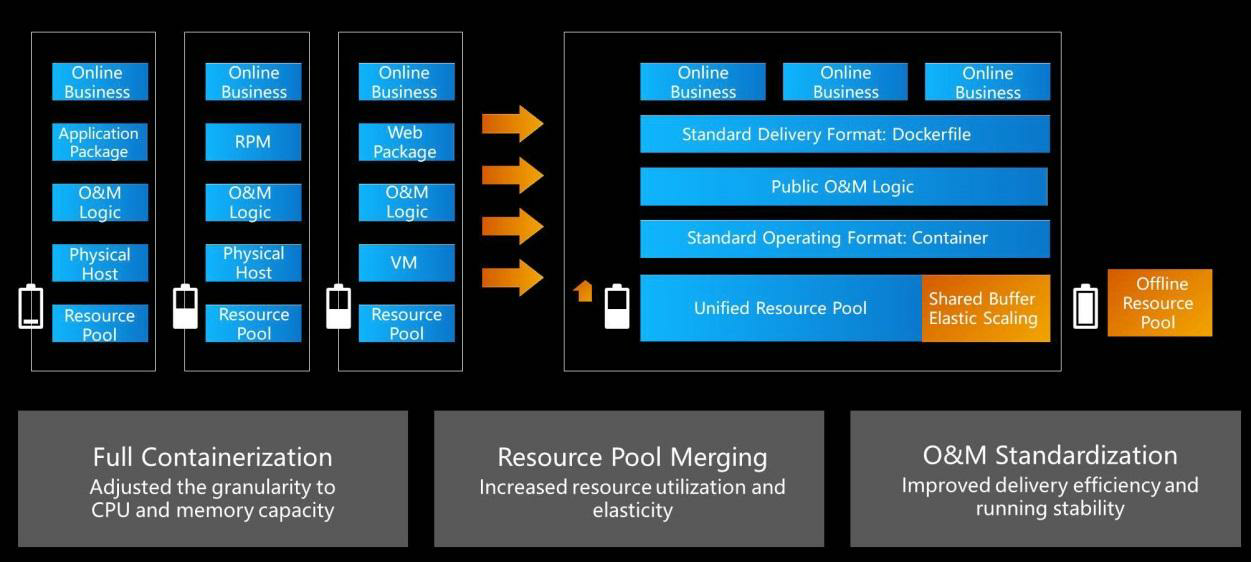
Full containerization is a prerequisite for centralized resource scheduling. We hoped that different applications, systems, middleware, and caches could run in containers to make centralized resource scheduling possible. After resource pools are merged, all resources get allocated and scheduled through the resource pool. Full containerization and resource pool merging allowed centralized scheduling of global resources. This solved the problem of resource sharing among different business units and improved resource and inventory utilization. Different business units, such as transaction, search, and cross-industry businesses, have different peak values and times. Therefore, merging the resource pool allowed us to provide ample resources. This solution is advantageous because centralized resource scheduling is preferable to the full use of resources by a business unit through the systems, machines, and code optimization.
Centralized resource scheduling reduces O&M costs and improves delivery efficiency and operational stability. Given that the resource scheduling methods are the same, investment in the R&D or O&M of centralized resource scheduling not only makes scheduling products more convenient and commercial but also reduces the need to invest in human resources. Containerization and centralized resource scheduling have gradually become dominant trends in industry evolution.
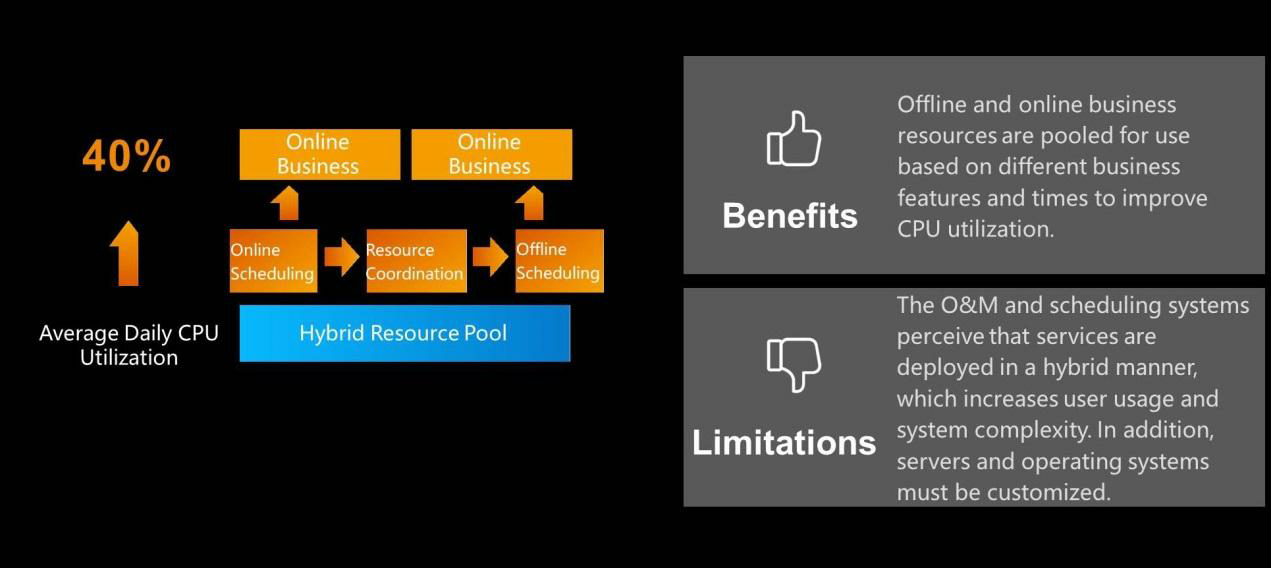
The hybrid resource pool raised our resource utilization rate to 40% because different systems have different peak values and times. For example, the peak traffic during Alibaba's Double 11 event is extremely high, up to 30 times greater than the peak value on normal days. Now, thanks to Alibaba Cloud, it is very easy to cope with the Double 11 traffic peak. In the past, only one-thirtieth of the resources prepared for Double 11 would be used during normal days, resulting in a severe waste of resources. From the perspective of technical evolution, online and offline data can be deployed in a hybrid manner. Offline data is generally used for offline computing after online data generation. The peak usage times of online and offline services differ, and offline services can tolerate slight delays in report generation but not the loss of data accuracy. However, online businesses cannot afford any delay or loss of accuracy. For example, real-time feedback is required when a user places an order. In this case, you don't ask the user to wait five minutes to see if the order was successfully placed. Currently, the hybrid deployment of resources is ideally the direction of the technical trend. This means offline services are deployed online and online services are deployed offline. With full containerization and centralized resource scheduling to cope with high traffic peaks during Double 11, online services are scheduled offline and offline resources are used to supplement online resources. Using offline resources to assist online services will greatly reduce daily resource consumption. Also, deploy offline resources to online services during normal days to obtain excellent performance.
After hybrid deployment, our resource usage efficiency increased from over 10% to 40%, effectively reducing required hardware investment.
Containerization, centralized scheduling, and hybrid deployment are all architecture optimization solutions. Moving offline processes online and online processes offline involve many problems. What the cloud needed was a product-based commercial solution that allowed users to purchase and use resources immediately. This would allow engineers and users to significantly improve their resource usage and labor efficiency without the need for complex architecture. Containerization, global resource scheduling, and hybrid deployment are the basic logic of the evolution of internet companies. They can greatly improve capability and resource efficiency and then evolve based on products. For example, Alibaba Cloud products have good performance and stability. The wide range of complex business scenarios, such as Double 11, that Alibaba Cloud must overcome has eventually refined our products.
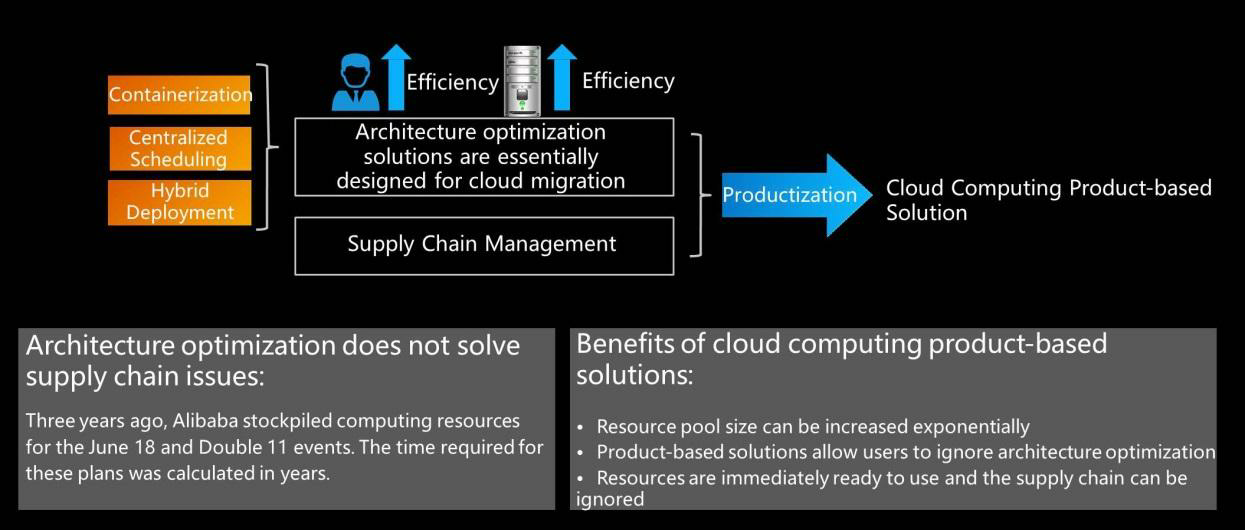
First, we need to understand the similarities and differences between cloud-oriented R&D models and internet-oriented R&D models. Both types of models attempt to make cloud computing resource management and system architecture development as simple as service management and development. The difference between the models is in their resource pool sizes. Architecture optimization solutions, such as containerization, centralized scheduling, and hybrid deployment, reduce e-commerce costs.
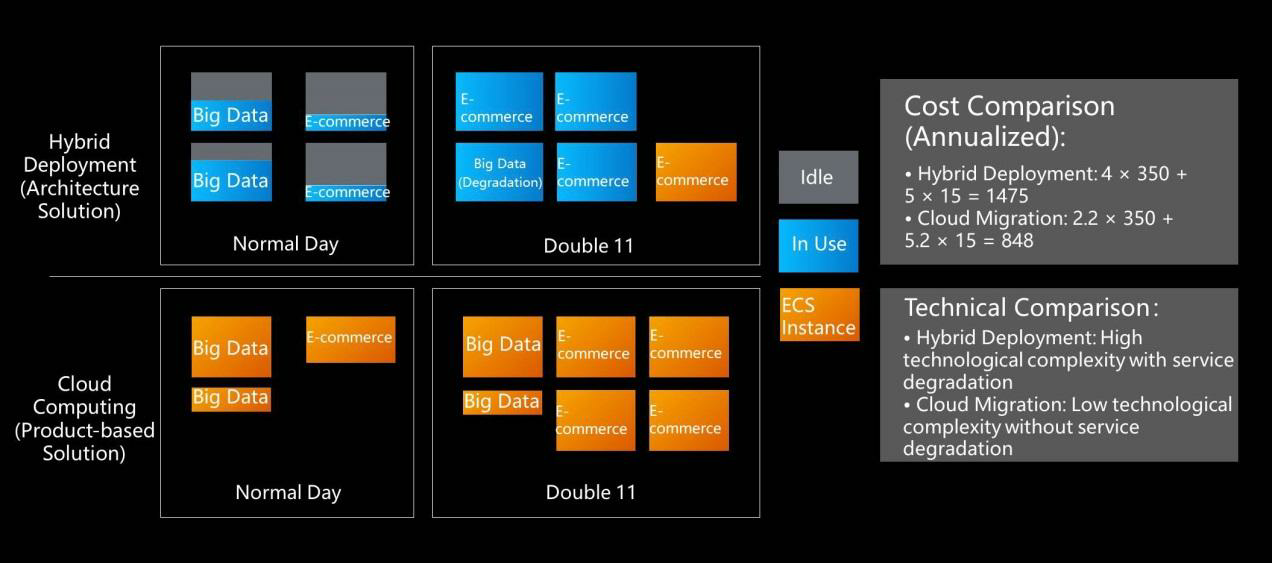
Using product-based solutions for cloud computing also reduces e-commerce costs. The following figure shows a comparison between simulated hybrid deployment and cloud computing in reducing e-commerce costs. The orange blocks represent cloud-based solutions, while the blue blocks represent hybrid deployment solutions. Every business has its ups and downs. This comparison shows that non-cloud hybrid deployment solutions use their own resources rather than cloud resources. As a result, except during service peaks, such solutions have a low resource utilization and cannot handle higher-than-expected peaks. For example, if a hybrid deployment solution does not have the resources to deal with the Double 11 peak, we would have to prepare or purchase additional cloud resources. In contrast, cloud computing solutions elastically release surplus resources so that they constantly maintain a high resource utilization, whether during normal days or the Double 11 traffic peak.
In scenarios such as hybrid deployment and global scheduling, the annual cost of the architecture solution is 1,475 units. In addition, this solution is technically complex, involves service degradation, and requires continuous attention from R&D personnel. By using relatively simple technology, the cloud-based solution costs only 848 units and requires a lower investment in human resources.
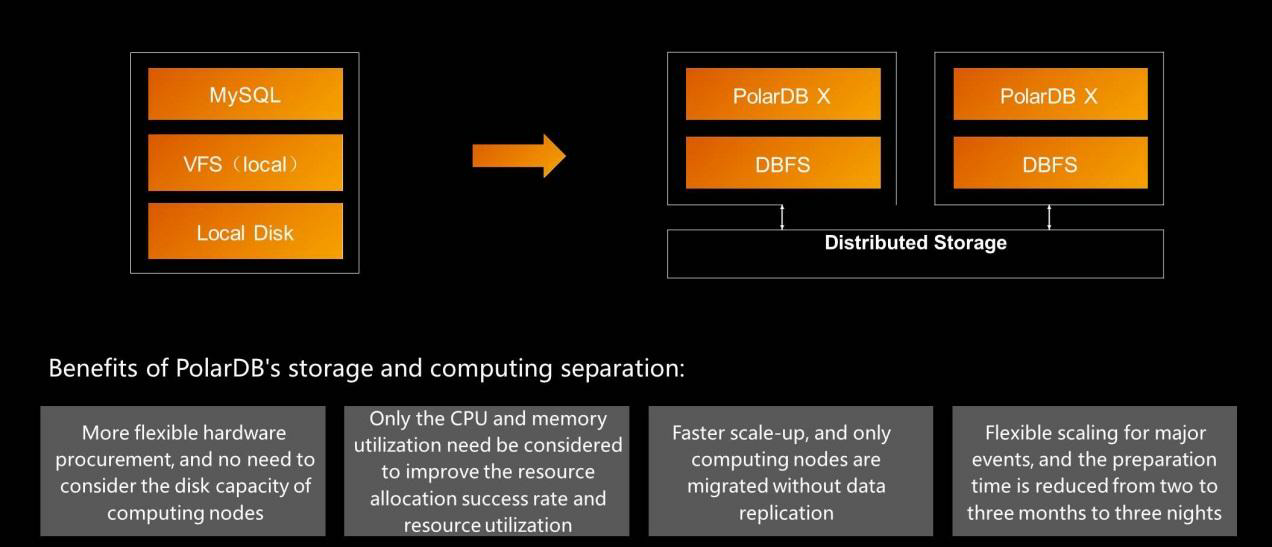
Database budgeting is a complicated matter. When the traffic or concurrency is high, you need to perform database and table sharding and ultimately hash an ID. Generally, a database budget is drawn up every three years to reserve resources, resulting in a serious waste of database resources. The main difficulty is that storage and computing are not separated, and databases consume a large number of computing resources even when they do not perform much computing. PolarDB X is a high-performance product developed by Alibaba Cloud. The evolution from MySQL database sharding to PolarDB X storage and computing separation is a typical process of database cloud migration.
PolarDB X adopts distributed storage. This architecture enables the elastic release of excess computing resources and the elastic reclamation of resources. Alibaba Cloud offers three basic products for different requirements: X-Dragon for computing, Apsara Distributed File System for storage, and Apsara Luoshen for the network. Apsara Distributed File System provided early support for various cloud and Alibaba Group businesses. It separates computing from storage and allows on-demand applications for storage resources. This offered many benefits to the businesses. After Apsara Distributed File System moved to the cloud, we turned it into a product. Now, customers directly use PolarDB and PolarDB X. Alibaba Cloud databases provide obvious advantages across performance and O&M. This implies customers now use Alibaba Cloud databases for R&D and other purposes to significantly reduce costs.
The service level agreement (SLA) guarantees for preemptible instances are not high and the instance prices are very low. Preemptible instances are not an original invention of Alibaba Cloud. They were already a mature mechanism on AWS and used to a great extent in many companies. The following figure shows a mobile advertising and data analysis company that uses preemptible instances to significantly reduce costs. The split servers contain some fragment resources and inventory resources, which can be purchased as preemptible instances. The SLA states that preemptible instances are not guaranteed. If another customer requires a complete resource, the instance may be released because it contains fragment resources of the required complete resource. However, the customer is notified five minutes before the instance is reclaimed. Of course, if the customer has strong R&D capabilities, they can build their own platform and use a large number of fragment resources for scheduling. This minimizes costs while ensuring SLA guarantees. For companies with strong R&D capabilities, such as Alibaba Cloud, the use of preemptible instances allows the company to reduce the number of normal computing instances by 80% while retaining the same level of computing power.

As shown in the following figure, some online travel websites adopt elastic billing to take advantage of the significant variations in business traffic. Some media companies perform elastic operations to take advantage of the varying popularity of content. Some rendering companies use preemptible instances and economic instances to reduce costs and improve rendering efficiency. The following figure shows past data, but the current data is probably even better.

Cloud-oriented R&D is different from the past. In the past, the resource pool could be regarded as a small pond, but a cloud-oriented resource pool is like an ocean. Although cloud resources may still be wasted, cloud-oriented resource pools offer overall greater advantages.
The following figure shows that the resource usage efficiency of an O2O enterprise is significantly improved after cloud migration. The company's business peaks occur during lunch and dinner hours, and the procurement costs of one-time servers are high. The company solved its daily peak problem with cloud solutions, such as global centralized resource scheduling, containerization, and elastic instance scaling in seconds, reducing costs, and improving service capabilities.

Stability is an aspect of performance that every company pays close attention to. Stability is highly related to product quality and customer satisfaction, making it very important. The evolution of stability can be roughly divided into three stages.
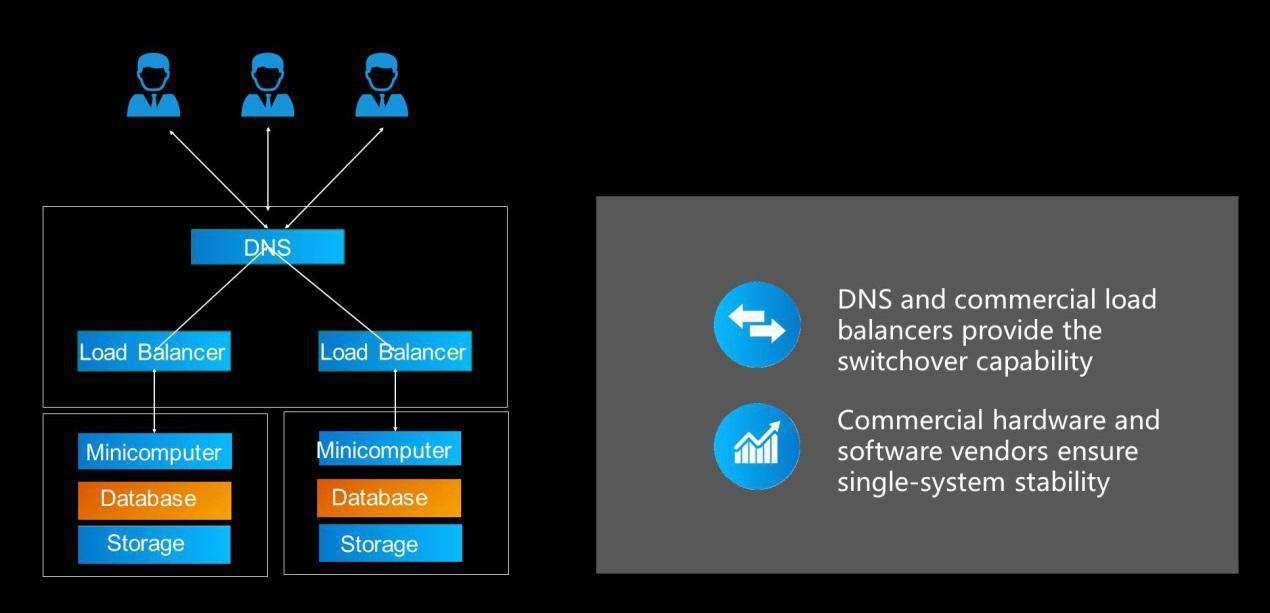
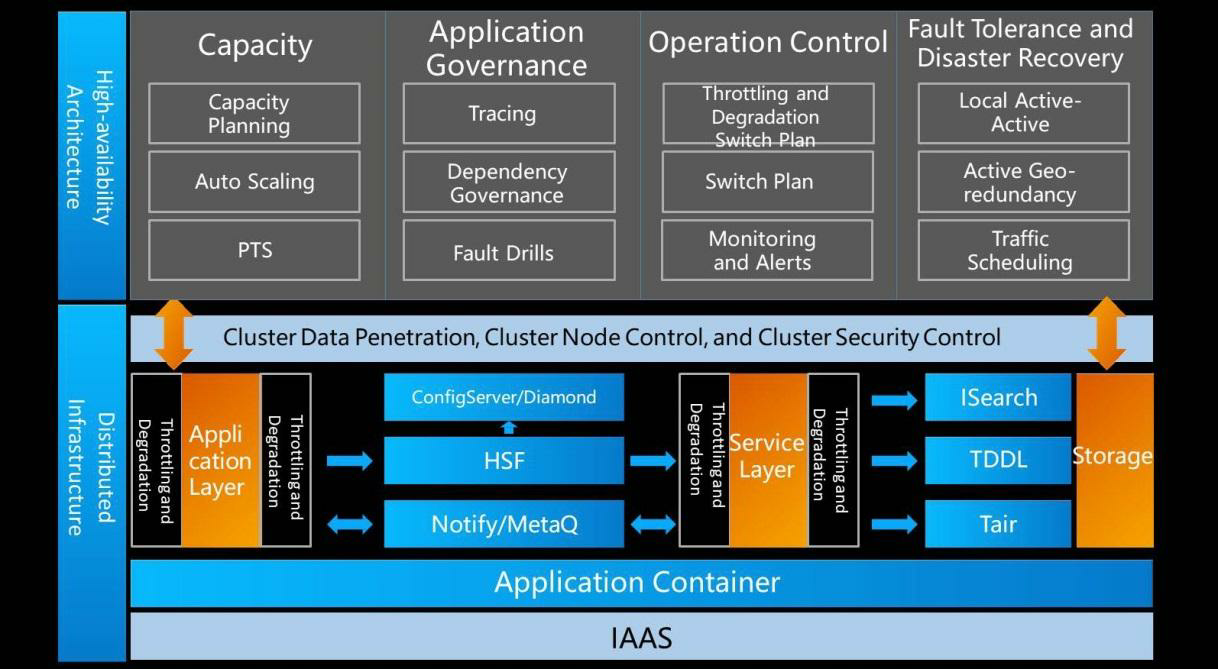
Cloud computing provides single-point stability and distributed full-stack products and solutions through market-based mechanisms. The following figure shows how to improve the stability of cloud computing. Considering an example, where hardware system monitoring along with AI-enabled fault prediction predicts metrics such as disk and motherboard failure times, failure rates, and fault causes, providing early warnings and facilitating the corresponding migration. Migration can be performed in the cloud. If failures can be predicted, the relevant compute instances can be promptly migrated to imperceptibly eliminate failures and reduce the probability of downtime by 80%. In addition, the high-availability network-wide deployment capability can eliminate hardware faults and single-points-of-failure (SPOF) threats to businesses. For example, you can distribute resources to different batches and different locations. These capabilities assume a certain business scale, so the larger the business scale, the more effective these methods are, and the higher the stability they provide.
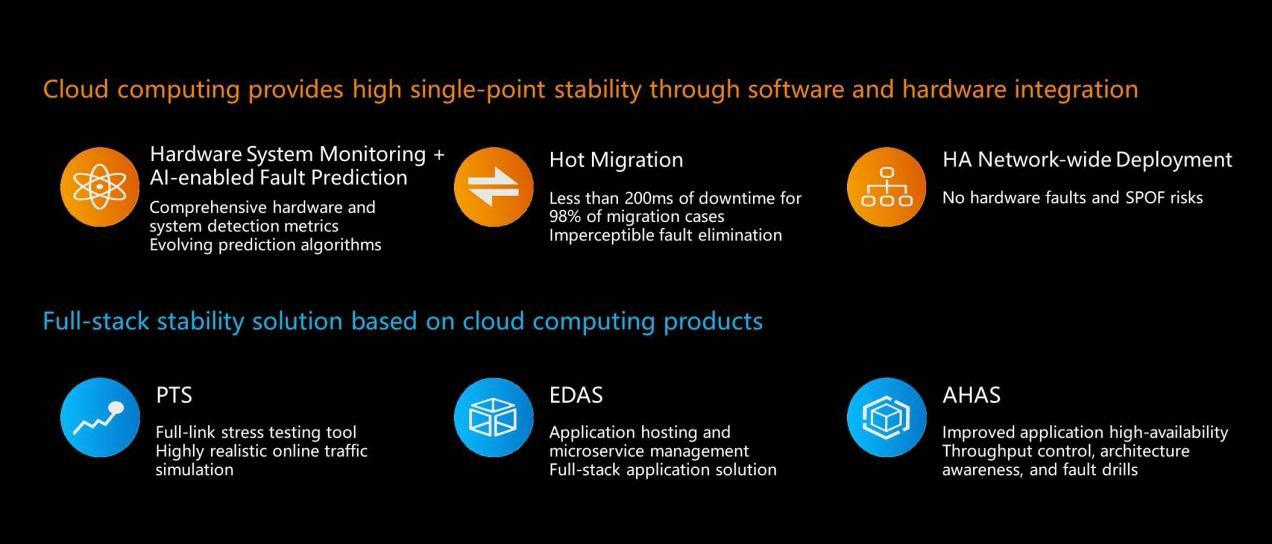
Physical machines or virtual machines? Containers are the current trend. Many companies provide container services based on physical machines. Objectively, it is not recommended to virtualize a container multiple times through virtual machines. Therefore, container services based on physical machines are preferable. However, physical machine-based container services waste the advantages of the cloud.
The cloud has five main advantages. First, it has strong elasticity, which greatly reduces costs and improves availability. Second, it enables highly efficient supply chains. Off the cloud, it's not possible to create a compute instance simply with a click. Instead, it requires to carry out many complex processes. Third, it provides high financial efficiency. Off the cloud, purchased assets are expected to last three or four years, but cloud servers do not depreciate or break. Fourth, the cloud is stable. Professional companies provide cloud services and hence these services are more stable than the customer's own services. Fifth, the cloud provides a rich selection of products, with new products constantly emerging. This includes both Alibaba Cloud products and our partners' products. Customers can also convert their own capabilities into products and services that can be provided to other customers in the cloud. Therefore, the cloud provides a richer ecosystem.
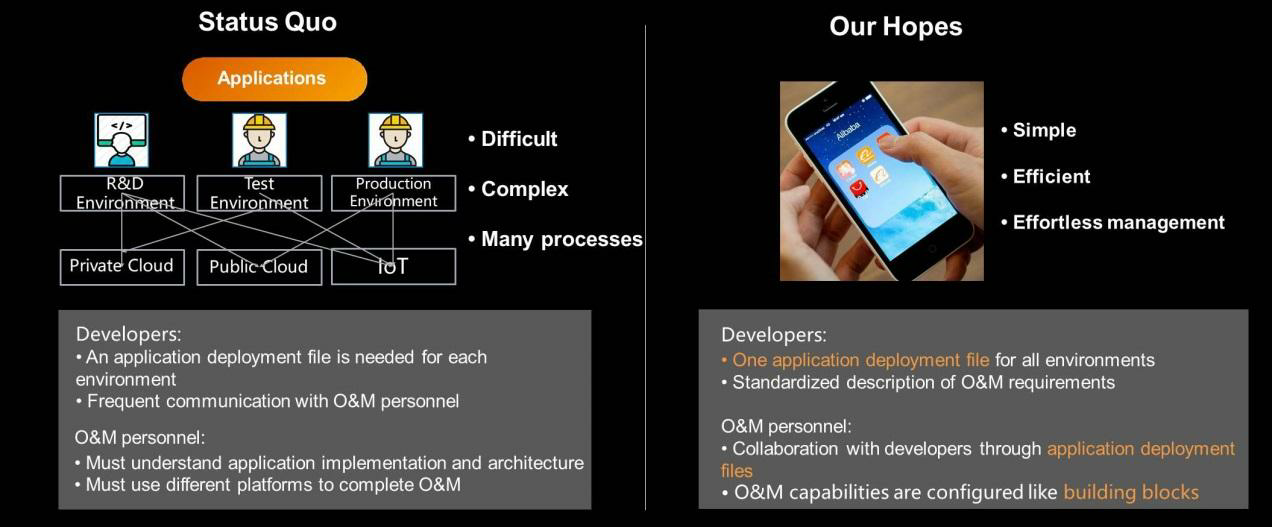
Alibaba seeks to use standardization to simplify the management of cloud applications. Otherwise, the services, software, and application systems provided by different companies will have different management methods. The resulting large number of R&D, testing, and production environments and private cloud, public cloud, and Internet-of-Things (IoT) environments will make management difficult. However, any mobile user can easily manage their mobile apps, due to the standardization of the operating system.
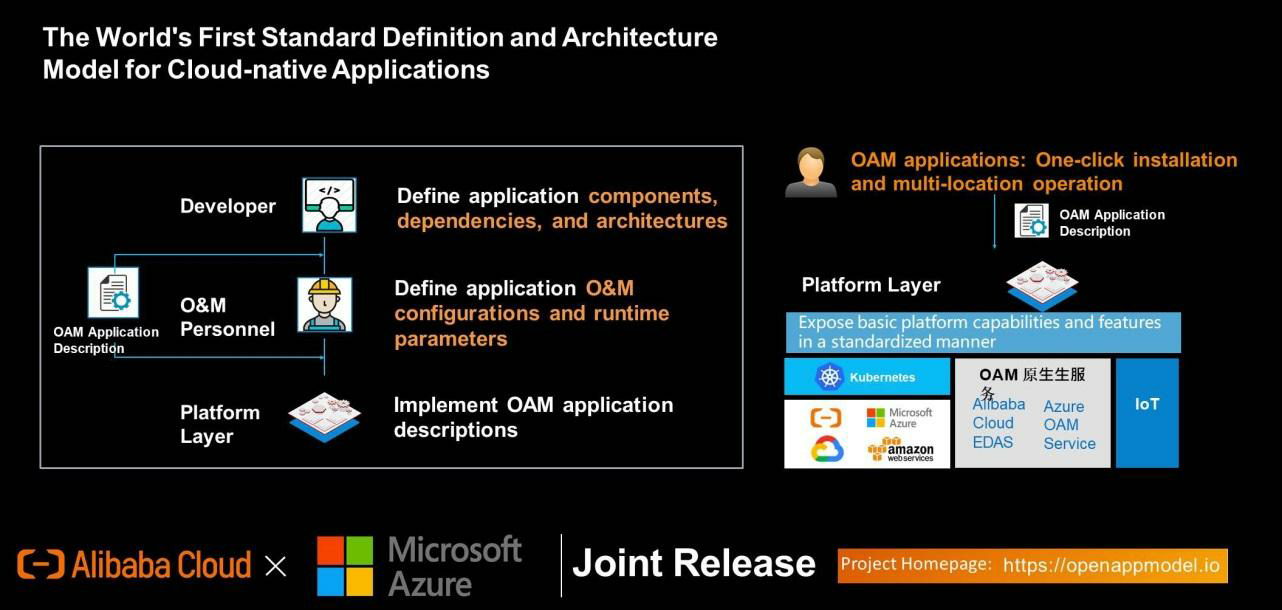
In cooperation with Microsoft Azure, Alibaba Cloud launched the Open Application Model (OAM), which is the first standard definition and architecture model for cloud-native applications. OAM defines the components, dependencies, and architecture of applications at the developer layer, the O&M configuration and runtime parameters of the application at the maintenance layer, and describes the application at the platform layer. Install OAM in a single click and run in multiple locations. It exposes the basic capabilities and features of the platform in a standardized way. As long as they meet the OAM standard, KPS environments built by Alibaba Cloud, other clouds, and other individuals can be managed more easily.
Get to know our core technologies and latest product updates from Alibaba's top senior experts on our Tech Show series
Enhancing the In-Store Retail Experience with the Big Data on the Cloud
Protecting Data Security through Robust and Hybrid Disaster Recovery Infrastructure

2,593 posts | 793 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native Community - November 22, 2022
Alibaba Tech - February 17, 2020
XianYu Tech - March 11, 2020
sunqi - February 12, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - July 27, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - September 24, 2020

2,593 posts | 793 followers
Follow Resource Management
Resource Management
Organize and manage your resources in a hierarchical manner by using resource directories, folders, accounts, and resource groups.
Learn More Cloud Shell
Cloud Shell
A Web browser-based admin tool that allows you to use command line tools to manage Alibaba Cloud resources.
Learn More Architecture and Structure Design
Architecture and Structure Design
Customized infrastructure to ensure high availability, scalability and high-performance
Learn More Apsara Stack
Apsara Stack
Apsara Stack is a full-stack cloud solution created by Alibaba Cloud for medium- and large-size enterprise-class customers.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder